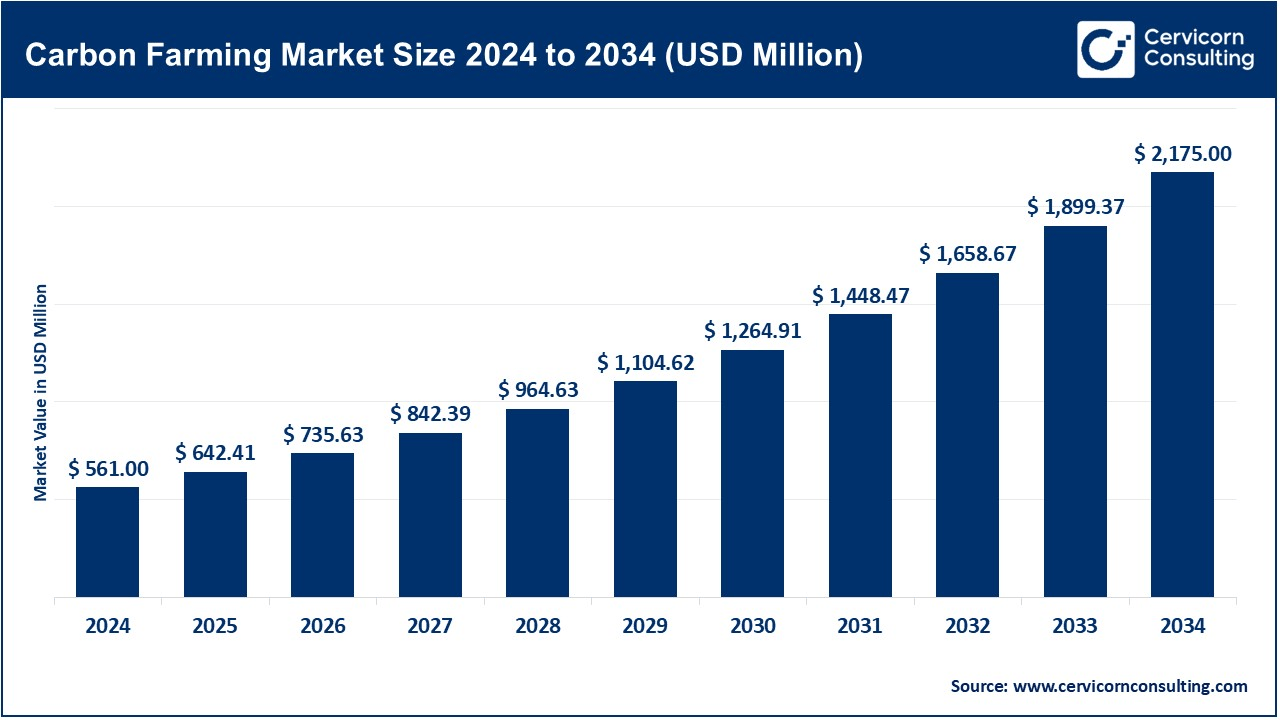
The global carbon farming market size was reached at USD 561 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 2,175 million by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.51% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The carbon farming market is rapidly expanding as industries push for net-zero emissions and sustainable agriculture. Governments worldwide are introducing carbon pricing mechanisms and subsidies, encouraging farmers to adopt carbon-friendly practices. Corporate buyers, especially in sectors like energy, manufacturing, and food production, are actively purchasing carbon credits to meet sustainability goals.
The increasing awareness of climate change and the demand for regenerative agriculture further drive this market. Technology advancements, such as satellite monitoring, AI-driven soil analysis, and blockchain-based carbon credit tracking, are improving transparency and efficiency. As voluntary and compliance carbon markets grow, investment opportunities in carbon farming are increasing. Future trends suggest that more regions will adopt carbon-friendly policies, making it a crucial part of the global strategy to combat climate change while supporting farmers financially.
What is Carbon Farming?
Carbon farming is a sustainable agricultural approach that helps capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in soil and plants. This method reduces greenhouse gas emissions, improves soil fertility, and enhances biodiversity. Farmers achieve this by using practices like cover cropping, agroforestry, conservation tillage, crop rotation, and managed grazing. These techniques increase soil organic matter, boost productivity, and create healthier ecosystems.
One of the biggest benefits of carbon farming is that farmers can earn carbon credits by adopting eco-friendly practices. Companies and industries looking to offset their carbon emissions buy these credits, providing an additional revenue stream for farmers. Governments and environmental organizations also support carbon farming through incentives, policies, and research programs. Additionally, these methods help in water conservation, reducing soil erosion, and improving climate resilience, making farms more sustainable in the long run.
Key benefits of Carbon Farming:
Expansion of Carbon Credit Trading Markets
Implementation of Regulatory Guidelines
Corporate Commitments to Net-Zero Emissions
Technological Advancements in Sustainable Agriculture
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 642.41 Million |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 2,175 Million |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 14.51% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Expanding Area | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Practice Type, Carbon Credit Type, End-User, Region |
| Key Companies | Carbon Clean Solutions, Indigo Ag, Land Life Company, Nori, BioCarbon Engineering, Cargill, Greenbelt Carbon, CarbonCure Technologies, Agreena, Reforest'Action, Climeworks, Soil Capital |
Rising Global Awareness of Climate Change: As global awareness of climate change and its impacts increases, the demand for carbon reduction strategies, including carbon farming, has grown. Public and private sector initiatives are becoming more proactive in addressing climate change, with more countries adopting carbon reduction targets. For instance, countries like Germany have committed to reducing emissions by 55% by 2030 as part of the European Union's Green Deal. This creates a strong need for carbon credits, which can be sourced from carbon farming activities. The growing public and governmental pressure to tackle climate change is driving greater investment and focus on carbon farming initiatives worldwide.
Growth of Corporate Sustainability Programs: Corporations around the world are increasingly integrating sustainability goals into their business models, driven by both regulatory requirements and consumer preferences. Large corporations are committed to reducing their carbon footprints and are turning to carbon credits as a tool to achieve these goals. For example, Microsoft has pledged to be carbon negative by 2030, and companies like Google have committed to using renewable energy sources for their data centers. The corporate sector's demand for high-quality carbon credits is a major driver for expanding carbon farming practices, offering farmers the opportunity to generate additional revenue through carbon credits.
High Initial Investment Costs: One of the primary constraints in the carbon farming market is the high initial investment costs involved in implementing carbon farming techniques. Practices such as cover cropping, agroforestry, and no-till farming often require substantial upfront investments in training, equipment, and labor. For example, the establishment of agroforestry systems requires long-term investment and a return period of 5-10 years before carbon credits can be generated. These high costs may deter small-scale farmers from adopting carbon farming practices, slowing market penetration.
Uncertainty in Carbon Credit Valuation: The uncertainty in carbon credit valuation is another restraint impacting the carbon farming market. Carbon credits are subject to market fluctuations, and factors such as regulatory changes, environmental factors, and demand shifts can cause credit prices to be volatile. According to some studies, the price of carbon credits can vary by as much as 50% within a year, creating uncertainty for farmers looking to invest in carbon farming practices. This price instability limits the market's ability to scale and grow consistently.
Potential for Carbon Credit Monetization for Small Farmers: Small-scale farmers, who traditionally face financial challenges, have an opportunity to monetize carbon credits through carbon farming practices. By adopting techniques like agroforestry, regenerative agriculture, and improved land management, these farmers can generate additional income streams from carbon credits, enhancing their financial stability. Initiatives like the World Bank’s Carbon Initiative for Development (Ci-Dev) are specifically designed to support smallholder farmers in carbon credit generation, helping them enter the market. This democratization of carbon credit access creates significant opportunities for small-scale farmers to benefit financially from their environmental stewardship.
Partnerships with Carbon Credit Certification Programs: Carbon farming initiatives can benefit from partnerships with carbon credit certification programs like the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard, which increase the credibility of carbon credits and open access to global markets. These certification programs help create a transparent and trustworthy carbon market, which is critical for attracting corporate buyers. With demand for certified carbon credits rising, farmers who can obtain certification for their carbon sequestration efforts stand to gain both revenue and credibility. Furthermore, partnerships with these programs help farmers gain the necessary training and support to implement carbon farming practices effectively, expanding market access and profitability.
Lack of Awareness and Education: A major challenge facing the carbon farming market is the lack of awareness and education among farmers about the potential benefits of carbon farming practices. Many farmers are unaware of the financial opportunities associated with carbon credit generation or may not understand how to implement carbon farming techniques effectively. This lack of knowledge hinders the widespread adoption of carbon farming practices, limiting the market's growth potential. According to some reports, only 30-40% of farmers are currently aware of the carbon credit markets, underscoring the need for more outreach and education.
Verification and Credibility of Carbon Credits: The verification and credibility of carbon credits continue to be a challenge in the carbon farming market. As the market grows, ensuring that carbon credits are accurately verified and that they represent real, permanent carbon sequestration is critical to maintaining the integrity of the market. Without stringent and transparent standards for credit verification, there is a risk of fraudulent credits flooding the market, which could damage the reputation of the carbon farming industry. This has been cited as one of the major challenges, with concerns that up to 30% of carbon credits could be ineffective or fraudulent if proper verification measures are not in place.
The carbon farming market is segmented into practice type, carbon credit type, end-user and region. Based on practice type, the market is classified into agroforestry, conservation tillage & no-till farming, managed grazing, crop rotation & diversification, cover cropping, composting & biochar and wetland & peatland restoration. Based on carbon credit type, the market is classified into soil carbon credits, forestry carbon credits, livestock methane reduction credits and biochar & compost credits. Based on end-user, the market is classified into farmers & ranchers, government agencies, corporations, non-profit organizations.
Agroforestry: The Agroforestry segment has dominated the market in 2024. Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs with crops or livestock, promoting biodiversity and carbon sequestration. This segment is expected to grow due to its dual benefits of enhancing farm productivity and capturing carbon. Agroforestry systems can store 1.1 to 2.6 billion metric tons of carbon per year globally, which highlights its significant potential for growth in carbon farming.
Conservation Tillage & No-Till Farming: Conservation tillage, including no-till farming, is a vital practice for improving soil carbon storage by reducing soil disturbance. As this practice reduces greenhouse gas emissions and enhances soil health, it is gaining momentum. No-till farming can sequester up to 5-6% more carbon annually compared to traditional tilling methods, contributing to the growth of the market.
Managed Grazing: Managed grazing improves soil health and boosts carbon sequestration through rotational grazing methods. This practice is expected to expand as farmers recognize its long-term benefits for pasture management and carbon storage. Managed grazing has been shown to sequester 0.5 to 1.5 metric tons of carbon per hectare per year, further driving the adoption of this practice.
Crop Rotation & Diversification: Crop rotation and diversification help reduce soil erosion and enhance soil carbon content. This segment is growing as more farmers diversify crop choices to improve resilience against climate change. Crop rotation can sequester up to 0.5 metric tons of carbon per hectare, contributing to its increasing popularity and adoption in carbon farming.
Cover Cropping: Cover cropping enhances soil health by preventing erosion and promoting carbon sequestration. This practice is rapidly expanding, with growing adoption as farmers see the benefits of improving soil health and increasing organic matter. Cover crops can sequester up to 1 metric ton of carbon per hectare per year, making it a highly effective method for carbon farming.
Composting & Biochar: Composting and biochar are effective methods of carbon sequestration. Composting, by increasing organic matter, can help store up to 1.5 tons of carbon per hectare per year. Biochar, on the other hand, is particularly promising due to its potential to sequester carbon for hundreds of years, further driving the adoption of this practice in the market.
Wetland & Peatland Restoration: Restoration of wetlands and peatlands plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration, as these areas store significant amounts of carbon in their soil. Peatland restoration alone can sequester up to 100 metric tons of carbon per hectare, positioning this practice as a major contributor to carbon farming’s growth and global carbon mitigation efforts.
Soil Carbon Credits: The soil carbon credits segment has dominated the market in 2024. Soil carbon credits are generated through practices that sequester carbon in the soil. This segment is expected to dominate the market due to its widespread applicability in agricultural practices. Soil carbon credits can sequester up to 1.1 to 2.6 billion metric tons of carbon annually, highlighting their potential to contribute significantly to global emissions reduction.
Forestry Carbon Credits: Forestry credits are generated through reforestation and forest conservation efforts. This market is expanding due to the significant role of forests in reducing greenhouse gases. Forestry carbon credits can represent up to 40% of the carbon credit market by 2030, driven by the large-scale efforts to halt deforestation and increase reforestation.
Livestock Methane Reduction Credits: These credits are generated through practices that reduce methane emissions from livestock, a significant contributor to global warming. The market for livestock methane reduction credits is expected to grow as technology improves in the sector. Methane reduction can help mitigate up to 1.3 billion metric tons of CO2 equivalent emissions annually.
Biochar & Compost Credits: Credits from biochar and composting represent a rapidly growing segment. Biochar is particularly effective in sequestering carbon for long periods, with the potential to capture up to 1.6 billion metric tons of carbon globally. These credits are becoming increasingly attractive as a long-term solution for carbon sequestration.
Farmers & Ranchers: The farmers and ranchers segment has dominated the market in 2024. Farmers and ranchers are the primary end-users of carbon farming practices, as they directly benefit from both environmental and financial incentives like carbon credits. The demand for carbon farming practices among farmers is expected to rise, particularly due to the financial benefits, such as earning USD 10 to USD 15 per ton of CO2 sequestered through carbon credits.
Government Agencies: Government bodies play a critical role in setting regulations and providing financial incentives for carbon farming. These agencies are instrumental in creating frameworks to encourage large-scale carbon farming initiatives. Governments worldwide are increasing funding for carbon farming practices, with some countries offering USD 1 billion in support for carbon sequestration projects over the next decade.
Corporations: Corporations are major buyers of carbon credits, as they strive to meet net-zero emissions targets. The corporate sector’s interest in carbon farming is growing as companies seek to purchase carbon credits for their sustainability goals. Corporations are expected to spend USD 1.2 trillion by 2050 on carbon offset projects, driving growth in the market.
Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profit organizations are pivotal in supporting carbon farming projects through funding and advocacy. They help fund large-scale carbon farming initiatives and direct resources to developing regions. Non-profits are increasingly focusing on carbon sequestration efforts, with some projects aiming to sequester up to 1.8 billion metric tons of carbon globally over the next decade.
The carbon farming market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
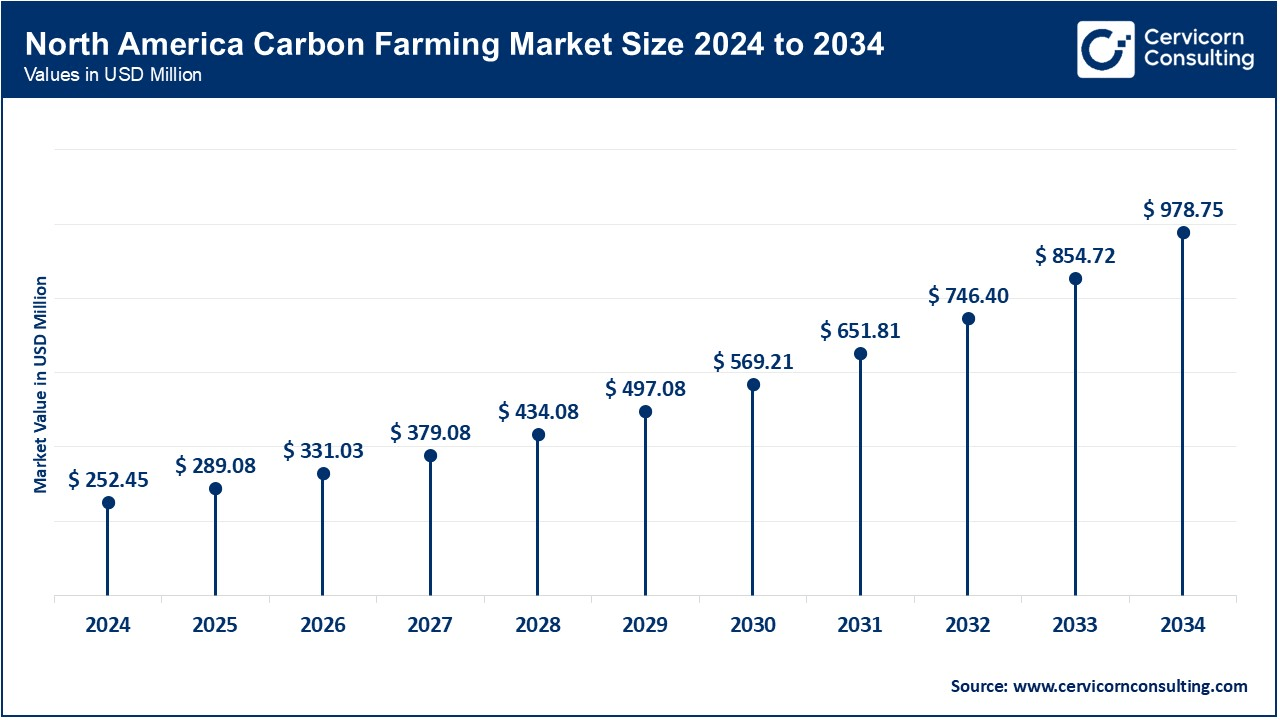
The North America carbon farming market size was reached at USD 252.45 million in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 978.75 million by 2034. North America holds a dominant position, driven primarily by the U.S. The region benefits from a well-established agricultural sector and increasing efforts to adopt sustainable farming practices for climate change mitigation. Government support plays a key role, with various subsidies and carbon credit programs encouraging the adoption of carbon farming methods such as agroforestry, conservation tillage, and managed grazing. The demand for carbon credits, spurred by corporations pursuing sustainability goals, further strengthens North America's leadership. Additionally, the region's regulatory framework and financial incentives are key factors driving the growth of carbon farming practices in the U.S.
The Asia-Pacific carbon farming market size was estimated at USD 117.81 million in 2024 and is forecasted to hit around USD 456.75 million by 2034. The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is witnessing rapid growth in the carbon farming industry. Countries like China, India, and Australia are increasingly adopting sustainable agricultural practices due to concerns about climate change and soil degradation. The region’s expanding agricultural sector and industrialization are contributing to the growing demand for carbon credits. In particular, China and India are integrating carbon farming methods to reduce their environmental impact, which has further sparked the region’s transition toward more eco-friendly farming practices. Government support and technological innovations are driving the expansion of carbon farming in APAC, making it a key region for future market growth.
The Europe carbon farming market size was accounted for USD 157.08 million in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 609 million by 2034. Europe continues to play a significant role, with a strong commitment to carbon neutrality and the European Union's green policies. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are at the forefront of adopting carbon farming techniques such as agroforestry, cover cropping, and crop diversification. The EU’s regulatory framework, which incentivizes carbon credit generation and supports sustainable farming practices, strengthens the market in the region. Europe’s agricultural sector has shown consistent engagement in carbon credit trading, with notable participation from farmers, corporations, and government entities. The region remains a key player in the global carbon farming market, supported by a stable and innovative environment.
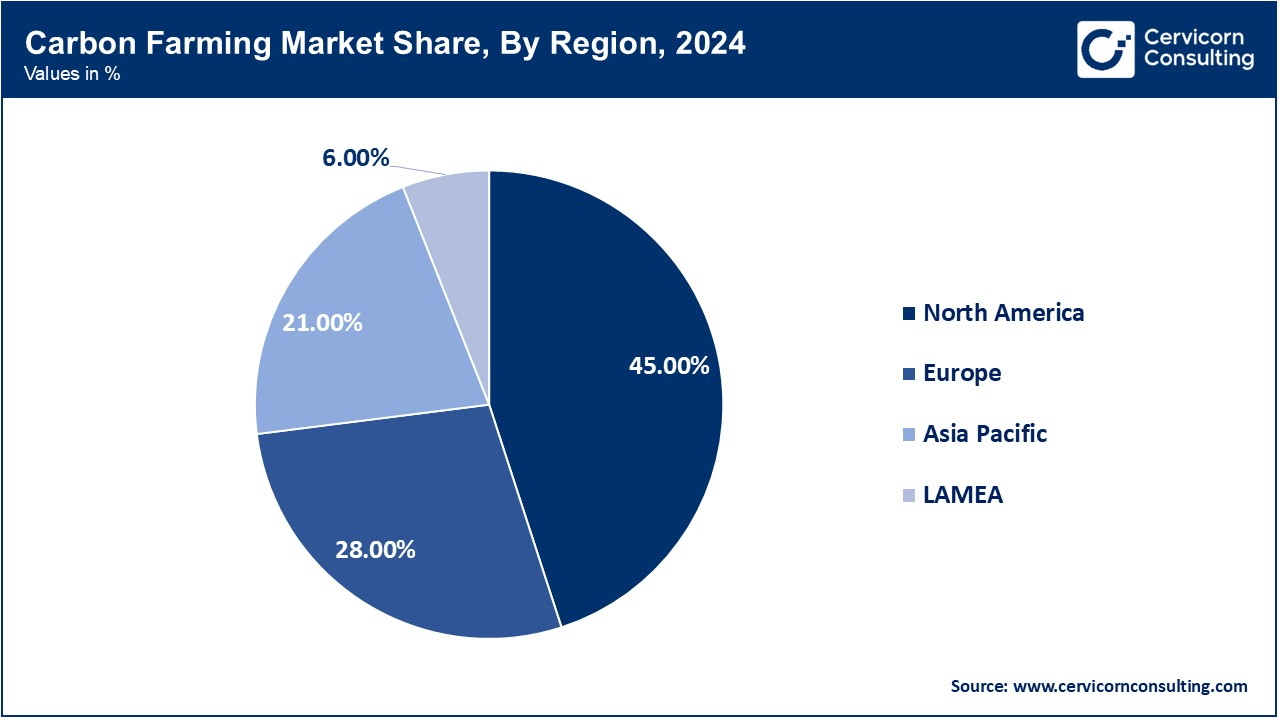
The LAMEA carbon farming market was valued at USD 33.66 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 130.50 million by 2034. The LAMEA region, comprising Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, represents an emerging market with substantial growth potential. While the region’s market is smaller compared to North America and Europe, increasing investment in sustainable agricultural practices and carbon credit programs is driving growth. Countries like Brazil and Mexico are adopting practices such as agroforestry and managed grazing, while parts of Africa and the Middle East are turning to carbon farming as part of broader climate change strategies. The region’s awareness of environmental issues and the growing demand for carbon credits contribute to its potential for further development in carbon farming over the coming years.
The carbon farming industry is populated by several key players that are leveraging innovative agricultural practices and technologies to mitigate climate change. Companies such as Indigo Ag, Cargill, and Nori are leading the way in offering carbon credit solutions and developing advanced farming techniques like regenerative agriculture and agroforestry. These players are supported by strong investments in research, sustainable farming technologies, and carbon offset programs. Carbon Clean Solutions and Climeworks focus on cutting-edge carbon capture technologies, complementing the efforts of companies involved in the more traditional farming-based methods. Partnerships with governmental bodies, NGOs, and global corporations further fuel market growth as these organizations seek to meet sustainability targets. As demand for carbon credits grows, companies are increasing their efforts to scale up carbon farming solutions, with a strong focus on data-driven insights, transparency, and market integrity to meet global climate goals.
Market Segmentation
By Practice Type
By Carbon Credit Type
By End-User
By Region