Floating Power Plant Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
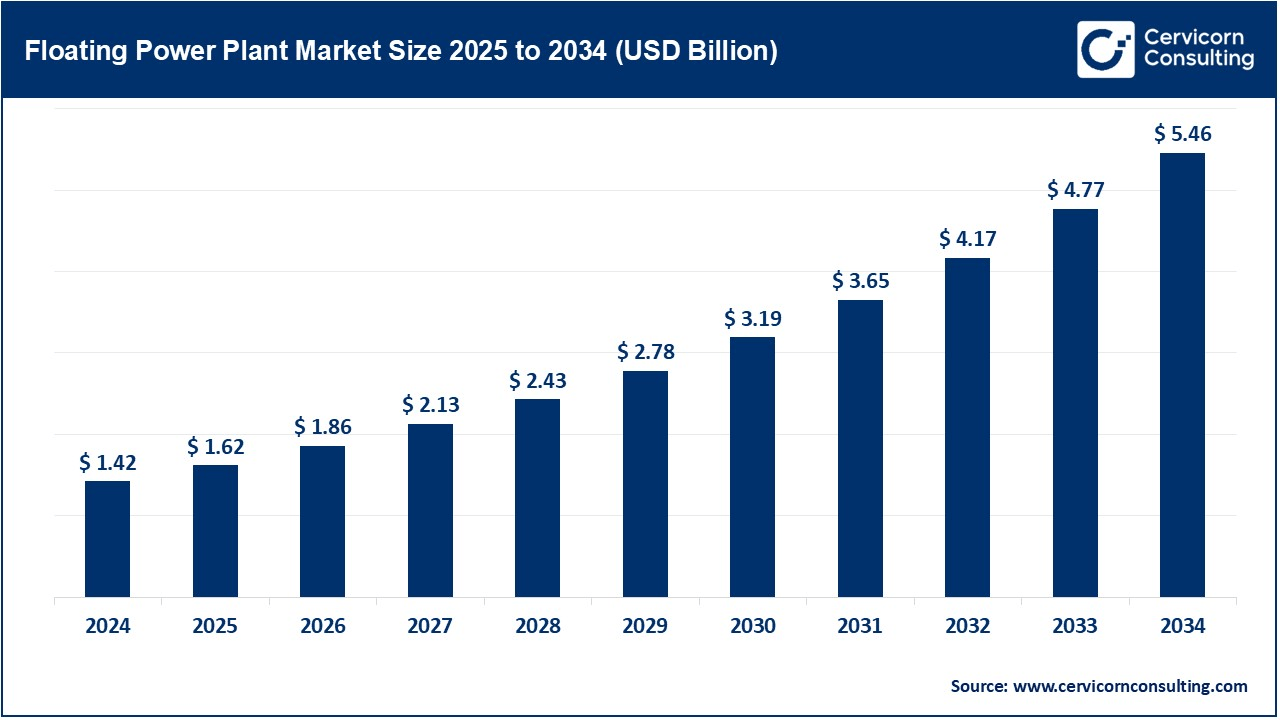
The global floating power plant market size was valued at USD 1.42 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach around USD 5.46 billion by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.41% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The floating power plant market is expected to grow as it has been recognized as an innovative option to address electricity needs, particularly in regions where conventional land-based power stations encounter logistical, environmental, or regulatory obstacles.
The floating power plant market is is expected to grow owing to the demand for decentralized and flexible generation solutions. These floating power plants can be mounted on offshore platforms, barges, or floating vessels, thus rendering electricity in remote coastal areas, islands, and regions with poor grid connectively. The rising investments in renewable energy, especially in floating solar and offshore wind power projects, are propelling the market, together with the need for rapid deployment of power generation solutions in the face of emergencies and disasters. Advances in technology, increased efficiency of generation mechanisms, and government support for sustainable energy solutions are responsible for the market growth. Major firms are working on innovative hybrid systems that would integrate different energy sources-wind, solar, and liquefied natural gas (LNG)-to increase reliability while minimizing carbon emissions.
Floating Power Plant Market Report Highlights
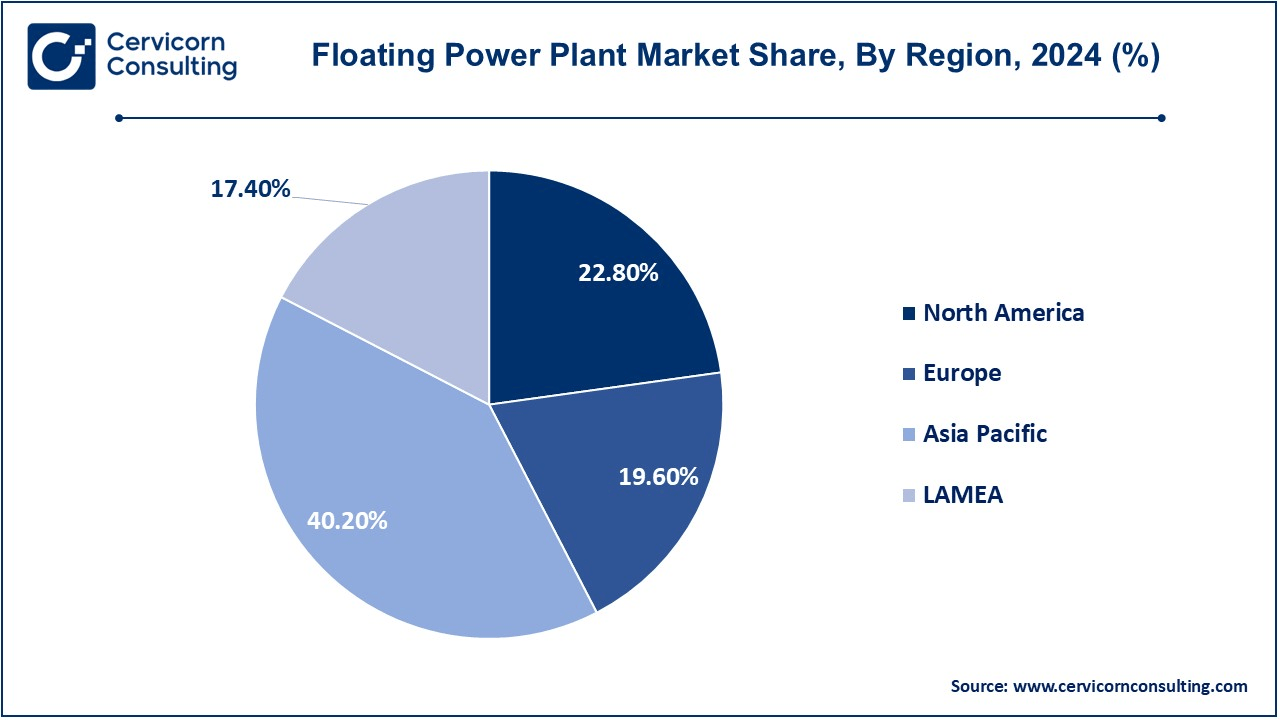
- The Asia-Pacific has dominated the market in 2024 and accounted revenue share of 40.20%.
- The North America has recorded revenue share of 22.80% in 2024.
- By power rating, the high (Greater than 100 MW) segment has generated revenue share of 67% in 2024.
- By power source, the non-renewable segment has recorded revenue share of 70.90% in 2024.
- By platform type, the power ships segment has leading the market in 2024.
- By application, the manmade water bodies has captured highest revenue share in 2024.
Floating Power Plant Market Growth Factors
- Growing Demand for Renewable Energy: As global interest in clean energy alternatives continues to expand, efforts begin to establish floating power plants, particularly in the offshore wind and solar floating energy sectors. Governments and industry are increasingly installing renewable energy sources to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and to decrease the amount of greenhouse gases emitted. Self-powered generators are a practical solution to overcome the limitation of land-based renewable energy generators, particularly in the case of land-based generation constraints.
- Increasing Energy Demand in Remote Areas: Many dispersed and insular regions suffer from bad grid availability and hence lack reliable power supply. DM floating power plants are an attractive alternative because they allow on-site, decentralized power generation without the need for bulk land-based infrastructure. These plants can be used in coastal areas near to where there is an opportunity to minimize power transmission losses and bring a stable electronic grid.
- Advancements in Floating Power Technology: The floating power plant market is enjoying the continuous technological advances leading to improvements in all parameters of efficiency, reliability and scalability. Advances in materials, floating structures and energy storage devices have enhanced the performance of floating power plants, and they are more resilient to marine harsh conditions. Benefitting from recent technological progresses of floating wind turbines combined with photovoltaic devices and hybrid power system setups, there are higher energy outputs with lower operational costs. In addition, digital monitoring and automation technologies enhance the remote operation of floating power plants by decreasing their operational maintenance.
- Rising Government Incentives & Policies: At present governments worldwide are implementing positive policies, subsidies, and incentives for the development of floating power plants as a green alternative technology and a sustainability application. Investments in floating solar and offshore wind are often promoted by tax credits, feed-in-tariffs, and grants in several countries. Furthermore, regulatory infrastructures are being developed to support timely permitting and environmental regulatory compliance. The trend towards public-private partnerships (PPPs) and cross-border sharing is also facilitated by market expansion.
- Quick Deployment & Scalability: The point of fast installation of the above floating units is one of the advantages of the floating power plant compared to stationary landâ€based power plants. Floating power plants are unwarranted to ascribe a lot of land area or civil works ability on the site, therefore floating power plants are most suitable energy option for emergency or disaster settlement condition and for temporary energy usage. Due to its modularity it is possible to install it flexibly, i.e., there is always an option how much to increase the capacity whenever the demand for it rises. With the rising demand for electricity around the world, there will be an urgent demand for deployable, mobile, floating electrical power generation plants.
Floating Power Plant Market Trends
- Increasing Focus on Carbon Neutrality: As the world becomes increasingly concerned about climate change, governments, business leaders, and other organizations are all left trying to develop carbon neutral approaches. Floating generation plants are a central part of this transition, providing a clean–green alternative to fossil fuels. Further (offshore) wind and floating PV reduced emissions of greenhouse gases by switching from fossil-fuel based electricity generation, so they are robust. Investments in floating renewables are encouraged worldwide because of extensive sustainability goals.
- Expansion of Offshore Wind Projects: Offshore wind power is of increasing interest as a high power, high power density renewable energy technology. However, there are the so-called fixed-bottom wind turbines that cannot be used in the offshore regions with greater depth. This constraint is overcome by moored offshore wind farms, which allow for electricity generation on the deeper parts of the ocean where wind speeds and energy are more consistent and ideal. As deep coastal water countries such as Japan, South Korea and the United States, they are also exploring the use of floating offshore wind technology to expand their renewable energy resource.
- Expansion of Offshore Wind Projects: Technological Integration of Hybrid Systems: Floating power plants are increasingly promoted to be hybrid systems incorporating several energy generation technologies, such as wind power, solar power, ocean wave power and LNG combined cycle power generation. By this hybrid approach it is also possible to better power reliability and intermittency and to achieve higher efficiency. As one case in point, the combination of floating solar panels and offshore wind turbines offers the ability of generating power under day/night and adverse weather conditions.
- Technological Integration of Hybrid Systems: Decentralized generation of energy is highly in demand by policymakers and the industry to alleviate dependence on centralized grid structures. For their ability to deliver power upstream close to the consumer, making transmission loss smaller and energy security better, floating power plants provide a desirable option. Independently powered sources are particularly beneficial in industries, insular communities, and offshore work because they are used to reduce dependence on traditional grids. With the increasingly flood of microgrid projects and distributed generation systems to the market, the development of floating power plant is therefore also fostered significantly.
- Growing Demand for Decentralized Power Generation: The floating power plant industry is attracting large amounts of public and private sector capital investment. All of these activities are currently facilitated by funding from government-funded research specifically aimed at improving the technical solution of the floating cells as well as the commercialisation of high-scale floating renewables. Both the venture capitalists and the energy firms understand the potential of floating power generators to cover the worldwide energy demand, thus, there is a growing financial support. Furthermore, the global reach due to strategic alliances between international companies is driving them to set up their floating power plants worldwide.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 1.62 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 5.46 Billion |
| Expected CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
14.41% |
| Dominant Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Rapidly Expanding Region |
North America |
| Key Segments |
Power Source, Power Rating, Platform Type, Application, Region |
| Key Companies |
CHN ENERGY Investment Group Co. LTD, Ciel et Terre International, SAS, Floating Power Plant A/S, GE Vernova, Karadeniz Holding, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD., Siemens Energy, Swimsol, Wärtsilä |
Floating Power Plant Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Resilience Against Natural Disasters
- Floating power plants have the unique advantage in regions often impacted by natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and flooding. By contrast with traditional power grid systems, i.e., with terrestrial power grid that are prone to severe seismic events, the floating power plants are able to operate stably and flexibly due to their mobility. Specifically, on the coast where flood landforms are common floating wind and solar farms can provide a continuous power grid for emergency power, the power system is not unreliable. This is one reason why floating power plants are an attractive technology for disaster response and mitigation events.
Declining Costs of Floating Infrastructure
- Costs related to floating power plants (solar panels, wind turbines, offshore platforms) continues to fluctuate down due to both technological innovation and economies of scale. The benefits of cost reduction in floating platform designs, of floating anchoring systems, and of the field of marine engineering as it relates to the installation and maintenance of the platforms itself has emerged that allow floating power to now be economically viable. Also, competition among manufacturers and suppliers has resulted in further cost reductions. In particular, the economic viability of floating power plants as a cost reduction alternative to land-based power plants is considered.
Market Restraints
Grid Integration Issues
- Integrating dedicated floating power plants to conventional power networks is a complex technical and logistical challenge. Offshore and marine variants of renewable energy technologies are often coupled with a requirement for specialized transmission infrastructure, viz., subsea cables and grid stabilizers. The uncertainty of renewables, such as wind and solar, resulted not only in complexity of integration work, but also demanded new energy storage systems and intelligent grids. In most sites aging grid infrastructures are not able to accommodate distributed generation of power, thus delays in bringing the projects online.
Environmental Concerns & Regulatory Hurdles
- The deployment of floating power plants in marine and freshwater environments, however, raises environmental problems, including adverse effects on the aquatic environment, marine organisms, and water quality. This means that floating power plants are a good candidate for promoting clean energy while important safeguard measures must be taken to prevent a cascade of negative consequences for the essential aquatic ecosystem and its inhabitants such as fishes and marine mammals. Regulatory authorities are constantly requiring strict environmental assessment and compliance to these standards, which in turn sometimes results in project delay or overbudget.
Market Opportunities
Expansion of Floating Solar Power Projects
- Floating solar farms offer a compelling opportunity since land availability for large scale solar projects is a problem that is becoming increasingly critical. These systems make use of reservoirs, lakes and shores for clean energy production that does not take up land. Floating solar panels in addition accumulate natural water cooling which increases the efficiency of systems in comparison to ground mounted ones. Floating solar plants are being actively encouraged by the governments and the private investors such as investors in China, Japan, India in many countries where land resources are scarce.
Development of Hybrid Floating Power Systems
- Since technologies are now being developed from a variety of energy sources (wind, solar, wave, methane, and most notably liquefied natural gas [LNG] for combined hybrid floating power plants), it is now a new opportunity to improve efficiencies and reliability levels. In each of these systems a reliable power supply is delivered in conjunction by balancing power sources based on intermittent renewable energy sources mixed with backup power systems. Hybrid FPPs may be used at offshore locations, islands, and industrial areas with a steady power load.
Market Challenges
Technological Limitations
- However, due to the development of floating power technologies, there are still issues of stability, life span, and efficiency of floating structures. In extreme marine environments, the influence of strong ocean currents and strong winds can have a direct impact on the structural performance of float power system, result in the management problems and expansion of operational price. The design of economical, stable floating structures that can withstand harsh weather is a prerequisite for the large-scale deployment. In addition, the energetic requirements of power sources such as wind, solar, and wave energy onto a single floating platform require intricate engineering and energy management of systems which are ever evolving and will require additional technological advancements.
Logistics & Supply Chain Disruptions
- Floating power plants are based upon sophisticated equipment, materials and installation technique which in turn make their supply chains complex and thus more vulnerable from disruptions. Transport and installation of large floating units is associated with logistical difficulties such as the presence of appropriate port infrastructure (e.g., berths, cranes, offshore boats) etc. Component manufacturing delays, geopolitical tensions and material shortages all lead to large slippage of deadlines and cost. Furthermore, maintenance and repair work offshore is carried out by properly trained personnel and appropriately equipped vessels, which increases the complexity of operations.
Floating Power Plant Market Segmental Analysis
Power Source Analysis
Renewable: Renewable energy sources, such as offshore wind, floating solar, and wave energy, are becoming the preferred choices for floating power plants due to their sustainability and low environmental impact. Offshore wind turbines utilize powerful ocean winds, while on water surface solar panels take the maximum advantage on energy production and do not utilize land. Wave and tidal power offer other sources of continuous power generation. These clean energy technologies help decrease carbon pollution and energy dependence.
Floating Power Plant Market Revenue Share, By Power Source, 2024 (%)
| Power Source |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Renewable |
29.90% |
| Non-Renewable |
70.10% |
Non-Renewable: Non-exhaustive renewable energy sources, for example, liquefied natural gas (LNG) and diesel, remain under application in power boats with particular emphasis on off-grid and emergency contexts. Floating power stations that operate on liquefied natural gas (LNG) provides a cleaner option to coal and oil, whereas the output of its power-stations is stable and high powered. Diesel generators are widely used for temporary or backup power supply, though their high emissions. As non-renewable floating power plants offer a steady electricity supply, increasing environmental and volatile fuel prices are compelling industries and governments to shift a systematic process from non-renewable options to greener solutions, which eventually reduces their appeal for longer terms in the energy picture.
Power Rating Analysis
Low (Less than 20 MW): Low-power floating power plants are mainly in small-scale applications, which are mainly used to light remote islands, coastal populations, and industrial centers with medium energy requirements. These plants commonly take advantage of renewable energy generation resources, such as floating solar panels or small-scale wind energy generators. Two characteristics are fast deployment, low cost to operate, and an adaptable design, that makes it suitable for off-grid and localized sources of energy. Moreover, they are also battery backups for emergencies and natural disasters.
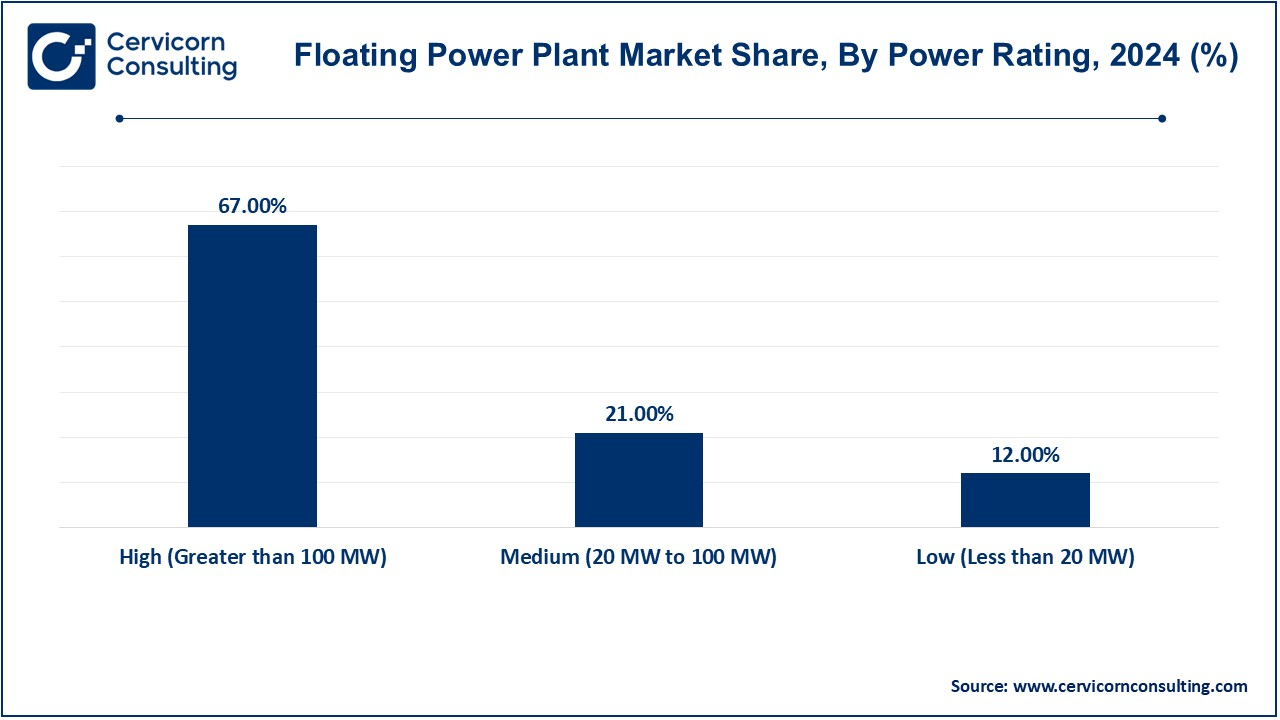
Medium (20 MW to 100 MW): Medium-power PFPPs offer an intermediate solution between scale-up and energy production and hence are appropriate for medium-sized cities, industrial areas and hybrid renewable energy applications. These plants use often energy sources in combination, e.g., LNG, wind, and solar, to provide a steady and continuous power supply. They provide a cost-efficient alternative for those areas with increasing energy needs and limited (land-based) infrastructure. Medium-sized floating power plants herein contribute significantly as well to the integration of renewable energy onto national grids, providing transitional platforms as well in energy diversification efforts while decreasing the reliance on fossil fuel-based generation.
High (Greater than 100 MW): High-power floating power plants are intended to deliver the power needs of large urban centers, heavy industries, and national grid augmentation. Such plants have traditionally been supplied by LNG, the energy of large-scale wind farms or combinations of both, to provide stable and high capacity electrical outputs. They are frequently installed in off-shore environments where terrestrial generation plants cannot be implemented. High-power floating power plants are technically demanding in terms of grid integration, need a lot of infrastructure, and can be expensive, but offer a reliable alternative to traditional on-shore power plants. With the development of technology, these big-scale floating power plants will be assumed to play an important role in global energy changes.
Floating Power Plant Market Regional Analysis
The floating power plant market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
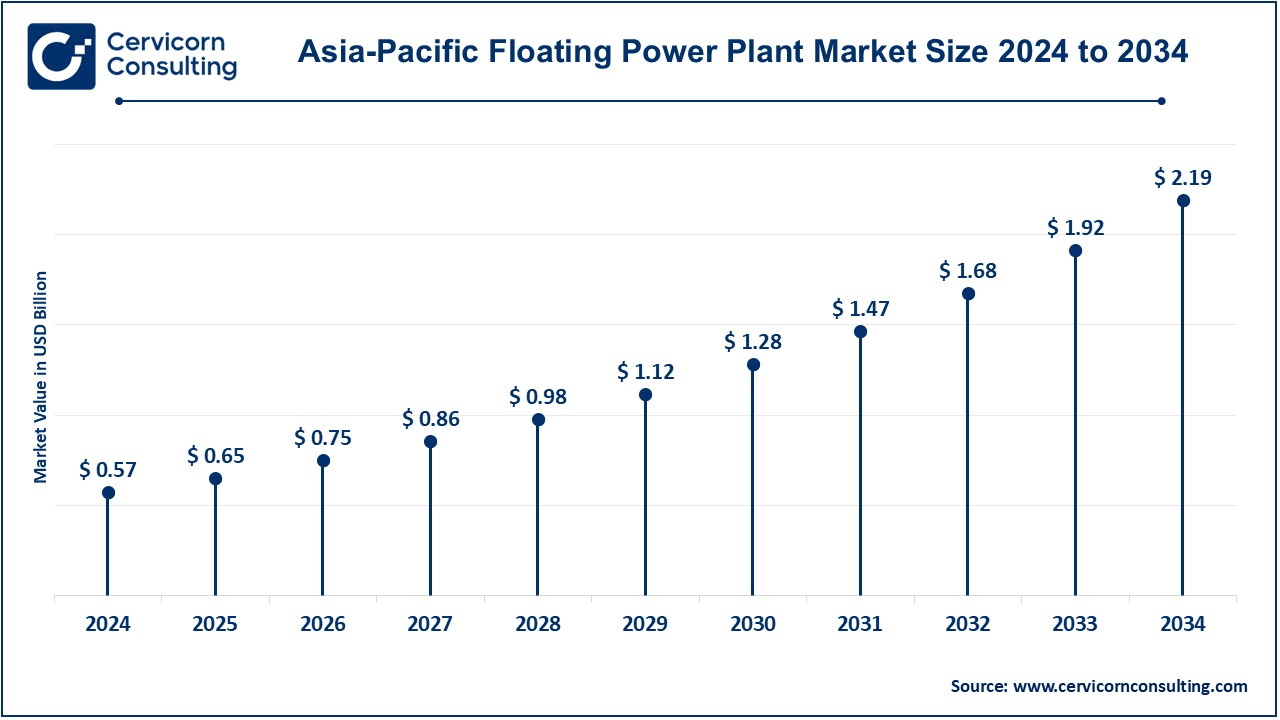
Asia-Pacific dominated the floating power plant market
The Asia-Pacific floating power plant market size was accounted for USD 0.57 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow around USD 2.19 billion by 2034. Riding a current of rapid growth, the Asia-Pacific market is propelled by growing energy needs, government subsidies, and geographic advantages fostering offshore power projects. In Japan, South Korea, China and India, oversupply of land and power increase of renewable energy sources through floating wind and solar farm investments are realized. In Southeast Asian countries, which have a large number of islands, ghosted power plants are being put into practice for decentralised generation. Also, floating LNG power plants are in reality to meet the increasingly demand of industrial electricity. However, in the wake of technological advancements, cost reductions, and supportive government regulations, the result and Asia-Pacific is a highly promising region for market expansion in the future.
North America Floating Power Plant Market Trends
The North America floating power plant market size was estimated at USD 0.32 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 1.24 billion by 2034. The North American market is built by newer investments on renewables, but mostly because of offshore wind up and running in the US and Canada. By promoting C emission reduction and energy system transformation, the area has been witnessing an increasing abundance of floating solar and hybrid power installations. US government policy creating a market for deep water offshore wind energy leads to an increase in market size. Also, floating LNG power plants have been deployed for energy security and emergency power applications. Although ongoing regulatory challenges, the development of floating technologies and generous public and private funding have made North America a strong market.
Europe Floating Power Plant Market Trends
The Europe floating power plant market size was reached at USD 0.28 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow around USD 1.07 billion by 2034. Europe is in a position of leadership, driven by the existence of strong policy support, substantial offshore wind farm deployments, and expedited carbon neutrality targets. Across the abyssal sea, the deployment of expanse wind farms is one of the goals of many countries, such as Great Britain, Germany, Norway and France, in order to capture as much possible renewable energy. Because the market is expanding that is fueled by the European Union's strategy for sustainability and energy, etc. Technological advancements in float platforms, energy storage, and in hybrid power systems are enabling performance to enhance and cost to reduce. However, regulatory complexities and environmental concerns pose challenges.
LAMEA Floating Power Plant Market Trends
The LAMEA floating power plant market was valued at USD 0.25 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 0.95 billion by 2034. The LAMEA is somewhat new, but there is a growing requirement for power systems which are resilient and decentralized. In Latin America, Brazil and Chile are currently constructing their floating photovoltaics to enhance their renewable energy mix. Floating LNG power plants are highly sought after in the Middle East for energy diversity and for power generation in isolated locations. Floating power stations (FPS) are being set up in Africa, a power-hungry nation suffering from the lack of electricity, to offer the off-grid power end-use to rural and coastal communities. However, economic, political unrest and lack of infrastructure limit its application. As one of the areas with high growth potential, the LAMEA region offers vast opportunities for strategic investments and international collaboration in the coming future.
Floating Power Plant Market Top Companies
Recent Developments
- In the year 2024, Floating Power Plant announced that it received one 4.3 megawatt SWT-DD-120 Wind Turbine Generator from Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy company. This development permits the company to further advance the flagship demonstrator project off the coast of Gran Canaria, Spain. The generator serves the vital role of integrating wave and wind power together with hydrogen storage technologies into this project. The project had received a grant of more than USD 27 million from the EU Innovation Fund, further marking the project's significance in taking forward the clean energy objectives of the EU.
- In the year 2024, Ciel & Terre Taiwan, developer of floating solar PV products, along with HEXA Renewables, an Asian renewable energy company, announced the completion of a near-shore floating solar project in Taiwan. The project lies within Changhua County's Changbin Industrial Park, boasting a capacity of approximately 440MWp, of which Ciel & Terre Taiwan claims 280MWp of floating photovoltaic (FPV). Ciel & Terre have also developed the New Pillar anchoring solution that minimizes displacement of FPV under any condition.
Market Segmentation
By Power Source
By Power Rating
- High (Greater than 100 MW)
- Medium (20 MW to 100 MW)
- Low (Less than 20 MW)
By Platform Type
- Floating Structure
- Power Barges
- Power Ships
By Application
- Manmade Water Bodies
- Natural Water Bodies
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA
...
...



