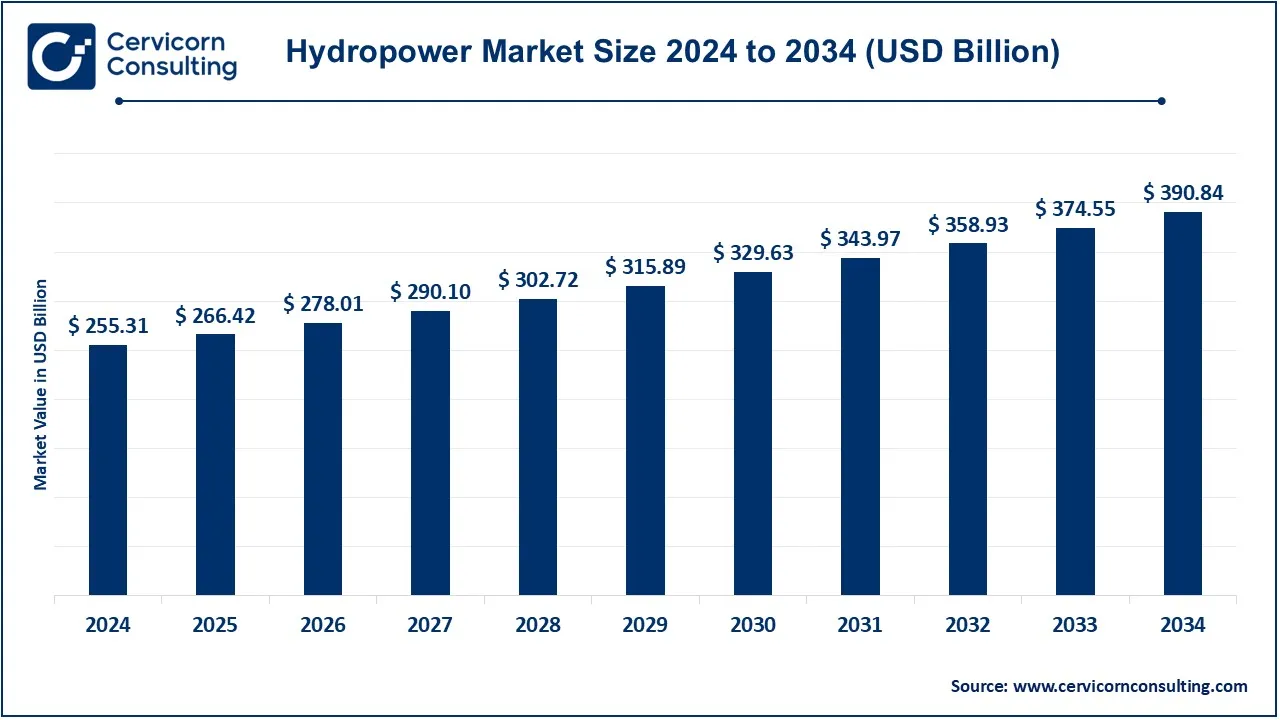
The global hydropower market size was valued at USD 255.31 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 390.84 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.35% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The global hydropower market has been growing steadily due to increasing demand for clean energy, government initiatives, and technological advancements. Many countries are investing in hydroelectric projects to meet renewable energy targets and reduce carbon footprints. Developing economies, especially in Asia and Africa, are expanding their hydropower capacity to support growing energy needs. Additionally, modernization of old hydro plants in Europe and North America is enhancing efficiency and sustainability. Floating hydropower systems and hybrid models combining solar and hydro energy are also driving market innovation.
Hydropower is the process of generating electricity using moving water. It works by capturing the energy of flowing or falling water, typically from a river or dam, and converting it into electricity through turbines and generators. Hydropower is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources, offering a clean and sustainable way to produce electricity without burning fossil fuels. One of the key benefits of hydropower is its reliability, as water flow can be controlled through reservoirs to generate power when needed. It also supports grid stability, provides flood control, and creates opportunities for irrigation. Unlike solar and wind energy, which depend on weather conditions, hydropower offers a steady and consistent energy supply. Additionally, it contributes to reducing carbon emissions and dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Key Insights related to the Hydropower:
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 266.42 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 390.84 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2034) | 4.35% |
| Leading Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Capacity, Component, Application, Region |
| Key Companies | GE Energy, Andritz AG, China Three Gorges Corporation, IHI Corporation, The Tata Power Company, Alstom Hydro, Sinohydro Corporation, ABB Ltd, Alfa Laval, Voith GmbH |
The global hydropower market is segmented into capacity, component and application. Based on capacity, the market is classified into mini, micro & pico-hydro plants, small hydropower and large hydropower. Based on component, the market is classified into electromechanical equipment, electric & power infrastructure, civil construction and others. Based on application, the market is classified into residential, commercial and industrial.
Small Hydropower: Small hydropower is regarded as constructions with a usual power output of up to 10 MW. Although their capital expenses are low and they support the environment, they generally vary from larger installations. Since small hydropower stations can easily be integrated into water infrastructure in remote or even rural regions, access to big power grids does not have to be the only possibility to receive electricity there. They also contribute to regional economies by availing communities of a source of power while at the same time reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Large Hydropower: Large hydropower projects have been defined as plants or facilities that generate over 10 MW of electricity. They often require hefty investments and other strategic infrastructure such as dams and reservoirs to tap large quantities of water flows for a very massive electricity production scale. Large hydropower also plays an essential role in the source of renewable energy globally that helps stabilize the grid and industrial energy requirements. This is however not free of such issues as environmental problems and forced eviction from the community.
Others: Under the heading "Others" falls a mixed bag of hydropower technologies and configurations that don't fit neatly into small or large. There's pumped storage hydropower, where the major applications are energy storage and grid balancing. And run-of-river systems, which generate electricity without much in the way of water storage. Such alternative technologies hold the key to diversifying the hydropower mix and meeting particular energy needs while minimizing ecological footprints.
Residential: The small hydropower installation can be used to power residential homes and communities. This represents off-grid schemes that utilize small hydropower installations to directly feed electricity into homes. In this regard, more access to energy has been realized, mostly in isolated areas; therefore, the people have a reliable sustainable source of power supply for lighting, heating, and appliances.
Commercial: Hydropower in commercial applications is used to power companies and commercial institutions. This part is a small installation similar to those required in hotels or resorts and big systems feeding urban centers. Hydropower for the commercial sector is essential in cutting costs and carbon footprint. It allows companies to produce power from renewable resources and facilitates the achievement of a greener and cleaner environment.
Hydropower Market Revenue Share, By Application, 2024 (%)
| Application | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Residential | 30% |
| Commercial | 23% |
| Industrial | 47% |
Industrial: Actually, the industrial sector is still the greatest consumer of hydropower, utilizing large plants that are still at the heart of high energy-intensive manufacturing and processing activities. Electricity generated from hydropower is much more reliable and less costly, thus being aligned with the interests of mining companies, metal manufacturers as well as chemical producers. The installation of renewable sources by industrial players can further aid them in improving their sustainability profiles and greenhouse gas emissions rates as well as providing them with stable long-term energy prices.
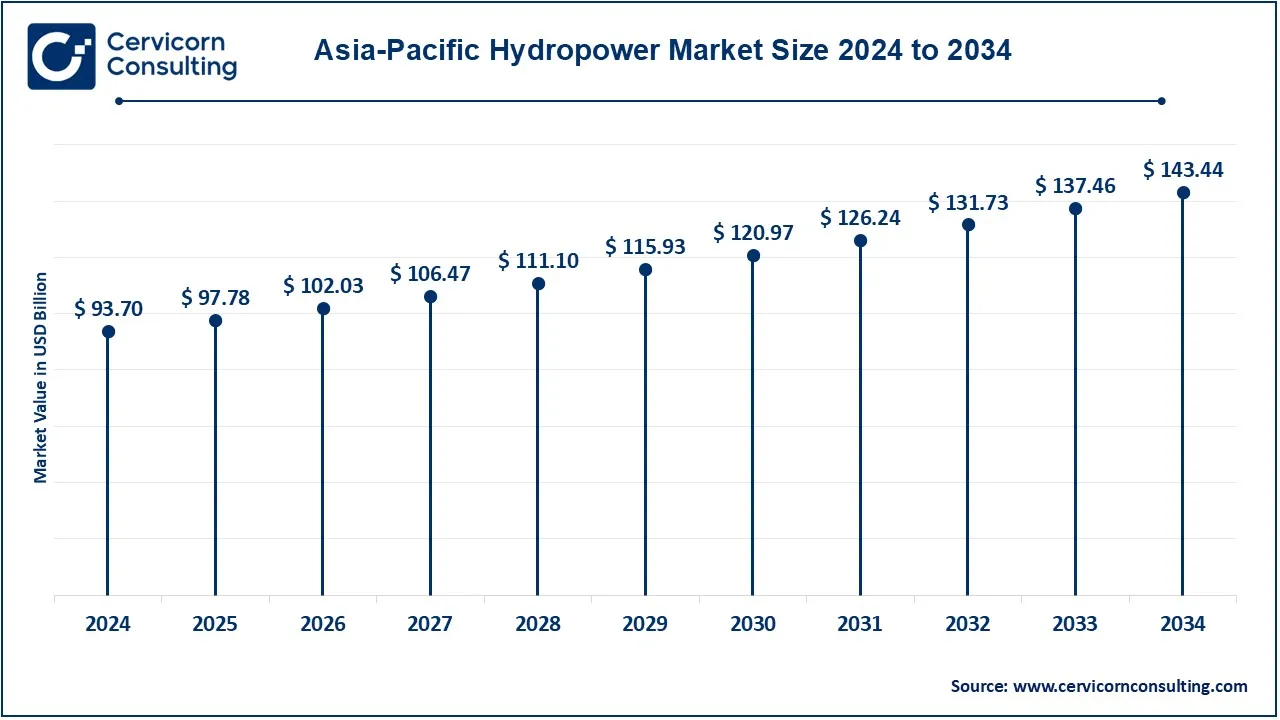
The global market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). The Asia-Pacific dominated the market in 2024.
The Asia-Pacific hydropower market size was accounted for USD 93.70 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 143.44 billion by 2034. Asia-Pacific is one of the key regions of hydropower development, and China boasts of having the largest hydropower capacity in the world. Of course, the epitome of this hydropower development in China could be seen in the Three Gorges Dam, which is the world's largest hydroelectric project. Other countries with vast potential for hydro electrical development are the Indian nation, with its mountainous areas, and Japan, whose government is keen on the promotion of small- and medium-sized hydropower plants in the wake of the Fukushima disaster. Countries like Nepal and Bhutan have also resorted to hydropower more as means of spurring economic growth and energy security.
The North America hydropower market size was valued at USD 56.93 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 87.16 billion by 2034. The North America market is dominated more by the United States and Canada. Among the world's biggest hydroelectric plants, the U.S. has several such as the Grand Coulee Dam and the Hoover Dam. These facilities are highly contributing to the renewable energy mix of the country. Canada contributes similarly in the hosting of enormous volumes of water resources and major projects like Sir Adam Beck Hydroelectric Generating Station. Simultaneously, both states target efficiency and minimum adverse effects on the environment through maintenance and upgrading of existing infrastructure.
The Europe hydropower market size was estimated at USD 72.51 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 111 billion by 2034. Hydropower in Europe is quite diversified; some of the leading contributors are Norway, Sweden, and France. Hydropower has been the backbone of Norway and accounted for up to 95% of the total electricity produced in the country. Hydropower in Sweden also boasts high capacity results because of a significant number of plants along its rivers. Hydropower is an important proportion in the energy supply system in France, mainly from the Rhône and Loire river systems. The European Union is ever more embracing renewable energy programs, leading to investments in hydropower infrastructure across the continent.
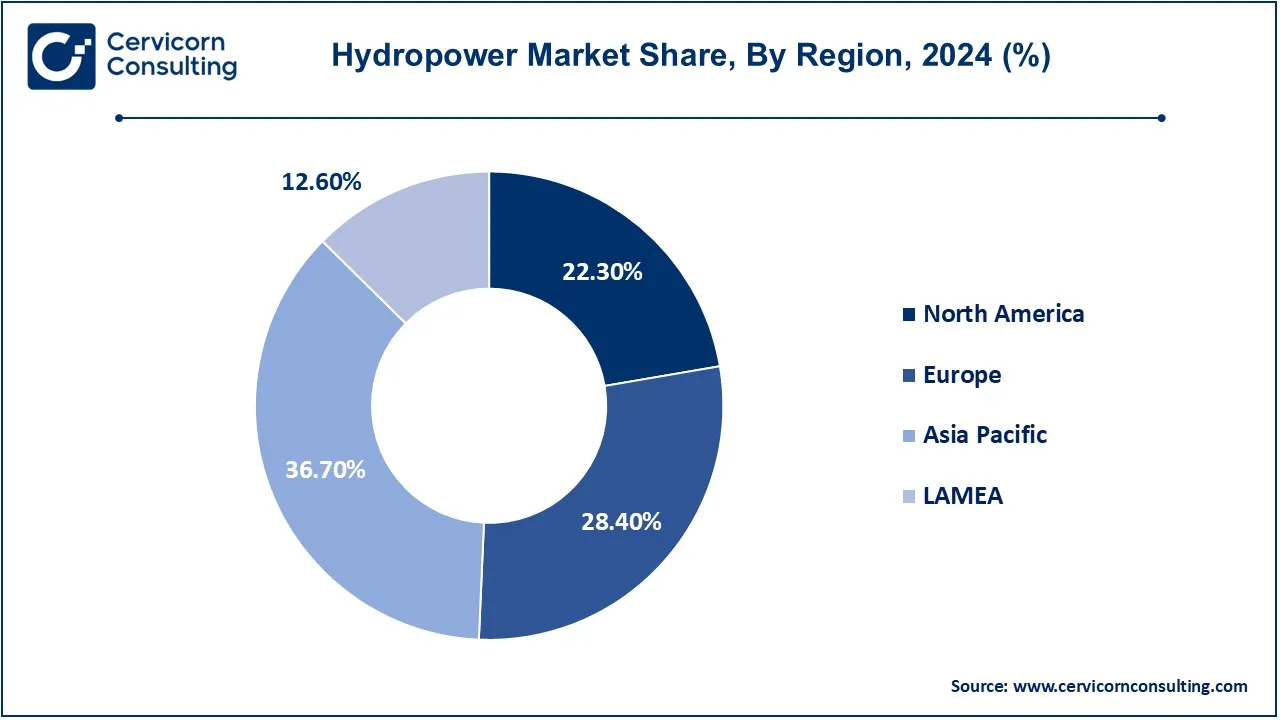
The LAMEA hydropower market was valued at USD 32.17 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 49.25 billion by 2034. The LAMEA region comprises Brazil and Colombia in the hydropower generation series. Brazil is highly dependent on hydropower; in fact, it gets around 60% of its electricity from this source, the greater portion of which comes from the Belo Monte and Itaipu dams. Colombia has also started to concentrate more on hydropower and is on the drawing boards with projects like the Guatapé Dam. This includes among others the hydropower projects in Africa, such as the giant Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam in Ethiopia and Zambia. The goals encompass better energy access, further regional integration, and simplification of cooperation within the region. Hydropower in the region has thus far been explored on a smaller scale mainly under the umbrella of the management of water resources as well as renewable energy diversification.
CEO Statements
Lawrence Culp, Jr., CEO of GE Energy
Joachim Schönbeck, CEO ofANDRITZ
Praveer Sinha, CEO of Tata Power Company
Proper investments and acquisitions within the hydropower industry reflect a shift towards innovation and strategic cooperation by key market participants. Among these innovators are GE Energy, Andritz AG, China Three Gorges Corporation, IHI Corporation, and Tata Power Company. They develop these through cooperation and new technologies into new operations that improve operating efficiencies, enhance the performance of turbines, and digitize solutions for better management of available resources. That is not to say this collaborative approach breeds innovation; it also positions the industry to meet the increasing demands of global energy while emphasizing sustainability and environmental stewardship. Thus, as they continually innovate, these leaders help shape the future of hydropower and underscore its importance in the renewable energy landscape. Some notable examples of key developments in the hydropower industry include:
Market Segmentation
By Capacity
By Component
By Application
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Hydropower
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Capacity Overview
2.2.2 By Component Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Hydropower Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Government Incentives
4.1.1.2 Public Awareness
4.1.1.3 Hydro Power Storage Solutions
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Upfront Expenditure Costs
4.1.2.2 Geographical Constraint
4.1.2.3 Public Opposition
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Financing
4.1.3.2 Balancing Energy Needs with Ecology
4.1.3.3 Capacity Planning
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Hydropower Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Hydropower Market, By Capacity
6.1 Global Hydropower Market Snapshot, By Capacity
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Mini
6.1.1.2 Micro & Pico-hydro Plants
6.1.1.3 Small Hydropower
6.1.1.4 Large Hydropower
Chapter 7. Hydropower Market, By Component
7.1 Global Hydropower Market Snapshot, By Component
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Electromechanical Equipment
7.1.1.2 Electric & Power Infrastructure
7.1.1.3 Civil Construction
7.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 8. Hydropower Market, By Application
8.1 Global Hydropower Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Residential
8.1.1.2 Commercial
8.1.1.3 Industrial
Chapter 9. Hydropower Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 Hydropower Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
9.3 Global Hydropower Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America Hydropower Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe Hydropower Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UK Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 France Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 Germany Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of Europe Market Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific Hydropower Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 China Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 Japan Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 India Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 Australia Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia Pacific Market Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA Hydropower Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCC Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 Africa Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 Brazil Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Hydropower Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEA Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 GE Energy
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Andritz AG
11.3 China Three Gorges Corporation
11.4 IHI Corporation
11.5 The Tata Power Company
11.6 Alstom Hydro
11.7 Sinohydro Corporation
11.8 ABB Ltd
11.9 Alfa Laval
11.10 Voith GmbH