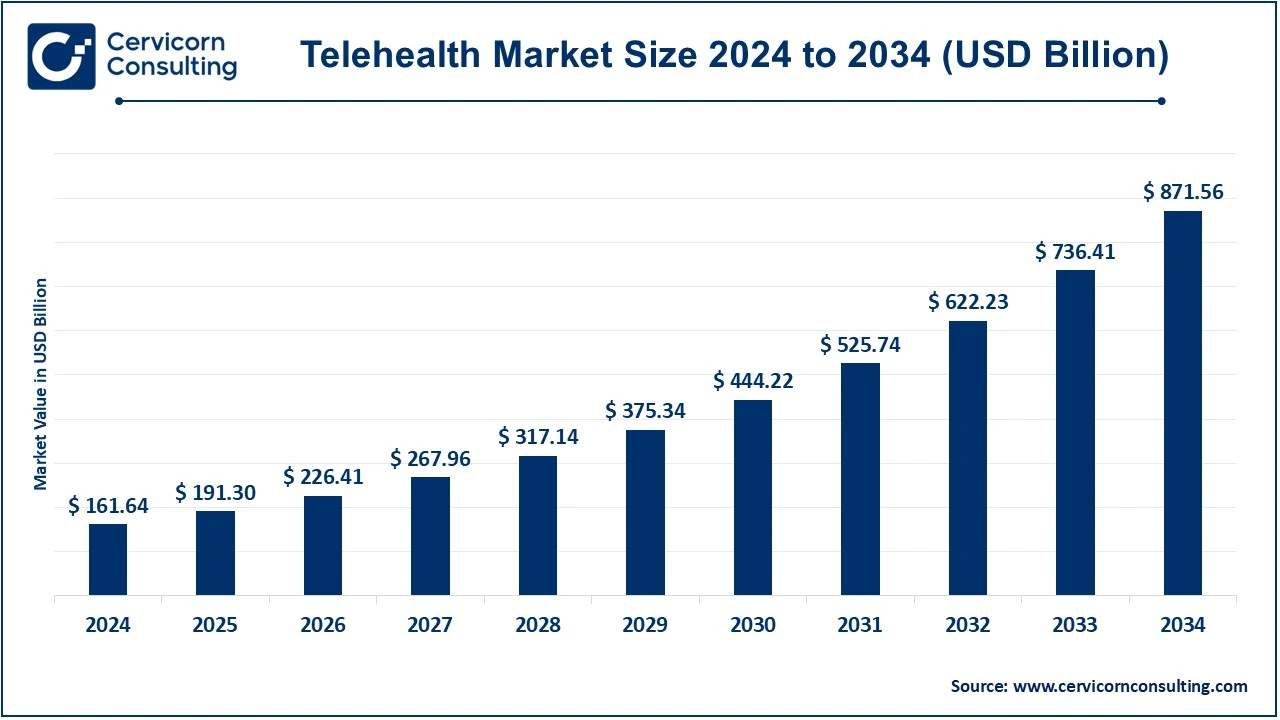
The global telehealth market size was valued at USD 161.64 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 871.56 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.35% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The increasing demand for accessible healthcare, higher development of digital technologies, and higher adoption of remote care support the growth of the telehealth market. Other prominent factors are the rise in the prevalence of chronic conditions, the aging population, and the increased penetration of smartphones and the Internet. Government and health sectors are implementing telehealth to minimize costs and provide better outcomes for patients. Due to the rapid spread of the COVID-19 epidemic, the pace of adoption and normalization of virtual consultations and home monitoring was facilitated. Innovations in the form of AI, wearable devices, and cloud-based platforms further propel growth through individualized and effective care. In addition, expansions in healthcare infrastructure in developing economies and regulatory support further contribute to rapid expansion in this market.
Telehealth market has recently gained momentum mainly because of advancements made in communication technologies and increased demands for accessible health. This major trend behind telehealth is growing virtual care where more and more patients have opted to view their healthcare providers online. Other important trends that fuel growth in the telehealth market are integration with artificial intelligence and wearable devices that help monitor patients remotely, making healthcare both efficient and accurate. Improved mental health services, such as teletherapy, have helped increase access to mental health providers for patients.
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 191.30 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 871.56 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 18.35% |
| Dominant Area | North America |
| Leading Growth Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Product, Service Type, Technology, Disease Area, Delivery Mode, Application, End-Users, Region |
| Key Companies | Teladoc Health, Amwell (American Well), One Medical, Doxy.me, Mend, VCDoctor, SecureVideo, Updox, athenaOne, Klara, Valant EHR Suite, NextGen Virtual Visits, SimplePractice, TheraNest, Sesame Care |
Growing demand for convenience and accessibility
Technology Advancement
Limited access to technology
Privacy and security issues
Expansion into Rural and Remote Areas
Expansion in Specialized Telehealth Services
Regulatory and Legal Challenges
Technology and infrastructure limitations
Based on product, the market is classified into hardware, software and services. Based on service type, the market is classified into telemedicine, telemonitoring and store-and-forward. Based on technology, the market is classified into video conferencing, mobile health (mHealth), wearable devices and remote patient monitoring (RPM). Based on disease area, the market is classified into psychiatry, substance use, radiology, endocrinology, dermatology, gastroenterology, neurological medicine, ENT, cardiology, oncology, dental, gynecology, general medicine and others. Based on delivery mode, the market is classified into on-premises, web-based and cloud-based. Based on application, the market is classified into telemedicine for primary care, mental health services, chronic disease management and emergency care. Based on end-users, the market is classified into healthcare providers, patients and healthcare payers.
Telemedicine: This is the use of technology for remote consultation with a patient via health care providers. It involves consultations through video calls, phone calls, or computer-based calls. With telemedicine, diagnosis, treatment, and even follow-up management can be done without an in-person consultation. It is applicable in general consultations and especially follow-ups and managing chronic conditions. Telemedicine provides health care to even the most remote, underserved areas. It also saves waiting and travel time, which this becoming very popular because it is convenient and cheap, hence is a core part of the telehealth market.
Telemonitoring: Telemonitoring is the tracking of patients' health data remotely through connected devices, including monitoring vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, glucose levels, and oxygen levels. The information is relayed to the healthcare providers to enable them to study the data and take action in case the patient's condition deteriorates. It is helpful to patients with chronic conditions because the healthcare provider can check the status of patients from time to time without requiring constant office visits. Telemonitoring also improves patient outcomes since timely intervention helps reduce hospital readmissions.
Store-and-Forward: This type of telehealth service involves gathering patient information like medical images or test results and delivering it to healthcare providers for later review. It does not require real-time interaction. For instance, a patient uploads a picture of a skin condition on the telehealth portal, and in some periods, a dermatologist analyzes it to give a diagnosis. It is especially useful in specialties such as dermatology, radiology, and pathology. It enables access to specialist care to be improved especially if there is a remote location as it helps improve the efficiency of providing health care by reducing the waiting time.
Video Conferencing: Video Conferencing is the most widely used technology in telehealth. It allows the patient to have face-to-face consultations with healthcare providers through video calls in real time. This is very useful for consultations that do not require physical examinations, such as mental health services, follow-up appointments, and general consultations. It saves time, is convenient, and reduces travel needs, especially for patients in rural areas. Video conferencing ensures that healthcare services remain accessible even when in-person visits are not possible, making it an essential part of telehealth.
Mobile Health (mHealth): This involves the use of mobile technology such as smartphones and tablets in the management of health. It is the application of monitoring vital signs, tracking drugs, and even providing healthcare counseling. Patient tools help them communicate with their physicians, remind them to take medications, or keep track of their symptoms. Therefore, access to healthcare becomes possible through technology, especially for those individuals with chronic diseases, which need continuous monitoring. This also gets very convenient to the patients because they can be attended to anywhere, anytime using the mobile devices of the patients.
Wearable Devices: In the case of telehealth, these wearable devices can be smartwatches and fitness trackers that monitor as well as observe the health situation of the patient in real-time. It will record their vital signs, sleep patterns, physical activities, and so on. Such information is mostly transferred to the health care provider to get analyzed. Wearables will help patients with chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease track their health, and healthcare providers intervene when necessary. These devices will make it easier for both the patient and provider to stay on top of health management and better long-term health outcomes.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Remote patient monitoring (RPM) uses digital devices to track patients' health from a remote location. All the vital signs are measured in these devices, including blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate. The received data is communicated to healthcare providers who monitor the patients. It helps to intervene promptly. RPM is useful for managing chronic conditions, minimizing hospital visits, and allowing the continued care of patients. It enhances the accessibility of patients in remote areas to health care, assists in lowering the costs of health care, and empowers the patient to control his or her health.
Telemedicine for Primary Care: Telemedicine for primary care is the type of telemedicine where a patient can get consultations with his or her primary healthcare provider via video calls or phone consultations. It is utilized for general health problems, regular check-ups, and non-emergency conditions. This application is especially useful for patients who require regular follow-ups or patients who cannot visit their doctor conveniently due to geographical distance or disability. Telehealth has been utilized to bring primary care closer to the patients by saving time for both doctors and patients, reducing waiting time, and making access to primary care services much easier.
Mental Health Services: Telehealth has also been applied to mental health services, which include counseling and therapy. A patient can talk to mental health professionals through video calls, phone calls, or messaging, which is convenient and discreet. It is useful for people who may not easily reach mental health care due to location, stigma, or inability to move about. Telehealth enables patients to obtain care in comfort settings and empowers professionals to render continuous care for anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
Chronic Disease Management: Telehealth is increasingly becoming a tool for chronic disease management, including diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. Healthcare providers continue to monitor patient health and reassess their treatment through remote monitoring and virtual consultations. The number of visits that patients have to make to a healthcare provider's office is also reduced because patients receive timely interventions in case their health worsens. Telehealth assists patients in managing their conditions from the comfort of their homes, which enhances their quality of life while reducing hospital visits. This technology also aids patients in changing their lifestyles and living healthier through continuous monitoring and feedback.
Emergency care: Telehealth is relatively rare in emergency care, but it can be seen in triaging and initial consultation. With telehealth, healthcare professionals may identify the severity of a situation, advise a patient immediately, or refer the patient to the nearest facility providing emergency care. Telehealth can fill the gap where emergency care is not available or easily accessed in rural or underserved areas. This application is valuable in urgent cases, where timely advice can make a difference in patient outcomes.
Healthcare Providers: Healthcare providers such as hospitals, clinics, and private practices use telehealth to extend their services to patients remotely. Providers are adopting telehealth platforms to reduce patient wait times, expand their patient base, and offer care to those who might otherwise struggle to access healthcare. More so, healthcare providers enhance the efficiency of care by reducing in-person consultations to accommodate more patients seen in one day. It also helps the provider maintain continuity of patient care in emergency scenarios such as during COVID-19.
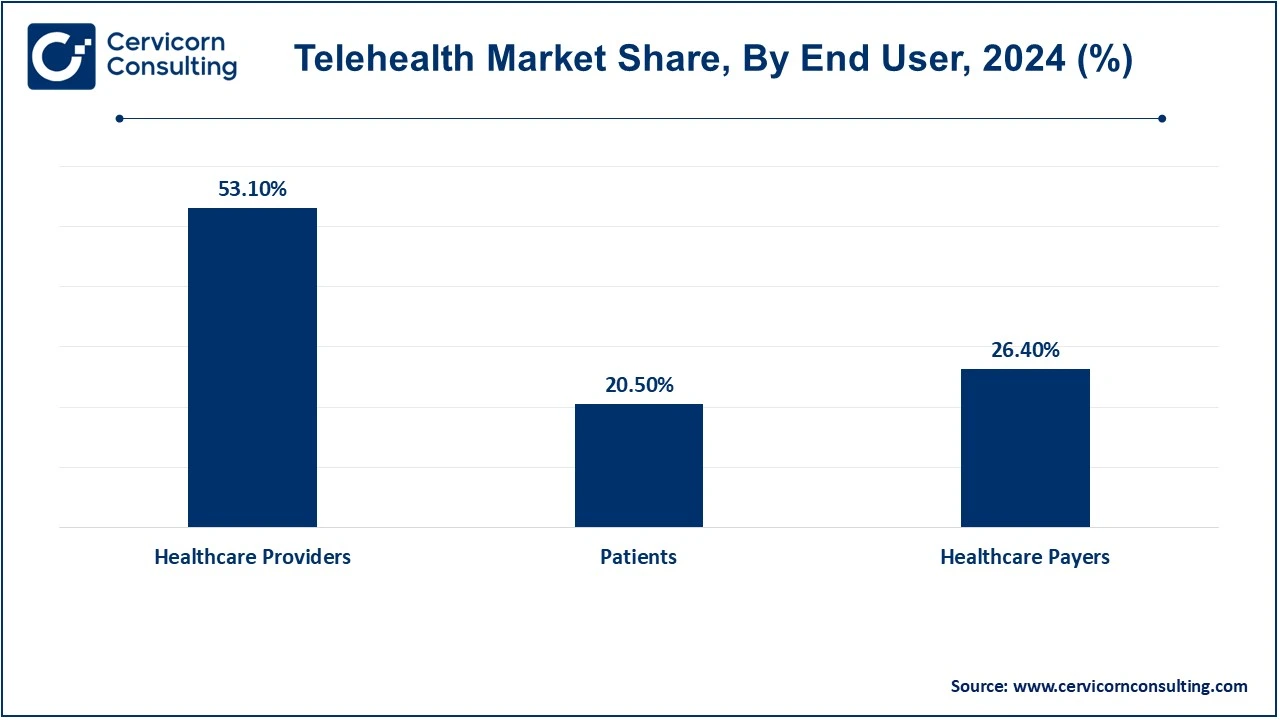
Patients: The direct users of telehealth are patients seeking healthcare services. Telehealth is a solution that offers access to healthcare for people who live in rural areas or have mobility problems or busy timetables, and it covers patients consulting different healthcare professionals related to general inquiries about health as well as disease management. Therefore, it also provides flexibility but ensures that accessibility to healthcare is better for a majority of the people.
Healthcare Payers: The payers of healthcare include insurance companies and government bodies such as Medicare and Medicaid. These are some of the most significant stakeholders in the telehealth market. The policies of these payers influence telehealth adoption since they set the policies and the rates of reimbursement for services. They also play a critical role in determining which telehealth services will be covered under the insurance plans. Telehealth increasingly is becoming one of the factors that benefit payers, and these factors are those of saving in healthcare costs, improving outcomes for patients, and expanding care accessibility. In line with this trend, as telehealth continues to develop, so too will healthcare need to adjust policies regarding coverage effectiveness.
The telehealth market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
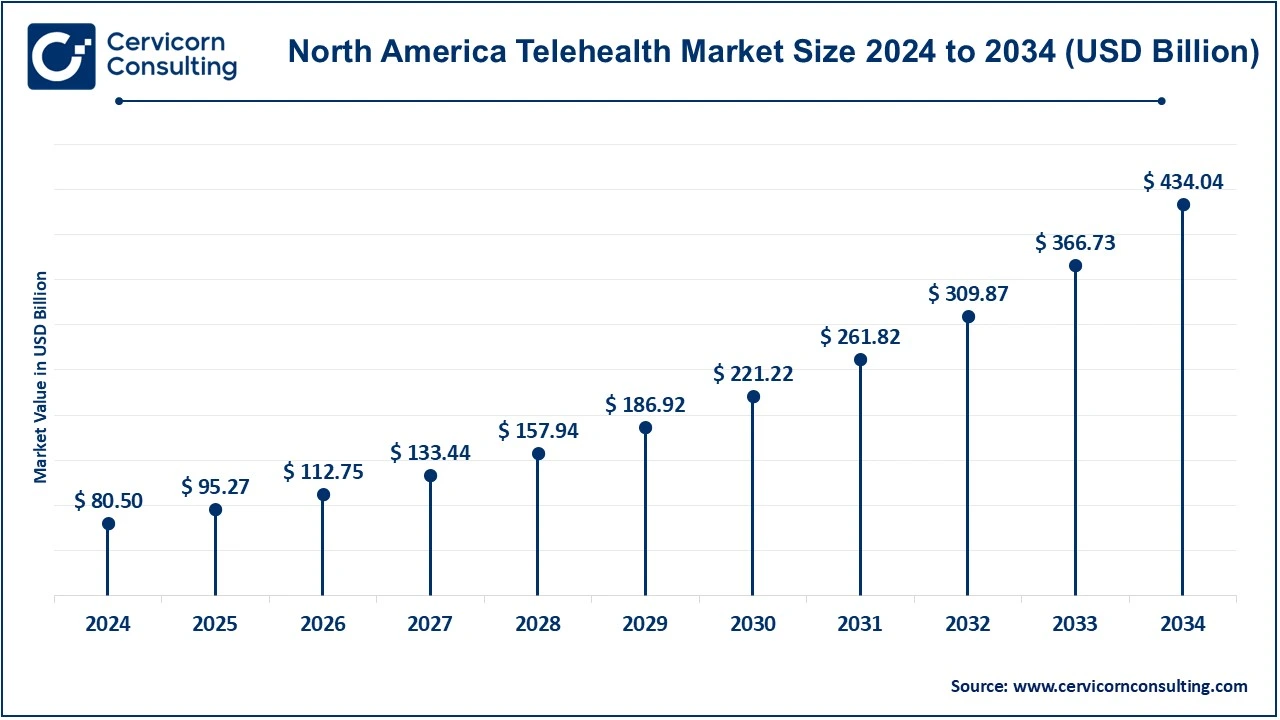
The North America telehealth market size was estimated at USD 80.50 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 434.04 billion by 2034. The United States and Canada have highly developed telehealth markets. Favorable government policies in the U.S., such as Medicare's reimbursement for telehealth services, have accelerated the adoption of telehealth. The region also benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure and high internet penetration. North America is expected to continue leading the market with increasing demand for remote consultations, mental health services, and chronic disease management. A strong focus on digital health innovation in the region also fuels market growth.
The Europe telehealth market size was reached at USD 36.21 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow USD 195.23 billion by 2034. The Europe is growing because various countries implement digital health strategies to increase access and enhance efficiency in healthcare. Countries like the UK, Germany, and France invest in telehealth infrastructure to increase access to care in remote regions. The European Union has also encouraged telehealth with several initiatives, such as saving healthcare costs and improving the delivery of healthcare services. The European telehealth market is expected to grow with a change in the regulatory framework and advancement in technology, which would emphasize upgrading access to primary and specialized care for patients.
The Asia-Pacific telehealth market size was accounted for USD 30.87 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 166.47 billion by 2034. Internet connectivity and the awareness of digital health are growing in the Asia Pacific region, making telehealth increasingly popular there. In this region, leaders include India, China, Japan, and Australia. Telehealth is rising as a significant alternative to bridge gaps in providing health care across remote locations in rurally remote areas, where it becomes practically impossible to reach medical facilities or even a doctor. Government bodies from these countries promote telehealth highly, primarily since overcrowding has already proved challenging to health care within many hospitals while their infrastructural elements continue to be somewhat wanting. Population and the spread of technology within Asia Pacific, going forward, should dramatically increase demands for telehealth.
Telehealth Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 49.80% |
| Europe | 22.40% |
| Asia-Pacific | 19.10% |
| LAMEA | 8.70% |
The LAMEA telehealth market size was valued at USD 14.06 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 75.83 billion by 2034. In countries like Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, telehealth is still evolving but growing exponentially. Latin American countries, Brazil and Mexico in particular, have started adopting telehealth to enhance the availability of healthcare services, especially in rural setups. Telehealth is also rapidly gaining ground in Africa and the Middle East with the region giving much emphasis on the improvement of healthcare infrastructure as well as increasing access. Despite these challenges such as internet connectivity and infrastructure, the potential for telehealth to increase accessibility to healthcare services while saving on costs is evident in these regions.
CEO Statements
Chuck Divita, CEO of Teladoc Health:
Ilan Schoenberg, CEO of Amwell:
Market Segmentation
By Product
By Service Type
By Technology
By Disease Area
By Delivery Mode
By Application
By End-Users
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Telehealth
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Product Overview
2.2.2 By Service Type Overview
2.2.3 By Technology Overview
2.2.4 By Disease Area Overview
2.2.5 By Delivery Mode Overview
2.2.6 By Application Overview
2.2.7 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Growing demand for convenience and accessibility
4.1.1.2 Technology Advancement
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Limited access to technology
4.1.2.2 Privacy and security issues
4.1.3 Market Opportunities
4.1.3.1 Expansion into Rural and Remote Areas
4.1.3.2 Expansion in Specialized Telehealth Services
4.1.4 Market Challenges
4.1.4.1 Regulatory and Legal Challenges
4.1.4.2 Technology and infrastructure limitations
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Telehealth Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Telehealth Market, By Product
6.1 Global Telehealth Market Snapshot, By Product
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Hardware
6.1.1.2 Software
6.1.1.3 Services
Chapter 7. Telehealth Market, By Service Type
7.1 Global Telehealth Market Snapshot, By Service Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Telemedicine
7.1.1.2 Telemonitoring
7.1.1.3 Store-and-Forward
Chapter 8. Telehealth Market, By Technology
8.1 Global Telehealth Market Snapshot, By Technology
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Video Conferencing
8.1.1.2 Mobile Health (mHealth)
8.1.1.3 Wearable Devices
8.1.1.4 Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Chapter 9. Telehealth Market, By Disease Area
9.1 Global Telehealth Market Snapshot, By Disease Area
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Psychiatry
9.1.1.2 Substance Use
9.1.1.3 Radiology
9.1.1.4 Endocrinology
9.1.1.5 Dermatology
9.1.1.6 Gastroenterology
9.1.1.7 Neurological Medicine
9.1.1.8 ENT
9.1.1.9 Cardiology
9.1.1.10 Oncology
9.1.1.11 Dental
9.1.1.12 Gynecology
9.1.1.13 General Medicine
9.1.1.14 Others
Chapter 10. Telehealth Market, By Delivery Mode
10.1 Global Telehealth Market Snapshot, By Delivery Mode
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 On-premises
10.1.1.2 Web-based
10.1.1.3 Cloud-based
Chapter 11. Telehealth Market, By Application
11.1 Global Telehealth Market Snapshot, By Application
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
11.1.1.1 Telemedicine for Primary Care
11.1.1.2 Mental Health Services
11.1.1.3 Chronic Disease Management
11.1.1.4 Emergency Care
Chapter 12. Telehealth Market, By End-User
12.1 Global Telehealth Market Snapshot, By End-User
12.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
12.1.1.1 Healthcare Providers
12.1.1.2 Patients
12.1.1.3 Healthcare Payers
Chapter 13. Telehealth Market, By Region
13.1 Overview
13.2 Telehealth Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
13.3 Global Telehealth Market, By Region
13.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
13.4 North America
13.4.1 North America Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.3 North America Telehealth Market, By Country
13.4.4 U.S.
13.4.4.1 U.S. Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
13.4.5 Canada
13.4.5.1 Canada Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
13.4.6 Mexico
13.4.6.1 Mexico Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
13.5 Europe
13.5.1 Europe Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.3 Europe Telehealth Market, By Country
13.5.4 UK
13.5.4.1 UK Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.5 France
13.5.5.1 France Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.6 Germany
13.5.6.1 Germany Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.7 Rest of Europe
13.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6 Asia Pacific
13.6.1 Asia Pacific Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.3 Asia Pacific Telehealth Market, By Country
13.6.4 China
13.6.4.1 China Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.5 Japan
13.6.5.1 Japan Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.6 India
13.6.6.1 India Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.7 Australia
13.6.7.1 Australia Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
13.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7 LAMEA
13.7.1 LAMEA Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.3 LAMEA Telehealth Market, By Country
13.7.4 GCC
13.7.4.1 GCC Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.5 Africa
13.7.5.1 Africa Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.6 Brazil
13.7.6.1 Brazil Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
13.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Telehealth Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 14. Competitive Landscape
14.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
14.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
14.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
14.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
14.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 15. Company Profiles
15.1 Teladoc Health
15.1.1 Company Snapshot
15.1.2 Company and Business Overview
15.1.3 Financial KPIs
15.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
15.1.5 Strategic Growth
15.1.6 Global Footprints
15.1.7 Recent Development
15.1.8 SWOT Analysis
15.2 Amwell (American Well)
15.3 One Medical
15.4 Doxy.me
15.5 Mend
15.6 VCDoctor
15.7 SecureVideo
15.8 Updox
15.9 athenaOne
15.10 Klara
15.11 Valant EHR Suite
15.12 NextGen Virtual Visits
15.13 SimplePractice
15.14 TheraNest
15.15 Sesame Care