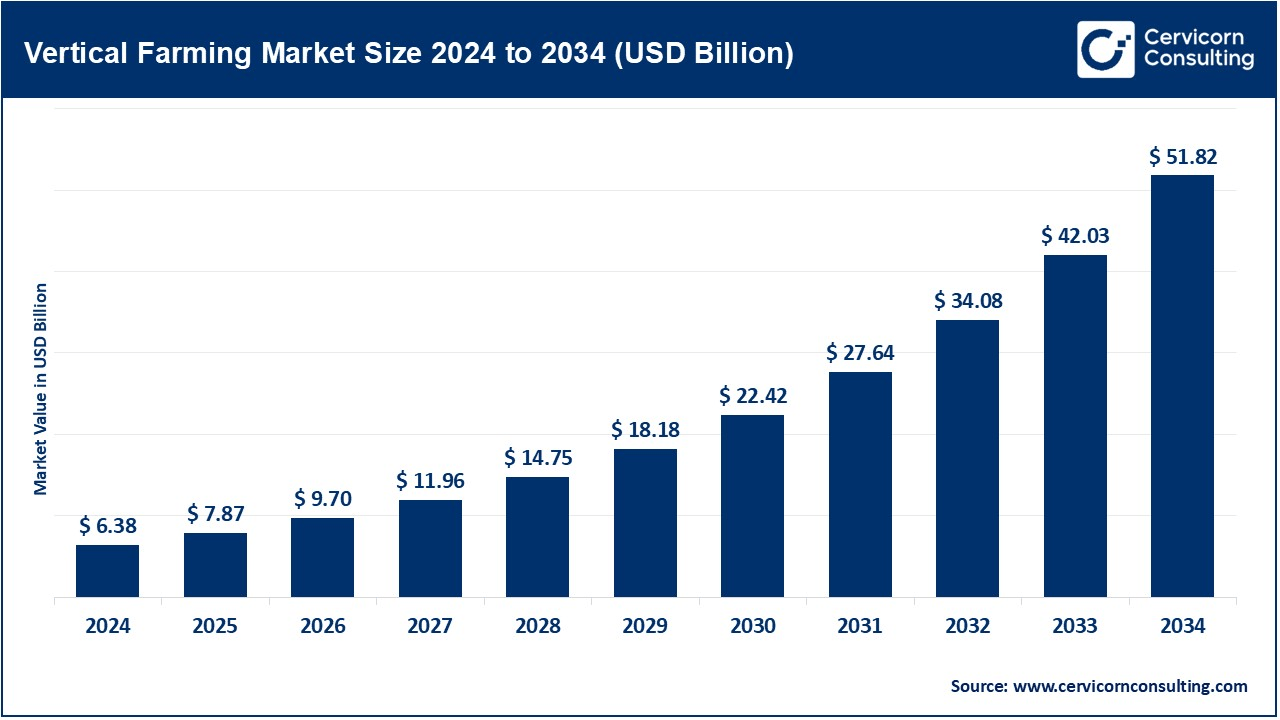
The global vertical farming market size was valued at USD 6.38 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach around USD 51.82 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.30% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. This is due to an increased demand for fresh produce, grown locally; technology development in the farm sector; less available arable land; scarce water supply; and more and more necessity to carry out farming practices in an eco-friendly way. Due to this reason, the market of vertical farming is rising. People prefer vertical farming because it uses less space to optimize resource utilizations and provides the ability to grow crops across the year under urbanized environment conditions. Support for further extension in the market is seen growing interest in food security, aligned with innovations by automation and AI-driven farming systems, as well as looking out for environmental sustainability.
Vertical farming is a way of agricultural growing where crops are grown in vertical layers or stacked systems, and it can take place in a controlled indoor setting. It utilizes vertically integrated space such as a high-rise building, a warehouse, or shipping containers in order to optimize the use of urban space. The latest innovation utilizes technologies such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics, which require far less soil and water, unlike traditional farming. This method is designed to enhance food production in high-populated regions, decrease the overall impact on the environment, and increase food production sustainability.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.87 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 51.82 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 23.30% |
| High-impact Region | North America |
| Hot Growth Market | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Structure, Growth Mechanism, Crop Category, Region |
| Key Companies | ams-OSRAM AG, Signify Holding, Heliospectra, EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS CO., LTD., Urban Crop Solutions, AeroFarms, Freight Farms, Inc, Plenty Unlimited Inc., VertiVegies, Sky Greens, iFarm |
Building Material: Building materials for vertical farming comprise of the actual physical framework which hosts the farm, including building frames and building material to construct the grow environment. Building materials used need to be hardy and long-lasting, supporting installations of systems that include irrigation, lighting, sensors, etc. These comprise metals like steel and glass besides sustainable composite. Suitable design of the building will enhance energy efficiency besides maximizing light exposure and temperature control to attain the best indoor conditions for plant growth.
Irrigation Component: The vertical farm will have to provide its crops with water and nutrients using the irrigation component.Generally, vertical farms use water-conserving irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation, hydroponics, or aeroponics, to ensure that water is consumed at a lesser rate. With these systems, the distribution of water can be closely monitored, resulting in less wastage and sufficient hydration for plants. The efficacy of irrigation components is crucial to maintaining optimal growth conditions, particularly in urban or resource-scarce environments.
Lighting: The artificial light systems used in vertical farming for supporting plant photosynthesis in the indoor environment is known as lighting. Since the natural sunlight could be limited in building-based or container-based farms, high-quality LED lights are used. Such lights are set to mimic the sun and sometimes adjustable in terms of intensity and spectrum to enhance plant growth in different stages. Proper lighting systems enhance crop yield and energy efficiency and are, therefore a fundamental part of any vertical farming operation.
Sensor: Sensors are part of the monitoring and control of the environmental factors within vertical farms. These include sensors for temperature, humidity, light, pH levels, and CO2 concentration, all which affect plant growth. The data collected by sensors enables farmers to make real-time adjustments to climate control systems, irrigation, and nutrient delivery so that plants are growing under ideal conditions. The use of sensors in vertical farming systems increases productivity, minimizes resource consumption, and promotes sustainability.
Climate Control: The aim of vertical farming in climate control systems is to regulate temperature, humidity, air circulation, and CO2 levels to condition an optimal environment for growing plants. Such climate control is usually automated, as responses are based upon data yielded from environmental sensors. Climate control is one of the essential components of an indoor farming environment in which natural weather conditions are not available. An optimal climate control condition does not let plants get distressed by temperature extremes and gets enough airflow and right humidity, allowing for better harvests and also the use of resources.
Building-based Vertical Farms: This is a style of large scale farming set in existing or new buildings, more so in towns. These plants may use several stories or layers built within the building that use hydroponic, aeroponic, among other soil less production of crops.The infrastructure of the structure will provide climate control, lighting, and irrigation for the facility to allow year-round production. This kind of structure utilizes space in cities as much as possible and provides an efficient way of food production close to urban areas. It saves on transportation cost and reduces the environment footprint.
Vertical Farming Market Share, By Structure, 2024 (%)
| Structure | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Building-based | 46.90% |
| Container-based | 53.10% |
Container-based vertical farms: The container-based segment has dominated the market in 2024. Container-based vertical farms comprise compact, mobile farming units which exist within shipping containers or modular structures. These container-based vertical farms could carry out crop cultivation in a controlled environment under a hydroponic or aeroponic system, artificial lighting, and climate control. They are portable, flexible, and can easily be placed anywhere in urban as well as rural areas. Another characteristic of the container-based farm is that such farms are really scalable and thereby on modular construction which is yet an innovative solution in small-scale and decentralized farming.
Hydroponics: The hydroponics segment garnered the largest market share in 2024. Hydroponics is a farming method by which crops grow without soil but immersed in nutrient-rich water solutions. In the case of vertically stacked crops, hydroponics is generally applied when crops are cultured. This is a more efficient way of water saving than other usual farming, which also does not need soil to cultivate crops. Hydroponic systems can be built around certain plants, so the controlled environment allows for the delivery of just the nutrients needed for maximum growth so as to maximize yields.
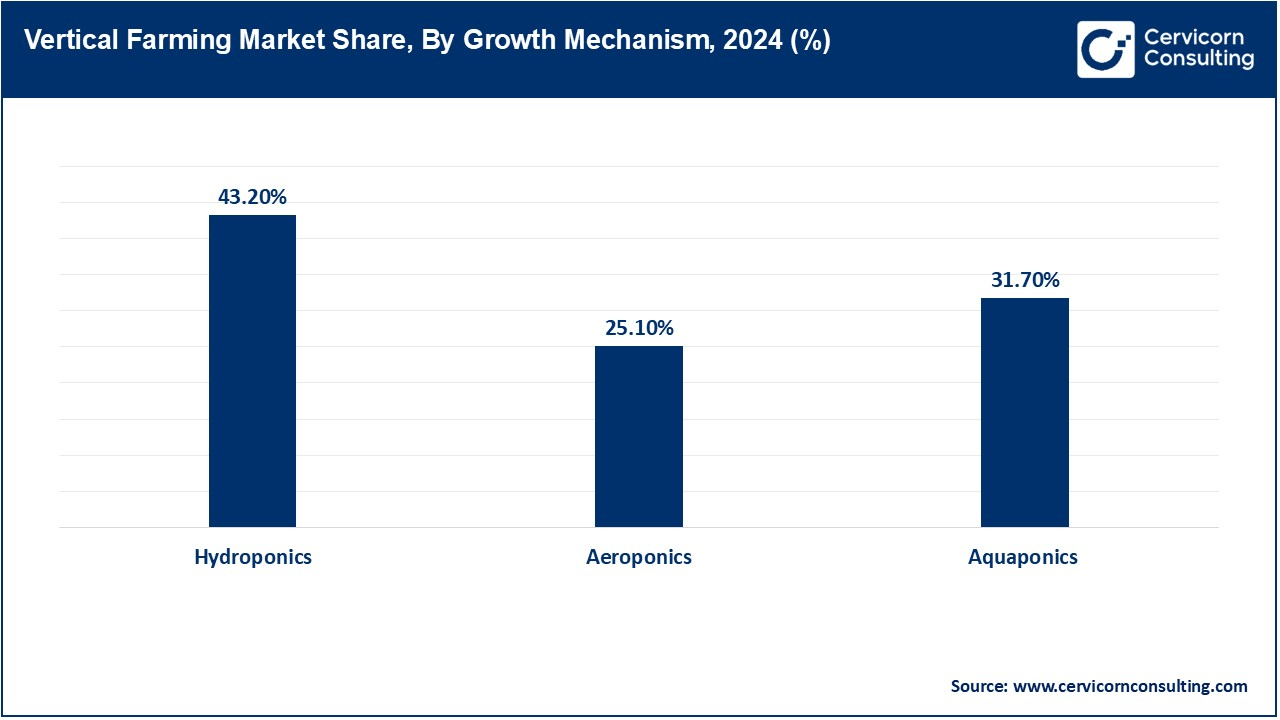
Aeroponics: This is a technique for growing where roots of plants dangle in the air and are sprayed with a nutrient solution. This technique is highly water-conserving, and plant growth occurs much faster because the roots have a better supply of oxygen. Aeroponics is particularly suitable for vertical farming, in which space is limited and high production is anticipated. It also saves the soil from the risk of pests and diseases. This technology, therefore, offers a sustainable option to traditional farming practices.
Aquaponics: The aquaponics is anticipated to gain significant market share over the forecast period. Aquaponics is a hybrid farming method that combines aquaculture and hydroponics Fish and plants will be raised together in a symbiotic relationship. In vertical farming, the waste from the fish provides nutrients for plants. The same way, plants help in filtering and purifying the water of the fish. This closed-loop system is highly sustainable to reduce the usage of water as well as resources. Through the system of aquaponics, it is, therefore, allowed to grow the crops and at the same time, fish all in one piece. This suits perfectly for multi-item production in city farming.
The vertical farming market is segmented into four key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Each of these regions is discussed in detail below
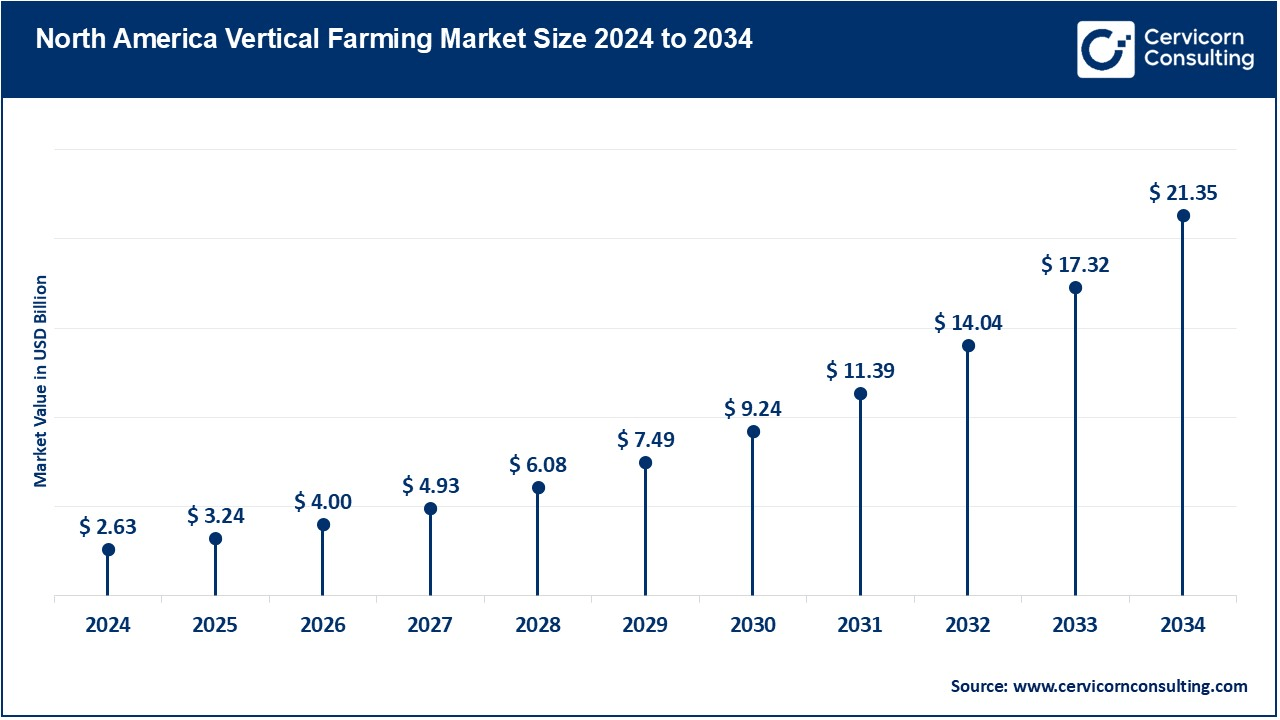
The North America vertical farming market size was valued at USD 2.63 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 21.35 billion by 2034. The North America is increasing at an incredible rate with technological innovation, the government support toward sustainable agriculture, and increased consumer demand for locally produced, organic produce. The U.S. and Canada are the major players, who have the largest number of vertical farming companies and a research institution that drive innovation. This is comprised of growing urbanization, and a keen interest in food security and sufficient access to venture capital and funding within the agriculture technology sectors.
The Europe vertical farming market size was estimated at USD 1.89 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 15.34 billion by 2034. Within a couple of years, this region has gained immense popularity for vertical farming, with the Netherlands at the forefront followed by the United Kingdom and then Germany. Sustaining aspects greatly impact through vertical farming in bringing down the carbon footprint. These drivers in Europe are essentially attached to the suitable regulatory framework; the added pressure with consumer needs will be for consumption of fresh as well as pest-free produce, which elevates consumption. Sustainable Food Systems, initiatives, and Urban Farming in Europe catalyze growth.
The Asia-Pacific vertical farming market size was accounted for USD 1.56 billion in 2024 and is poised to grow around USD 12.70 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region holds much promise for vertical farms since it is so populated, having a high urbanization rate and more demand in terms of food security. These countries include Japan, China, and India that focus more on vertical farming to bring more projects concerning arable land and water scarcity. In this region, further rural to urban areas migration and new agricultural technologies adaptation increase the tendency of vertical farming.
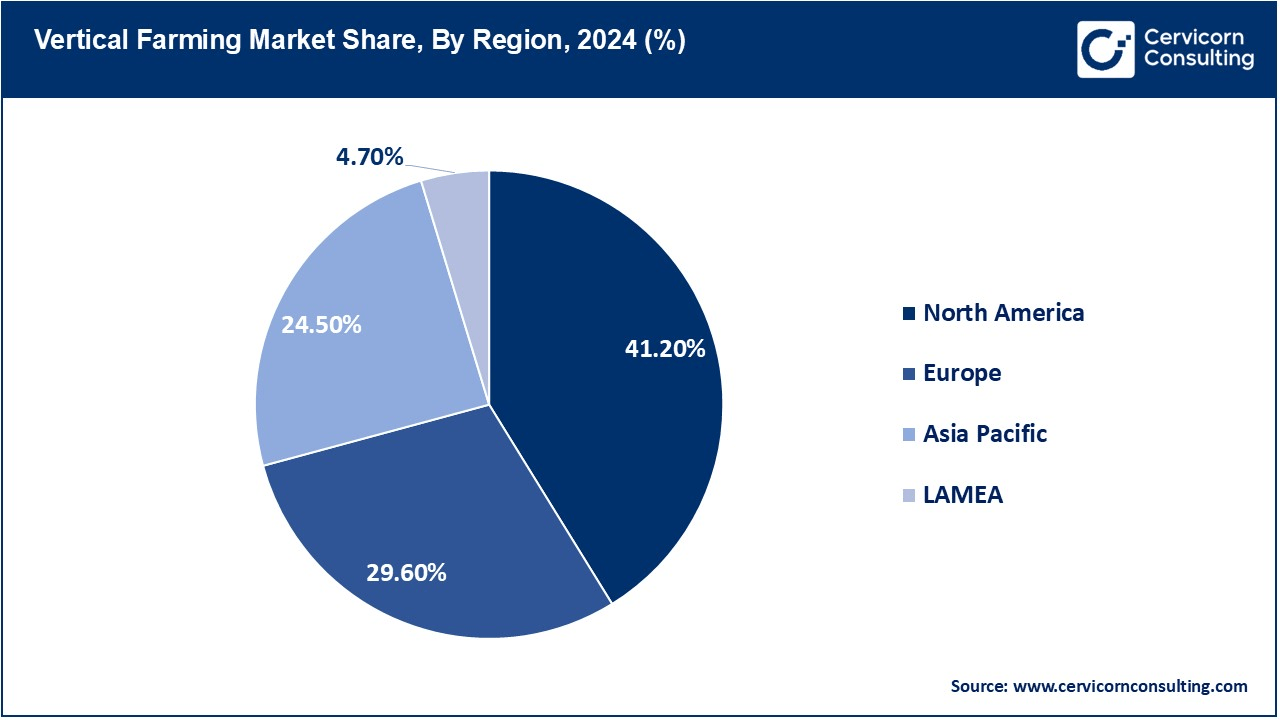
The LAMEA vertical farming market was valued at USD 0.30 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 2.44 billion by 2034. In LAMEA, interest in vertical farming intervention seems to be developing as a direct approach to issues of water scarcity, land degradation, and food insecurity. In this regard, the Middle East region is significantly investing in innovative agricultural technologies such as vertical farming. Africa and Latin America are promising regions as vertical farming offers an improvement in local food production and a way to have sustainable urban farming practices.
CEO Statements
Arama Kukutai, CEO of Plenty
David Rosenberg, CEO of AeroFarms
Alexander Olesen, CEO of Babylon Micro-Farms
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Structure
By Growth mechanism
By Crop Category
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Vertical Farming
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Component Overview
2.2.2 By Structure Overview
2.2.3 By Growth Mechanism Overview
2.2.4 By Crop Category Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Benefits of Vertical Farming Compared to Traditional Farming
4.1.1.2 Advancement in LED Technology
4.1.1.3 All-round-year crop production independent of weather
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High setup cost
4.1.2.2 Technical complexity
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Initial Investment
4.1.3.2 Energy Consumption
4.1.3.3 Technical Complexity
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Urbanization
4.1.4.2 Integrate sources of renewable energy like solar, wind, or geothermal energy
4.1.4.3 Growing Demand for Organic Produce
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Vertical Farming Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Vertical Farming Market, By Component
6.1 Global Vertical Farming Market Snapshot, By Component
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Hardware
6.1.1.2 Software
6.1.1.3 Services
Chapter 7. Vertical Farming Market, By Structure
7.1 Global Vertical Farming Market Snapshot, By Structure
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Building-based
7.1.1.2 Container-based
Chapter 8. Vertical Farming Market, By Growth Mechanism
8.1 Global Vertical Farming Market Snapshot, By Growth Mechanism
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Hydroponics
8.1.1.2 Aeroponics
8.1.1.3 Aquaponics
Chapter 9. Vertical Farming Market, By Crop Category
9.1 Global Vertical Farming Market Snapshot, By Crop Category
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Fruits Vegetables, & Herbs
9.1.1.2 Flowers & Ornamentals
9.1.1.3 Others (Cannabis, Microgreens)
Chapter 10. Vertical Farming Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 Vertical Farming Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
10.3 Global Vertical Farming Market, By Region
10.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
10.4 North America
10.4.1 North America Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.3 North America Vertical Farming Market, By Country
10.4.4 U.S.
10.4.4.1 U.S. Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.5 Canada
10.4.5.1 Canada Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.6 Mexico
10.4.6.1 Mexico Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
10.5 Europe
10.5.1 Europe Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.3 Europe Vertical Farming Market, By Country
10.5.4 UK
10.5.4.1 UK Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.5 France
10.5.5.1 France Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.6 Germany
10.5.6.1 Germany Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.7 Rest of Europe
10.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6 Asia Pacific
10.6.1 Asia Pacific Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.3 Asia Pacific Vertical Farming Market, By Country
10.6.4 China
10.6.4.1 China Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.5 Japan
10.6.5.1 Japan Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.6 India
10.6.6.1 India Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.7 Australia
10.6.7.1 Australia Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7 LAMEA
10.7.1 LAMEA Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.3 LAMEA Vertical Farming Market, By Country
10.7.4 GCC
10.7.4.1 GCC Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.5 Africa
10.7.5.1 Africa Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.6 Brazil
10.7.6.1 Brazil Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
10.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Vertical Farming Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11. Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 12 Company Profiles
12.1 ams-OSRAM AG
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 Global Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 Signify Holding
12.3 Heliospectra
12.4 EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS CO., LTD.
12.5 Urban Crop Solutions
12.6 AeroFarms
12.7 Freight Farms, Inc
12.8 Plenty Unlimited Inc.
12.9 VertiVegies
12.10 Sky Greens
12.11 iFarm