Agrivoltaics Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The global agrivoltaics market size was reached at USD 4.65 billion in 2024 and is estimated to surpass around USD 12.26 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.18% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The agrivoltaics market is expected to witness substantial growth as there has been a huge installations of solar along with the innovative solar designs being integrated with the agriculture.
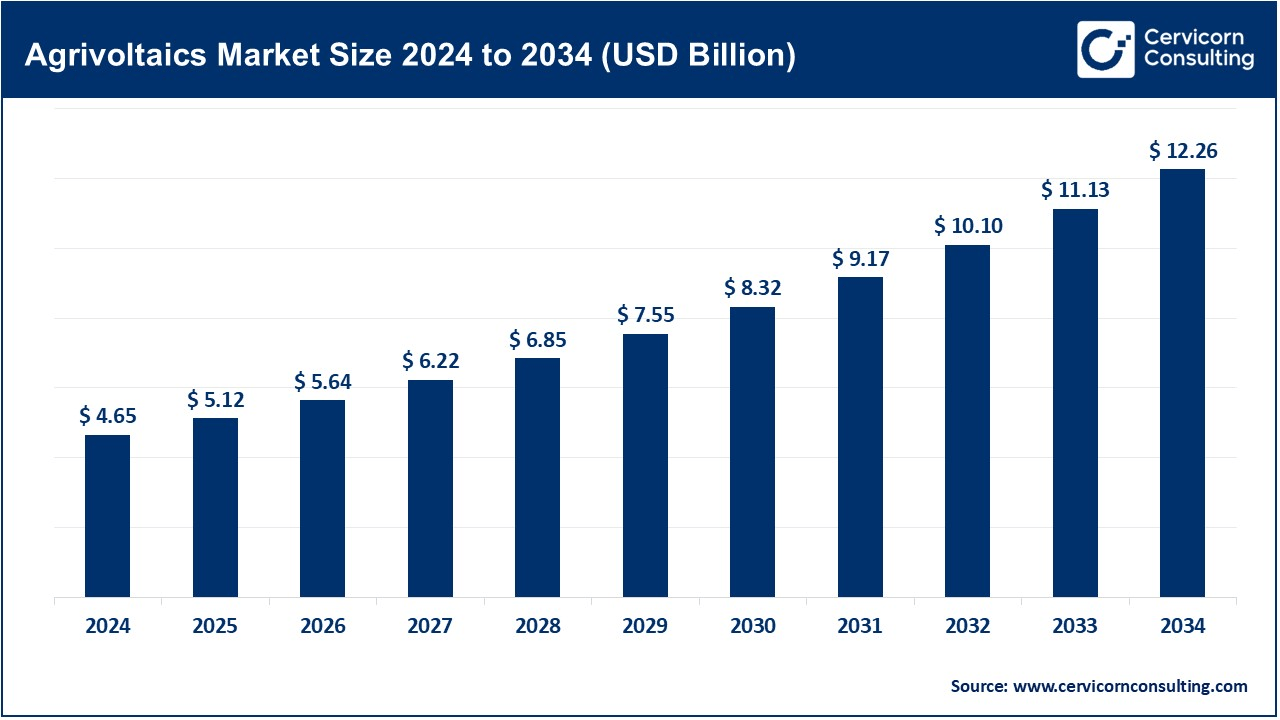
The agrivoltaics market is expected to grow in as solar energy will start becoming part of all integration with agricultural activities. Agrivoltaics is the dual use of solar farming-create installations of solar panels over crops, around livestock or aquaculture systems, basically any area where one might want to maximize land use for renewable energy generation while, at the same time, supporting agricultural productivity. This market is driven by a creeping momentum towards sustainable farming produce, increased costs of energy, and government incentives on the adoption of solar power. Benefits include improved land quality, less evaporation of water from under, and better yields in the crops because of moderated microclimates under the solar panels. However, this market predominantly experiences growth on strong grounds in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, mostly places having high solar irradiance. These regions will prosper from policy encouragement in clean energy and climate resilience campaigns. Challenges, such as high capital costs for setting up the facility or the need for some customized designs of the solar panels valid for different crop types, may also influence growth in the market.
Agrivoltaics Market Report Highlights
- The U.S. agrivoltaics market size was valued at USD 1.25 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 3.29 billion by 2034.
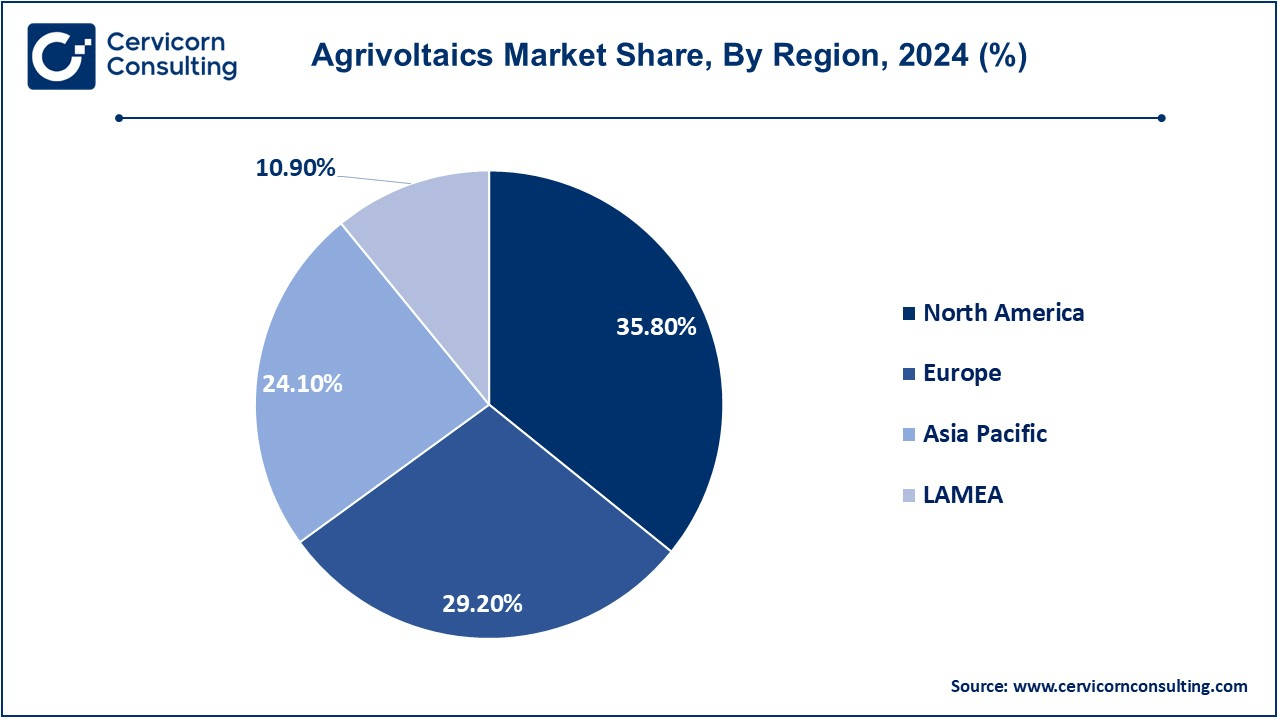
- The North America has accounted highest revenue share of 35.80% in 2024.
- The Europe has held revenue share of 29.20% in 2024.
- By system design, the dynamic segment has captured revenue share of 86.40% in 2024.
- By cell type, the monocrystalline segment has garnered revenue share of 56% in 2024.
- By crop, the field crops segment dominated the market in 2024.
Agrivoltaics Market Growth Factors
- Rising Demand for Renewable Energy: The major driving forces for agrivoltaic development is the demand generated by national governments as well as private initiatives for renewable energy solutions to replace fossil fuels. Solar is among the fastest-growing renewable sources, with simultaneous benefits for energy generation and improved, or enhanced, agricultural practices by integrating solar PV systems into agriculture. The efforts that governments are putting into treaties like the Paris Agreement or national policies will ultimately, for example, run toward achieving net zero emissions and would incentivize such investments in agrivoltaics further.
- Land-Use Optimization: Given the simultaneous problem of rapid urbanization and rising demand for food, efficient land use must be found. Agrivoltaics allow for multiple-use land-management strategies by combining solar panels with food cropping, and livestock grazing, allowing farmers to both generate electricity and maintain their crop production or livestock rearing. This is especially beneficial in regions with limited arable land or competing land-use priorities. By maximizing productivity per acre, agrivoltaic systems improve land efficiency and reduce pressure on natural ecosystems.
- Government Incentives & Policies: Governments worldwide are promoting agrivoltaics through subsidies, tax benefits, and policy frameworks to accelerate the transition to renewable energy. Incentives, including feed-in tariffs, net metering and investment tax credits, increase the financial feasibility of agrivoltaic projects for farmers and energy developers. In EU, USA, and China, strategic policies are in place to promote agrivoltaic use as part of climate policy and energy policy and security. Public-private partnerships are also incubating research, developing infrastructure and regulatory support, so that agrivoltaics can efficiently scale.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Agrivoltaics are highly relevant in the fight against climate change through energy savings and crop resilience. Through the combination of solar power and agriculture, agrivoltaic systems alleviate reliance on fossil fuels at the same time as they offer a reliable renewable energy source. Additionally, the microclimate created under solar panels helps protect crops from extreme weather conditions such as heatwaves, droughts, and heavy rainfall, which are becoming more frequent due to climate change.
- Water Conservation Benefits: Water scarcity is an increasing global problem, and agrivoltaic (AG) systems are of great interest for saving water. Shade provided by photovoltaic (solar) panels decreases the amount of direct sunlight reaching the soil, thereby decreasing the rates of soil evaporation and decreasing water loss from plants. In particular, this is useful in arid and semi-arid areas, where irrigation is costly or unavailable. Moreover, in some agrivoltaic configurations, small rainwater collection and intelligent irrigation systems are also implemented, which further increase water saving.
Agrivoltaics Market Trends
- Enhanced Crop Yields: Agrivoltaic systems produce a regulated microclimate that may be beneficial to plant growth. The shading effect the solar panels impart mitigates excessive heat stress on plants, thereby reducing the incidence of dehydration and thus increasing overall yield, particularly for shade-adapted crops, such as lettuce, berries, and tomatoes. Further, the controlled temperature and humidity ranges under solar panels are conducive for plant growth, minimizing plant's exposure to the severe weather phenomenon. Research has demonstrated that agrivoltaic farming can increase photosynthetic efficiency in a limited number of crop types, thereby increasing yield.
- Advancements in Solar Technology: Rapid developments in photovoltaic technology are leading to more efficient and inexpensive agrivoltaic systems. Innovations such as bifacial solar panels, translucent solar modules, and solar tracking systems optimize energy generation while minimizing shading effects on crops. Artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) assisted smart photovoltaic (PV) systems optimize both power generation and agricultural production by continuously optimizing panel position for solar availability and crop needs.
- Increasing Energy Costs: As electricity prices increase, farmers and agribusinesses are looking for alternatives to power their operations at low cost. Agrivoltaic systems can provide farmers with both onsite power generation to cut their dependence on the grid as well as protection against variations in energy purchase costs. Excess electricity also can be sold back to the grid, generating a secondary revenue stream. Powering energy-hungry agricultural activities, including irrigation and cooling, with reliable power, agrivoltaics provide a sustainable and economical energy solution.
- Growing Food Demand: Global population is predicted to be 10 billion by 2050, which in turn increases demand for food production. Yet, agricultural land is scarce, and crop yields are in danger from climate change. Agrivoltaics offer a solution by allowing, at the same time, food production and renewable energy generation, land use optimization and creating agricultural resilience. Through the ability to protect crops from heat stress and prevent soil erosion, agrivoltaic systems help achieve sustainable food production.
- Public & Private Investments: Investment from public and private sectors is fueling the growth of the agrivoltaic market. Government, research, and industrial bodies are providing funding for pilot schemes, infrastructure development, and technological advances to improve the viability of agrivoltaic deployments. Venture capitalists and institutional investors are more and more seeing agrivoltaics as a viable, profitable and sustainable investment opportunity and are thus providing funding for startups and large-scale projects. Agreements among agricultural companies and energy companies are also driving the emergence of new business models and revenue models, e.g., power purchase agreements (PPAs), to accelerate the adoption of the new technology.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 5.12 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2025 |
USD 12.26 Billion |
| Expected CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
10.18% |
| Dominant Region |
North America |
| Fastest Growing Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments |
System Design, Cell Type, Crop, Material Type, Power Output, Region |
| Key Companies |
SunAgri, Namaste Solar, Insolight SA, Next2Sun Technology GmbH, BayWa AG, Ombrea, Enel Green Power Spa, SunSeed APV Private Limited, Mirai Solar, JA Solar Holdings Co. Ltd. |
Agrivoltaics Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Smart Farming Integration
- The rising productivity in the agriculture along with optimum usage of energy have led in the productivity improvements from the smart farming technologies which are integrated with agrivoltaic systems. Internet of Things sensors, artificial intelligence data auto-processors, and automated irrigation systems will ensure resource optimization during optimal growing conditions with solar panels. The smart monitoring of soil moisture, temperature, and light levels for crop growth will be able to dynamically adjust irrigation and panel positioning in order to maximize output of both crop and solar energy. Indeed, all these advances have indeed made agrivoltaics even more readily applicable to different farming settings, thereby further boosting adoption rates amongst farmers.
Rural Electrification Initiatives
- Agrivoltaics can resolve the problems of electrification problems in rural areas especially in the areas that are underdeveloped. Agrivoltaics systems offer reliable electricity for on-farm operations, residential household consumption, and local businesses by providing renewable energy to agricultural areas. This will not only raise the levels of agricultural productivity but will also help in rural economic development. Agrivoltaics could now operate irrigation systems, cold storage facilities, and processing units, reducing post-harvest losses and improving food supply chains, where accessing the electric grid could be difficult. Both governments and NGOs are pushing agrivoltaic initiatives as the best strategy to empower rural areas towards energy access, better human welfare, and sustainable development.
Market Restraints
High Initial Investment Costs
- There is a huge cost involved in financing the initial stages of agrivoltaics systems since solar panel installation and its mounting structures are accompanied by setting specialized infrastructure to integrate such agricultural systems with energy generation. Most very small farmers will find it difficult to finance agrivoltaics because they will probably rely on government subsidies or some other form of financial support to invest in it. The initial costs are high, and although long-term energy savings and increased crop yield returns could offset some of the investments, this model remains a hindrance for most people. Other considerations, including maintenance costs, battery storage installations for the energy not consumed during sunny hours, and adaptation of existing on-farm practices into agrivoltaic systems, also further build to the financial constraints and inhibit widespread adoption, especially in developing economic agricultural countries.
Technical Issues
- This will also require successful agrivoltaic system implementation in relation to the right aid of sunlight to crops and solar cells in various regions, crop types, and the orientation of the panels. Designing customized solutions towards various agricultural settings would require a lot of research and planning, which adds to the complexity of the situation. Besides, uneven shading, height adjustments for access of farm machinery, and systems of solar tracking are some of the ambigous challenges in agrivoltaic projects execution. Apart from these, energy storage and grid integration could constitute a technical hurdle because the surplus generated electricity needs to be distributed efficiently. Without proper planning and technological advancement, agrivoltaic farms can expect either reduced agricultural yields or inefficient energy production restraining market growth.
Market Opportunities
Expansion in Emerging Market
- Agrivoltaics have the best development potential in emerging regions such as Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America due to their high solar radiation and heavy reliance on agriculture. Many of these areas are disposing largely of electricity shortfalls while having very poor farming practices. Agrivoltaics offer not only better energy supply, but also food security to many people. Initiatives by governments or international organizations towards rural electrification or sustainable farming will create the right thrust for agrivoltaic development-more and less expensive land, labor, and other project costs such as engineering, facilitate agrivoltaic construction at larger scales making renewable investments from energy firms, development agencies, and impact-driven financial institutions more viable under such circumstances.
Technological Innovations
- The development in the solar panesl like bifacial and translucent solar panels makes it better for the agrivoltaic efficiency owing to optimized light transmission in the crops while electricity generation These smart agrivoltaic systems, embedded with AI and IoT-enabled sensors, dynamically change the angles of the panels and monitor crop conditions in real-time, hence improving productivity. Innovations in vertical agrivoltaics, floating solar farms and agrivoltaic greenhouses are making it even more applicable to different scenarios. These innovations make agrivoltaics adaptable more towards different agricultural landscapes making for new income opportunities for farmers and energy providers while driving the market towards more highly efficient and scalable developments.
Market Challenges
Land Use Conflicts
- While agrivoltaics present an innovative application of land use by integrating farming with solar power, stakeholders argue over the land's availability for traditional agriculture due to the size of large-scale solar installations. Farmers might limit the use of these systems due to the interference of solar panels in crop cultivation or grazing livestock. Restrictions, such as zoning laws and land use, are further hurdles to agrivoltaic deployment in certain areas. Lastly, disagreement over land leasing agreements can occur if both solar developers and agricultural landowners want a prime location, subjecting agrivoltaic projects to scaling problems from the farms themselves.
Regulatory & Policy Uncertainty
- The agrivoltaics market is maturing, and this evolving state of affairs in various regions brings uncertainty to both investors and farmers alike. There are no clear regulations in many nations regarding agrivoltaic land use, grid interconnections, and incentives for dual-use solar farming. Such unclear policies such as about electricity tariffs, land rights, or even environmental impact assessments can delay project approvals and dissuade large-scale investment. Changes of policy by the government, like reducing solar subsidies or changing energy priorities, may affect market growth. To ensure that agrivoltaics becomes successful in the long run, stable and clearly defined policies supporting the uptake will encourage investment and technology development in the sector.
Agrivoltaics Market Segmental Analysis
The agrivoltaics market is segmented into system design, cell type, crop, material type, power output and region. Based on system design, the market is classified into dynamic and fixed solar panles. Based on cell type, the market is classified into polycrystalline and monocrystalline. Based on crop, the market is classified into field crops, fruits, vegetables and others. Based on material type, the market is classified into panel and paints. Based on power output, the market is classified into Up to 10 MWp, 10.1 to 50 MWp and more than 50 MWp. Based on placement, the market is classified into ground mounted, shading nets, greenhouses and others.
System Design Analysis
Fixed Solar Panels: Fixed solar panels are one of the most adopted system designs in agrivoltaics for their simplicity, low cost and low maintenance. These panels have a fixed angle of inclination and height, which allows to get maximum solar energy yield while applying some partial shading to crops or animals. Fixed-panel systems are especially useful for medium- and small-scale farms where budget and durability are top concerns. Yet, they might fail to do the best job of energy efficiency and yield, since solar irradiation is constant throughout the day. Although this is a restriction, solar panels of a fixed type are, by the same token, an efficient option for farmers needing a viable format of generating renewable energy while engaged in agriculture.
Agrivoltaics Market Revenue Share, By System Design, 2024 (%)
| System Design |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Dynamic Solar Panles |
86.40% |
| Fixed Solar Panles |
13.60% |
Dynamic Solar Panels: Dynamic solar panels are used to improve agrivoltaic efficiency by following the sun. The systems employ single and dual-axis tracking technologies to track the sun's movement, boosting energy production and providing the optimal light to crops. Dynamic panels are used to control microclimates through the shading adjustment according to crop requirements, alleviating heat stress enhancing water use efficiency. Although more expensive and need high tech infrastructure, they result in higher long-term returns through higher electricity generation and better agricultural output.
Cell Type Analysis
Monocrystalline: Highly efficient and ubiquitous, monocrystalline solar cells are used in agrivoltaic systems because of their high conversion rates and robustness. Based on a single-crystal silicon architecture, these cells deliver efficiency with a range from 18-22 and are accordingly well suited to maximize electricity production in a small footprint. Due to their increased efficiency, it is possible to use fewer panels per acre reducing the shading effects on crops and maximizing energy production.
Agrivoltaics Market Revenue Share, By Cell Type, 2024 (%)
| Cell Type |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Polycrystalline |
44% |
| Monocrystalline |
56% |
Polycrystalline: Polycrystalline solar cells, which are assembled from several silicon pieces, are a cost-effective solution for agrivoltaic systems. At efficiencies of 15–18%, these panels provide less power than monocrystalline counterparts but are relatively cheaper and thereby attainable to farmers who have a limited amount of budget. Their production process is less complex, with consequent lower overall cost, and stable energy yield. [See also] Yet polycrystalline panels are less efficient in high temperatures and take up more space than monocrystalline to produce the same amount of power.
Crop Analysis
Vegetables: Vegetables like lettuce, spinach, kale, and tomatoes) can be grown which are resistant to partial shading in agrivoltaic systems. The lack of sunlight results in less heat stress, which in turn optimizes water retention and irrigation demand. In the case, leafy greens, more specifically, gain the most advantages from the cooler environment provided by solar panels, resulting in higher yields and better quality. Agrivoltaic systems also help prevent the destruction of fragile crops from very adverse weather events such as heatwaves and hail. Specifically, vertical farming approaches can be combined with solar light panels to get the best use of the space.
Fruits: In areas of agrivoltaic farming, crops including berries, grapes and citrus fruits find themselves in a favorable position with respect to partial shading. Solar panels provide protective cover for fruit plants against excessive heat and UV radiation, therefore avoiding sun damage and improving fruit quality. Vineyards, in particular, have successfully adopted agrivoltaic systems, where solar panels regulate microclimates and reduce water evaporation. Moreover, agrivoltaic farms can be used to support vertical fruit-production systems, thus maximizing land use efficacy. The integration of solar energy into fruit orchards can be used to power various automated irrigation and processing systems, thus agrivoltaics is a highly suitable means for sustainable farm practice and enhanced crop resilience.
Field Crops: Integrating field crops such as wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans with agrivoltaic systems is possible, but depends on requirements with regard to radiation and tolerance to shading. Some shade-loving grains and legumes stand to gain from "cool-weather" conditions under solar collectors that alleviate drought stress and increase soil water retention. In arid areas, agrivoltaics play a role in improving crop stress by avoiding runaway evapotranspiration. Nevertheless, row crops that need full sunlight, such as maize, soybean, etc., may also require some type of solar panel design with adjustable parameters in an attempt to maximize energy production with minimal yield reduction.
Other: Apart from conventional crops, agrivoltaic systems are supporting a variety of alternative agricultural needs, for example livestock grazing, mushroom cultivation and beekeeping. Livestock, such as sheep and goats, can graze beneath solar panels, benefiting from shaded environments while maintaining land productivity. Mushroom cultivation is thriving in the dark conditions caused by solar panel structures. Beekeeping further complements agrivoltaic farms, as solar farms can offer pollinator-friendly habitat supporting a richer biodiversity with higher yields. Additionally, agrivoltaic greenhouses offer controlled environments for specialty crops such as herbs and flowers. By diversifying agricultural activities, agrivoltaic systems increase profitability and promote sustainable, multifunctional land use.
Agrivoltaics Market Regional Analysis
The agrivoltaics market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
What factors are driving North America's growth in the agrivoltaics market?
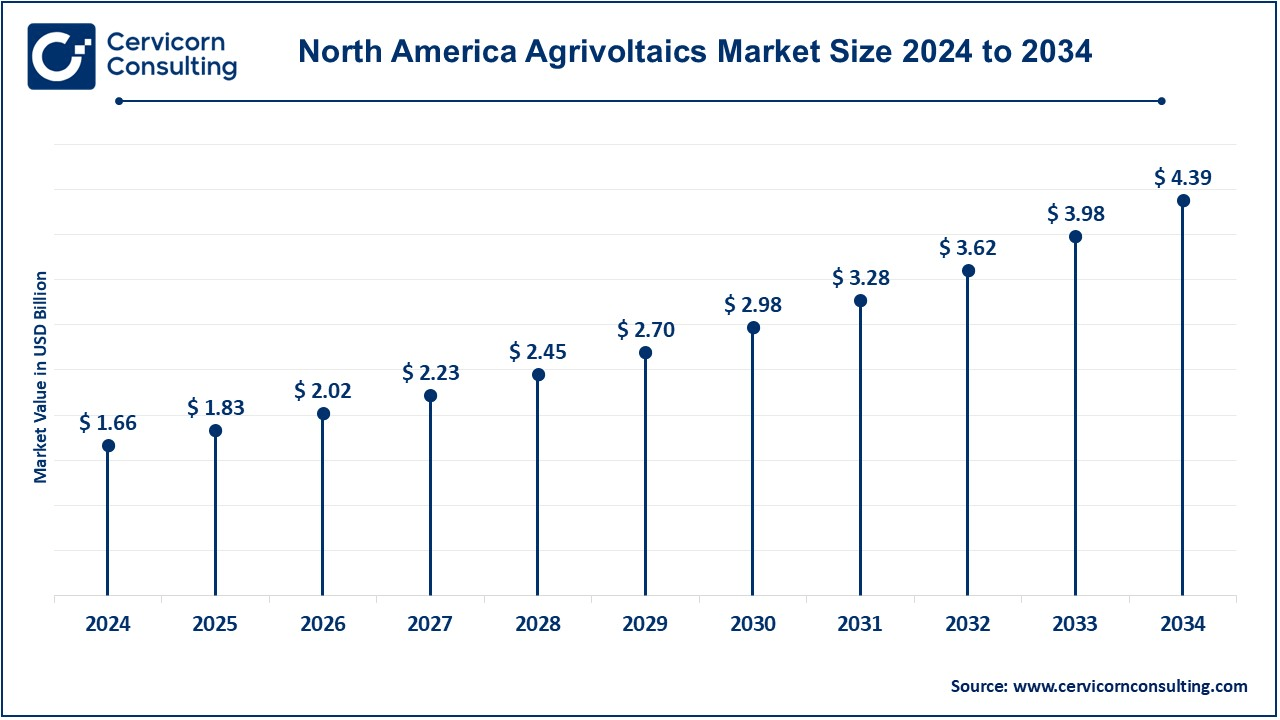
The North America agrivoltaics market size was valued at USD 1.66 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 4.39 billion by 2034. The North American market is expanding, as there is more investment in renewables, favourable government regulation, and the imperative to develop sustainable agriculture. The United States and Canada are at the forefront of the agrivoltaic trend, motivated by tax credits, grants, and research programs. Significantly more, the market is growing in desert areas, such as California and Arizona, where "agrivoltaics" can assist to resolve both water scarcity and crop stress. Especially, interinstitutional collaborations and research activities among academia and solar energy companies are accelerating technological innovations.
Why is Europe at the forefront of agrivoltaic adoption?
The Europe agrivoltaics market size was estimated at USD 1.36 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 3.58 billion by 2034. Europe is at the forefront of agrivoltaic adoption, driven by strong renewable energy policies, carbon neutrality goals, and agricultural sustainability initiatives. Large area agrivoltaic projects based on solar panels combined with vineyards, greenhouses, and dairy farms are pioneered by countries such as Germany, France and the Netherlands. Financial support for agrivoltaic research and deployment is offered through the European Union, by the Green Deal and funding programs. Further, land-use optimization, which is driven in particular by areas with high population density, in which space is most constrained. Nonetheless, regulatory differences between EU Member States and land use conflicts provide restrictions.
What factors are contributing the Asia-Pacific explosive growth in the agrivoltaics market?
The Asia-Pacific agrivoltaics market size was accounted for USD 1.12 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow around USD 2.95 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific market is in a state of explosive growth, especially China, Japan, India and South Korea. All these market expansions are driven by increasing need for renewable energy generation, government subsidies and demand for climate-resistant agriculture. In small-scale agriculture environments, Japan has led the way with agrivoltaic technology, and China has begun to connect giant arrays of solar panels with rural agriculture. In India, agrivoltaics is being promoted as a solution for energy access in remote farming communities. Nonetheless, the high land costs in certain areas and the farmer awareness requirements are major barriers to their adoption.
LAMEA Agrivoltaics Market Trends
The LAMEA agrivoltaics market size was reached at USD 0.51 billion in 2024 and is estimated to surpass around USD 1.34 billion by 2034. The LAMEA is developing as a sustainable option for addressing food and energy security issues. Latin American countries such as Brazil and Mexico are investigating the use of agrivoltaic integration on agricultural sites to increase renewable energy generation capacity. In the Middle East agrivoltaics is becoming more popular under the constraints of water scarcity and high temperatures, as projects exist in Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates to show proof of concept. In Africa, agrivoltaic systems can provide a way to bring electricity to remote farming communities, as well as enhance agricultural production.
Agrivoltaics Market Top Companies
Recent Developments
- In 2024, Next2sun opened its Agri solar park in Germany , which consists of highly innovative three-row vertical Agri PV systems. It covers a field area of 11 hectares and has a capacity of 4,800 MWh per year, which is enough energy for about 1,400 households. Additionally, the very well 4.3 MW power station has vertical photovoltaics with 13.5 meters row spacing to maximize arable land usage to be termed as the power plant will propagate renewables and produce food while creating footprints of value on the local economy.
Market Segmentation
By System Design
- Dynamic
- Fixed Solar Panles
By Cell Type
- Polycrystalline
- Monocrystalline
By Crop
- Field Crops
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Others
By Material Type
By Power Output
- Up to 10 MWp
- 10.1 to 50 MWp
- More than 50 MWp
By Placement
- Ground Mounted
- Shading Nets
- Greenhouses
- Others
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA
...
...


