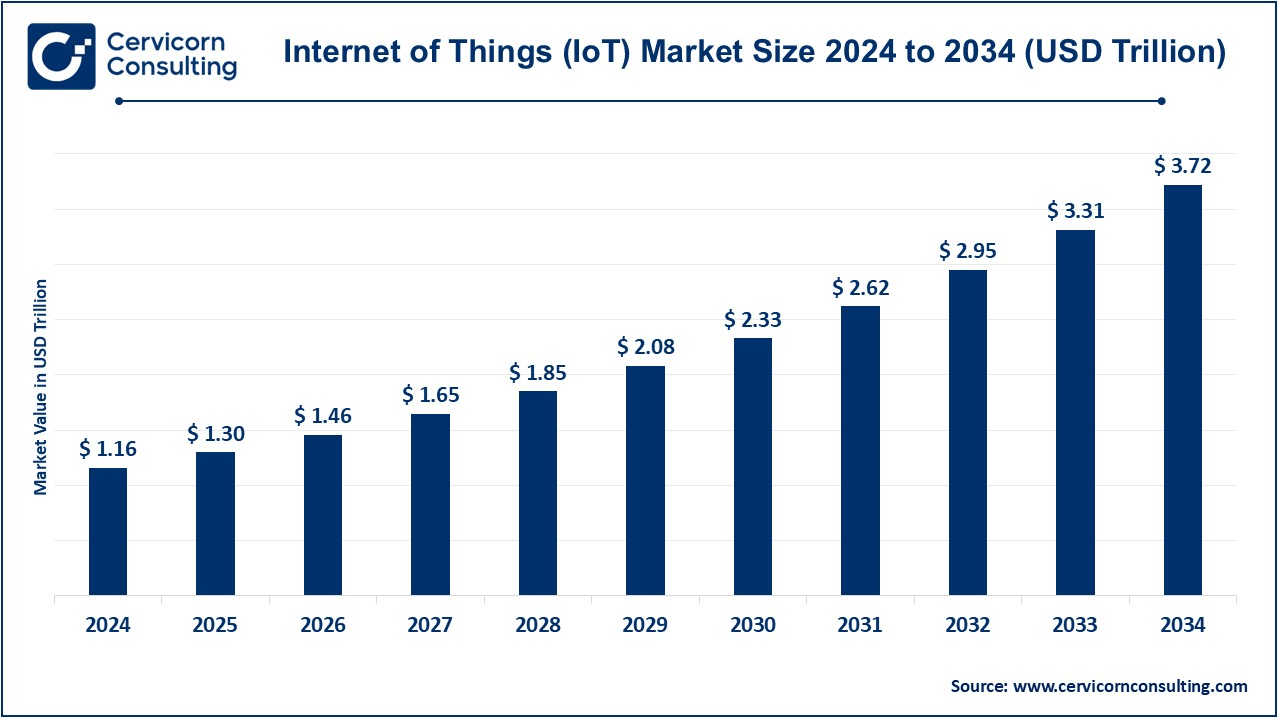
The global internet of things (IoT) market size was reached at USD 1.16 trillion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 3.72 trillion by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.35% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The global internet of things (IoT) market is expected to grow owing to expanding high-speed technologies along with low latency and high-speed networks.
The Internet of Things (IoT) devices market is growing and fast spreading into industries like Healthcare, Manufacturing, Transportation, and Smart Homes. IoT installs sensors in the devices, incorporates software, connect devices, so they communicate seamlessly with each other over the network. This brings great efficiency and improved decision-making in operations. With the introduction of 5G technology and improved AI and machine learning algorithms, IoT is coping with real-time analytical and predictive potential. Some driving factors include the emergence of smart cities, increased needs for automation, and rising investment in digital transformation. However, issues such as data security along with privacy concerns and demand for the robust infrastructure remains important. At the same time, North America and Asia-Pacific are spearheading the adoption of IoT due to their technological ecosystem and strong support from their governments. Continuous reinvention and convergence towards blockchain and edge computing will keep the sector growing, transforming the industries and the world's daily life.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.30 Trillion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 3.72 Trillion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 12.35% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Deployment, Enterprise Type, Connectivity, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Siemens, SAP SE, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc, PTC, Oracle, Microsoft, Intel Corporation, General Electric Company, Cisco Systems, Inc., Amazon.com, Inc |
Emergence of Blockchain for IoT Security
Rising Consumer Awareness
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
High Implementation Costs
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Integration
Smart Cities and Smart Homes
Interoperability Issues
Scalability and Management Challenges
Platform: The platforms of the IoT are essential, accounting for the execution of the whole IoT ecosystem in seamless connectivity, device management, and data aggregation and infrastructure with real-time analytics. Thus, multiple objects would be connected, and the data will be exchanged in real-time. Finally, the platform offers application programming interfaces (APIs) and developer tools to develop an individualized IoT solution that reflects specific industry needs. However, a totally scalable cloud-based IoT platform becomes prominent in use due to cost-effectiveness and a large-scale deployment potential. Leading IoT platforms introduce the use of advanced technologies like machine learning, AI, and edge computing to their users to promote better decision-making and efficient operations.
Solutions: Well-tailored to specific industry issues such as predictive maintenance for manufacturing or remote monitoring for healthcare operations, these are custom software solutions, consulting, implementation and managed services that comprise most key areas of the IoT market. Deploying such managed services or IoT solutions into an organization can obviously help by ensuring seamless installations coupled with integrations and manual maintenance of the solutions. The right technologies for IoT are likely to be determined by consulting services while ensuring that the managed services cover the operation, security, and updates of the system.
Cloud: The model of cloud deployment is the reigning king in the IoT market, touted with the great benefits of scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. By exploiting the cloud infrastructure, businesses can store, process, and analyze large blocks of IoT data in real-time; thus, making faster decisions, better operational execution. For organizations that have vast networks, cloud-based IoT solutions prove to be an advantage in giving seamless connectivity to the devices and remote access. Moreover, cloud platforms give higher-end tools like AI, machine learning, and big data analytics, further increasing IoT system values. With features such as data encryption and regular updates, the cloud deployments are more reliable.
Internet of Things (IoT) Market Revenue Share, By Deployment, 2024 (%)
| Deployment | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| On-Premise | 60% |
| Cloud | 40% |
On-Premise: On-Premise Deployment continues to be a possible option in the IoT market for organizations that consider data control and protection as their priorities. Such a model has the components of IoT infrastructure and their data hosted within the premises of an organization, thus ensuring total ownership with stringent compliance adherence. They are important in finance, defense, and manufacturing industries, as these industries use applications that are highly sensitive and very critical; hence, they minimize any dependencies outside the organization. These kinds of deployments also have the advantage of no internet or third-party access issues, which results in high reliability.
Small-Medium Enterprises (SMEs): IoT has been embraced by many SMEs as a path towards operational efficiency, cost-reduction, and competitive advantage. This helps SMEs make their inventory management, predictive maintenance, customer engagement, and other processes easily manageable using IoT. Cloud-based IoT solutions resonate well with SMEs because they can easily be scaled and made affordable thus allowing SMEs to easily roll out IoT without cash-trapping capital investments. The IoT also provides SMEs the real-time data access along with insights which empowers the SMEs for making the informed decisions along with optimized resource allocation.
Large Enterprises: The large enterprises are at the forefront of IoT use, creating transformation engines for the business operating framework and its attendant digital transformation goals. They apply IoT to their operations across-the-board, from the supply chain, through smart manufacturing, down to customer service. This has translated into efficiency and innovation within the enterprise. As a result, they are able to spend on cutting-edge IoT technologies such as AI-powered analytics, edge computing, even blockchain for secure data management. They usually house hybrid models of IoT; combining the on-prem and the cloud for purposes of scalability and compliance.
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI): There has been a rising adoption of IoT for enhancing the operational efficiencies, customer experience, and security. IoT-enabled provisions such as smart ATMs and connected kiosks betters service delivery, while wearable devices and IoT sensors enable an affordable personal insurance scheme. The progressive advanced IoT applications come in handy at fraud detection and risk management by means of real-time monitoring and analyzing transactions. There is also asset tracking and branch operations that optimize resource posts. Concerns regarding data privacy and cybersecurity are both critical and require strong defense mechanisms against them from time to time.
Retail: The retail environment is transforming under the IoT generation. Smart shelves and inventory tracking make personalized shopping experiences possible. Connected devices would provide retailers with real-time information about the behavior of consumers, allowing optimization of inventory and layout. The emerging scenario develops an increasing number of solutions for mobile payments and self-service checkout lines. All of these indulge in better convenience for customers. Others include predictive analytics for demand forecasting and efficiency in the supply chain.
Government: This is used in cities by governments to develop city smart projects, incorporating different management systems around traffic, waste collection, and public safety. conserve and optimize energy in public buildings as well as streetlight; really make a cost-effective approach towards environmental impacts. Disaster management and environmental monitoring are advanced with respect to IoT-based early warning systems.
Healthcare: IoT has indeed changed the life of the healthcare sector; it has managed to get in the use of wearables, intelligent monitoring devices, and smart medical systems. These would drastically improve the process of diagnosis and treatment by instantly acquiring patient data. Hospital and health facility operations greatly improve their reach when it comes to optimizing both workflow and patient safety, asset tracking-optimizing workflows, and patient safety.
Manufacturing: This is just part of how the Internet of Things industrializes an Industry 4.0 manufacturing plant, with intelligent maintenance, automated production line processes, and production supply chain optimization in view. Equipment founded on IoT sensors optimizes the performance of equipment during its operation hours whilst minimizing its downtimes. Analyses in real-time also help foster the efficiency-enhancing processes related to the control of quality and resources management.
Agriculture: IoT provides live data about the soil health and environmental weather condition and crop growth during a period precising farming. Smart irrigation systems and connected equipment further resource optimization result in increased output and minimized waste. Besides that, IoT could also provide some degree of remote access to livestock health and farm operations.
Sustainable Energy: The concept of the smart grid, the energy management system, and renewable integration are the tools in IoT that drive the creation of a more viable energy future. The sensors measure consumption, manage supply and consumption, and can predict maintenance, thus cutting on costs and environmental footprints.
Transportation: IoT in transport is associated with connected vehicles, intelligent traffic systems, and optimized logistics; thus, one would link real-time vehicle and cargo tracking to the effective administration of fleets and delivery. Autonomous vehicles and IoT-based infrastructures eliminate traffic and increase road safety.
IT and Telecom: In the same way, it is also said that adopting IoT applications in the fresh facilitation of the IT and telecom sectors enables improved network performance and decreased downtime with service improvements. Also, IoT monitoring tools will optimize the infrastructure and create reliability in connectivity to support services such as 5G and edge computing.
The Internet of Things (IoT) Market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
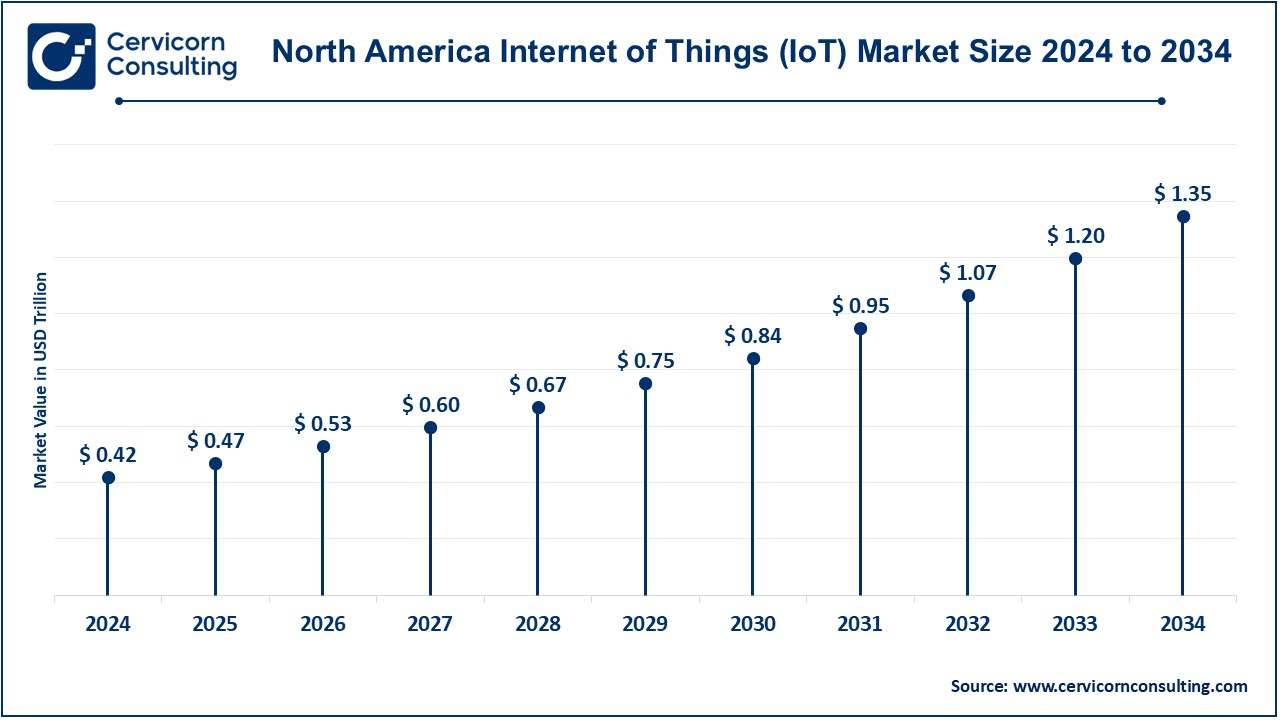
The North America IoT market size was valued at USD 0.42 trillion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 1.35 trillion by 2034. North America is currently the continent leading in the IoT deployment market because of very robust technological infrastructure, early adoption of high-end technologies and budgets with intent to allocate IoT solutions or systems. Along these lines, North America has hosted several innovators, as well as start-up companies who innovate across different sectors such healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities. Governments, such as those in the U.S. and Canada, are also promoting IoT through schemes, such as smart and energy-efficient infrastructure and many others. Also, with 5G networks now widely distributed, the barriers of entry for implementing IoT-based applications are less daunting, especially in areas such as real-time analytics of connected devices.
The Europe IoT market size was reached at USD 0.33 trillion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 1.07 trillion by 2034. The rising government initiatives like smart city along with industry 4.0 are expected to boost the growth of the market in Europe. Countries such as Germany, UK and France accounted for the major share in the region as these countries are using IoT for transforming conventional to future manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation. The other angle the EU decided to use has been on sustainability, which has also promoted the area of IoT applications in energy management and greener technologies. AI and IoT-enabled analytics have also increased the productivity of different sectors. Still, some stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR have adverse effects on IoT deployments, thus requiring high compliance measures.
The Asia-Pacific IoT market size was accounted for USD 0.30 trillion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow around USD 0.95 trillion by 2034. Asia-Pacific has experienced rapid growth due to industrialization on a grand scale, smart city projects, and changing consumer behaviour regarding connected devices. China, Japan, and India are at the forefront of adoption because strong government backing and consequent extensive 5G networks have proven and tested manufacturing and retail sectors. Relevant IoT solutions deployed in agriculture, health, and energy management would solve the pockets of the nation's challenges. In addition, the integration of AI and cloud computing rapidly accelerates IoT innovation. The growing tech ecosystem of the region continues to demonstrate leadership in the expansion of IoT despite challenges such as cost-sensitive markets and a lack of standardization.
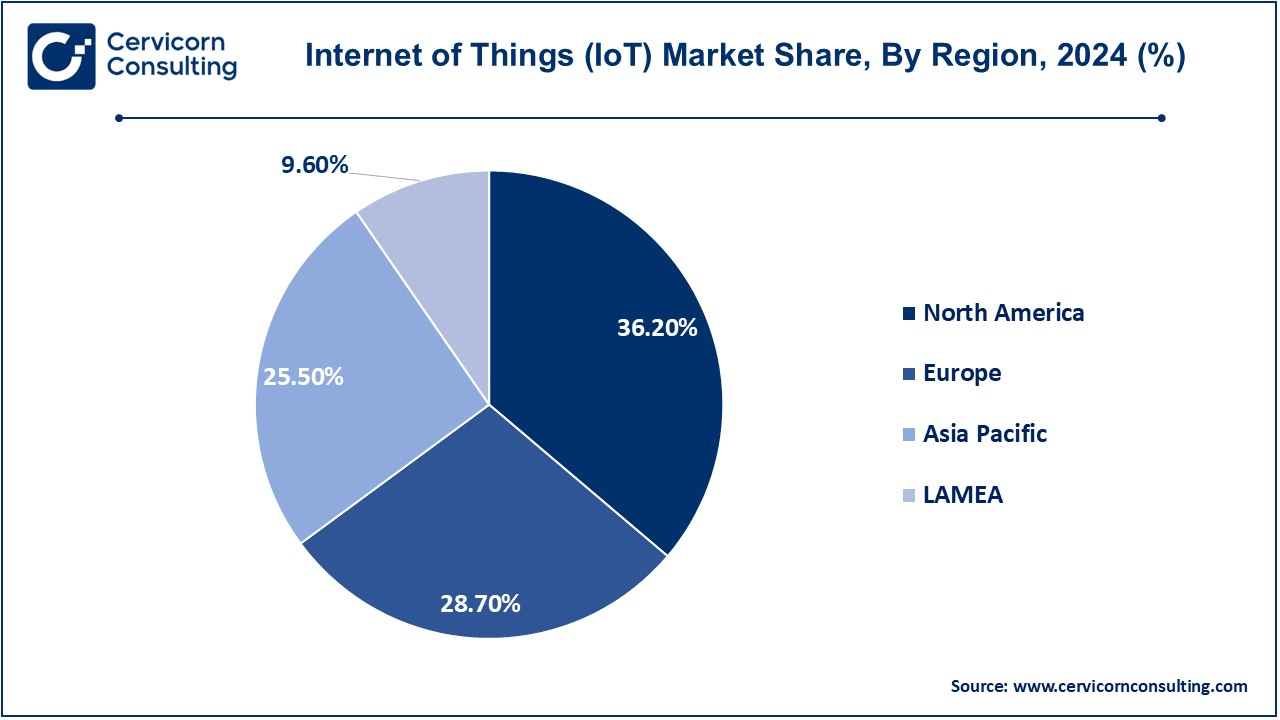
The LAMEA IoT market size was surpassed at USD 0.11 trillion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 0.36 trillion by 2034. The LAMEA market will be driven primarily by the increased investments in smart cities, industrial automation and energy management. Some of the countries that will greatly contribute to IoT in terms of solid returns are Brazil, the UAE, and South Africa, which have been using IoT to provide solutions in the urban built environment and resource optimization. For agricultural applications without exception, IoT applications will thus be focused on enhancing productivity and eliminating wastage as they address challenges related to food security. Still, barriers exist, including: lack of infrastructure; very high costs during deployment; varying degrees of technological readiness among farmers/institutions. It is true, however, that while these factors have been insurmountable, various government initiatives and increasing private sector interests have contributed toward growth moving in the direction of the market.
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Deployment
By Enterprise Type
By Connectivity
By End User
By Region