Asia Pacific Solar Power Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
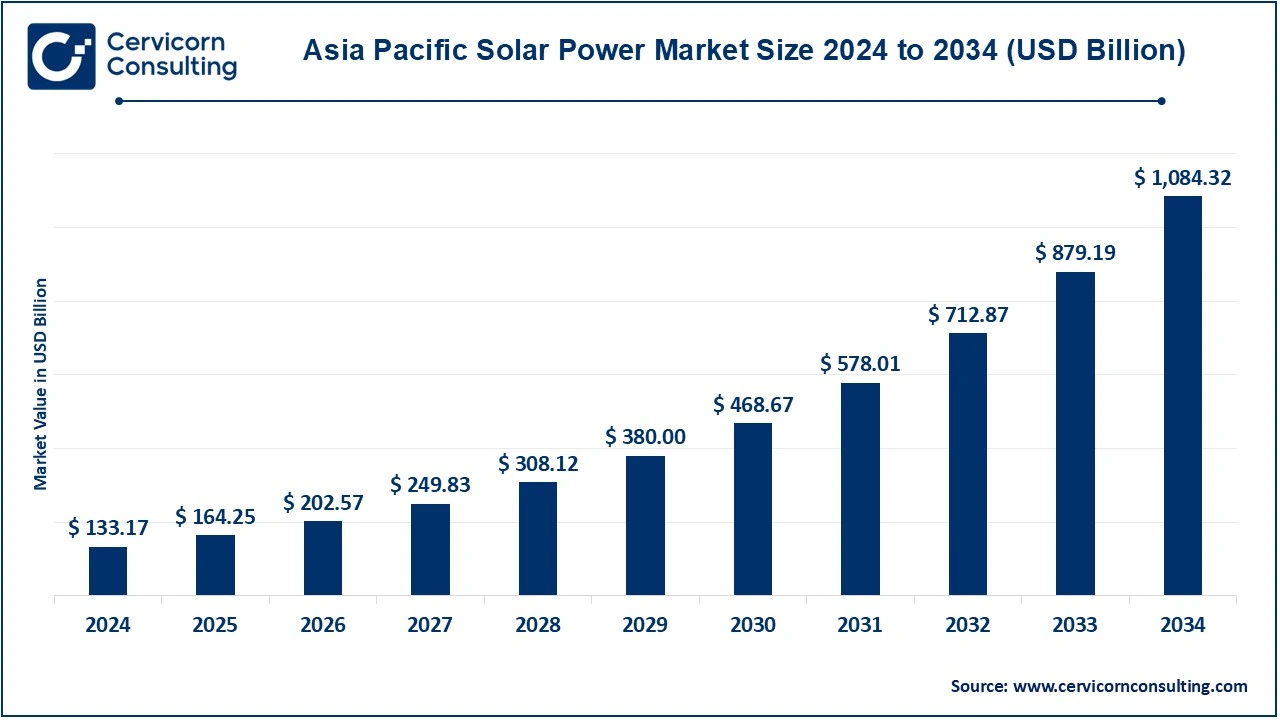
The Asia-Pacific solar power market size was valued at USD 133.17 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1,084.32 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.31% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The solar power market is growing very fast due to the vast demand for renewable energy sources, driven by global concerns over climate change and the need for sustainable energy solutions. Key factors contributing to the growth include government incentives and subsidies, which promote solar energy adoption, as well as technological advancements that make solar power more efficient and affordable. Moreover, rising electricity prices and increased consumer awareness about environmental impact are further fueling the demand. Companies like First Solar, Tata Power Solar, and Adani Green Energy are capitalizing on these trends to expand their solar power capacities.
Asia-Pacific Solar Power Market Growth Factors
- Initiatives and Policies of the Government: Governments from all corners of the Asia-Pacific region have introduced strict policies to make way for the growth of solar power. Such examples include multiple incentives, tax benefits, subsidies, and renewable energy targets, making way for the development of solar energy. Notably, India's government National Solar Mission, whose goal is to provide 100 GW of solar power by 2022, provides a big boost for the sector. That is why China's policies have made it into the global lead in solar panel production. Initiatives such as these enhance the economic feasibility of solar investments.
- Price Reductions: The price of solar panels has fallen drastically, nearly 90% over the last decade, because of advanced manufacturing technology and economies of scale in production. Suntech and JA Solar in China have contributed to the reduction of prices across the globe. Hence other countries, India and Japan, are now ready to increase their solar energy capacities sustainably aware that it has gone price competitive to satisfy the increasing demands for electricity.
- Increase in the Global Demand for Clean Energy: This keener vision to reduce carbon footprints with clean energy sources such as solar power has increased demand for clean energy globally. With nations committing to carbon neutrality, e.g., Japan pledges to achieve zero carbon emissions by 2050, renewable energies become integral. Such requests are now driven by a realization that solar power stands an opportunity to contribute to some climate change resistance, energy security, and dependence reduction on fossil fuels.
Asia-Pacific Solar Power Market Trends
- Modular Solar Power Systems: The modular nature of solar power systems is increasingly becoming a growth factor, diversifying in terms of energy usage. Modular systems can work for small residential applications or be enlarged for large commercial and industrial installations. Small modular solar panels are usually used in homes, and huge-scale projects use modular designs to produce enormous amounts of energy, such as India's Bhadla Solar Park.
- Use of Digital Technologies in Solar: Integrating digital technologies such as AI, machine learning, and IoT disrupts the performance of solar power systems. Implementing predictive maintenance helps the proper functioning, real-time monitoring, and optimized generation of energy. For example, a digital platform by Oorjan in India helps customers monitor solar energy production and adjust consumption according to the requirement, which substantially reduces operational costs.
- Incorporating ENERGY Storage Options: As solar energy generation is based on sunlight, connecting it to energy storage options such as batteries becomes an important facilitator of uninterrupted energy. Asia-Pacific will receive ambitious attention for solar-plus-storage solutions, where countries like Australia and Japan enable domestic and commercial storage of surplus energy generated during the day for nighttime use. A growing presence in the Australian market for solar systems incorporates energy storage, like the Tesla Powerwall.
- The Growth of Solar Rooftop Installations: Rooftop solar installations are growing significantly in the region due to the pursuit of energy independence and sustainability. For instance, in India, the Rooftop Solar Scheme under various government schemes encourages urban homes and businesses to put solar panels on their roofs. There is an increasing emphasis on ROOFTOP solar schemes because of factors such as reduction in installation expenditure and government incentives, for example in the Rooftop Solar Scheme by CleanMax Solar in New Delhi.
- Growth of Solar Rooftop Installations: The region is seeing an aggressive growth in solar rooftop installations owing to energy independence and sustainability. In countries like India, government schemes like the Rooftop Solar Scheme are motivating the urban homes and businesses to take up the installation of solar panels. Rooftop solar projects like that installed in New Delhi by CleanMax Solar are seeing benefits of cost decline for installations and a boost through incentives by governments.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 164.25 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 1084.32 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
25.31% |
| Key Segments |
Technology, Solar Module, Application |
| Key Companies |
Trina Solar Limited, JinkoSolar, LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd., First Solar, Canadian Solar, Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd., JA Solar Technology Co., Ltd., Hanwha Q CELLS, REC Group, GCL-Poly Energy Holdings Limited, BYD Company Ltd., Sharp Corporation, Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd., LG Electronics, Suzlon Energy Limited |
Asia-Pacific Solar Power Market Dynamics
Drivers
Technological Innovation
- Market growth is driven by increasing improvements in solar panel technology, including more efficient photovoltaic cells and bifacial panels' entry into the market. For instance, SunPower solar panels have high levels of efficiency and have the ability to produce the most output of power per square meter. Technological gains enhance energy yield and make solar power more attractive to residential and industrial end-users in the Asia-Pacific region.
Escalating Energy Prices
- Solar power is thus viewed as a cheaper and more carefree possibility as the cost of conventional energy increases owing to the fluctuations in global markets. Policy measures rooted in the rising prices of coal and natural gas in India and China have created an environment that literally prodded the transformation toward solar energy. China's shift, for instance, is partly driven by a desire to lessen dependence on imported coal and oil that has been going up in price.
Electricity Demand Surge
- Rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to surging demand for electricity in countries such as India and China. Solar power is seen as a reliable sustainable solution for fulfilling this requirement. The establishment of solar power plants is being accelerated in the country, owing to boost from the government in rural electrification and strengthening the grid infrastructure. Such rising incidences strongly reflect in the ambitious target of the country to attain a renewable energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030, out of which a major chunk is solar energy.
Restraints
Intermittency of Solar Energy
- Solar energy is inconsistent, depending on the supply of solar radiation. The interruption of light during cloudy days or nights has limited both the demand and supply side grid connection. Such intermittent flow of power is therefore among the main impediments to the increasing popularity of solar energy in the region.
Grid Integration Challenges
- Integrating solar power into existing grids comes with a number of difficult issues. These issues essentially result from the need for much better grid infrastructure, primarily capable of managing and controlling variable energy supplies. Countries like India, in particular, have found it difficult to render their grid systems compatible with solar energy, which has caused a loss of and inefficient use of energy during peak solar generating times.
High Initial Costs
- Upfront costs for the installation of solar systems are very high notwithstanding the drastic decline in the cost of solar panels, especially among residential customers. For example, while costs have dropped significantly in India, pre-subsidized installation costs remain beyond the reach of several families. Financing schemes and policies are, therefore, a major requirement to sidestep this challenge.
Opportunities
Rural Electrification
- The Asia-Pacific region, exemplified in India and Bangladesh, indeed has a bright opportunity for solar energy in rural electrification. While remote and off-grid areas are many, solar energy can be an affordable, clean, and sustainable approach. One of the most ambitious rural electrification programs in India, using solar technologies, is helping prove how solar can power the energy requirements of these regions.
Integration With Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- With more countries such as China, India, and Japan adopting electric vehicles, there is a new integration opportunity between solar energy and electric cars in charging. Solar recharging stations that inject their energy through solar power may significantly reduce emissions and advocate for sustainable mobility, particularly as business houses like Tata Power set up such plants in India.
Solar Microgrids
- Solar microgrids are gaining traction in traditional rural and non-urban areas where conventional energy infrastructure is limited. Powered by a combination of solar panels and storage, these self-contained energy systems can provide consistent continuous electricity to local communities. The Philippines has set up solar microgrids in far-flung islands, for instance, to assure stable power there.
Challenges
Intermittency of Solar Energy
- The inherent intermittency of solar power is still one of the biggest challenges, as energy generation becomes tied directly to the availability of sunlight. This difficulty can be overcome by aligning solar with energy storage systems, increasing the costs and complexity of infrastructure required. In India, among other countries, solar-generated electricity peaks during the day, significantly dropping off at night.
Infrastructure Limitations
- Many regions in the Asia-Pacific lack good and proper infrastructure to ensure solar power can be connected into the grid. It therefore becomes inefficient to deliver the solar energy. India experiences regular power cuts and hence a huge challenge for integration into the solar grid due to its existing infrastructure that fails to support the integration of renewable energies.
Land Scarcity for Large Projects
- Land availability is one of the difficult things in densely populated areas as it is often land-scarce and cost-intensive. Urban areas of India and China have similar problems that are hampering the expansion of solar infrastructure. Bhadla Solar Park in India is the world's largest solar park that was established over vast uninhabited desert land.
Asia-Pacific Solar Power Market Segmental Analysis
Technology Analysis
Solar Photovoltaic (PV): The solar PV segment has dominated the market with revenue share of 88% in 2024. Solar Photovoltaic (PV) technology dominates the Asia-Pacific solar power market due to its proficiency, cost-effective, and scalable set-up. Such PV systems use semiconductor materials to convert sunlight directly into electricity. In China, India, and Japan, PV systems are used widely for residential and commercial applications. Decreasing costs of PV modules, complemented with government incentives, have made solar power affordable and easily accessible. For instance, China has aggressively invested in PV technology and is the world's leading producer of solar panels, thus helping to push the region's market growth.
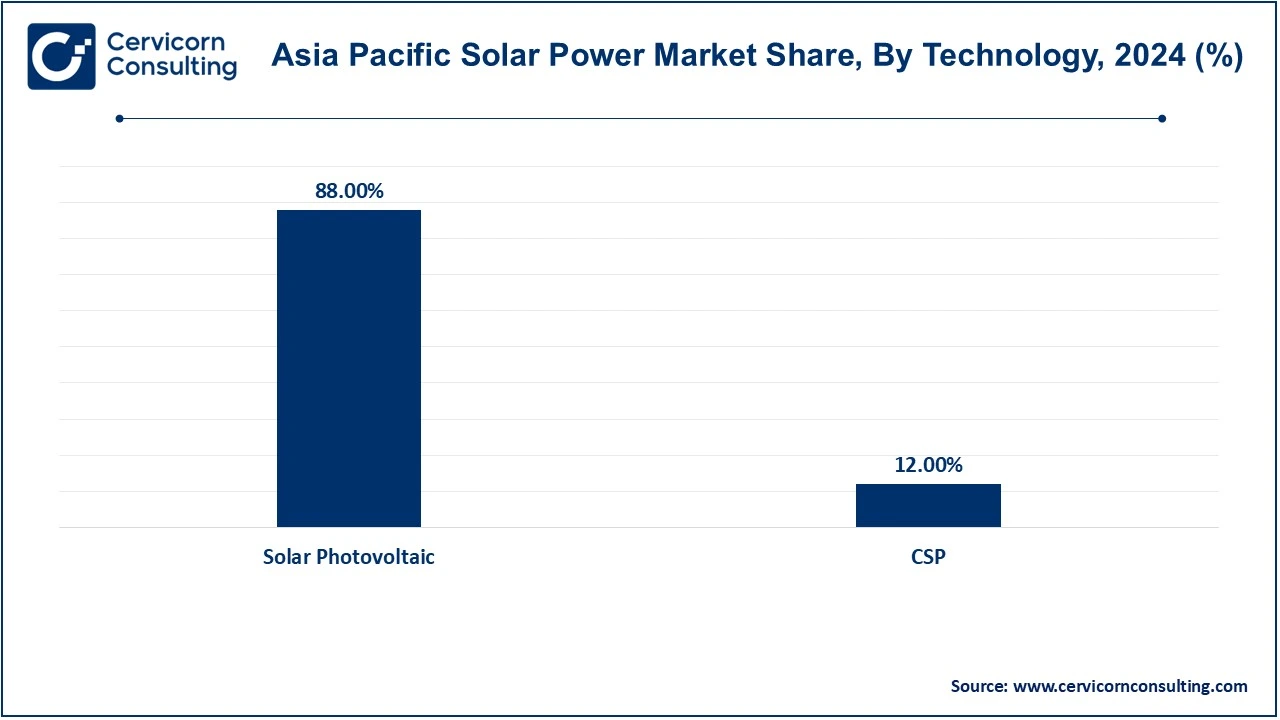
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): The CSP segment has captured revenue share of 12% in 2024. CSP technology utilizes mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area which uses the heat to drive a steam turbine for electricity generation. Though CSP is not as common as PV, it boasts a good potential for the APAC market especially in sun-rich regions like Australia and India. CSP stores heat in the form of energy and thus generates electricity even after sunset. This aspect of CSP makes it very suitable for large-scale solar power plants; one of the most well-known ones is the Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex in Morocco. While this will have its impact on ongoing initiatives in the region, it will change the outlook for CSP development.
Application Analysis
Residential: Solar power generation, practically speaking, mostly happens in the residential sector through rooftop installations. Growing energy independence and the push for sustainability are making many residential solar systems supra appealing in some countries such as Australia, Japan, and India. Various incentives, subsidies, and net metering policies have made rooftop solar more affordable for homeowners. For instance, in Australia, rooftop solar is becoming more common, with over 2.5 million households having installed solar power systems. Residential solar power supplies clean energy at a lower price, thus greatly reducing dependence on the grid.
Non-residential: Non-residential solar power includes commercial, industrial, and institutional use. They are usually deployed for large-scale solar systems to meet the higher demands of energy units. This is being intertwined with the increased solar adoption in the Asia-Pacific, as businesses and industries seek to cut operational costs and attain their sustainability goals. An example is TATA Power of India, which has entered the commercial solar space with solar solutions for businesses. Countries such as Japan and South Korea are finally getting into solar in the commercial sector because, in such economic circumstances, expensive conventional energy sources make solar a feasible alternative.
Utility: Utility-scale solar power is major, large-scale solar farms which produce electricity for the grid. This sector of industry is growing rapidly within the Asian-Pacific region due to favorable governmental initiatives and increasing demand in Asia Pacific region for renewable energy, hence India, China and Australia, have developed large-sized projects, to meet their requirement as well as fulfill environment-oriented goals. India’s Bhadla Solar Park, the world’s largest solar park, exemplifies the potential of utility-scale solar projects. Utility-scale solar is increasingly seen as a reliable and cost-efficient solution to meet the energy needs of growing populations and industries across the region.
Asia-Pacific Solar Power Market Top Companies
- Trina Solar Limited
- JinkoSolar
- LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
- First Solar
- Canadian Solar
- Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
- JA Solar Technology Co., Ltd.
- Hanwha Q CELLS
- REC Group
- GCL-Poly Energy Holdings Limited
- BYD Company Ltd.
- Sharp Corporation
- Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd.
- LG Electronics
- Suzlon Energy Limited
The new entrants in the solar power sector are employing technology to enhance energy efficiency, optimize performance, and reduce costs. By adopting advanced solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, integrated energy storage solutions, and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven grid management, these companies are positioning themselves as competitive players. For instance, newer players are utilizing cutting-edge solar panel manufacturing techniques, such as bifacial and tandem solar cells, to increase energy capture. Companies like Trina Solar and LONGi Green Energy are also exploring innovations in smart solar systems, incorporating IoT technology to monitor and optimize energy production in real-time. These technological advancements help them better meet the growing demand for clean and efficient energy solutions in regions like Asia-Pacific, where solar energy adoption is rapidly increasing.
CEO Statements
SunPower– Tom Werner, CEO
- Maintaining low solar costs is crucial to ensure solar remains competitive with other energy sources. Solar power's role is critical in providing electricity to regions without access to traditional grid systems, with microgrids serving as an essential solution. We're investing in innovative partnerships and technological advancements to improve solar efficiency and storage capabilities."
Ascent Solar– Jeffrey Max, CEO
- "I am excited to lead Ascent Solar through this pivotal phase of growth. Our advanced photovoltaic technology offers immense potential for industries like agriculture, infrastructure, and space missions. Our team’s focus on innovation and execution positions us well to capture new opportunities in the solar market."
Recent Developments
- In March 2022, Solaria introduced its PowerXT 430R-PL (430-watt) solar panel, designed to optimize next-generation Module-Level Power Electronics (MLPE). These advanced devices, which include micro-inverters and Direct Current (DC) power optimizers, are integrated into solar PV systems to enhance performance, particularly in challenging conditions such as shading. By improving energy production efficiency, MLPE devices enable solar power systems to operate more effectively, contributing to higher overall energy output.
Market Segmentation
By Technology
- Solar Photovoltaic
- Mono-Si
- Thin Film
- Multi-Si
- Others
- CSP
- Parabolic Trough
- Power Tower
- Linear Fresnel
By Solar Module
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- Thin-Film Solar Cells
- Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell
- Cadmium Telluride Solar Cell
- Others
By Application
- Residential
- Non-Residential
- Utility
...
...

