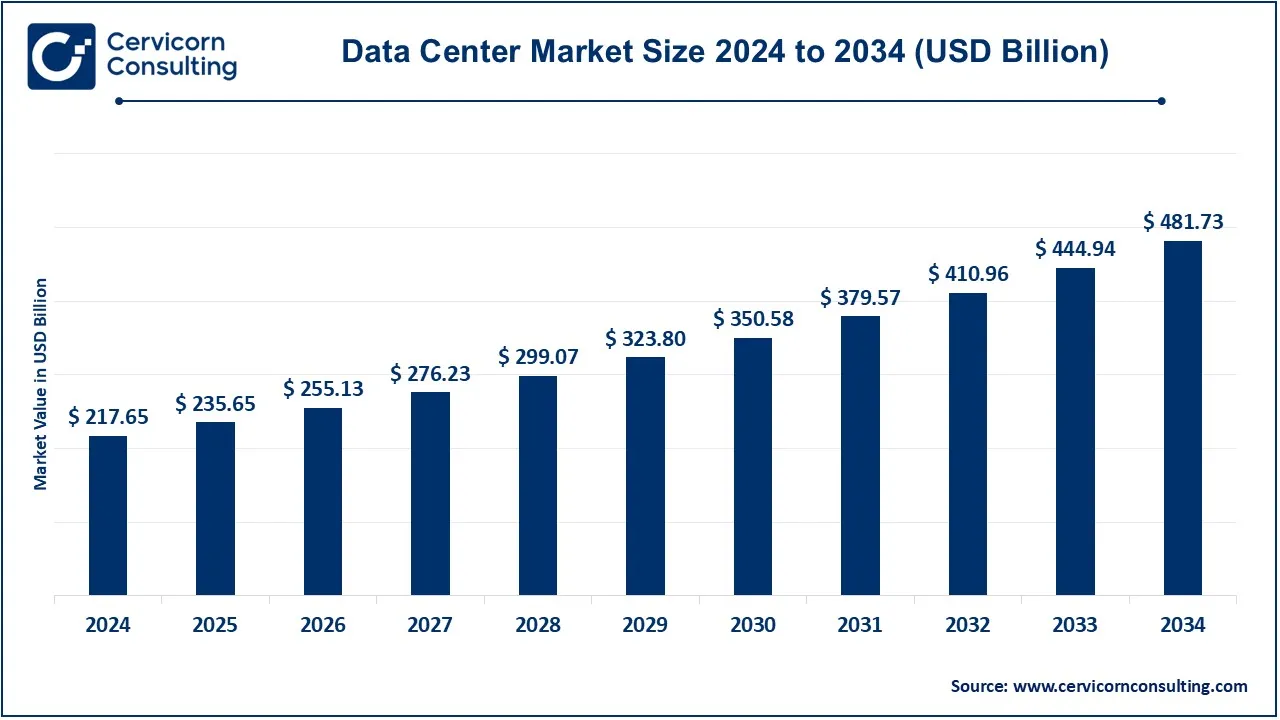
The global data center market size was accounted for USD 217.65 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 481.73 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% from 2025 to 2034. The U.S. data center market size was estimated at USD 54.42 billion in 2024. The data center market is driven by cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the increasing demand for data storage. Enterprises are shifting to hyperscale and edge data centers to process data faster and closer to users. The rise of 5G networks, smart devices, and streaming services further accelerates expansion. Additionally, governments and businesses are investing in data sovereignty and security to comply with regulations. Sustainability is a key focus, leading to innovations in liquid cooling, renewable energy, and modular data centers. With the increasing reliance on digital services, the future of data centers lies in automation, AI-powered optimization, and energy-efficient infrastructure to handle exponential data growth.
What is a data center?
A data center is a facility that houses computing infrastructure like servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and security systems. It is used to store, process, and manage data, supporting business operations, cloud computing, and online services. These centers ensure uninterrupted access to data and applications, offering high security, power backup, and cooling systems for optimal performance. Data centers are classified into on-premises, colocation, cloud, and edge data centers, each serving different needs. They are critical for businesses, governments, and tech giants like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft. The demand for data centers has surged due to cloud adoption, AI, internet of things (IoT), and big data analytics. Companies now focus on energy-efficient and green data centers to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Key insights beneficial to the data center market:
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 235.65 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 481.73 Billion |
| Expected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 8.26% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Components, Type, Capacity, Design, Tier Level, Data Center Redundancy, PUE, End Use, Region |
| Key Companies | Digital Realty, Dataspan, Equinix, Inc., Google Cloud, IBM, Schneider Electric SE, Microsoft, NTT Communications Corporation, Oracle, ABB Ltd, Cisco Systems Inc., Tencent Cloud, Amazon Web Services, Inc., Eaton Corporation, AT&T Intellectual Property, CyrusOne, Alibaba Cloud, Lumen Technologies (CenturyLink), IBM Corporation, China Telecom Americas, Inc., CoreSite, Siemens AG |
Increased Automation
Increasing Server Virtualization
Concerns Related to Environmental Issues
Strict Sustainability Regulations
Rising Data Center Investments
Rising Government Initiatives
Increasing Power and Cooling Concerns
Growing Cybersecurity Issues
The data center market is segmented into components, type, capacity, design, tier level, data center redundancy, PUE, end use and region. Based on components, the market is classified into hardware, software and services. Based on type, the market is classified into edge, colocation, enterprise, hyperscale, and HPC. Based on capacity, the market is classified into below 100 MW, 101–800 MW, and above 801 MW. Based on design, the market is classified into traditional, modular and containerized. Based on tier type, the market is classified into tier 1, tier 2, tier 3 and tier 4. Based on end use, the market is classified into BFSI, government, IT & telecom, healthcare and others. Based on data center redundancy, the market is classified into N+1, 2N, N+2 and N. Based on PUE, the market is classified into less than 1.2, 1.2 - 1.5, 1.5 - 2.0 and Greater than 2.0.
Hardware: The hardware segment has dominated the market in 2024. The physical infrastructure of data centers is made up of hardware, which includes servers, storage devices, networking hardware, and other tangible assets. Hardware market growth is being driven by the increasing need for networking hardware, storage solutions, and high-performance computing.
Software: The data centers help in processing, managing, and securing data. For this purpose, the data centers use a variety of operating systems, apps, management tools, and virtualization software. The primary reason for the rising demand for the development of automation and software-defined infrastructure technologies is the enhancement of operational performance and resource optimization.
Data Center Market Revenue Share, By Components, 2024 (%)
| Components | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Hardware | 64% |
| Software | 24% |
| Services | 13% |
Services: Specialized services are necessary for businesses to thrive in this dynamic environment and optimize investments. The vendors support data center management and performance optimization by offering installation, maintenance, and consulting services. The fundamental architecture of data centers is made up of solutions, but services provide expertise, support, and customization to adapt to changing requirements and ensure smooth operations.
Enterprise: This segment has captured highest revenue share in 2024. Corporate data centers are privately owned assets that corporations own and administer to manage their inbuilt IT infrastructure and run business activities. They give specialized control over data and programs, assuring security and adherence to specific corporate needs.
Edge: Edge data centers focus on decentralizing data processing and storage, positioning infrastructure closer to end users or data sources. They minimize latency in real-time applications including IoT gadgets, media streaming, and edge analytics. These centers are frequently located in scattered or remote areas and serve developing technologies that require real-time data processing.
Colocation: Colocation centers provide infrastructure and facilities to several tenants. They provide organizations low-cost choices for keeping servers and technology assets while benefiting from common facilities, security, and connectivity.
Hyperscale: Hyperscale data centers are massive facilities designed to accommodate the massive size of cloud services and global internet platforms. They offer significant computation and storage capacity to handle enormous volumes of data and meet the scalability needs of a cloud-based applications as well as services.
HPC: High-performance computing (HPC) data centers are designed to be the most energy-efficient data centers in the world. The data center uses world-class technologies and serves as a showcase facility to demonstrate data center energy efficiency. An HPC data center can process large amounts of computations faster than any single commercially available computer using multiple servers and "supercomputers." Specifically, HPC refers to the use of aggregated computing resources and simultaneous processing techniques to run advanced programs and solve complex computational problems, increasing performance better than a single computer or server.
Below 100 MW: The sub-100 MW sector is often used for smaller data centers or establishments with low computing requirements. It is designed for smaller businesses, minor activities, or applications that require a modest amount of electricity.
101-800 MW: Mid-sized data centers serve a broader range of businesses and operations with medium to high computing and storage requirements. These data centers handle large workloads but are not at hyperscale levels.
Above 801 MW: Over 800 MW data centers operate with massive power capacities and meet the needs of large cloud service providers, technology giants, and enterprises with high computing needs. These facilities handle workloads, manage global data storage, and provide infrastructure for large-scale cloud services.
Traditional: This segment has dominated the market in 2024. Traditional data centres follow a certain architectural design that includes network infrastructure, computer resources, and storage devices. They usually include custom-built infrastructure and rigid configurations with limited flexibility for rapid scalability.
Modular: Modular data centers use prefabricated modules or containers that can be quickly deployed and scaled. They offer flexibility in design and allow for rapid expansion or contraction based on changing requirements. The modular approach speeds up deployment times and provides efficient use of space.
Containerized: Containerized data centers host information technology tools inside shipping container-like buildings. They provide mobility and ease of deployment in a variety of situations, making them suited for temporary or distant deployments. This architecture encourages agility and enables the quick deployment of computer equipment.
Tier 1: Tier 1 facilities provide basic infrastructure with minimal redundancy. They provide a single path for power and cooling. These data centres are appropriate for small enterprises or non-essential applications where maintenance disruption may be accepted without causing major disruption to operations. They lack overlapping elements and networks, making them more vulnerable to disruption while maintaining or equipment failure.
Tier 2: Tier 2 data centres feature several redundant components and provide greater dependability than Tier 1. Sometimes there may be outages for maintenance or enhancements to equipment, regardless of having multiple cooling processes and power supply systems. These facilities are geared at small and medium-sized organisations with slightly greater uptime needs.
Tier 3: Tier 3 facilities offer a higher level of redundancy and availability. They are equipped with numerous electrical and coolant distribution lines, as well as concurrent maintenance capabilities. Tier 3 data centers have merit for companies that need constant dependability for critical programs and enables scheduled repairs without interfering with company operations.
Tier 4: The strongest and most reliable data centers are Tier 4 facilities. They provide 100% redundant systems and parts, so there isn't a possibility of failure. These facilities offer the highest degree of fault acceptance, allow for concurrent maintenance, and ensures that services continue even in the case of ongoing repairs or equipment failure. Big businesses and financial organizations, who rely on critical infrastructure that require substantial downtime, are common users of Tier 4 data centers.
BFSI: Security, compliance, and high availability are key components of the data center needs for the banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) industry. The sector requires a strong infrastructure to facilitate regular transactions, secure financial information, and comply with rules.
Government: With individuals' increasing expectations of internet-based services and the government's introduction of several e-government projects, the need for data centers is increasing tremendously. A strategy framework for high availability, rapid scalability, skilled leadership, and optimal resource use must be created. The government prioritizes the development of a robust data center infrastructure that allows data preservation, cloud computing protection, including constant internet access. Government subsidies and an first policy framework have been designed to encourage assets.
IT & Telecom: Modern data centers have become a crucial part of IT infrastructure. Storage and data centers are being designed to meet the needs of the clientele. It is important to restructure the traditional data center infrastructure as any kind of disruption in a data center can result in a huge loss to the structure of an organization. Telecom companies and IT service providers are looking for agile and scalable data center architectures to adapt to the evolving technology landscape and enable faster data processing, lower latency, and improved network performance.
Healthcare: Data centers store a tremendous amount of patient information that is crucial for medical management. Since the digitization of healthcare, electronic health records are stored that contain all the medical histories, test results, and medication histories. To maintain all the benefits of digital healthcare infrastructure, the healthcare industry needs data centers and data experts. They can ensure flawless managed services along with data privacy and security compliance. A resilient and trustworthy data center facility is important for handling all of the information gathered in the medical field, both now and in the future.
Others: Others include energy, retail & e-commerce, and entertainment. Data centers help energy companies manage complex operations such as grid management, energy trading, and resource optimization. Data centers specialize in offering analysis tools that optimize energy and enable renewable energy innovation. Data centres are used in retail and e-commerce to manage transactions carried out online, inventory, customer relationships, and personalised marketing. These centers support high-volume, real-time transactions and provide a seamless online shopping experience. Entertainment media has evolved dramatically over the past few decades. Data centers are the backbone of a seamless, high-performance streaming experience. By providing space, computing power, and connections, data centers store and distribute content while ensuring its performance, reliability, and security. Data centers also provide content delivery networks (CDN), Internet service providers (ISP), content providers, and other centralized locations to enhance the streaming experience and strengthen their businesses. To properly supply these services, data centers must provide stable environments that are constantly available to meet the changing needs of ever-increasing amounts of high-density, constrained by latency content.
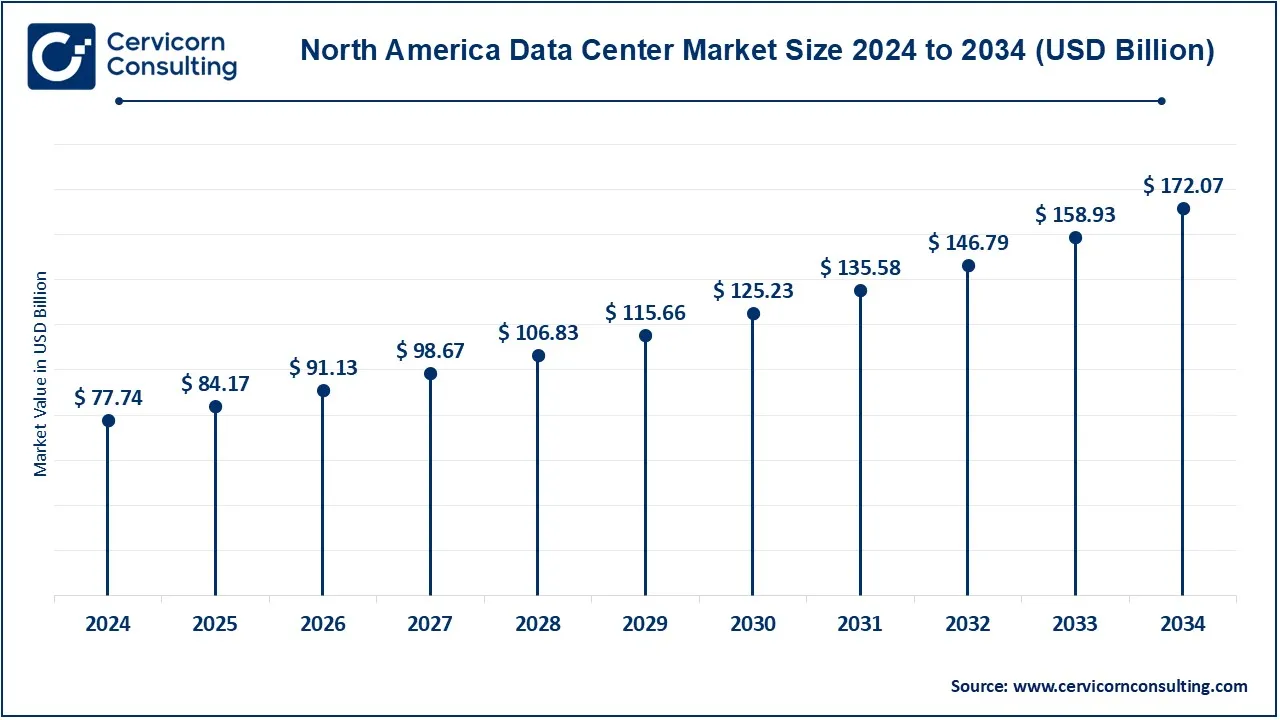
The data center market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. The North America region has dominated the market in 2024.
The North America data center market size was valued at USD 77.74 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 172.07 billion by 2034. In North America, the data center market is witnessing a surge in the construction of hyperscale data centers, driven by the demand for cloud services and digital transformation. The region prioritizes sustainability and is gradually using green data center methods. Hybrid cloud solutions and edge computing are increasing in popularity, demonstrating the need for adaptable and effective data processing facilities to support various industries in the changing digital landscape.
The Europe data center market size was valued at USD 49.41 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 109.35 billion by 2034. In Europe, the data center market reflects a commitment to sustainability and technological innovation. The region is witnessing a growing demand for energy-efficient and green data centers. Hybrid cloud solutions are gaining traction, emphasizing the flexibility of data processing strategies. Europe's data center ecosystem exemplifies a harmonic combination of advances in AI integration, sustainable energy practices, and durable infrastructure, putting the region at the top of the list of data center developments.
The Asia-Pacific data center market size was valued at USD 67.82 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 150.11 billion by 2034. Asia Pacific exhibits a robust growth characterized by significant investments in data center infrastructure. To meet scalable demands, the area is experiencing an expansion of flexible and modular data centers. Asia Pacific, with a dynamic combination of developed and emerging markets, is well-positioned to embrace cutting-edge technologies like AI and edge computing to meet increasing expectations for digital services along with information storage.
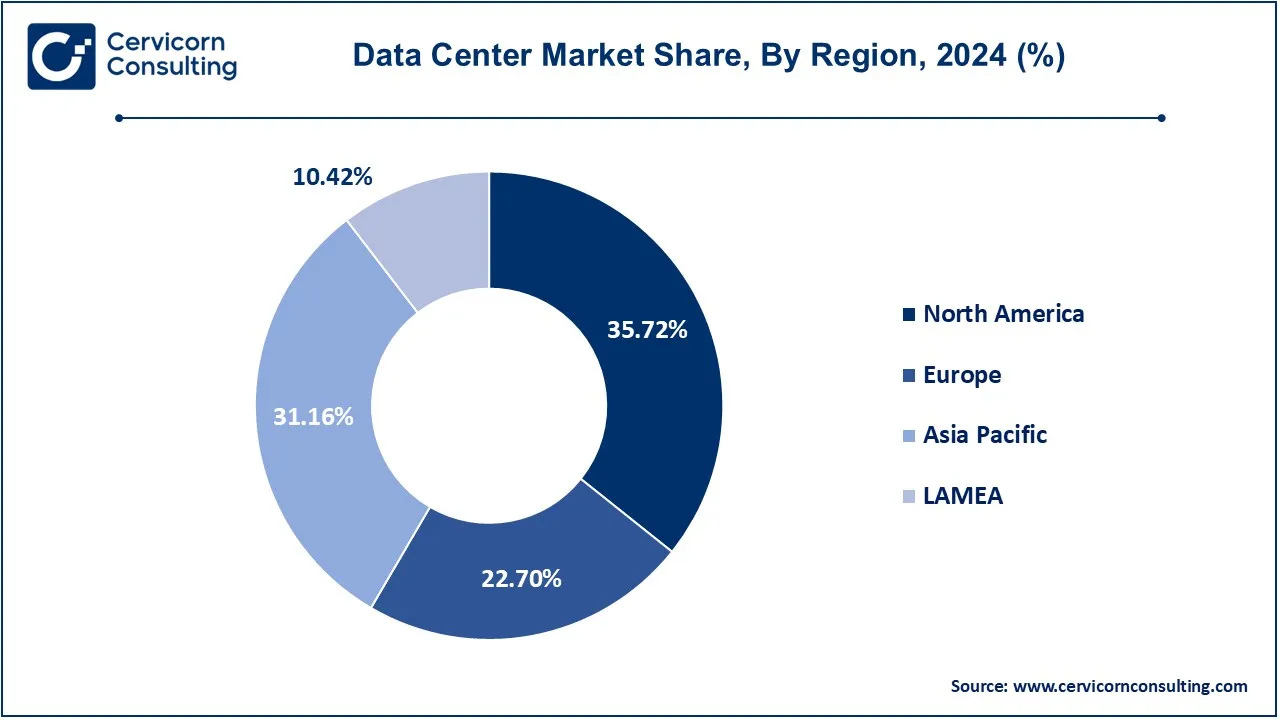
The LAMEA data center market size was valued at USD 22.68 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 50.20 billion by 2034. The LAMEA region is expected to exhibit remarkable growth during the forecast period. The region is witnessing a tremendous digital revolution, which is accelerating economic growth. Data center investments help with this since they provide crucial infrastructure for AI, cloud computing, and IoT technologies. For example, Microsoft's new data centers in the UAE and South Africa are expected to create significant economic opportunities, including local innovation and job creation. Added to that, the South American market is continually expanding due to increased demand for initiatives related to digital transformation, cloud services, and the development of e-commerce and technical services.
Most companies are actively conducting research and development. Companies are pursuing strategies to seize new market opportunities and target new customers by developing sustainable products. Intense competition among leading players to launch advanced and innovative products encourages companies to invest in the research and development of energy-efficient data centers. Also, numerous end customers are shifting to data center solutions, making it much simpler for data centers to implement green practices while maintaining performance. Akamai Technologies Inc. has announced the official launch of three new cloud data centers in Paris (France), Washington DC, and Chicago (USA) in July 2023, with additional facilities in Seattle (USA) and Chennai (India). Moreover, Akamai's cloud architecture now includes improved instance types. Ardian, an investment business, said in October 2023 that it has reached a partnership with Verne, a green data center infrastructure based in the UK. Ardian's latest agreements benefited Verne's strong development plan in Northern Europe, which was further strengthened by a $1 billion capital expenditure. This massive project might be funded by a newly developed free-floating environmentally friendly financing package sponsored by major European and international banks.
Market Segmentation
By Components
By Type
By Capacity
By Design
By Tier
By Data Center Redundancy
By PUE
By End Use
By Region