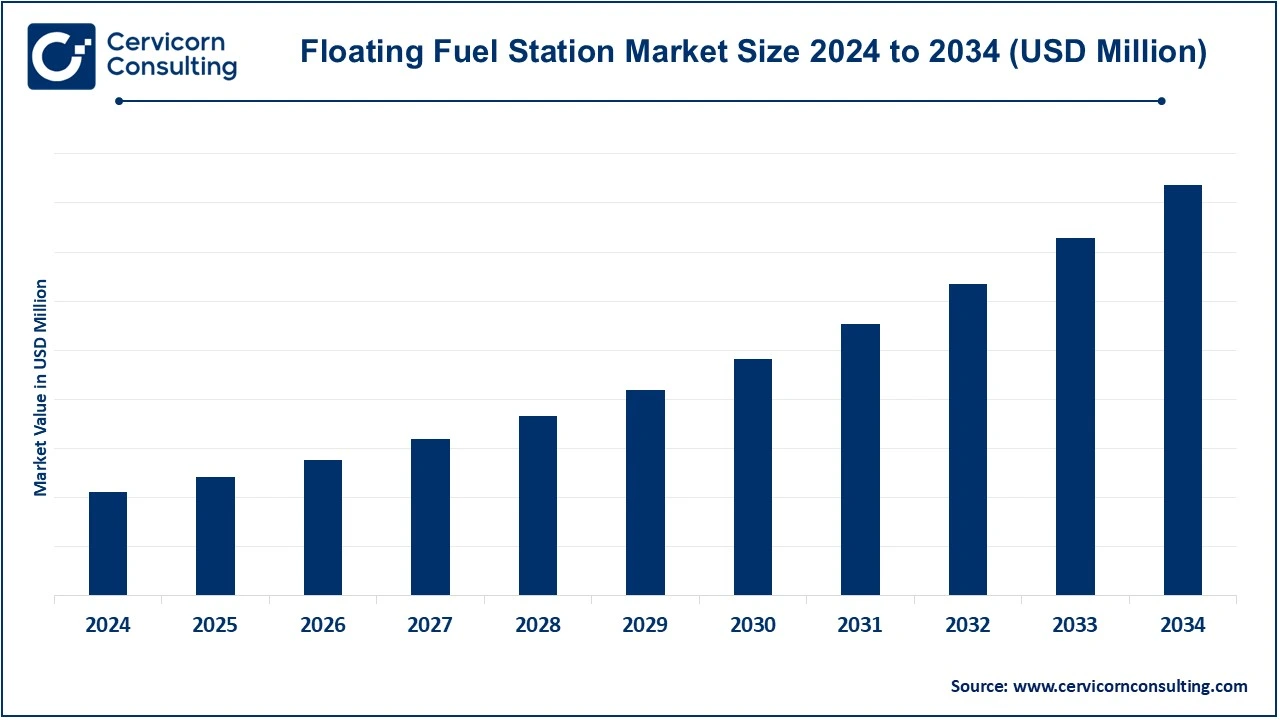
The floating fuel station market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8% from 2025 to 2034. The floating fuel station market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the rising demand for efficient fueling solutions in remote offshore locations, maritime transport, and oil and gas exploration activities. Increasing global trade and maritime logistics have expanded the need for reliable and mobile fuel supply systems to support commercial vessels, fishing fleets, and offshore platforms. Technological advancements in floating storage units, combined with the growing adoption of cleaner fuels like LNG, are further boosting market expansion. Additionally, emerging economies in the Asia-Pacific and Middle East regions are investing heavily in offshore energy projects and port infrastructure, contributing to the market's upward trajectory. Environmental regulations and a shift toward sustainable energy solutions are also influencing the development of innovative, eco-friendly floating fuel stations, making this a promising market for the foreseeable future.
What is a Floating Fuel Station?
A floating fuel station is a specialized structure or vessel designed to store and supply fuel to various types of watercraft, offshore installations, or remote locations where traditional fuel stations are unavailable. These stations are typically moored or anchored in water bodies, such as harbors, rivers, or offshore areas, and are equipped with storage tanks, fueling pumps, and distribution systems.
Floating fuel stations are used to refuel commercial ships, fishing boats, recreational vessels, and offshore platforms. They can store various types of fuel, such as diesel, gasoline, and liquefied natural gas (LNG). Some advanced models also include features like spill prevention systems, environmental monitoring equipment, and the ability to handle multiple fuel types. These stations are essential for supporting maritime and offshore operations, ensuring efficient fuel delivery in locations where land-based refueling infrastructure is impractical.
Key Insights
Increasing Maritime Activities
Offshore Oil and Gas Exploration
Technological Advancements
Environmental Regulations and Shift to Cleaner Fuels
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Floating Fuel Station Market Leading Region | North America |
| Floating Fuel Station Market Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Floating Fuel Station Market Key Segments | Type, Application, End User, Region |
| Floating Fuel Station Market Key Companies | Shell, TotalEnergies, ExxonMobil, Kongsberg Gruppen, Golar LNG, Knutsen OAS Shipping, Siemens Energy, ENGIE, Sapura Energy |
The floating fuel station market is segmented into type, application, end user and region. Based on type, the market is classified into floating storage regasification units (FSRU), floating storage units (FSU) and mobile fueling stations. Based on application, the market is classified into offshore oil and gas platforms, marine transport, fishing vessels and military operations. Based on end-user, the market is classified into commercial, industrial and government/military.
Floating Storage Regasification Units (FSRU) dominate the market because they provide an efficient, flexible, and cost-effective solution for importing liquefied natural gas (LNG). FSRUs eliminate the need for permanent onshore regasification facilities, which are costly and time-consuming to build. Regions like Asia-Pacific and Europe have heavily adopted FSRUs to meet growing energy demands while transitioning toward cleaner fuel alternatives. Governments, particularly in India and China, are investing in FSRUs to support LNG imports. For instance, India plans to enhance its LNG import capacity to 12 million tons annually via FSRUs by 2030.
Mobile fueling stations are the fastest-growing due to their convenience and rising demand from remote offshore operations and marine tourism. They offer flexibility and mobility, enabling vessels to refuel without returning to shore. This is particularly significant for fishing vessels and small-scale maritime activities in regions with limited access to conventional fueling infrastructure. Increasing adoption in Southeast Asia and the Middle East is driven by growing marine transport and government initiatives to develop maritime fuel accessibility.
Marine transport dominates the application segment due to its significant contribution to global trade and commerce. Approximately 80% of global goods trade is carried via maritime transport. The demand for cost-effective fueling options for cargo ships and tankers is a major factor. Governments in regions such as Europe and Asia are modernizing port infrastructure to ensure fuel availability for maritime transport. For example, the European Green Deal promotes LNG fueling to lower maritime emissions, driving demand for floating fuel stations.
The offshore oil and gas platforms segment are growing rapidly due to the surge in offshore oil and gas exploration activities. Floating fuel stations ensure continuous fueling operations for supply vessels and platforms operating in remote areas, especially in regions like the Gulf of Mexico, North Sea, and West Africa. Governments such as Brazil’s have introduced tax incentives and leasing programs to encourage offshore oil exploration, fueling the demand for floating fuel stations in these regions.
The commercial sector dominates due to the heavy reliance of industries like shipping, fishing, and offshore operations on floating fuel stations. With the maritime industry transitioning to cleaner energy, the commercial sector drives demand for alternative fuel solutions like LNG. Investments by companies such as Shell and TotalEnergies in LNG fueling infrastructure underline this dominance.
The government/military segment is the fastest-growing due to increasing defense budgets and the strategic importance of ensuring operational readiness for naval fleets. Governments are investing in floating fuel stations to support military vessels operating in remote areas. For instance, the U.S. Navy has expanded its floating fueling capabilities in the Indo-Pacific region to ensure uninterrupted operations, emphasizing the growth of this sub-segment.
The floating fuel station market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
North America is a key market for floating fuel stations due to its advanced offshore oil and gas industry and strong investments in maritime infrastructure. The Gulf of Mexico continues to serve as a hub for offshore exploration, with floating fuel stations playing a vital role in supporting supply vessels and offshore platforms. The U.S. government has encouraged offshore exploration by offering incentives and lease opportunities, particularly in the Biden administration’s push for energy diversification. Moreover, private companies such as ExxonMobil and Chevron are heavily investing in offshore projects, driving demand for fueling solutions. In Canada, government initiatives to modernize marine transport and reduce emissions, including investments in LNG-powered vessels, are also boosting the market.
APAC is witnessing rapid growth in the floating fuel station market due to increasing energy demand and expansion in maritime transport. Countries like China, India, and Indonesia are heavily investing in port infrastructure and LNG import facilities. For instance, China’s Belt and Road Initiative has fueled the development of floating fuel infrastructure to support trade and connectivity. India is investing in floating storage regasification units (FSRUs) to increase LNG imports and cater to its growing energy needs. Private companies such as Shell and Petronas are collaborating with governments in the region to establish sustainable fuel solutions. Additionally, the region’s strong reliance on fishing and marine tourism is creating demand for mobile fueling stations, particularly in Southeast Asia.
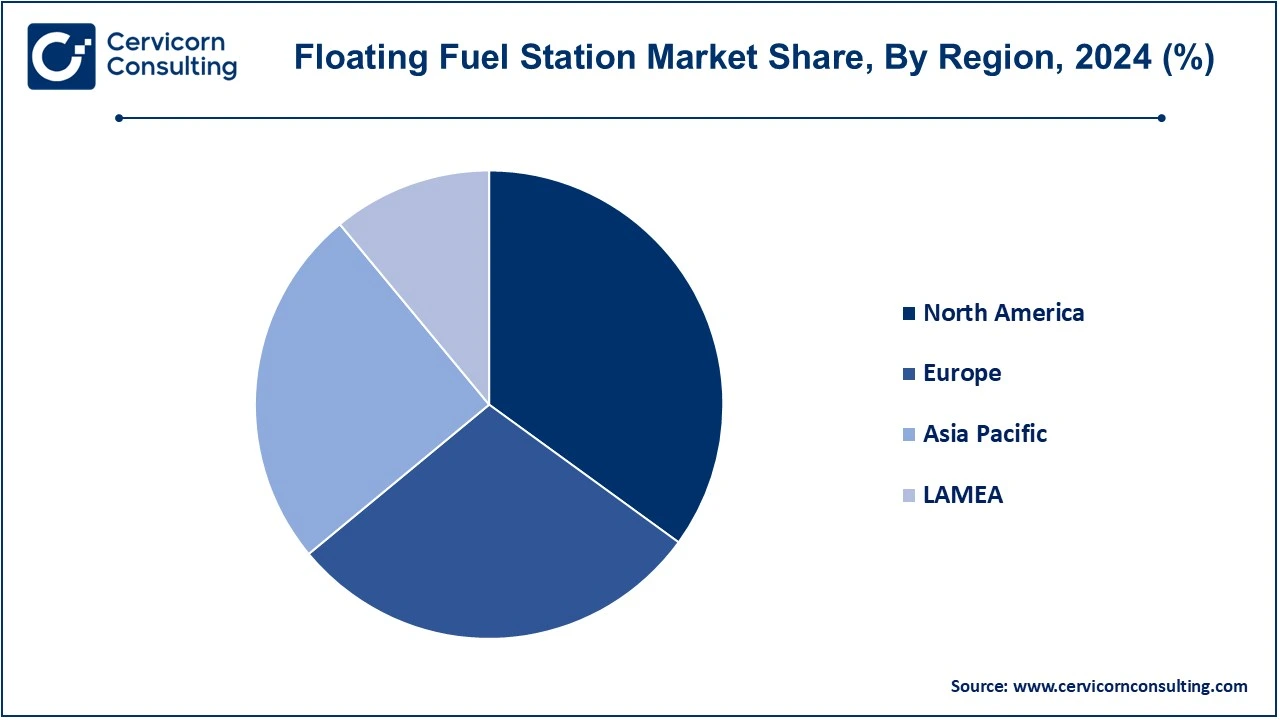
Europe is at the forefront of transitioning to cleaner marine fuel solutions, making it a significant market for floating fuel stations. The European Union’s Green Deal mandates reducing maritime emissions, which has encouraged investments in LNG bunkering and biofuels. Governments in countries like Germany, Norway, and the Netherlands have committed to building sustainable maritime infrastructure, including floating fuel stations. Norway, for example, has been a pioneer in electrifying its marine fleet and has introduced hybrid fuel solutions for vessels. Leading companies like TotalEnergies and Wärtsilä are investing in biofuel and hydrogen-based fueling stations to align with European regulations. The strong focus on sustainability and decarbonization continues to drive the floating fuel station market in this region.
The LAMEA region is emerging as a promising market for floating fuel stations due to its abundant natural resources and expanding offshore oil and gas activities. Brazil, a leader in offshore oil production, has seen increased investments in floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) units, which require efficient fueling solutions. The Brazilian government has introduced tax incentives to attract foreign investments in the oil and gas sector, supporting market growth. In the Middle East, countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia are expanding their maritime capabilities, with floating fuel stations becoming critical for supplying naval fleets and commercial vessels. Africa, particularly West Africa, is seeing rising demand for floating fuel stations as governments and companies like BP and Total invest in offshore exploration. These initiatives are fueling growth in both energy and maritime transport sectors across the region.
The floating fuel station industry is largely driven by major energy companies like Shell, TotalEnergies, and ExxonMobil, which are investing in LNG bunkering solutions and offshore fuel infrastructure. Shell and TotalEnergies are focusing on developing Floating Storage Regasification Units (FSRUs) to meet the growing demand for cleaner marine fuels, especially in regions with stringent emissions regulations like Europe and Asia. ExxonMobil is also expanding its offshore fueling infrastructure, providing sustainable solutions to support global energy needs.
Additionally, companies like Wärtsilä, Kongsberg Gruppen, and Golar LNG are pivotal in enhancing floating fuel station technologies. Wärtsilä is known for providing eco-friendly marine propulsion and fueling systems, while Kongsberg offers advanced maritime technology solutions. Golar LNG specializes in floating regasification and storage, helping reduce costs for LNG supply. These companies are driving innovation and ensuring floating fuel stations become a critical part of the future energy and maritime industries.
Market Segmentations
By Type
By Application
By End-User
By Region