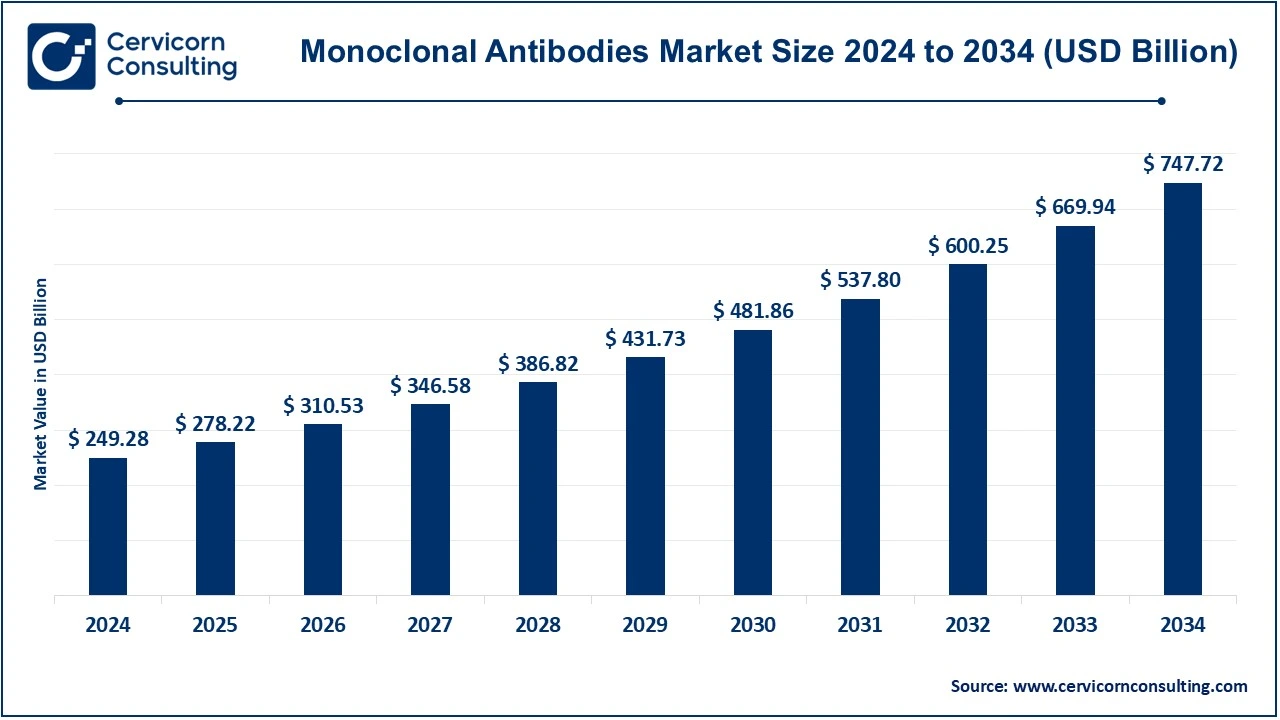
The global monoclonal antibodies market size was valued at USD 249.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 747.72 billion by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.61% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The global monoclonal antibodies market is expected to grow due to rising number of diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer and others.
The monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) market is important in modern biopharmaceutical innovation, embracing areas from oncology through immunology and infections to neurology. With mAbs being directed towards the treatment of chronic diseases like cancer or autoimmune conditions, their promise of being targeted and excellent therapeutic modalities is indeed bright. Advances in biotechnology, like antibody-drug conjugates and bispecific antibodies, have widened the therapeutic horizon for mAbs. New investments to promote personalized medicine as well as in the development of biosimilars fuel the market's growth, as well as increased, emerging demand from developing regions with improving healthcare infrastructure. However, there are significant challenges that can hold back the growth of the market such as the high cost of production and stringent regulatory requirements which can lead to delays in product development. The rising usage of AI in drug discovery along with the rising adoption of subcutaneous formulations and strategic collaborations among the players are improving innovation and accessibility which is expected to boost the growth of the market.
Merck KGaA– Belén Garijo, CEO: “Together with IAVI and Serum Institute, we look forward to demonstrating the potential application of these monoclonal antibodies in the management of COVID-19. We share a common purpose to accelerate this promising science and deliver effective solutions that address global challenges presented by this pandemic.”
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 278.22 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 747.72 Billion |
| Estimated CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 11.61% |
| Key Region | North America |
| Booming Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Source Type, Production Type, Application, End-Use, Region |
| Key Companies | Abbott Laboratories, Amgen Inc., AstraZeneca plc, Bayer AG, Biogen Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Eli Lilly And Company, F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Merck KGaA, Novartis AG, Novo Nordisk A/S, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi S.A., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Viatris Inc. |
Technological Integration
Rising Geriatric Population
High Development Costs
Stringent Regulatory Requirements
Expanding Therapeutic Areas
Rise of Biosimilars and Biobetters
Immunogenicity and Side Effects
Resistance and Escape Mechanisms
The monoclonal antibodies market source type, production type, application, end-use and region. Based on source type, the market is classified into murine, chimeric, human and humanized. Based on production type, the market is classified into in vitro and in vivo. Based on application, the market is classified into oncology, autoimmune diseases, neurological diseases, infectious diseases and others. Based on end-use, the market is classified into specialty centers, hospitals and others.
Murine Monoclonal Antibodies: Murine monoclonal antibodies are almost fully mouse-derived and using hybridoma technology, produce antibodies from one type of mouse source. These are highly specific, being the first generation of mAbs specifically for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Their use is however limited in humans due to immunogenicity problems as the mouse protein structure will usually trigger an adverse immune reaction.
Chimeric Monoclonal Antibodies: In addition, the term "chimeric monoclonal antibodies" refers to antibodies created when murine variable regions are applied with human constant regions to make a hybrid structure. This combination reduces immunogenicity as compared to pure murine antibodies while retaining strong binding activities to antigens. Chimeric antibodies, for example, such as rituximab, are well applied in oncology and autoimmune disease treatments.
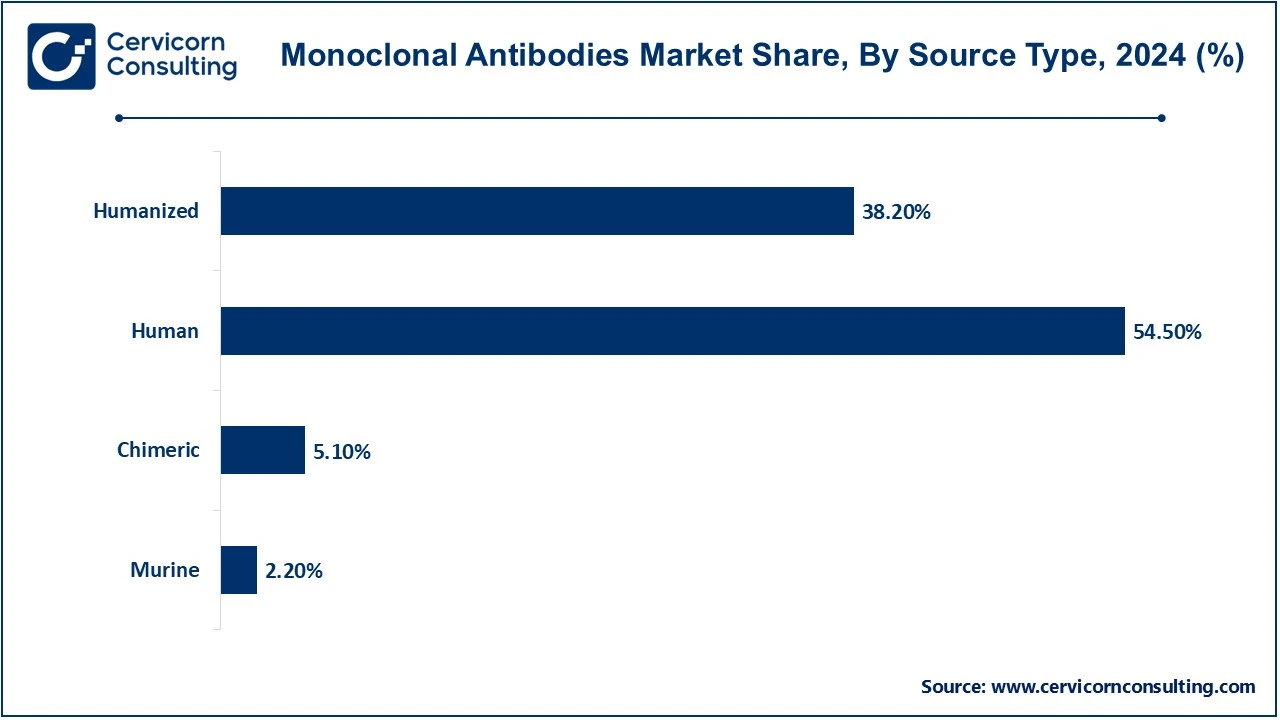
Humanized Monoclonal Antibodies: Humanized monoclonal antibodies have been formed by grafting murine antigen binding regions onto to human antibody framework. This will reduce non-human contents in the antibodies to reduce immunogenicity but at a high specificity level. Such as trastuzumab and bevacizumab work in a range of cancers and autoimmune diseases.
Human Monoclonal Antibodies: Fully emerging human monoclonal antibodies are produced solely from humans mostly using technologies like phage display or transgenic mice. Antibodies as such are less immunogenic and of such higher compatibility with the human immune system, making them suitable for therapeutic applications. Examples include adalimumab and pembrolizumab, which commonly occur in use against autoimmune diseases and cancers.
In Vivo Production: The term in vivo production is used in the context of generating monoclonal antibodies within living organisms; this is usually achieved by hybridoma technology in mice. This offers high-yield, cost-effective antibodies with excellent affinity and specificity. In vivo production is largely used for research purposes; the resulting murine antibodies can then be further modified into chimeric or humanized forms for therapeutic use. However, there are some limitations for this approach which includes ethical concerns, scaling issues, and the risk of containments. Nevertheless, in vivo production continues being a stronghold especially for early development and small-scale manufacture of monoclonal antibodies in the monoclonal antibodies market.
Monoclonal Antibodies Market Revenue Share, By Production Type, 2024 (%)
| Production Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| In Vitro | 77.20% |
| In Vivo | 22.80% |
In Vitro Production: It refers to the monoclonal antibody production through a set of cell cultivation methods in a controlled laboratory environment. These methods of monoclonal antibody production involve mammalian, bacterial, or yeast cell systems. Such a method offers superior scalability, consistency, and safety such that it is acceptable for the production of therapeutic antibodies at a large scale. Within vitro systems, there would be controlled environments over their growth conditions and thus improved quality of antibodies with less impact of contamination. It also has the potential to bring forward next-generation antibodies such as fully humanized and bispecific mAbs. Of course, compared to in vivo technique, it is expensive and more technical in nature, but it forms a good complement with the increasing need for higher-quality and larger-sized volume monoclonal antibodies for clinical and commercial use.
Oncology: The oncology segment dominated the mAb market owing to the rising prevalence of cancer and the important role of mAbs in targeted therapies. Some of the antibodies most frequently found in the treatment of breast, lung, and colorectal cancers are trastuzumab, bevacizumab, and pembrolizumab. mAb works by uniquely targeting cancer cells, blocking growth signals and enhancing immune responses. A major advancement in the efficacy of mAbs in oncology has been the development of bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates.
Autoimmune Diseases: The autoimmune diseases of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn's disease are important factors stimulating the demand for monoclonal antibodies. Treatment includes adalimumab and infliximab, which target critical inflammatory pathways to relieve symptoms and slow disease progression. Compared to older immunosuppressants, monoclonal antibodies are more targeted, with fewer systemic side effects. This condition would be compounded by the increasing incidence of autoimmune diseases, the development of mAb formulations, such as subcutaneous delivery, and many others to propel them to be well-acceptable and in use.
Infectious Diseases: There is now a lot of excitement and promise with monoclonal antibodies as possible new treatments to satisfy some of the many unmet needs of current antiviral and antibacterial therapy. For example, palivizumab mAbs prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections in high-risk infants. Elsewhere, a demonstration of the efficacy of such mAbs was evident during the pandemic which showed promise in alleviating severity. They neutralize pathogens or modulate immune responses and thus provide targeted therapeutic options. They also become an important tool in managing infectious diseases due to the increased incidence of infected drug-resistant people and new and emerging diseases.
Neurological Disorders Monoclonal antibodies are changing treatment protocols in neurological diseases targeting specific pathways involved in diseases, including Alzheimer's, multiple sclerosis, and migraines. For example, mAbs like aducanumab address amyloid-beta plaques in Alzheimer disease, while ocrelizumab modulates immune responses in multiple sclerosis. Such targeted therapies offer hope for achieving the better management of the disease along with symptom control-even for the conditions that are diagnoses as incurable. With rapid demographic aging and the increasing incidence of neurological disorders, the demand for new mAb therapies will continue to grow.
Others: Apart from the main diseases, applications of monoclonal antibodies extend to cardiovascular diseases, ophthalmology, and metabolic diseases. For cholesterol-lowering therapies and age-associated macular degeneration, there will be monoclonal antibodies in use. They are also being utilized in rare diseases and for diagnostics, thereby further contributing to the broad spectrum from therapeutic to non-therapeutic areas. Such advances in mAb engineering, such as bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates, promise to widen their scope for addressing diverse conditions.
Hospitals: Hospitals are the premier end-users of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) based on their very sophisticated infrastructure and more advanced healthcare professionals who are designated to administer complex treatment. These mAbs find maximum application in oncology, immunology, and infectious disease wards where specificity would be crucial for therapies. Hospitals also carry out clinical trials with new mAb therapies that result from adding their input into the adoption of these monoclonal antibodies. These hospitals' services in the management of critical and chronic conditions thus guarantee permanent demand regarding monoclonal antibodies.
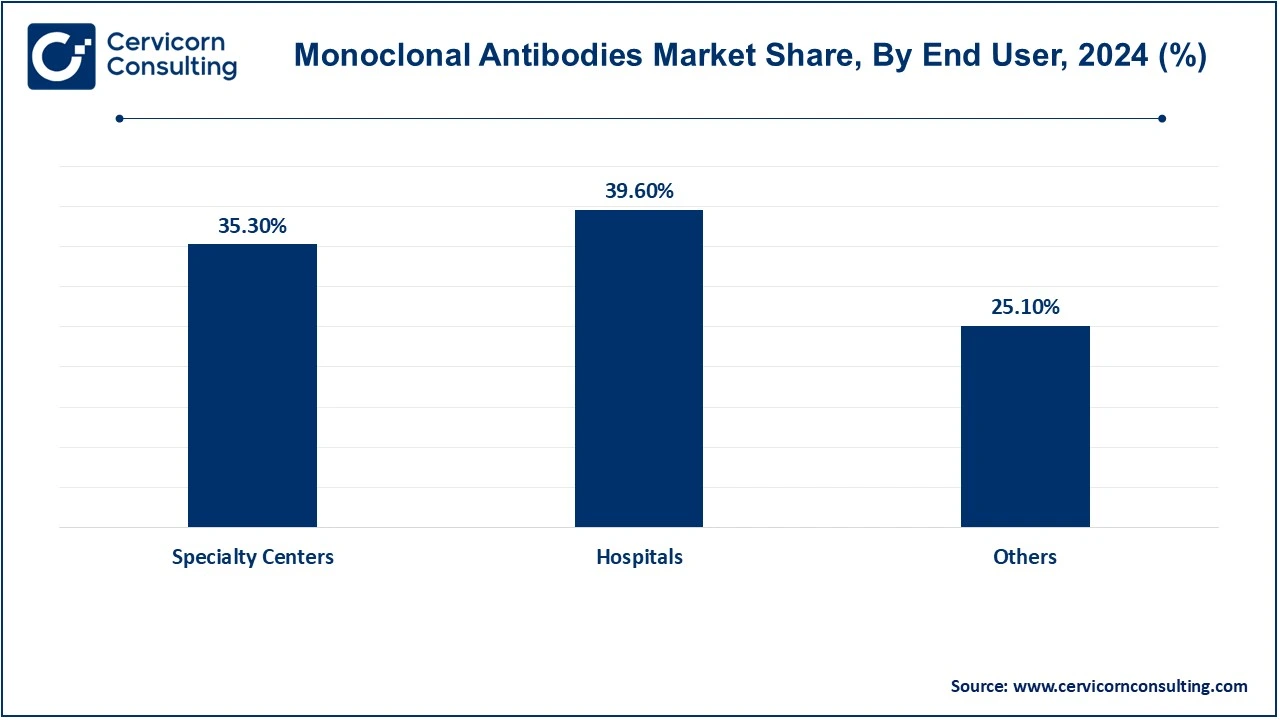
Specialty Centers: Specialty centers are also dedicated to isolated areas of treatment, for example oncology or autoimmune disease; hence, they become key end-users of monoclonal antibodies. These centers can thus perform intensive practices of mAbs such as targeted immunotherapies for solid tumors or multiple sclerosis. They provide onsite high-quality and efficient mAb treatment delivery with fast-tracked care pathways and advanced technology. By increasing the number of patients diagnosed with chronic diseases and most preferring to seek specialized treatment instead of visits to the general hospital, this segment is expected to drive further growth.
Others: This includes clinics, homecare settings, and research organizations as end-users of monoclonal antibodies. Clinics generally deal in outpatient treatments, particularly for conditions requiring repeated administration of mAbs for life-long treatment, e.g., with patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Homecare is gaining acceptance with sub-cutaneous mAb formulations, making things convenient for patients suffering from chronic conditions. The research organization is a significant end-user for developing and testing new mAb structures for innovation.
The monoclonal antibodies market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
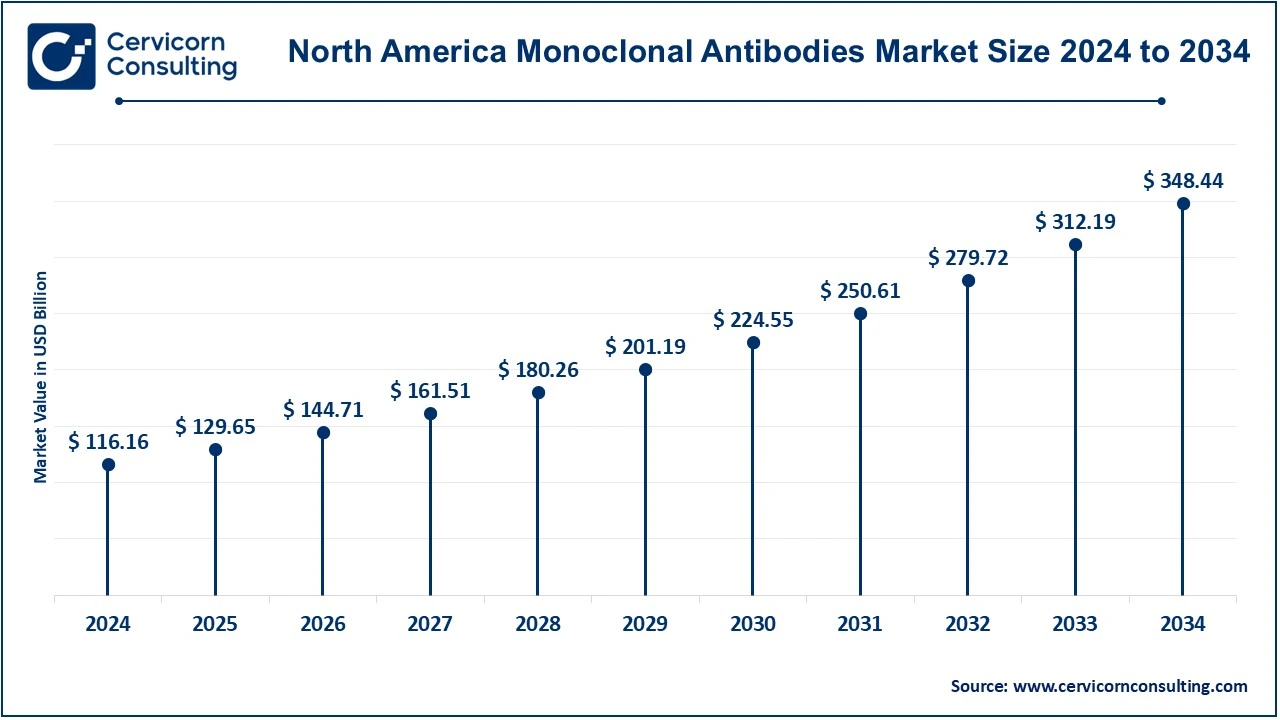
The North America monoclonal antibodies market size was valued USD 116.16 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 348.44 billion by 2034. The mAB market is highly dominated by North America primarily owing to a strong health infrastructure in the region. Various research and development (R&D) activities have been tremendously invested by numerous pharmaceutical companies throughout Europe. The increase in chronic diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders has subsequently created demand for targeted therapies. In addition to all this, favorable government policies, enhanced biomanufacturing capabilities, and early adoption of innovative treatments have been supportive to the market. USA is the one that has led the region as far as extensive clinical trial and approval of mAb therapies are concerned.
The Europe monoclonal antibodies market size was reached at USD 62.57 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 187.68 billion by 2034. Europe accounts for a notable market share in relation to monoclonal antibodies given the advancement in healthcare systems and research initiatives. Germany, the UK, and France take the lead among countries with the most government support on innovation and strong biopharmaceutical industries to their names when it comes to mAb adoption. Increasing cases of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and neurological disorders have created demand for targeted mAb therapies in the region. The region, as well, has a good regulatory structure for the development and market entry of biosimilars.
The Asia-Pacific monoclonal antibodies market size was accounted for USD 56.59 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow USD 169.73 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region is developing rapidly, owing to the enormous population, increased incidence of chronic diseases, and developing healthcare infrastructures. It is primarily China, India, and Japan that are fuelling the growth in monoclonal antibody development with their increasingly competitive investment climate for biopharmaceutical research and development and better accessibility to new therapeutics. The government is also extending local manufacturing and promotion of biosimilars, which further creates momentum in the sector. Growing medical tourism and increasing middle-class populations with better healthcare spending further help the scenario.
Monoclonal Antibodies Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 46.60% |
| EUrope | 25.10% |
| Asia-Pacific | 22.70% |
| LAMEA | 5.60% |
The LAMEA monoclonal antibodies market was valued at USD 13.96 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 41.87 billion by 2034. Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (LAMEA) represent the emerging territory, availed of the improvements in the access to healthcare and the increases in the disease incidence figures. In Latin America, Brazil and Paraguay are the leading markets, with contributors being the enhancement in healthcare infrastructure and government initiatives toward increasing the access of biologic treatments. With government advancement to transform health care, this area in the Middle East is endowed with increased growth in the market for monoclonal antibodies. Africa still has room for growth but has received considerable international collaborations and increased biosimilar uptake.
Market Segmentation
By Source Type
By Production Type
By Application
By End-Use
By Region