The sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) market is expanding with mounting regulatory support, airline net-zero ambitions, and technology advancements in biofuels and synthetic fuels. Growing scrutiny of carbon emissions and the aviation industry's carbon footprint has catalysed unprecedented investment in SAF large-scale manufacturing, as market participants build capacity and establish strategic alliances. Government mandates, incentives, and blending requirements are also driving adoption, as continued innovation in feedstocks such as used cooking oil, algae, and synthetic e-fuels is driving scalability. As airlines and fuel producers increase activity to lower their fossil fuel dependence, the SAF market will see rapid growth over the next few years.
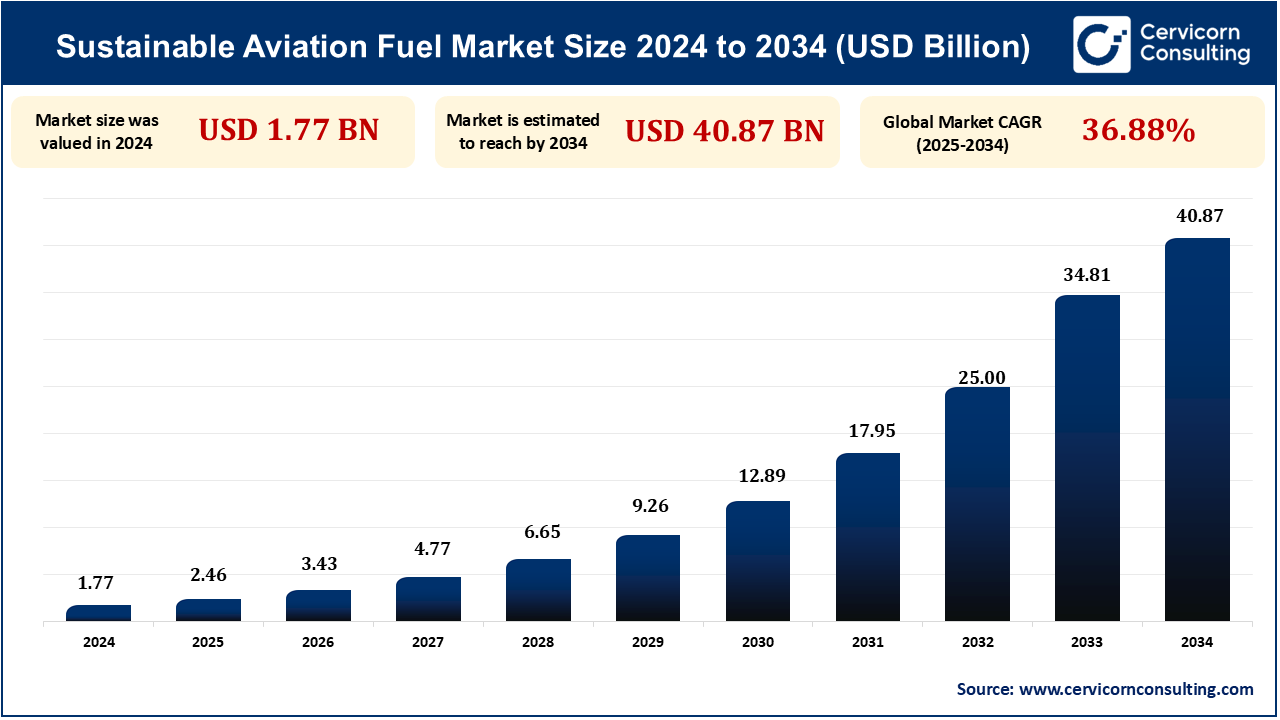
The global sustainable aviation fuel market size is calculated at USD 2.46 billion in 2025 and is expected to surge around USD 40.87 billion by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.88% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Airlines globally are increasingly adopting sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) to achieve net-zero by 2050. United Airlines, for instance, is aiming for 100% green flights by 2050 through the use of SAF, which lowers lifecycle emissions by as much as 85% and can be added to existing planes without changing them. United Airlines was also the first to use SAF in normal flying operations and offers customers a way to pay for the production of SAF through its sustainable flight account. Despite its present limitations and cost, the airline sees SAF as the most scalable solution and emphasizes lower-carbon flying options. United collaborates with multiple SAF producers and energy firms, investing in the production of the future to propel the sustainability of flight.
Technological innovations in SAF production are making it more efficient and less expensive, thus more commercially feasible. LanzaJet's Georgia-based Freedom Pines Fuels, the world's first ethanol-to-jet SAF refinery, will produce 0.009 billion gallons of SAF annually. Supported by the DOE since 2016, the plant will generate USD 0.07 billion in economic activity, USD 0.005 billion in salaries, and 80 new jobs. This achievement drives the DOE's Synthetic Aviation Fuel Grand Challenge and accelerates SAF adoption via LanzaJet's proprietary ATJ technology, introducing sustainable fuels to airlines and advancing aviation decarbonization.
One of the largest barriers to SAF adoption is insufficient infrastructure for large-scale production, storage, and distribution. Airports have a key role to play in upscaling SAF to serve 2050 net-zero aspirations since it can substantially lower Scope 3 emissions. Adoptions are however limited by factors like policy risk, cost, technology availability, and feedstock supply. Airports can shape the evolution of SAF by encouraging incentives, policy support, and industry collaboration to establish supply chains. Nevertheless, retrofitting current fuel infrastructure to accommodate higher SAF blends remains challenging without costly modifications.
SAF demand is growing outside North America and Europe, and Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are becoming serious players. India has set energy independence by 2047 and net-zero by 2070, with the inaugural commercial SAF-flown flight from Pune to Delhi as a milestone. The government aims for 1% blending of SAF by 2025, which will demand 14 crore litres per year, and is gearing up for 5%. SAF production utilizing sugarcane molasses as feedstock will give an impetus to the rural economy and generate green jobs, and India can emerge as a global SAF hub potential.
| Attributes | Details |
| Sustainable Aviation Fuel Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.46 Billion |
| Sustainable Aviation Fuel Market CAGR | 36.88% from 2025 to 2034 |
| Key Companies |
|
| By Fuel Type |
|
| By Manufacturing Technology |
|
| By Blending Capacity |
|
| By Platform |
|
| By Region |
|
North America leads as a viable market for the Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) market with the United States and Canada ruling in SAF consumption and production. The region is blessed with commendable government policies, including the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) in America and various incentives for the manufacturing of biofuel. North America's largest carriers, including Delta, United, and American Airlines, have committed to increasing SAF consumption in a bid to meet carbon reduction goals. Additionally, the presence of advanced biofuel production facilities and technological innovations makes North America an important market for SAF development.
Asia-Pacific is also experiencing growth in the SAF market as a result of increasing demand for air travel and government-endorsed initiatives for sustainability. China, India, Japan, and Australia take the lead in developing and researching SAF. Japan, for example, has formed the Green Innovation Fund to help spur the development of SAF, while Australia is investing in refineries for biofuels to diversify its aviation industry. China and India, with growing air travel markets, are also inclined towards SAF substitutes to reduce their carbon footprint. The presence of burgeoning economies as well as mounting airline fleets is sure to cement Asia-Pacific as a high-growth market for SAF.
The most widely applied variant, Biofuel-based Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), consists of renewable biomass feedstocks like used cooking oil, animal fat, crop residue, and algae. HEFA-SPK (Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids - Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene) process is the leader due to scalability and efficiency. Large manufacturers like Neste, World Energy, and TotalEnergies are quickly scaling up biofuel-based SAF production. Straw demand aside, feedstock constraint and land use issues render widespread adoption unfeasible.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel Market Revenue Share, By Fuel Type, 2024 (%)
| Fuel Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Biofuel | 79% |
| Hydrogen Fuel | 10% |
| Power to Liquid | 7% |
| Gas to Liquid | 4% |
HEFA-SPK is the most commercially established and most prevalent SAF production technology, which uses vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste cooking oils to generate jet fuel. Over 75% of current SAF production employs this technology, with pioneers in its expansion being Neste, World Energy, and BP. The key advantages are high efficiency, refinery compatibility, and top-notch regulator support, although feedstock availability is a limiting factor.
Fixed-wing aircraft, such as commercial airliners, cargo aircraft, and military aircraft, are the largest consumer segment of SAF. Airlines are increasingly using SAF to lower carbon emissions, with United, Delta, and Lufthansa making long-term commitments to SAF use. The sector benefits from established supply chains for fuels, but the expense of SAF prevents widespread take-up.
Above 50% blending of SAF is yet in the experiment stage since existing aviation regulations restrict SAF blending to 50%. Still, successful flights operated on 100% SAF (such as Virgin Atlantic's transatlantic flight in 2023) suggest that higher blends of SAF will become the new normal once regulations improve.
Commercial aviation accounts for the greatest use of SAF, and major airlines such as British Airways, American Airlines, and Qantas have pledged to achieve net-zero by 2050. Governments around the globe are encouraging the use of SAF by making blending mandates and subsidies available, and commercial aviation is the fastest-growing driver of the SAF market.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel Market Revenue Share, By Platform, 2024 (%)
| Platform | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Commercial Aviation | 73% |
| Military Aviation | 14% |
| Business & General Aviation | 9% |
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicles | 4% |
Empower your strategy with expert insights, purchase this premium research@ https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/buy-now/2321
Ask here for more details@ sales@cervicornconsulting.com