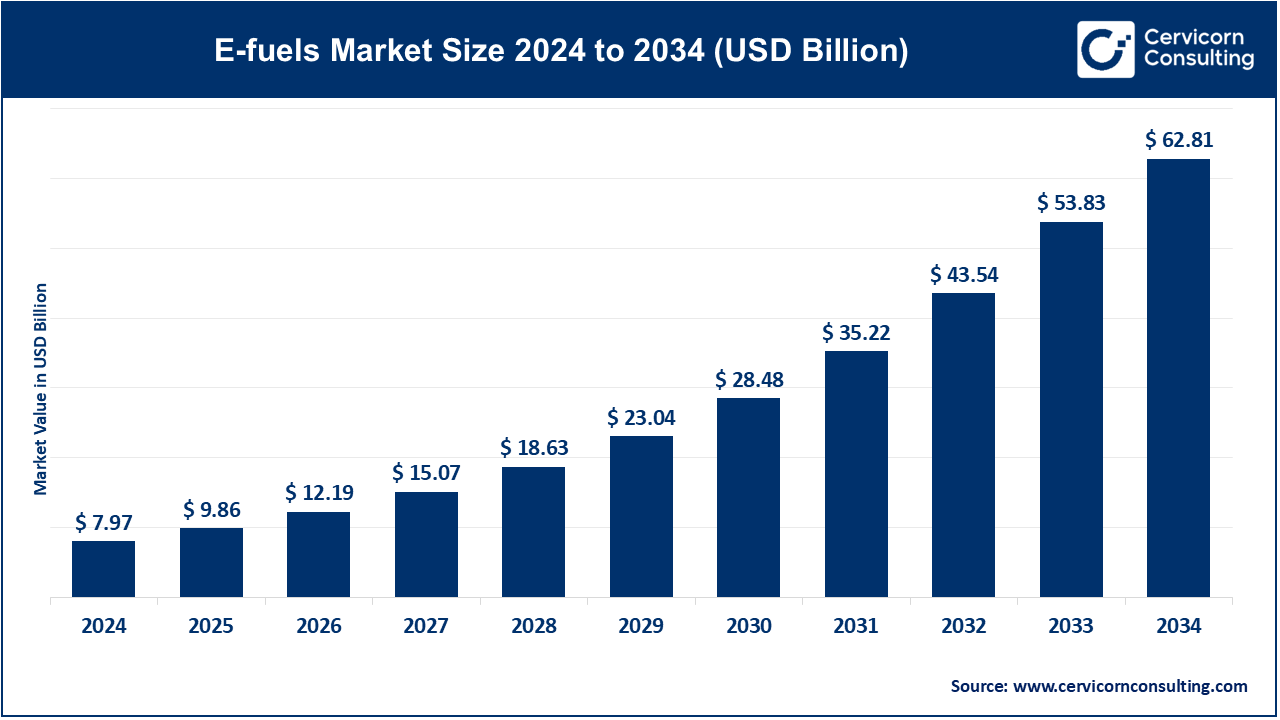
The global E-fuels market size was valued at USD 7.97 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 62.81 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.93% from 2025 to 2034.
The e-fuels market is growing rapidly, driven by the global shift towards sustainability and decarbonization. As governments introduce stricter regulations on carbon emissions and the need for green energy solutions increases, e-fuels are gaining attention as a viable alternative to traditional fuels. Companies, especially in the automotive and aviation sectors, are investing in e-fuel technologies to comply with carbon reduction targets. E-fuels offer an attractive solution because they can integrate seamlessly into existing infrastructures, such as refueling stations and pipelines, minimizing the need for drastic changes. Furthermore, their potential to be stored and transported like conventional fuels makes them highly adaptable. As the renewable energy sector continues to expand and technological advancements improve the efficiency of e-fuel production, the market is expected to grow significantly over the next decade. The European Union has implemented mandates requiring a minimum percentage of SAF in aviation fuel, starting at 2% by 2025 and increasing to 70% by 2050. This policy is expected to drive demand for e-fuels and stimulate international trade.
E-fuels are synthetic fuels produced by using renewable electricity to convert carbon dioxide (COâ‚‚) and water (Hâ‚‚O) into hydrocarbons. This process is known as the power-to-liquid (PtL) method. Essentially, e-fuels are a type of synthetic fuel that can be used as a direct substitute for traditional fossil fuels like gasoline or diesel. The key advantage is that e-fuels can be used in existing internal combustion engines and infrastructure without the need for significant modifications. E-fuels are considered a promising solution to reduce carbon emissions in sectors that are difficult to electrify, such as aviation, maritime transport, and heavy-duty road transport.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 9.86 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 62.81 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | 22.93% |
| Dominant Region | Euorpe |
| Booming Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Product, State, Production Method, Technology, Carbon Source, Carbon Capture Type, End User |
| Key Companies | Archer Daniels Midland Co., Ballard Power Systems, Inc., Ceres Power Holding Plc, Clean Fuels Alliance America, Climeworks AG, E-Fuel Corporation, eFuel Pacific Limited, Hexagon Agility, Neste, Norsk e-Fuel AS |
The E-fuels market is segmented into product, state, production method, technology, carbon source, carbon capture type, end user and region. Based on product, the market is classified into e-diesel, e-gasoline, ethanol, hydrogen, e-kerosene, e-methane, e-methanol, and others. Based on state, the market is classified into liquid, and gas. Based on production method, the market is classified into power-to-liquid, power-to-gas, gas-to-liquid, and biologically derived fuels. Based on technology, the market is classified into hydrogen technology (Electrolysis), Fischer-Tropsch, and Reverse-Water-Gas-Shift (RWGS). Based on carbon source, the market is classified into point source, and direct air capture. Based on carbon capture type, the market is classified into post-combustion, and pre-combustion. Based on end user, the market is classified into automotive, marine, industrial, railway, aviation, and others.
E-Diesel: E-Diesel is synthetic fuel gained via carbon dioxide and hydrogen synthesis that demonstrates a comparable energy content and operation to that of normal diesel. It is, however, less polluting compared to diesel fuel. Particularly for those whose heavy-duty transportation depends on high energy density, like trucking and marine shipping, this is very important. It has compatibility with existing diesel engines, which makes it a versatile drop-in fuel to wean from fossil fuels without cropping new changes on existing infrastructures.
E-Gasoline: E-Gasoline, also called synthetic gasoline, comes from the hydrogenation of carbon dioxide and acts as a carbon-neutral alternative to regular gasoline. This fuel supports the move toward carbon-neutrality in transportation on par with gasoline that can be used in internal combustion engines workloads without modification. The compatibility of this fuel with existing infrastructure also allows for a smooth transition, especially for hybrid systems and light vehicles offering an emission-cutting solution until electric vehicles find footing.
Ethanol: Therefore, it would be ethanol-a blend that in general finds use with gasoline mediums such as E10 or E85. Ethanol is produced from biomass fermentation or, in some cases, by the electrochemical synthetic method aided by renewable energy and is intended to lower greenhouse gas emissions in the transport arena. Generally said, the low-energy density ethanol shows more suitedness in light-duty vehicle-biofuel policies. Ethanol potential as a renewable alternative depends on some extent towards future developments in feedstock sourcing and production efficiencies.
Hydrogen: Hydrogen is the major component of E-fuels, mainly produced by using electrolysis with renewable energy. Hydrogen in pure form can be used for fuel cells or internal combustion engines as a zero-emission fuel option. The hydrogen market is exhibiting rapid growth due to versatility, not just for automotive industrial but also aviation usage. Nevertheless, the rather limited infrastructures for hydrogen storage and transport, together with continuous interactions with-users, provide some level of assurance regarding future hydrogen usefulness.
E-Kerosene: E-Kerosene is also known as synthetic kerosene. An alternative considered less harmful for commercial aviation than conventional aviation fuels, syn-fuel, E-Kerosene is a reputedly promising option for aircraft because of its technically feasible assimilation with aircraft jet engines. This makes the prospect of gradual decarbonization of aviation all the more alluring. One of the best bets to establish feasibility in long-distance travel, electrically out of reach, is ethylene methane.
E-Methane: E-Methane is synthetic methane produced from hydrogen and carbon dioxide and used in gas-fed engines. In particular, it finds applications in the transportation and energy sectors. E-Methane is a renewable gas that can displace natural gas in power, heat, and transport, providing climate benefits by limiting methane releases and making use of existing natural gas infrastructure as a transition to a lower-carbon economy.
E-Methanol: E-Methanol can be characterized as an engined low-emission fuel derived from green hydrogen plus carbon dioxide. E-Methanol finds applications across marine, automotive, and industrial sectors. In the past decade, as far as shipping and offshore construction were concerned, E-Methanol has made rapid inroads into these following domains thanks to being a clean alternative to conventional fuels while boosting supply density while transporting and storing the commodity. Not limited to transportation alone, its usefulness extends to serving as a fossil feedstock-chemical and energy storage.
Others: It includes those lesser-known E-fuels, such as E-ammonia and synthesized propane. While most of the foregoing have hardly started being scrutinized or have completely been taken out of the game, it is believed that they are quite advantageous in specialized applications, particularly in agriculture and energy storage pursuits and in industrial processes. But this category has been little used until now; they are likely to benefit from further R&D on production and efficiency conditions.
Automotive: E-fuels are mostly relevant to hybrid automobiles and regions still not completely transitioned to full electrification. E-fuels like E-Gasoline and E-Diesel offer immediate emission-reducing solutions for the existing internal combustion engine vehicles. Secondly, as an intermediate technology will ease the automakers towards an internal combustion-free drift, E-fuels will serve regions which still lack ubiquitous electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure with the least pollution alternative when compared to conventional fuels.
Marine: As the global society pursues the goals of reducing emissions, the marine sector is likely contributing to the pressure, thus becoming a significant end-user of E-fuels like E-Methanol and E-Diesel. These fuels present environmentally friendly alternatives to the use of heavy fuel oils background equipage in shipping. In short, E-fuels provide a way forward in decarbonizing maritime transport for distant journeys, where resorting to battery-electric solutions would be impractical because of energy density. The industry is increasing investments into synthetic fuels to comply with prevailing environmental regulations globally.
Industrial: The industry overview within the E-fuels comprises the use of highly polluting emissions alternative fuels in its heavy engines and industrial processes. To be more specific, the use of Hydrogen and E-Methane can bring about cleaner emissions and clean applications. Heavy industrial processes remain one of the most energy-intensive and most polluting activities in the world and therefore comply with producing e-fuels that can be stored and transported either in gases form or in liquid for various industrial applications such as manufacturing, construction, and power production available in the market aiming at meeting the current environmental regulations.
Railway: The railway sector, particularly within regions employing diesel trains, is converting to E-Diesel and hydrogen-based E-fuels as means to reduce their carbon footprint. While electrification could be a plausible strategy for most railways, E-fuels give an alternative where many non-electrified routes stewarding their infrastructure to such changes would be too costly. Heat fuels allow for a relatively cheaper, short-run conversion and, thus, would be perceived as an elegant transition to phase II of diesel away from traditional diesel.
Aviation: E-fuels are vital for aviation, especially E-Kerosene, due to high energy density, and compatibility with existing aircraft engines. Industry comes under pressure to decarbonize, especially for long-haul flights where electrification is not applicable. Sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs), including E-fuels, would represent one of the most viable directions for aviation emission reduction. Major airlines are investing in E-fuel technology to meet upcoming emissions regulations and push their sustainability profile up.
Others: This category covers new applications developing for E-fuels in agriculture, power generation, and even heating for residential purposes. E-methane and E-ammonia, are promising options for energy storage and off-grid power supply. These include steel manufacture and other industrial processes that need intense heating. New end-user markets will emerge as research on E-fuels progresses, expanding the ambit of their applications.
The E-fuels market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
North America-Attractive as a market for E-fuels, North America is where stringent environmental regulations and investments for clean energy meet. The U.S. and Canada are the two main providers of a policy position targeted to support decarbonization in transportation and industry to promote low-carbon fuels just as California spearheads green technology. Canada's efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions complement what the U.S. is developing, resulting in the region's E-fuel pipeline development. Substantial investment is forthcoming from both nations in hydrogen and other synthetic fuels infrastructures.
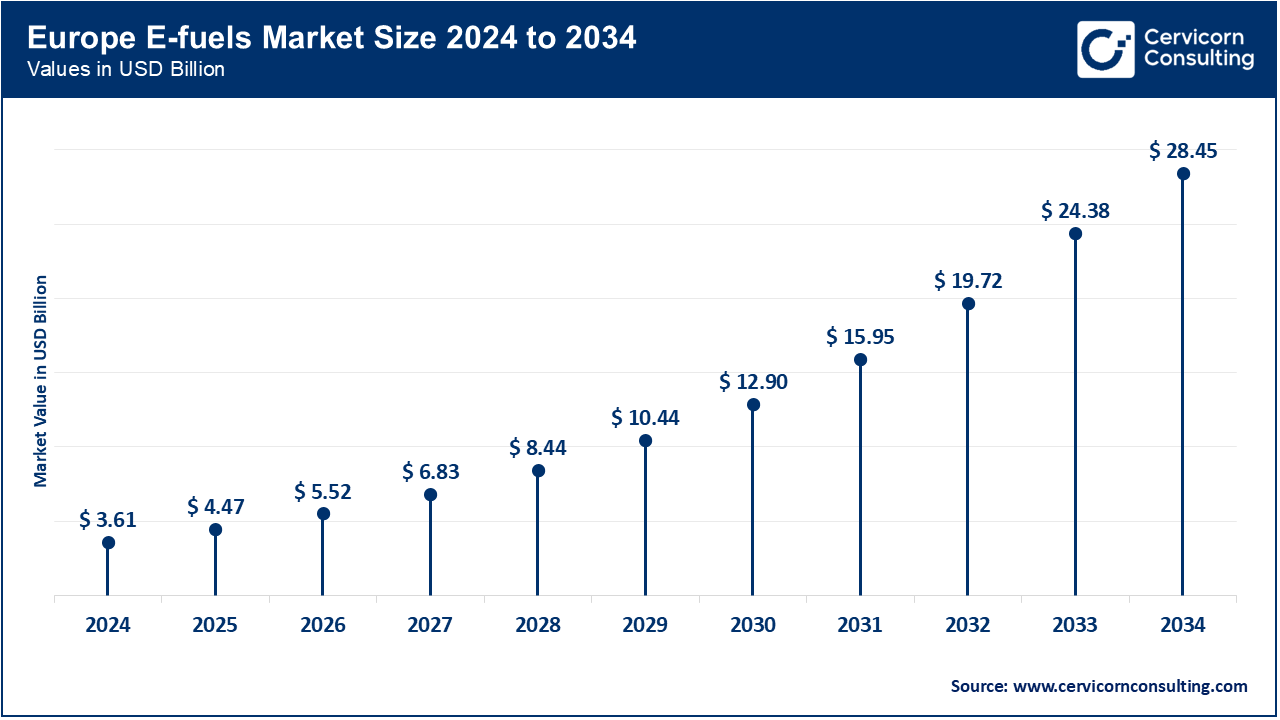
Europe reigns supreme as regards the E-fuels market because of tough climate policies, notably through the aegis of the European Green Deal. Germany, France, and the Netherlands stand at the forefront of E-fuel production and uptake, with Germany being an important hydrogen and synthetic fuel innovation hub while France is making progress in the domains of sustainable aviation fuels. The EU's "Fit for 55," which aims to cut emissions by 55% by 2030, fuels an additional demand. With this commitment to the decarbonization of transport and aviation, the region leads the global E-fuels market.
Asia-Pacific is yet another emerging destination in the E-Fuels market, with countries like Japan, China, and South Korea investing heavily in hydrogen technology and renewable energy. While Japan and South Korea are early adopters focused on hydrogen fuels to decrease their carbon footprints, China is scaling up its clean energy programs at lightning speed. Similar industrial growth and the need to diversify its energy supply would be driving forces behind the region's adoption of E-fuels by automotive, marine, and industrial sectors. The region is also hiked by promoting government policies for greening energy to adhere to international climate agreements.
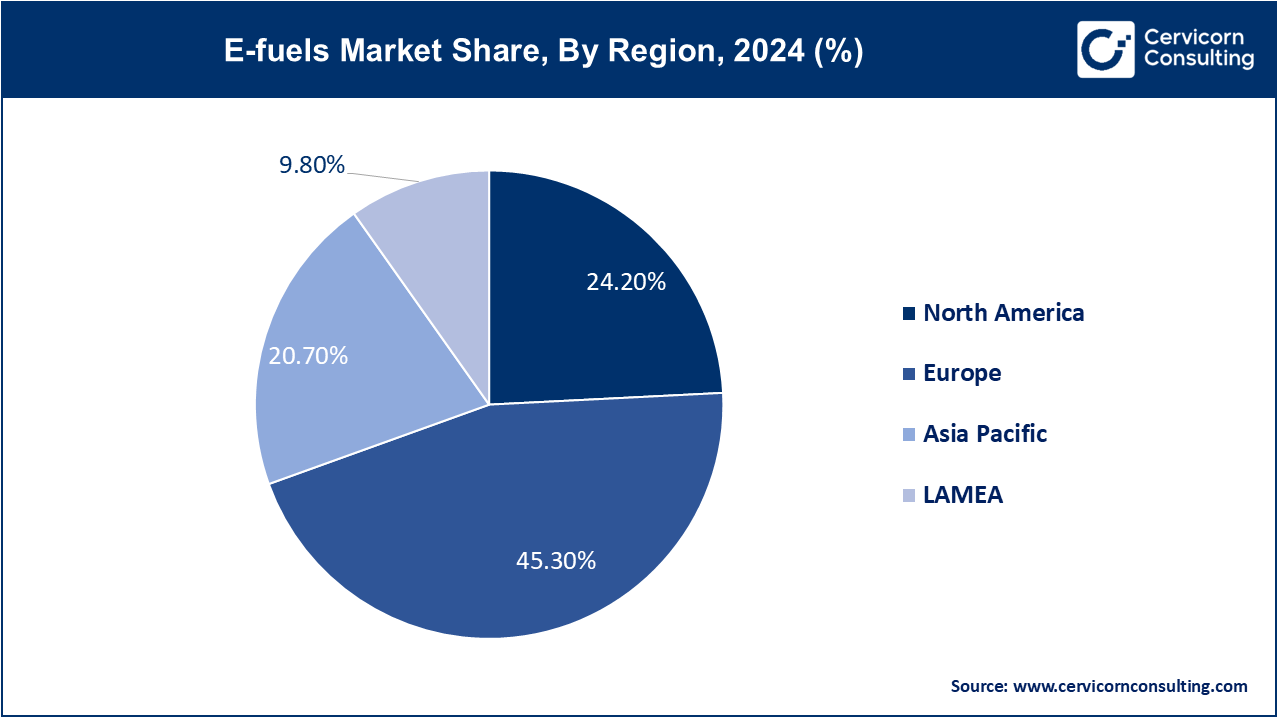
LAMEA is hosting rising interest in E-fuels, largely because of the Middle East's focus on hydrogen and renewable energy. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are investing in green hydrogen projects in order to further diversify their economies beyond oil. Countries in Latin America including Brazil are investigating biofuels and synthetic fuels in an effort to uplift their farming sector. The E-fuels market in Africa is still at a nascent phase but growing fast due to the increasing investments coming in for clean energy especially in South Africa that is introducing low carbon alternatives into the energy security mix.
CEO Statements
Olivier Zipse, CEO of BMW Group
Patrick Pouyanné, CEO of TotalEnergies
Carlos Tavares, CEO of Stellantis
Recent partnerships in the E-fuels industry highlight a strong trend toward innovation and collaboration among leading industry players. Companies such as Archer Daniels Midland Co., Ballard Power Systems, Inc., Ceres Power Holding Plc, Climeworks AG, Neste, and Norsk e-Fuel AS are actively developing advanced carbon capture and hydrogen technologies. These partnerships focus on scaling production capabilities, reducing costs, and improving the commercial viability of E-fuels. Strategic collaborations are essential for accelerating the adoption of E-fuels in hard-to-decarbonize sectors like aviation, shipping, and industrial processes. Some notable examples of key developments in the E-fuels industry include:
These developments underscore significant advancements in the E-fuels sector, with companies like Archer Daniels Midland Co., Ballard Power Systems, Inc., Ceres Power Holding Plc, Climeworks AG, Neste, and Norsk e-Fuel enhancing their product offerings to meet the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions. By innovating in carbon capture, hydrogen production, and biofuel technologies, these companies are positioning themselves as leaders in the transition to a low-carbon economy. Their initiatives aim to provide cleaner alternatives in transportation, aviation, and industrial applications, aligning with global climate goals and regulatory frameworks.
Market Segmentation
By Product
By State
By Production Method
By Technology
By Carbon Source
By Carbon Capture Type
By End User
By Region