Solar Tracker Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The global solar tracker market size was estimated at USD 10.67 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 42.43 billion by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.07% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The demand for solar trackers is growing because of the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the urge to harness out efficiency in harnessing solar energy. Solar trackers are devices used to augment the orientation of solar panels with respect to the path of the sun to overly maximize energy capture by the trackers. The market can be segmented by type, such as single-axis and dual-axis trackers, with single-axis trackers having the largest share in volume owing to its lower cost and a wider realm of application in utility-scale projects.
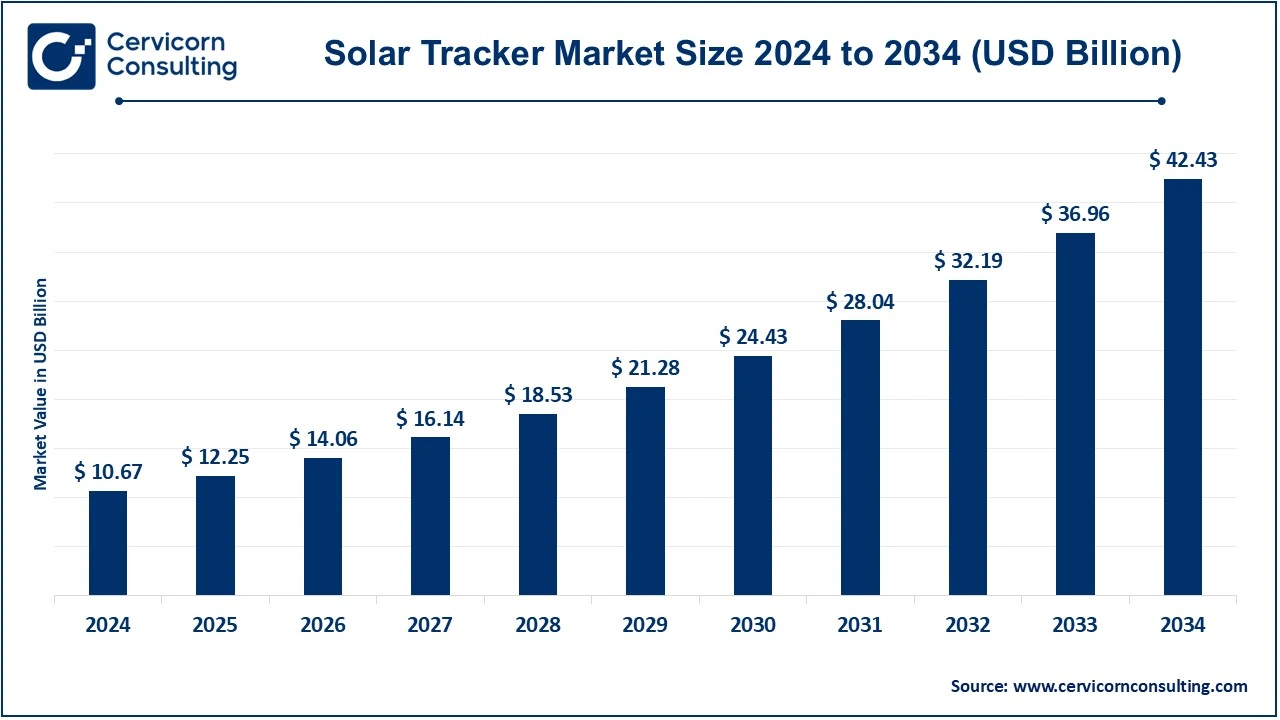
Emerging trends are accelerating advancements in solar tracking technologies, even as the incentives extended towards adoption of solar energy by the specific country governments spur growth. Some of the big players are highly focused on innovations and trackers with enhanced durability and performance. Geographically, North America and Asia-Pacific are the largest markets because of massive investments in solar projects in the U.S., China, and India. Certain challenges exist in terms of high initial costs and maintenance requirements, but increased energy yield and declining cost of components provide much opportunity for further growth.
Report Highlights
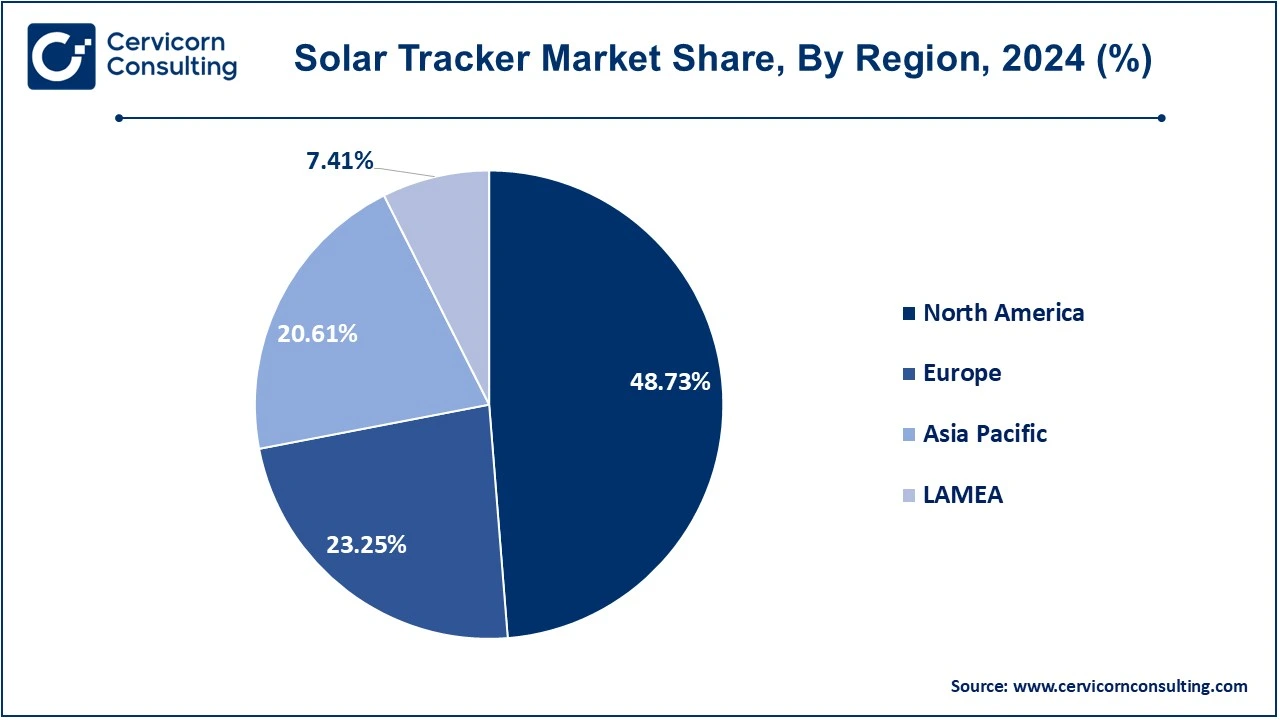
- The North America has dominated the market with revenue share of 48.73% in 2024.
- The Europe has garnered revenue share of 23.25% in 2024.
- By type, the single-axis segment has captured highest revenue share of 54.86% in 2024.
- By technology, the solar photovoltaic (PV) has held revenue share of 90.20% in 2024.
- By application, the utility segment has registered revenue share of 85.37% in 2024.
Solar Tracker Market Growth Factors
- Increase in Solar Energy Installations: The worldwide rush toward solar energy installations is driving the solar tracker market significantly, with increased energy demands and environmental awareness. Increasingly, solar trackers are fitted onto utility-scale or residential solar power projects to maximize energy. They increase energy capture by 15-30% by adjusting the angle of solar panels toward the sun's path, making them essential for efficacy maximization. The regions like North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are racing towards the installation of solar energy systems because of some government initiatives and dwindling costs of solar PV.
- Government Incentives: Various national governments have been formulating different components of their policies for renewable energy in conjunction with those of solar energy; how it all meets the sustainability and climate change goals of each nation in the world to encourage adoption in those renewables. Incentives such as tax credits, feed-in tariffs, subsidies, and grants are increasing the feasibility of the solar projects. An example of this type of assistance is the U.S. Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which reduces the upfront cost of solar installations and supports using solar trackers to enhance performance. These monetary incentives particularly favor utility-scale projects, which typically incur increased initial expense. The cost offsets, however, permit reinvestment of savings into advanced technologies such as dual axis and single-axis trackers for energy generation maximization. Emerging markets like India and Brazil have a huge scope to gain revenue through solar missions along with the governmental funding, promoting the growth of these markets.
- Technological Advances: New and ongoing advancements in solar tracker technologies are changing the terrain of the market. Modern tracking systems currently have advanced artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things technologies to optimally position the panels to maximize energy capture. Such systems helps in the predictions of the weather along with modifying the tracking mechanism accordingly for ensuring minimal downtimes. Furthermore, new materials also ensure improved durability and reliability of the tracker, thus contributing to reduced maintenance and operational costs. Take for instance AI-based trackers that enhance on their performances through real-time analysis of the varying conditions such as clouds or high winds.
- Cost Decline of Solar PV Systems: Given that these solar photovoltaic (PV) systems are bound to reduce costs, they will additionally contribute to the market growth of solar trackers. The past 10 years have experienced very high price reductions associated with solar panels, inverters, and other components, consequently making solar power affordable. Such reduction in the prices owing to the economies of scale, technological advancement along with manufacturing efficiencies. Thus, solar projects, especially those that are utility-scale installations, are now being competitive in the market relative to traditional energy sources such as fossil fuels.
- Rising Energy Demand: The emerging energy-needy world has seen rapid urbanization, industrialization, and population increase-the catalysts for investments in renewable energy solutions such as solar energy. If ever the solar trackers will play a vital role in resolving this issue, it's through improving the efficiency of all solar energy systems. Most of the utility-scale solar farms rely on solar trackers in maximizing energy output for a steady and reliable power supply in regions where there is high solar insolation.
Solar Tracker Market Trends
- Climate Change Initiatives: The global efforts for catering the climate changes have resulted in the ambitious renewable energy targets, boosting the growth of the solar tracker market. The governments along with corporates and international organization are improving the transition from the fossil fuels for the clean sources of energy such as solar by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. High efficiency in energy harvest without requiring higher land for operation is made possible by solar tracks. Some initiatives like Paris Agreement and European Green Deal underscore the importance of solar in the ends toward achieving net-zero emissions. Solar trackers are also deployed by corporations for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance criteria for sustainable operations.
- Achievements in Grid Parity: Marking the event when solar power becomes competitive and/or cheaper than fossil fuel energy has been the most momentous achievement for the renewable energy sector. Solar trackers make a vital contribution to this since they maximize the performance of solar PV systems and thus lower the levelized cost of energy. These projects, thus, have trackers that maximize energy collection during the entire day to increase electricity generated, thereby improving returns to the developers and investors. Europe, North America, and A-Pac have all achieved this peak, and with the new solar grid parity arrives the imminent deploy of solar trackers for both utility and commercial projects ensuring that maximum electricity output comes with minimum costs.
- Utility Scale Projects: A utility-scale solar project has attracted many customers demanding solar trackers, and this will drive sales. These projects, often occupying hundreds of acres, require appliances that can maximize energy generation while optimizing land usage. Solar trackers are of great benefit to such installations, enabling energy output increases of 15-30% against fixed-tilt systems. With these emerging utility-scale projects operating in developed areas such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, they have played a significant role in driving investments from the state and private sector and in making solar costs fall.
- Hybrid Power Plants: The integration of solar with other renewable resources like wind or an energy storage system is rising as a strong driving force for the solar tracker market. The concepts behind such plants were different; they require efficient and reliable technologies because there will be various sources of generation, and even solar trackers will be friendly in providing better solar energy production but still ensuring dependable supply with these other systems.
- Emerging Markets: Emerging economies are increasingly focusing on solar energy features in new projects to meet energy requirements. The huge opportunities are in the solar tracker market. Typically, these regions have high solar insolation, which is why their harnessing for solar energy makes sense. Countries like India with its ambitious solar energy program plan to meet energy needs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels by South Africa, Brazil, and other developing countries. Such solar trackers easily integrate in energy capture optimization; hence such projects will use trackers in their development for better efficiency and returns on investment.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 12.25 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 42.43 Billion |
| CAGR 2025 to 2034 |
25.07% |
| Top-performing Region |
North America |
| Top Expanding Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments |
Type, Application, Technology, Region |
| Key Companies |
Trina Solar Limited, Titan Tracker, SunPower Corporation, Soltec Tracker, Powerway Renewable Energy Co. Ltd., Nclave, DEGERenergie GmbH & Co. KG, Array Technologies Inc., AllEarth Renewables, Abengoa Solar S.A. |
Solar Tracker Market Dynamics
Drivers
Enhanced Efficiency
- Solar trackers enhance efficiency for solar PV systems as they follow solar panels with the sun during the day. It increases energy production by 15% to 30% with respect to fixed-tilt systems, hence makes trackers a competent option for utility scale and commercial projects. The improved efficiency improves land and resource use making solar projects feasible and cost effective on its own. Such advanced tracking technologies like dual axis systems can further optimize energy capture, especially in regions with different solar angles. With enhanced yield in energy, the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) gets reduced, thereby attracting more investment in solar projects with trackers. This enhanced efficiency is particularly relevant for regions with either very high energy demand or little land availability and ensures that solar trackers act as a major pillar in advancing the solar energy adoption.
Corporate ESG Goals
- The corporate goals for environmental, social and governance (ESG) have proved to be another major driver for solar trackers in the market. Most corporations are investing into renewable energy solutions, solar being one of them, to transition towards being a "greener" company in terms of carbon footprints and their sustainability goals. Hence, with solar trackers, such companies can maximize their solar installations for optimum energy generation while reducing their impact on the environment. This applies to manufacturing, technology, retail businesses, as industries are investing in their onsite solar farms, leasing projects at utility scale to satisfy their targets for renewable energy. Moreover, stakeholders and investors will also prioritize the company with strong ESG commitments, putting a further edge for adopting solar trackers.
Restraints
Initial High Prices
- High initial costs for solar trackers are a major market constraint for most of the projects, especially for small or residential projects. Even though trackers make a solar installation more efficient, their installation costs, including structural components, motor, and control systems, are much higher than those of fixed tilt systems. At the utility scales, these costs are capable of eating into the overall budgets, making it tough for developers to adopt this technology in price-sensitive markets. In addition, funding by financial institutions may prove difficult given that their projects involve higher capital expenditures, thus making it more limiting in the adoption of the trackers. In developing parts of the world where solar energy is very much critical as a source of energy access, the financial burden imposed by the trackers usually leads to fixed systems being preferred.
Maintenance Problems
- Solar trackers generally require periodic maintenance, especially having mechanical and electronic parts which may add on to operational complexity and costs. Also, they have moving parts like motors and actuators, requiring regular inspections or lubrication or even been replaced to operate normally. Extreme weather, dust, and debris can all exacerbate the conditions that deteriorate equipment performance. It is mainly the case with those that are situated in more remoter places or harsher geographical environments, where most solar plants are located; maintenance thus becomes logistically complicated and expensive. Apart from that, any downtime owing to malfunction of the tracker will, obviously, affect energy production, severely reducing the efficacy and profitability of solar projects in general. These situations are heavier on smaller developers or in areas that are poorly endowed in terms of technicians and spare parts.
Opportunities
Reduced Cost of Solar Panels
- These factors among others are likely to fuel the growth of the solar tracker market because they would benefit from reduced costs of solar panels. Cheap solar panels have become extremely viable for people, thus creating a call for a strong shift toward solar farms, where solar trackers become indispensable in order to maximize generation. The panels can be oriented exactly to receive maximum sunlight throughout the day by the solar trackers. More of these advanced tracking systems are required to improve output and return on investment as the project costs become economically attractive.
Government Policies and Incentives
- Such are the vital factors driving the market of solar trackers. Although subsidies, tax benefits, and renewable energy mandates motivate solar energy use and increase the market for solar tracker systems. An investments incentive motivating energy efficiency and decarbonization policies is guaranteed through solar farms, which benefit from the use of trackers significantly, a factor which directly increases demand. Furthermore, the clones funded through state backing for R&D for innovations in the tracker technology improve and reduce their cost. This is a favorable regulatory environment, thus hastening the making full-scale solar trackers as pan-continental components of the global renewable energy strategies.
Challenges
Weather-Related Risks
- Weather-related risks are a primary barrier for the solar tracker market. High winds, intense snowfall, and severe weather events can damage solar trackers, which may make these trek maintenances costly and add to operational downtime. The right deal to ensure tracker durability under adverse conditions will require being robust in design as this may elevate production costs. Again, such unpredictable weather patterns would also negatively affect energy generation, hence diminishing the benefits that accrues from the efficiency of trackers. As such, most investors would shy away from the introduction of solar trackers in these extreme weather regions, thus reducing the market size.
Competition from Fixed-Tilt Systems
- Fixed tilt systems, such as those from fixed-axis systems, constraint and challenge growth within the solar tracker market. Fixed tilt systems cost less and do not need much maintenance compared to tracking systems, which is why they seem to be more pragmatic for installing smaller solar projects or installations where sunlight patterns are not highly variable. Although trackers have greater energy yields, such investments can lead cost-sensitive markets to have higher initial and maintenance costs, making them a poor investment under certain situations. Therefore, the simplifications and reliability of fixed-tilt systems will attract developers keeping their budget as a priority and thus create a more competitive but slower-moving market toward solar trackers in some segments.
Solar Tracker Market Segmental Analysis
The solar tracker market is segmented into type, technology, application and region. Based on type, the market is classified into dual-axis and single-axis. Based on technology, the market is classified into concentrated photovoltaic (CPV), concentrated solar power (CSP), and solar photovoltaic (PV). Based on application, the market is classified into non-utility, and utility.
Type Analysis
Single Axis: Single-axis solar trackers are the most common type known in the solar tracker market. They rotate panels along a single axis that is typically oriented north-south. Thus, the movement along the rotational axis, east-to-west, allows them to follow sun's daily travel across the horizon. With adjustment in the tilt of the panels, single-axis trackers increase energy production as much as 15-25% above fixed systems. Clearly, they are more economically effective than dual axis trackers and therefore fit into the category for utility-scale solar farms. Their simplistic design, easy maintenance, and low initial investments ensure their prevalence in sunlight-abundant and good climates.
Solar Tracker Market Revenue Share, By Type, 2024 (%)
| Type |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Single-Axis |
45.14% |
| Dual-Axis |
54.86% |
Dual Axis: The position of the panels along both axes- horizontally and vertically- moves from an east position to a north position to have dual-axis solar trackers that give better sun tracking. This type of panel ensures that the sun follows the path throughout the day and year, thus maximizing energy capture. The amount of energy production increased by dual-axis trackers ranges between 25-40% in comparison to fixed systems. Although it is more expensive and difficult to maintain compared to the single-axis tracker, it is more advantageous in efficiency, making it ideal for use where sunlight varies or occupies a limited land area. Mostly, these trackers are used for high insolation areas or applications meant for maximum output of solar energy.
Technology Analysis
Solar Photovoltaic (PV): This is the widely used technology for the solar trackers. These systems use the sunlight for directly producing the electricity via semiconductor based panels. These systems can be connected with the single-axis and dual-axis which captures the energy while tilt-aligning these panels as per the movement of the sun. The gain brought by solar trackers, particularly for utility-scale projects, is that they enhance energy output and lower levelized kilowatt-hour cost (LCOE). Solar technologies have thus been vastly propelled by reduced costs and simplified installation and play an active role in the rising demand for solar trackers.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP converts sunlight using mirrors or lenses focused onto a receiver, thus producing thermal energy to generate electricity. Usage of solar trackers in CSP systems are many for better alignment of solar rays with each receiver and thus concentrate solar energy. CSP installations usually employ dual-axis trackers because they can define very precise positioning for the receiver and the mirrors. CSP plants are predominantly installed at places with high solar isolation, such as deserts.
Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV): Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) uses lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight onto high efficiency PV cells that generate electricity. Solar Trackers complement CPV projects to ensure accurate sun alignment at all times for maximum energy concentration and efficiency. Areas with high direct sunlight, limited land and low power densities were most considered for this technology since higher power densities were achieved in CPV compared to conventional PV systems. The adoption of CPV technology has lagged behind that of PV and CSP systems due to its higher costs and higher sensitivity to diffuse sunlight.
Application Analysis
Utility: Utility-scale solar projects are the major consumers of solar trackers, designed to generate large amounts of electricity to be supplied to the grid. They benefit mostly from solar trackers that increase the energy yield of solar panels by changing their position throughout the day, following the track of the sun. This improves energy captures by about 15-30 percent equal to fixed-tilt systems, creating a lot of efficiency in huge solar farms. Utility-scale applications are for areas sunny enough to be interested in large installations capable of helping meet targets for renewable energy and lowering the costs of solar power generation.
Solar Tracker Market Revenue Share, By Application, 2024 (%)
| Application |
Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Non-Utility |
14.63% |
| Utility |
85.37% |
Non-Utility: Non-utility applications of solar trackers include homes, companies, and industries. Although all these are smaller compared to utilities, solar trackers prove highly efficient in generating more energy, especially in high-insolation regions. Single-axis trackers perform the function of increasing energy generation most cost-effectively by tilting panels for non-utility applications. Solar trackers in non-utility applications help businesses and homeowners maximize solar energy gains, minimize grid reliance, and reach sustainability goals. This segment is growing as more businesses and residential customers embrace solar.
Solar Tracker Market Regional Analysis
The solar tracker market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
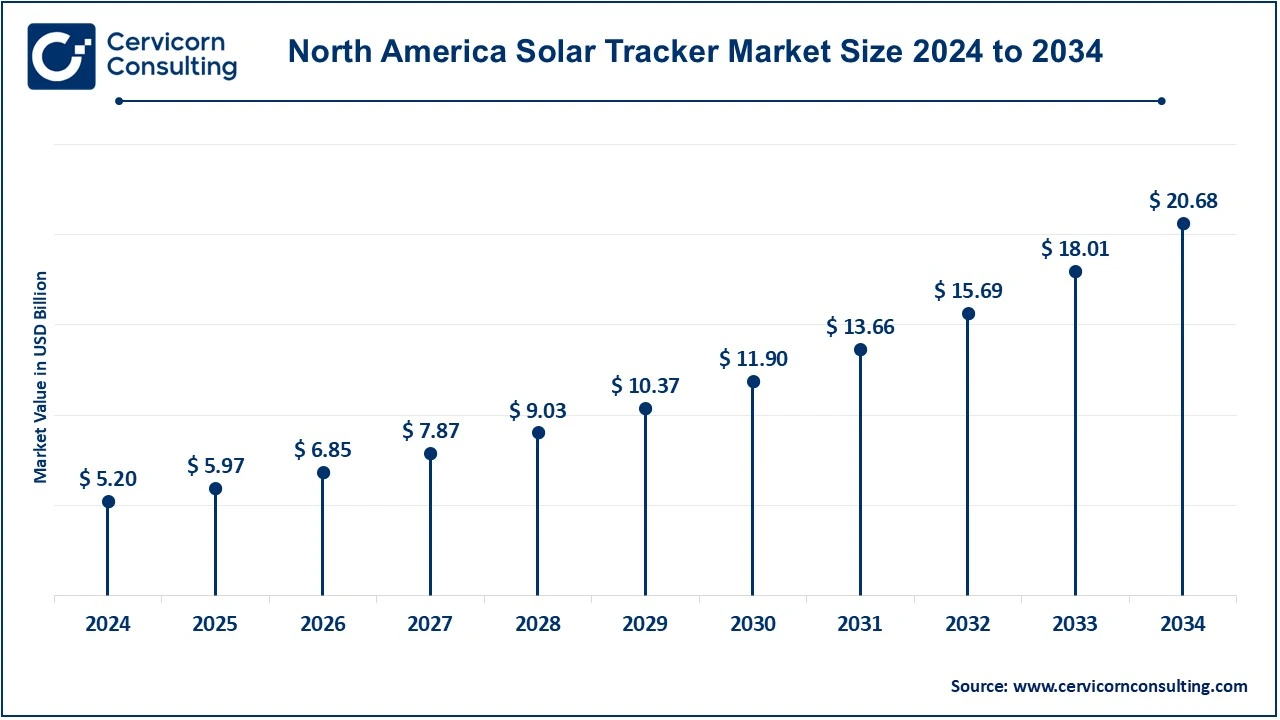
The North America solar tracker market size was estimated at USD 5.20 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 20.68 billion by 2034. The North American is highly driven through a good number of investments that are encouraged for renewable energy and policy support from governmental agencies. The U.S., especially, is very much growing in utility-scale solar projects, in which solar trackers are mostly fitted for a higher productive efficiency in energy conversion. Tax incentives such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) have made installations cheaper and have thus further led to heightened demand for advancements in solar technologies.
The Europe solar tracker market size was estimated at USD 2.48 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 9.86 billion by 2034. The Europe benefits from a commitment of the European Union to net-zero emissions by 2050. In Spain, Germany, and Italy, for example-the pioneers in solar energy adoption-utility-as well as commercial-scale solar projects have seen an increase in investments. Solar trackers help maximize the efficiency of these installations, thus, their wide adoption. In addition, government grants and the EU's Green Deal further promote the solar sector growth.
The Asia-Pacific solar tracker market size was accounted for USD 2.20 billion in 2024 and is predicted to hit around USD 8.74 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific market experiences high-speed growth owing to the increasing demand for energy in the region and strong shifts toward renewable energy. Countries such as China and India, with enormous investments in large-scale solar farms, are vital targets for solar trackers in the near future.
The LAMEA solar tracker market size was estimated at USD 0.79 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 3.14 billion by 2034. The LAMEA is picking up steam as countries in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa focus on renewable energy solutions to fill their energy gaps and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Brazil, Mexico, and South Africa are leading in such investments among countries in the region.
Solar Tracker Market Top Companies
The emerging players in the solar tracker sector are getting into space with ideas that would probably transform and make the trackers work more efficiently, less expensive, and more reliable in operation. A lot of these new firms seem to harness advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and IoT integration to work on the optimal functioning of solar trackers. These new entrants set to use AI-based algorithms produce adjustments for real-time tracking and advance predictive maintenance for the production of their systems-as well as energy production improvements. Also, new entrants are investing in low-weight modular designs, which will reduce installation costs and allow for scalability. A few of these entrants also lean toward providing solutions that can stand extreme weather conditions with low maintenance at work, hence elongating the equipment's lifespan. The new entrants in the market have to offer their cost-effective solutions to a very niche segment of the market, for example, hybrid energy systems or small to mid-sized solar farms, in order to compete with established players.
CEO Statements
Dan Shugar, CEO Nextracker
- “It demonstrates our ability to ramp and scale operations that directly benefit our customers—and sets a new standard for local supply chain resilience and operational excellence. By systematically focusing our manufacturing partnerships close to our customer project sites, we secure the supply chain and provide superior on-time delivery and cost savings for project development and construction. We also significantly de-carbonize our products by incorporating clean steel manufactured in the United States.”
Recent Developments
- In 2023, Nextracker Inc. plans to boost up its solar tracker manufacturing capacity in India to 10 gigawatts. Under the production-linked incentive scheme, they will produce the semiconductors and established an aim to domesticate all products. The company stated that India's objective of 500 GW renewable capacity by 2030 would create at least 7-8 GW of projects per year which will use trackers.
- In 2023, PVHardware declared that it would back into building the largest solar tracker factory in Spain, covering an area of 65,000 sq. m. within its operations and subsidiaries. This company aims to increase production capacity to 25 GW and become the world's top manufacturer of solar trackers.
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Technology
- Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV)
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV)
By Application
By Region
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA
...
...
![]()
![]()
![]()