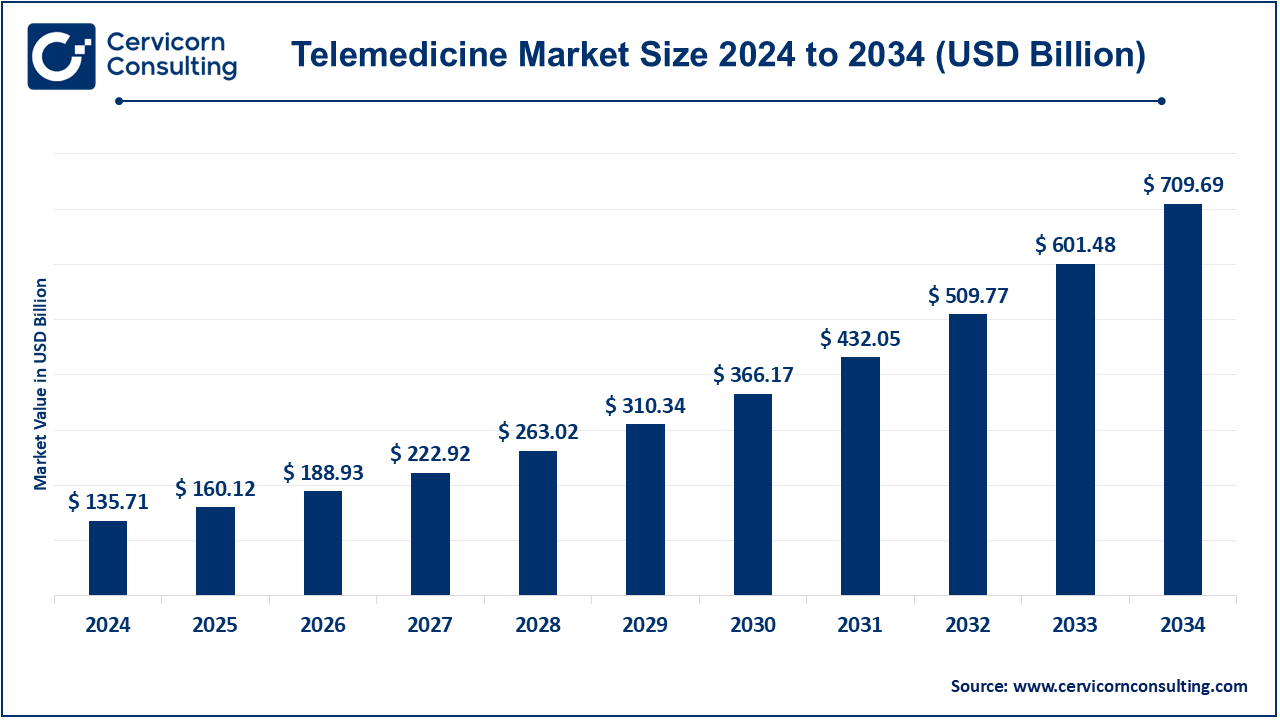
The global telemedicine market size was valued at USD 135.71 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 709.69 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 17.99% from 2025 to 2034. There's something more, which has contributed immensely to the increasing degrees of growth in telemedicine. This is convenience: patients want to be able to consult from their homes rather than travel, saving time and effort. This is made possible through the latest technology improvements that have proved to motivate virtual healthcare efficacy through enhanced internet connections, mobile health applications, and wearable devices. However, the costs of telemedicine are low for professionals and patients - without in-person office consultations. Also, it is noted that with an increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the expectation is that more and more patients will need constant remote monitoring, which is one area where telemedicine will be most valuable. Moreover, stimulation to that development comes through growing government regulations such as increased reimbursement and liberalization of licensing limits. There is also an increased awareness of mental health issues, thus increased demand for virtual therapy and counselling services. All these aspects of telemedicine make it an attractive and fast-growing market.
Its great importance in healthcare can be borne out by data, as telehealth has always been above 20 per cent between 2021 and 2022. This trend mostly reflects the strong and persistent demand for remote health access, which has surged during the pandemic of COVID-19 but does not end there, nor do care services which are highly needed today. Such inequalities remain salient, particularly within the domain of video telehealth, and consumer-based on income, type of insurance, and area. Above-average usage is seen among Black, lower-income, and Medicare and Medicaid recipients, whereas young adults and uninsured individuals account for lower adoption rates. penniless. It is exclusive to White and insured individuals. With the increase in satellite broadband access and technological literacy programs, we may resolve the differences in this huge growing market today for telehealth at the primary sector, namely, the continued evolution of telehealth, public policy extension, and legislative support, all expected to create continued growth in this area, especially in video-based service.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 160.12 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 709.69 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 17.99% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Application, Technology, Delivery Mode, Facility, End User, Regions |
| Key Companies | SmartClinix, Teladoc Health, Amwell (American Well Corporation), MDLIVE Inc., Doctor on Demand, Inc., Babylon Health, NXGN Management, LLC, Zoom Video Communications, Inc., VSee, Practo, Sesame, Inc., Allscripts Healthcare Solutions Inc., Medtronic, Koninklijke Philips N.V., CISCO Systems Inc. |
Increased Patient Demand for Convenience
Telemedicine technology has undergone a rapid embrace due to telecommunications advancements
Regulatory and Legal Complexities
Technological Barriers to Rural Areas
Demand for Mental Health Increasingly
Combination of AI and Machine Learning
Patient Privacy and Data Security
Resistance from Healthcare Professionals
The telemedicine market is segmented into component, application, technology, delivery mode, facility, end user and region. Based on component, the market is classified into product, and services. Based on application, the market is classified into teleradiology, telepsychiatry, telepathology, teledermatology, telecardiology, and others. Based on delivery mode, the market is classified into web/mobile, and call centers. Based on facility, the market is classified into tele-hospital, and tele-home. Based on end user, the market is classified into hospitals, clinics and physician offices, patients, insurance companies, and others.
Teleconsultation: Teleconsultation allows patients to consult doctor remotely via video, phone or text, making care accessible. It is useful for any general health concern, make follow-up appointments and consult with specialists to reduce the need for a physical visit. The teleconsultation is most beneficial to rural people as it saves both time and effort for the patients and providers.
Telemonitoring: To monitor some vital signs of patients: like blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate, by connection with a medical device. Sending information to healthcare providers assists in keeping track of them. This approach to health and diseases helps in the management of chronic diseases and timely intervention without taking the patient to the hospital, thus favoring the outcome for the patient and money-saving.
Telehealth Education: Distant learning platforms for patients and healthcare providers where information and options are related to health advice, wellness programs, and disease management education make up this component of telehealth. These might include video tutorials, online courses, and webinars. Its value in improving health literacy, making people better able to manage their conditions, and teaching best practices to healthcare workers in care delivery cannot be underestimated.
Remote Patient Management: Continuous management of chronic infections and diseases is done through remote monitoring and virtual care. The physician draws personalized care plans; healthcare data from patients are gathered and adjusted with what they are actually using. It helps relevant engagement of the patients, better chances of good outcome with diseases, and decreased frequency of hospital visits or emergency care.
Others: Teletherapy (mental health), teleradiology (remote reading of medical images), telepharmacy (remote prescription management). Such specialized services provide very specific telemedicine access to some medical fields, making it possible for patients to receive comprehensive care without geographic or logistic barriers. Thus, such services are made available for many medical needs through better accessibility and efficiency of healthcare.
Telemedicine for Chronic Diseases: Long-term conditions which require long-term treatment and follow up such as diabetes, cardiovascular conditions including congestive heart failure, and hypertension are evaluated remotely through telemonitoring and virtual consultations. Ongoing health parameter tracking by the healthcare provider allows immediate intervention, treatment modification, and consequent improvement in patient prognosis. This also reduces the incidence of readmission and allows the patients to be managed more effectively at home.
Telemedicine for Mental Health: This involves an online therapy session where people with mental health issues like anxiety, depression, or stress can receive therapy without going to a clinic or hospital. This makes therapy much easier for individuals with access problems in remote areas. However, it can also be beneficial for those uncomfortable with going into a clinic but find that the telemedicine option would enable them to receive the help they need. Telemedicine has become one of the best facilitators in terms of achieving mental health care remotely, especially in the post-pandemic world.
Telemedicine for Dermatology: Teledermatology consults patients with skin disorders to upload their skin images to dermatologists for diagnosis and treatment. It is most convenient for non-emergency cases such as acne, skin rashes, and moles since it allows patients access to dermatological care very quickly by minimizing the waiting time to see a dermatologist.
Telemedicine for Cardiology: Remote consultations and monitoring are used for heart health tracking in patients suffering from hypertension, arrhythmia, and other cardiovascular problems. Wearable devices tracking one's heart rate and blood pressure deliver continuous real-time information to healthcare professionals to act with regard to heart-related symptoms timely, improving the degree of prevention from serious complications.
Others: General health-related consultations, consultations for pediatric service, oncology and surgery consultations, and many other areas fall under these applications for telemedicine. Good, easy, on-demand accessibility to health care is ensured for the patient visiting anywhere at any time. Specialized telemedicine services solve various needs and provide added values like faster diagnosis, lower travel costs, as well as greater convenience.
Hospitals: Telemedicine at hospitals stands to amplify their boundary and virtual consultation avenues while efficiently cutting waste time on patients. Patients received better care via telemedicine to comprehensively monitor them. Telemedicine can make healthcare more beneficial to rural or underserved populations without losing time for all interventions.
Clinics and Physician Offices: The small provider use telemedicine to run their population with accountable care beyond offering telehealth visits for patients discharged after outpatient procedures, emergency visits, or even lower-priority visits. Telemedicine allows these clinics to gain more patients who would benefit from this option and thereby streamline its operations through reduction or elimination of in-person visits while enabling doctors to take care of more patients without it.
Patients: Telemedicine creates an avenue for patients to get health care from the comfort of their homes without the cost of traveling to different places. This is very handy for the newly ill, particularly immobile persons; those in fairly remote settings; and those who want specific consultation without traveling unnecessarily. It opens avenues for patients and translates into increased accessibility and satisfaction of healthcare by modes of care both urgent or routine visits.
Insurance Companies: Most plans become a part of telemedicine, as the ability to use telemedicine in preventive health will save health costs in the long run. Costs are involved in treating patients in person, excluding from hospitalization, and while managing a chronic disease, covering more services under preventive care and avoiding high costs at the latter stage of health. Most insurance companies will have a few services available through telemedicine.
Others: This involves educational institutions, research organizations, and health IT providers supporting telemedicine platforms.
The telemedicine market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
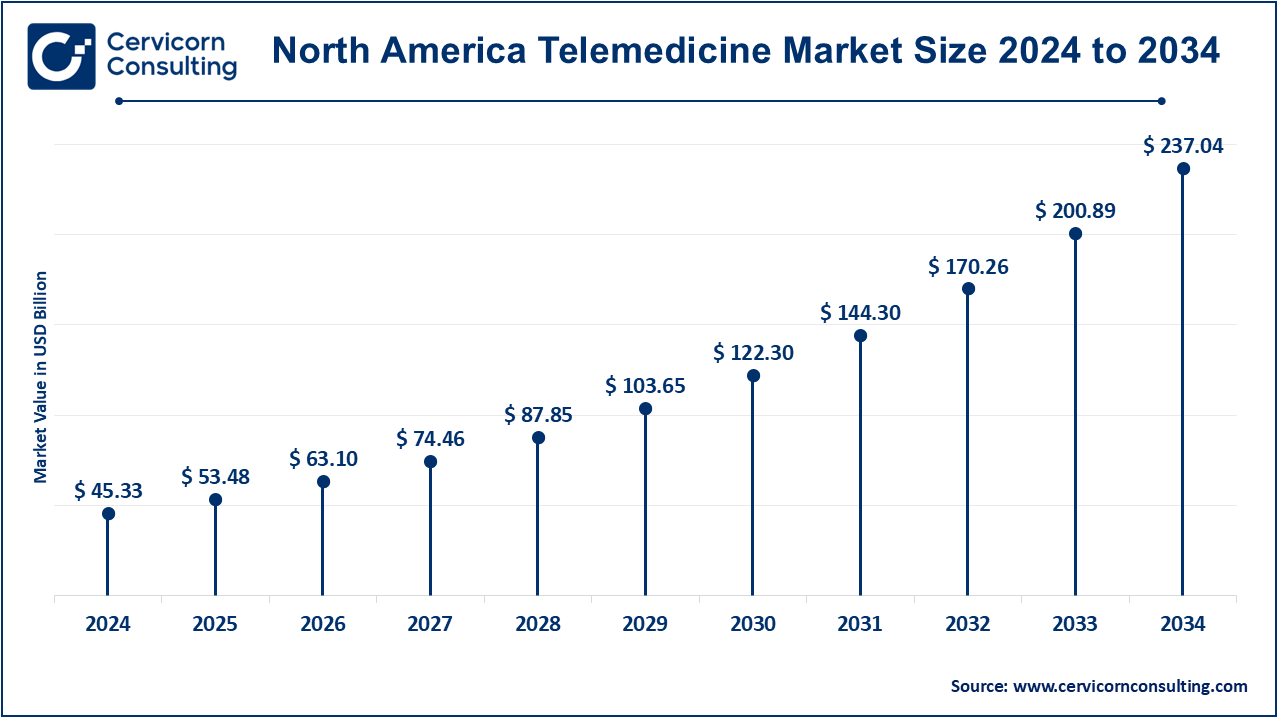
The North America telemedicine market size was estimated at USD 45.33 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 237.04 billion by 2034. It has been defined as the largest telemedicine market with advanced healthcare infrastructure, improved Internet penetration, and appropriate government and regulatory support. In the U.S. and Canada, telemedicine in public health programs has leaned more towards the place to improve access to care and the efficiency of healthcare systems. Growth in telemedicine might further increase with government-supporting policies and reimbursement models.
The Europe telemedicine market size was valued at USD 40.46 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach around USD 211.56 billion by 2034. Telemedicine is becoming adopted much faster than it ever happened in Europe these days, especially in the UK, Germany, and France, where the healthcare systems look to cut costs while at the same time increasing access. Much of the possible drive towards telemedicine comes from the regulations and funding from the EU, which promotes the use of telemedicine for cross-border healthcare service provision and digital health innovation in member states.
The Asia Pacific telemedicine market size was reached at USD 35.88 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to hit around USD 187.64 billion by 2034. The Asia Pacific is on a turbo boost due to the huge numbers of population, the increasing penetration stage of smartphones, and the initiatives taken by governments. Remote healthcare facilitation is more common in countries like India, China, and Japan. They're already gaining momentum towards building telemedicine infrastructure.
Telemedicine Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 33.4% |
| Europe | 29.81% |
| Asia-Pacific | 26.44% |
| LAMEA | 10.35% |
The LAMEA telemedicine market size was valued at USD 14.05 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 73.45 billion by 2034. Telemedicine adoption is slow and gradual in Latin America, spurred by increasing health needs and evolving digital infrastructure. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are quite ahead in providing telemedicine and are focused on narrowing health gaps in the region while decongesting health systems in densely populated areas. The telemedicine market in this region is emerging. Governments from countries like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia have all shifted to priority digital healthcare services. Remote areas would now be attended to from long ranges as healthcare services are almost not available. Plus, it is enhanced through the improvement of healthcare structure and easy access to specialized services.
CEO statements
Here are some recent CEO statements from key players in the Telemedicine Market:
Teladoc Health (CEO: Jason Gorevic)
"Teladoc Health continues to lead the telemedicine industry by delivering comprehensive virtual care solutions that address the full spectrum of healthcare needs. Our focus remains on integrating AI and data analytics to provide personalized, proactive care, while expanding access to underserved populations. The future of healthcare is hybrid, and we are committed to bridging the gap between in-person and virtual care."
Amwell (American Well Corporation) (CEO: Ido Schoenberg)
"Amwell is dedicated to transforming healthcare delivery through our Converge platform, which connects patients, providers, and payers in a seamless digital ecosystem. Our investments in AI, interoperability, and telehealth infrastructure are paving the way for a more connected and efficient healthcare system. We believe telemedicine will play a central role in the future of care delivery."
MDLIVE Inc. (CEO: Charles Jones)
"At MDLIVE, our mission is to make high-quality virtual care accessible to everyone, everywhere. We are focused on expanding our services to include behavioral health, chronic care management, and urgent care, while leveraging technology to improve patient engagement and outcomes. Telemedicine is no longer a convenience—it’s a necessity, and we are proud to be at the forefront of this transformation."
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Application
By Delivery Mode
By Facility
By End User
By Region