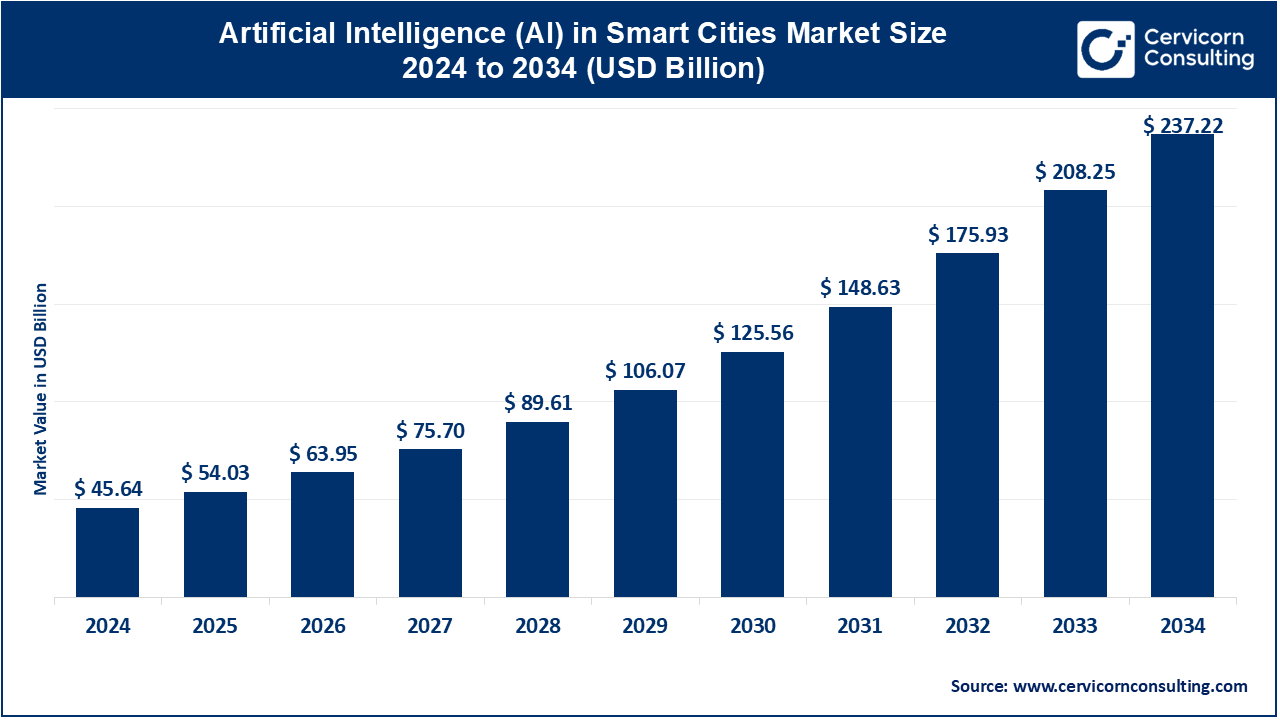
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in smart cities market size was valued at USD 45.64 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 237.22 billion by 2034, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.92% from 2025 to 2034.
The AI market for smart cities has been experiencing rapid growth, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for sustainable urban solutions. According to market report, the AI in smart cities market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with investments flowing into areas like transportation management, energy optimization, and smart buildings. Governments and private companies are investing in AI to improve urban infrastructure and offer residents a higher quality of life. This market growth is also fueled by the rising adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, enabling cities to collect and analyze more data than ever before, making AI a crucial part of modern urban development. As urban populations grow, AI in smart cities is becoming essential for managing the increasing complexity of urban environments. According to surveys and analysis, over 60% of cities globally are adopting AI technologies for at least one aspect of urban life, with AI investments in smart city projects expected to increase. The global push for sustainability, coupled with AI’s ability to provide cost-effective solutions, is accelerating the market.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in smart cities refers to the use of advanced technologies to improve urban living, increase efficiency, and solve problems related to transportation, energy, healthcare, and infrastructure. AI-powered systems in smart cities analyze vast amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and devices to make real-time decisions. For example, AI can optimize traffic flow, manage energy use, predict public transportation needs, and monitor pollution levels. Smart streetlights that adjust based on traffic, AI-based waste management systems, and predictive maintenance for infrastructure are some examples of AI applications. By enhancing decision-making and automating processes, AI helps cities become more sustainable, safe, and livable.
Drivers: The growing need for intelligent urban solutions and automation, coupled with significant investments in AI R&D, are key drivers of market growth. The demand for enhanced efficiency and quality of life in cities further accelerates AI adoption.
Restraints: High development costs and the complexity of integrating AI systems into existing urban infrastructure present challenges. Additionally, regulatory and ethical concerns related to AI in smart cities can impact market growth.
Opportunities: Emerging markets and advancements in AI technology offer substantial growth opportunities. The development of innovative AI solutions and strategic partnerships within the smart cities sector provide avenues for market expansion.
Challenges: Navigating regulatory frameworks and ensuring the seamless integration of AI technologies into existing systems are significant challenges. Maintaining high standards of accuracy, safety, and reliability while scaling up AI capabilities remains a critical concern for the industry.
The artificial intelligence (AI) in smart cities market is segmented into application, technology, deployment mode and region. Based on application, the market is classified into traffic management, public safety and security, energy management, infrastructure management, environmental monitoring, and smart governance. Based on technology, the market is classified into machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, IoT integration, and big data analytics. Based on deployment mode, the market is classified into cloud-based, and on-premises.
Traffic Management: AI in traffic management plays a crucial role in optimizing traffic flow, reducing congestion, and improving overall transportation efficiency in smart cities. Through the use of real-time data from sensors, cameras, and connected vehicles, AI algorithms can predict traffic patterns, adjust traffic signals dynamically, and provide real-time routing suggestions to drivers. These systems help in minimizing traffic jams, reducing travel times, and lowering emissions, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient urban transportation network.
Public Safety and Security: AI-driven public safety and security systems are essential for enhancing urban safety in smart cities. These systems leverage advanced surveillance technologies, facial recognition, and predictive analytics to monitor public spaces, detect potential threats, and respond to emergencies swiftly. AI can analyse vast amounts of data from CCTV cameras, social media, and other sources to predict crime hotspots, enabling law enforcement to take proactive measures. Additionally, AI-powered emergency response systems can optimize dispatch times, ensuring that help arrives faster in critical situations.
Energy Management: AI applications in energy management focus on optimizing the distribution and consumption of energy within smart cities. By analysing data from smart grids, buildings, and appliances, AI can predict energy demand, reduce wastage, and manage renewable energy sources more effectively. These systems can automatically adjust energy use during peak times, integrate energy storage solutions, and balance supply and demand in real-time. This not only reduces energy costs but also supports the transition to sustainable energy sources, making cities more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Infrastructure Management: AI is transforming infrastructure management in smart cities by enabling continuous monitoring and maintenance of critical urban infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and utilities. AI systems can analyse data from IoT sensors embedded in infrastructure to detect wear and tear, predict failures, and schedule preventive maintenance. This proactive approach helps in extending the lifespan of infrastructure, reducing downtime, and ensuring the safety and reliability of essential services. By optimizing maintenance schedules and resource allocation, AI helps cities manage their infrastructure more effectively and cost-efficiently.
Environmental Monitoring: Environmental monitoring in smart cities is enhanced by AI technologies that track and manage air quality, waste management, and pollution control. AI systems can process data from environmental sensors, weather stations, and satellite imagery to provide real-time insights into pollution levels, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation. These insights enable city authorities to take timely actions, such as regulating traffic during high pollution periods, optimizing waste collection routes, and implementing targeted environmental policies. AI-driven environmental monitoring helps cities achieve sustainability goals and improve the quality of life for residents.
Smart Governance: AI platforms for smart governance support city administration, citizen services, and decision-making processes by analyzing data from various urban systems. These platforms enable more efficient management of public resources, streamline administrative processes, and enhance citizen engagement through digital platforms. AI can assist in automating tasks such as permit processing, service delivery, and public consultations, making governance more transparent and responsive. By leveraging AI, cities can provide better services to residents, improve policy outcomes, and foster greater civic participation.
Machine Learning: Machine learning is a core technology in AI for smart cities, enabling systems to analyze city data, predict trends, and optimize operations. By learning from historical and real-time data, machine learning algorithms can forecast traffic congestion, energy demand, and public service needs. These predictions help city planners and administrators make informed decisions that improve efficiency and reduce costs. Machine learning also enhances the adaptability of smart city systems, allowing them to respond to changing conditions and continuously improve their performance over time.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP technology in smart cities facilitates better communication between city officials and residents through AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants. These tools can handle a wide range of inquiries, from providing information about public services to collecting feedback from citizens. NLP allows residents to interact with city systems in natural language, making services more accessible and user-friendly. Additionally, NLP can analyze large volumes of text data, such as social media posts and public comments, to gauge public sentiment and inform policy decisions.
Computer Vision: Computer vision is a critical AI technology for interpreting visual data from cameras and sensors in smart cities. It is used in applications such as traffic monitoring, security surveillance, and waste management. Computer vision systems can automatically detect traffic violations, monitor public spaces for safety threats, and identify waste disposal issues. By processing visual data in real-time, these systems enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of urban management. Computer vision also supports advanced applications like facial recognition and object detection, which are essential for smart city security and automation.
IoT Integration: AI-driven IoT integration involves the seamless connection and coordination of various smart devices and sensors across the city. AI processes data collected from IoT devices to make real-time decisions that improve urban living. For instance, AI can optimize energy use in smart buildings, manage traffic lights based on real-time traffic flow, and monitor environmental conditions. IoT integration with AI enables a more connected and responsive urban environment, where systems work together to enhance the quality of life and operational efficiency.
Big Data Analytics: Big Data Analytics in smart cities involves processing and analyzing vast amounts of data generated by urban systems to derive actionable insights. AI-driven analytics platforms can handle complex datasets from transportation networks, energy grids, public safety systems, and more. These platforms help city planners and administrators make data-driven decisions that improve urban operations and services. For example, big data analytics can identify patterns in traffic congestion, optimize waste collection routes, and forecast energy demand. By leveraging big data, smart cities can enhance their decision-making capabilities and deliver better outcomes for residents.
Cloud-based Solutions: Cloud-based AI solutions offer scalability and flexibility for smart city initiatives, allowing cities to deploy and manage AI applications with ease. These solutions are hosted on cloud platforms, enabling remote access, data sharing, and collaboration across different city departments. Cloud-based AI systems can quickly scale to accommodate growing data volumes and processing demands, making them ideal for dynamic urban environments. Additionally, they provide cost-effective infrastructure for implementing AI-driven smart city projects, reducing the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and software.
On-Premises Solutions: On-premises AI solutions are deployed within the city's own infrastructure, providing enhanced security and control over data. These systems are preferred by cities with stringent data privacy and security requirements, as they allow for greater oversight of AI operations and data management. On-premises solutions are often used in critical applications such as public safety, where data sensitivity and real-time processing are paramount. While they may require more significant investment in infrastructure and maintenance, on-premises AI systems offer robust and secure solutions for smart city management.
The artificial intelligence (AI) in smart cities market is segmented into key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region:
North America is at the forefront of AI integration in smart cities, with the United States and Canada spearheading advancements. The U.S. excels in implementing AI for smart infrastructure, traffic management, and public safety systems, driven by substantial investment in technology and innovation. Canada complements this with progress in smart buildings and energy management solutions. The region benefits from a robust technological ecosystem and a strong emphasis on integrating AI across urban applications, fostering a smart city environment that sets a global standard.
Europe is a significant contributor to the AI integration in smart cities market, with key players like Germany, France, and the UK leading in urban innovation and regulatory frameworks. The European market focuses on sustainability and high regulatory standards, which drive the development of AI technologies for energy efficiency, environmental monitoring, and smart governance. The region's commitment to green technology and strategic urban planning supports the deployment of advanced AI solutions, enhancing the quality of life in its cities.
The Asia-Pacific region is rapidly advancing in the AI for smart cities sector, driven by major economies such as China, Japan, and India. This growth is supported by large-scale infrastructure projects, increasing adoption of AI technologies, and significant investments in smart transportation, environmental monitoring, and urban planning. The region’s focus on integrating AI to improve traffic flow, energy management, and public services reflects its ambition to create more efficient and sustainable urban environments.
LAMEA is emerging, with a growing interest in enhancing urban infrastructure and services through AI. Brazil and South Africa are leading the way with investments in smart city technologies, focusing on improving public safety and transportation systems. In the Middle East, there is a push towards AI-driven solutions for urban development despite facing economic and infrastructure challenges. The region shows promising potential for growth, with increasing investments and a gradual adoption of AI technologies aimed at transforming urban living.
New players such as Hydrogen Pro and Power Cell Sweden AB are leveraging advancements in high-efficiency electrolyzer technology for green hydrogen production, focuses on innovative fuel cell systems. While dominating players like Air Liquide and Linde plc stand out due to their extensive global hydrogen infrastructure and industry expertise. Air Liquide excels with its expansive hydrogen networks and advanced storage solutions, while Linde plc drives innovation through its strategic partnerships and R&D efforts. Both established and emerging players are crucial in advancing hydrogen storage technologies and integrating them into broader energy systems.
CEO Statements
IBM Corporation: “Integrating AI into smart cities represents a transformative leap forward in urban management. By leveraging cutting-edge AI technologies, we can create more efficient, sustainable, and liveable urban environments, driving innovation and improving the quality of life for city residents."
Microsoft: “AI is at the heart of smart city innovations. Our focus is on harnessing AI to enhance infrastructure, optimize resource management, and deliver intelligent solutions that address the complexities of modern urban life, ensuring that our technologies meet the evolving needs of smart cities.”
Cisco: " The implementation of AI in smart cities is revolutionizing urban operations. By optimizing processes through AI-driven insights, we are improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring that city services are delivered seamlessly and effectively.”
Strategic partnerships highlight the rapid advancements and collaborative efforts in the AI in smart cities sector. Industry players are involved in various aspects of AI in Smart Cities, including, AI & ML integration, technological advancement, and product innovation, and play a significant role in advancing the market. Some notable examples of key developments in the market include:
Market Segmentation
By Application
By Technology
By Deployment Mode
Regional
Chapter 1 Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of AI in Smart Cities
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Application Overview
2.2.2 By Technology Overview
2.2.3 By Deployment Mode Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3 Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on AI in Smart Cities Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4 Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Driver 1
4.1.1.2 Driver 2
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Restraint 1
4.1.2.2 Restraint 2
4.1.3 Market Opportunity
4.1.3.1 Opportunity 1
4.1.3.2 Opportunity 2
4.1.4 Market Challenges
4.1.4.1 Challenge 1
4.1.4.2 Challenge 2
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5 Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global AI in Smart Cities Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6 AI in Smart Cities Market, By Application
6.1 Global AI in Smart Cities Market Snapshot, By Application
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Traffic Management
6.1.1.2 Public Safety and Security
6.1.1.3 Energy Management
6.1.1.4 Infrastructure Management
6.1.1.5 Environmental Monitoring
6.1.1.6 Smart Governance
Chapter 7 AI in Smart Cities Market, By Technology
7.1 Global AI in Smart Cities Market Snapshot, By Technology
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Machine Learning
7.1.1.2 Natural Language Processing (NLP)
7.1.1.3 Computer Vision
7.1.1.4 IoT Integration
7.1.1.5 Big Data Analytics
Chapter 8 AI in Smart Cities Market, By Deployment Mode
8.1 Global AI in Smart Cities Market Snapshot, By Deployment Mode
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Cloud-based
8.1.1.2 On-Premises
Chapter 9 AI in Smart Cities Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
9.3 Global AI in Smart Cities Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America AI in Smart Cities Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe AI in Smart Cities Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UK Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 France Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 Germany Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of Europe Market Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific AI in Smart Cities Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 China Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 Japan Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 India Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 Australia Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia Pacific Market Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA AI in Smart Cities Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCC Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 Africa Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 Brazil Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA AI in Smart Cities Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEA Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10 Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
11.1 IBM Corporation
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Microsoft Corporation
11.3 Google (Alphabet Inc.)
11.4 Cisco Systems, Inc.
11.5 Intel Corporation
11.6 Siemens AG
11.7 General Electric (GE)
11.8 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11.9 Oracle Corporation
11.10 SAP SE