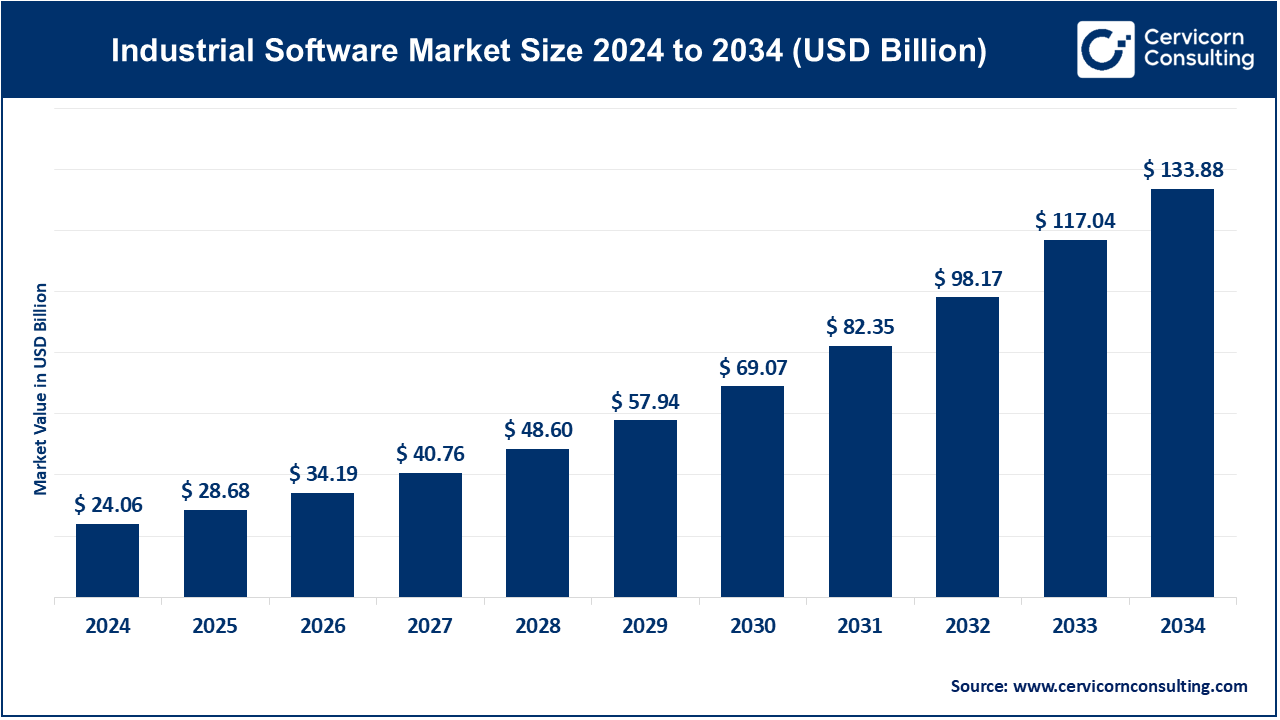
The global industrial software market size was valued at USD 24.06 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 133.88 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.72% from 2025 to 2034.
The industrial software market is expanding rapidly, fueled by the increasing adoption of advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and cloud computing. Companies are prioritizing digital transformation to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and meet the growing demand for automation. The shift toward smart factories and Industry 4.0 has created a significant demand for software that can integrate with connected devices and enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and seamless process automation. Additionally, regions like Asia-Pacific are emerging as key players due to rapid industrialization and technological adoption in countries such as China, India, and Japan. In developed regions like North America and Europe, the focus on sustainability and energy-efficient solutions is increasing investments in industrial software, particularly in sectors like energy, healthcare, and automotive. In recent, Siemens is set to acquire Altair Engineering, a U.S.-based industrial software maker, for approximately USD 10 billion. Altair specializes in simulation software, particularly in creating 'digital twins' virtual simulations of products under various conditions. This acquisition aims to bolster Siemens' software offerings in mechanical and electromagnetic simulation.
Industrial software refers to specialized computer programs designed to streamline and automate processes in manufacturing, engineering, and other industrial sectors. These tools help companies design, simulate, monitor, and control operations, ensuring efficiency, precision, and safety. For instance, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software aids in designing products, while SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems manage and monitor industrial equipment in real time. Industrial software often integrates with IoT (Internet of Things) devices, enabling smart factories where machines and systems communicate to optimize performance. Key industries using industrial software include automotive, energy, aerospace, and healthcare, where quality and accuracy are critical.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 28.68 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 133.88 Billion |
| Growth Rate 2025 to 2034 | 18.72% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Expanding Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Type, Deployment, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, Autodesk, Honeywell, Siemens AG, IBM, ABB Group, Microsoft, Oracle, Infor, PTC Inc., AVEVA Group plc, Epicor, SAP SE, Hitachi, JK Technosoft, Wonderware, Industrial Software Solutions, Emerson Electric Co. |
Increased Complexities Associated with Operations
Growing Use of Asset Performance Management (APM) Solutions
High Installation Costs
Restrictions Related to Regulatory Compliance and Interoperability
Growing Use of Digital Twin Technology
Advancements in Manufacturing Processes
Susceptibility to Cyberattacks
Shortage of Skilled Professionals
The industrial software market is segmented into type, deployment, end-users and region. Based on type, the market is classified into Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), CAD/CAM, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA), Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), Distributed Control System (DCS), Privileged Access Management (PAM), Human Machine Interface (HMI), and Production Process Management and Control. Based on deployment, the market is classified into on-premise, and cloud-based. Based on end-users, the market is classified into manufacturing, energy & utilities, transportation & logistics, healthcare & life sciences.
Based on type, the global market is segmented into product lifecycle management (PLM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), manufacturing execution systems (MES), CAD/CAM, SCADA, programmable logic controller (PLC), distributed control system (DCS), privileged access management (PAM), human machine interface (HMI), production process management and control. The manufacturing execution system (MES) segment dominating the market in 2024 with highest revenue share.
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): PLM software manages all information and processes in each step of a product or service lifecycle across globalized supply chains. This comprises of the data of items, products, parts, documents, requirements, quality workflows, and engineering change orders. Business processes are aligned on a single platform with PLM software, with the product value chain driving faster innovation with integrated business planning and supply chain execution, improving the way products are designed, manufactured, serviced, and maintained.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): ERP systems are a type of manufacturing management software that increases the organizational efficiency of a manufacturing company by managing and improving the utilization of the company's resources. Improving and/or reducing the number of resources required without sacrificing quality and performance is the key to effectively improving the growth and profitability of the manufacturing business. ERP software enables manufacturing companies to manage critical aspects of everything from shop floor operations to delivery and inventory planning. Software used for managing the key business operations, include finance, accounting, human resources, and supply chain, is known as enterprise resource planning, or ERP.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): An unique and dynamic software system known as manufacturing execution system (MES) helps in keeping track of documents, and managing the production process of goods from raw materials to final goods. The MES software acts as a functional intermediary between enterprise resource planning (ERP) and process control systems, providing decision-makers the information they need for maximizing production and making the factory floor more effective. An MES is essential to achieving optimal performance in the competitive and rapidly changing manufacturing environment.
CAD/CAM: CAD/CAM is the integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). CAD/CAM software is used for designing and manufacturing prototypes, finished products, and production runs of products by using a single design tool. CAD/CAM software allows companies to create 2D and 3D models, simulate various production processes, and generate toolpaths for CNC machines. CAD/CAM software is used in many industries, that include aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA): Systems used for monitoring, controlling, and analyzing industrial processes and equipment are known as Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA). The system contains both software and hardware components and provides remote and on-site collection of data from the industrial equipment. It also allows companies to manage industrial sites remotely. The main purpose of a SCADA system is to monitor and control equipment in industrial processes. Therefore, SCADA systems are found almost everywhere.
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): PLC software is the tool for programming, monitoring and controlling. It allows you to create and edit control logic in various programming languages such as ladder logic, function block diagram and structured text. Popular brands for PLC software include Siemens TIA Portal, Rockwell Automation Studio 5000 and Mitsubishi GX Works. These tools provide features such as simulation, debugging and real-time monitoring, making it easier to develop and troubleshoot PLC programs. Using the right PLC software ensures efficient and reliable automation of industrial processes.
Distributed Control System (DCS): A distributed control system (DCS) is a digital automated industrial control system (ICS) that uses geographically distributed control loops in a factory, machine, or control area. The goal of a DCS is to control industrial processes to increase their safety, cost-effectiveness, and reliability.
Privileged Access Management (PAM): The process of controlling and monitoring all privileged access to a system via a central platform is known as privileged access management (PAM). Any organization that uses PAM can get a thorough picture of who is accessing what information in the systems and what tasks are being completed. PAM provides companies with complete control and visibility into which users have access to systems and what types of actions they can perform.
Human Machine Interface (HMI): Human-machine interface (HMI) software provides an intuitive graphical user interface with input/output controls to monitor and operate sophisticated industrial equipment. HMI software can be installed on HMI hardware or regular PCs, mobile devices, and wearables. HMI software is primarily an input/output solution; it only performs most of its functions when integrated with other industrial solutions.
Production Process Management and Control: Production process management and control software enables fast and secure process automation to maximize efficiency and productivity. This software is used to manage bills of materials, assembly designs, and quality inspections. It helps visualize progress, track daily operations, ensure consistent quality, and improve relationships with suppliers.
Based on deployment, the global market is segmented into on-premise and cloud-based.
On-Premise: Systems that are installed inside a particular infrastructure are referred to as on-premise. This kind of software requires a substantial amount of setup and upkeep from the user and is then installed on-site. Industrial software that is installed on-site provides users with good control and flexibility, however, it also comes with extra maintenance, scalability, and security overhead.
Cloud-Based: Industrial software that runs on the cloud is known as cloud-based software. Some of the characteristics of cloud-based industrial software include Pay-as-you-go pricing, self-provisioning capabilities, automatic scalability, and low upfront costs. Industrial software hosted in the cloud can be accessed from any remote location with the help of a strong internet connection. The cloud-based software is generally more secure than on-premise software.
Based on end user, the global market is segmented into manufacturing, energy and utility, transportation and logistics, and healthcare and life sciences.
Manufacturing: Industrial software has become important to modern manufacturers because it offers solutions that can reduce costs and increase the efficiency of the production process. These software solutions can automate complex processes, offer real-time data analytics, streamline logistics, reduce downtime, and provide operational insights to improve performance. Some industrial software solutions are specifically targeted at the manufacturing sector, while many also offer customized features so they can be used in other types of businesses.
Energy & Utilities: Energy and utility companies use industrial software to assist with predictive maintenance, data collection, process optimization, and intelligent forecasting. These software solutions can be used for maintaining and enhancing the current systems and procedures in the oil and gas, electricity and power, and renewable energy sectors. Additionally, the industrial software can offer data that can be utilized for guiding decisions regarding infrastructure investments, which can in turn reduce expenses and boost productivity.
Transportation & Logistics: In the transportation and logistics sector, industrial software is used for optimizing operations. These solutions can support demand forecasting and optimization, asset and freight tracking, and route planning and scheduling. Players in this industry can further optimize efficiency and profitability by gaining insights into customer behavior, thereby saving time and money by incorporating automation into systems and processes.
Healthcare & Life Sciences: Industrial software is used by healthcare and life sciences sector for the purpose of handling patient data, processing medical records, and storing digital data. With the use of the industrial software solutions all the processes in the organization are streamlined, patient care is enhanced, and legal and regulatory compliance is guaranteed. In addition, by incorporating automation into daily operations healthcare companies can save time and money, enhance patient satisfaction and experience, and lower the risk of error.
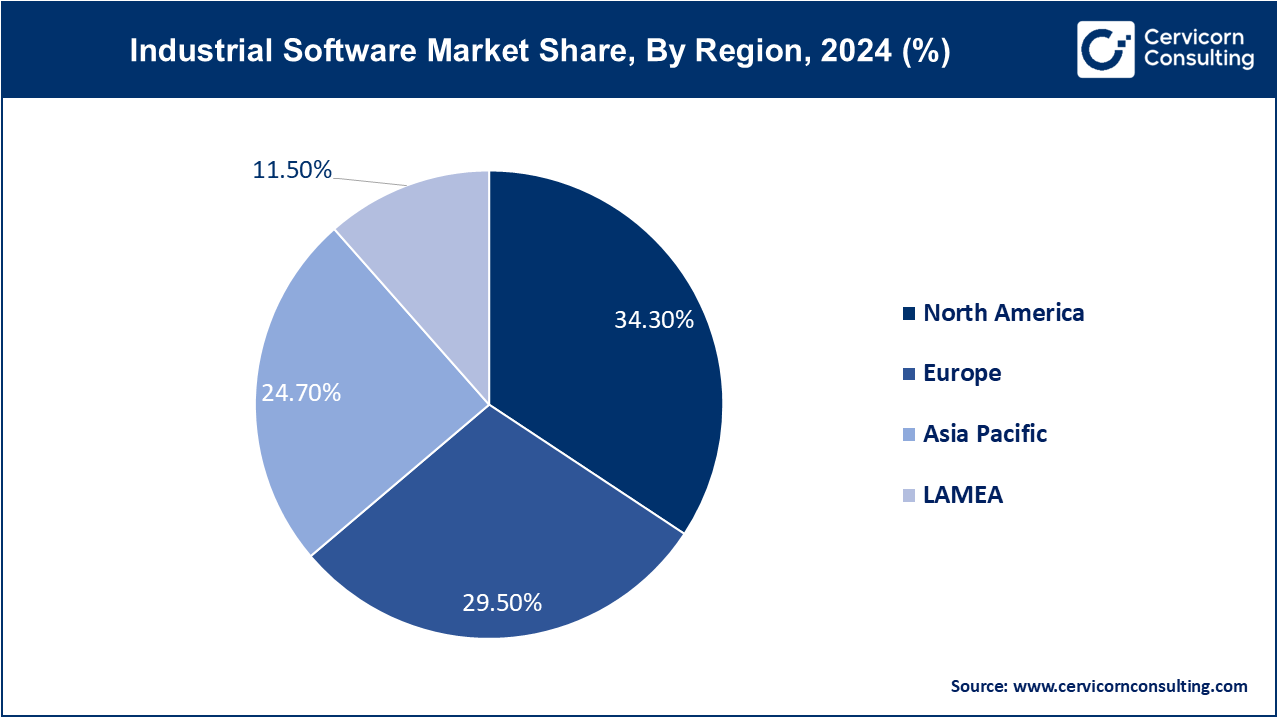
The industrial software market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. North America is dominating the market with higfhest revenue share in 2024. Here is a brief overview of each region:
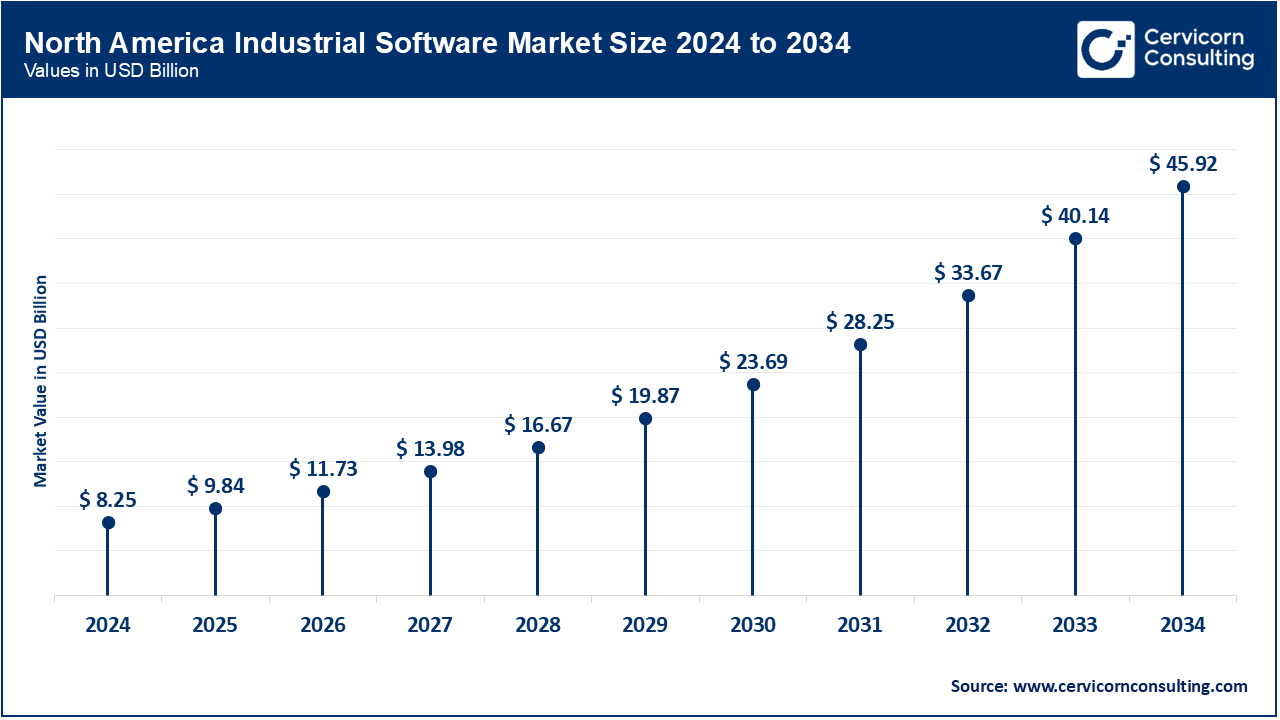
The North America industrial software market size was valued at USD 8.25 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 45.92 billion by 2034. The growing demand for automation and digital transformation in the industrial sector of the region is driving the market growth. Companies are spending money on software solutions for boosting productivity, cutting expenses, and increasing efficiency. Additionally, the number of startups in the region providing cutting-edge software solutions is also constantly rising. The North American market has the presence of significant technology companies, such as Microsoft, IBM, and Oracle, which is advantageous for the growth of the market. These companies are investing a lot of money in developing industrial software solutions.
The Europe industrial software market size was estimated at USD 7.10 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 39.49 billion by 2034. The rising number of startups providing cutting-edge software solutions are paving their way into the European industrial software industry. This promotes market innovation and competition, which in turn results in higher-quality goods and services. Furthermore, a favorable environment is created by the growing number of government initiatives to support the use of industrial software leading to investment by companies in software solutions which is driving the market growth in the region.
The Asia-Pacific industrial software market size was accounted for USD 5.94 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 33.07 billion by 2034. The primary drivers of the industrial software market in Asia Pacific are the region's growing number of creative startups, low-cost internet service availability, and the industry's rapid growth as a result of growing demand for automation and digitization of industrial processes. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore are at the forefront of strategic initiatives and investments that are focused on advancing manufacturing by using advanced technologies. Combining robotics, IoT, and AI to increase manufacturing productivity and innovation is the main focus of the "Made in China 2025" initiative.
The LAMEA industrial software market was valued at USD 2.77 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to hit around USD 15.40 billion by 2034. The Middle East is home to large-scale industrial projects, such as manufacturing, construction, and oil and gas sectors. For these projects, industrial software is required for managing and optimizing operations. Major players are investing more money into industrial software as they try to capitalize on the developing economies of emerging markets like the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar. Further, LAMEA has a skilled labor pool and attractive tax incentives that are contributing to the growing number of foreign investments in the region, which benefits the market. In addition, the growing digital infrastructure in the region is further driving the growth of the industrial software market.
The global market is highly competitive and includes various SMEs and large companies including Autodesk, Siemens, Rockwell Automation and ABB Group. Agreements, acquisitions, mergers and contracts are some of the key strategies adopted by these companies. Moreover, the companies place great emphasis on using cutting-edge technologies in software for smart manufacturing applications. Schneider Electric and ArcelorMittal Nippon Steel India forged a partnership in June 2023 for the purpose of offering advanced training in smart manufacturing. As a part of the partnership, Schneider Electric developed training facilities and smart labs for AM/NS India's NAMTECH as an educational initiative.
In addition, to create new manufacturing opportunities, Rockwell Automation Inc. and Autonox Robotics had also teamed up in May 2023. The partnership expanded and innovated robot mechanics, wherein Rockwell's Kinetix motors and drives were combined with Autonox's robot mechanics.
Blake Moret, President and CEO of Rockwell Automation:
Barbara Humpton, President & CEO, Siemens USA:
Key players in the industrial software industry are pivotal in delivering a variety of innovative construction solutions, such as prefabrication techniques, sustainable materials, and advanced digital technologies. Some notable developments in the industrial software industry include:
These advancements mark a notable expansion in the industrial software market, driven by strategic acquisitions and innovative projects. The focus is on boosting sustainability, enhancing construction efficiency, and broadening product offerings to meet diverse building needs.
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Deployment
By End-Users
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Industrial Software
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Type Overview
2.2.2 By Deployment Overview
2.2.3 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Industrial Software Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Increased Complexities Associated with Operations
4.1.1.2 Growing Use of Asset Performance Management (APM) Solutions
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Installation Costs
4.1.2.2 Restrictions Related to Regulatory Compliance and Interoperability
4.1.3 Market Opportunity
4.1.3.1 Growing Use of Digital Twin Technology
4.1.3.2 Advancements in Manufacturing Processes
4.1.4 Market Challenges
4.1.4.1 Susceptibility to Cyberattacks
4.1.4.2 Shortage of Skilled Professionals
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Industrial Software Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Industrial Software Market, By Type
6.1 Global Industrial Software Market Snapshot, By Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
6.1.1.2 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
6.1.1.3 Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
6.1.1.4 CAD/CAM
6.1.1.5 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
6.1.1.6 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
6.1.1.7 Distributed Control System (DCS)
6.1.1.8 Privileged Access Management (PAM)
6.1.1.9 Human Machine Interface (HMI)
6.1.1.10 Production Process Management and Control
Chapter 7. Industrial Software Market, By Deployment
7.1 Global Industrial Software Market Snapshot, By Deployment
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 On-Premise
7.1.1.2 Cloud-Based
Chapter 8. Industrial Software Market, By End User
8.1 Global Industrial Software Market Snapshot, By End User
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Manufacturing
8.1.1.2 Energy & Utilities
8.1.1.3 Transportation & Logistics
8.1.1.4 Healthcare & Life Sciences
Chapter 9. Industrial Software Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 Industrial Software Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
9.3 Global Industrial Software Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America Industrial Software Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe Industrial Software Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific Industrial Software Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA Industrial Software Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Industrial Software Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11.Company Profiles
11.1 Rockwell Automation
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Schneider Electric
11.3 Autodesk
11.4 Honeywell
11.5 Siemens AG
11.6 IBM
11.7 ABB Group
11.8 Microsoft
11.9 Oracle
11.10 Infor
11.11 PTC Inc.
11.12 AVEVA Group plc
11.13 Epicor
11.14 SAP SE
11.15 Hitachi