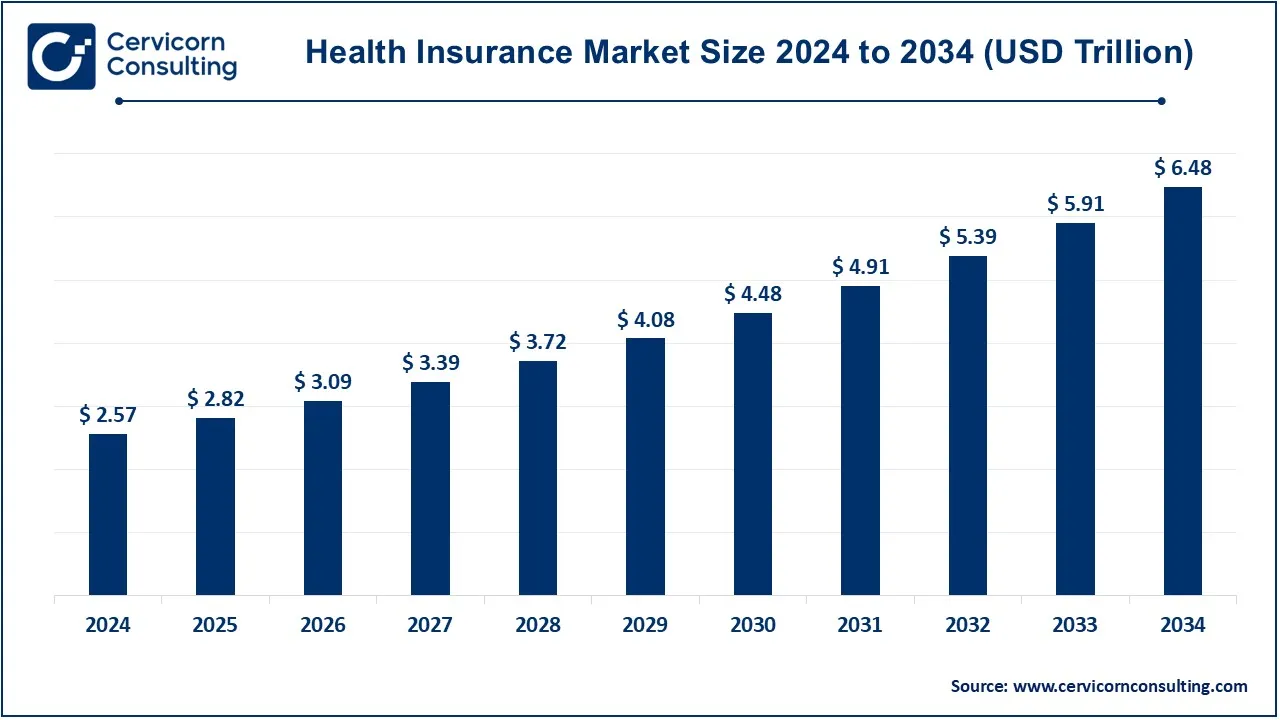
The global health insurance market size was valued at USD 2.57 trillion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 6.48 trillion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.68% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The health insurance market has seen consistent growth in recent years due to factors such as rising healthcare costs, an aging population, and increased awareness of the importance of health coverage. As medical expenses rise globally, more individuals and businesses are seeking comprehensive insurance options to mitigate these costs. The demand for health insurance is also driven by an increasing focus on preventive healthcare and wellness programs, which encourage people to seek insurance early to avoid costly treatments down the road. The emergence of digital health platforms and telemedicine services further boosts the market, making insurance access more convenient and efficient for consumers. In addition, government policies and regulations, such as the Affordable Care Act in the U.S., have increased the number of people covered by health insurance. The growing prevalence of chronic diseases and lifestyle-related health issues is another key factor driving market growth, as people require more frequent medical attention.
Health insurance is a type of coverage that helps pay for medical expenses. It can cover a variety of healthcare costs, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgeries, and medications. Health insurance plans typically require individuals or employers to pay a premium, either monthly or annually. In return, the insurance company covers the cost of certain medical services, reducing out-of-pocket expenses. The coverage may also include preventive care, such as vaccinations and screenings, which helps people maintain better overall health. Health insurance varies by plan, with different levels of coverage, deductibles, and co-pays. Having health insurance provides peace of mind, as it reduces the financial burden of unexpected medical costs and encourages individuals to seek timely care when needed.
Key Insights on Health Insurance:
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.82 Trillion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 6.48 Trillion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2034) | 9.68% |
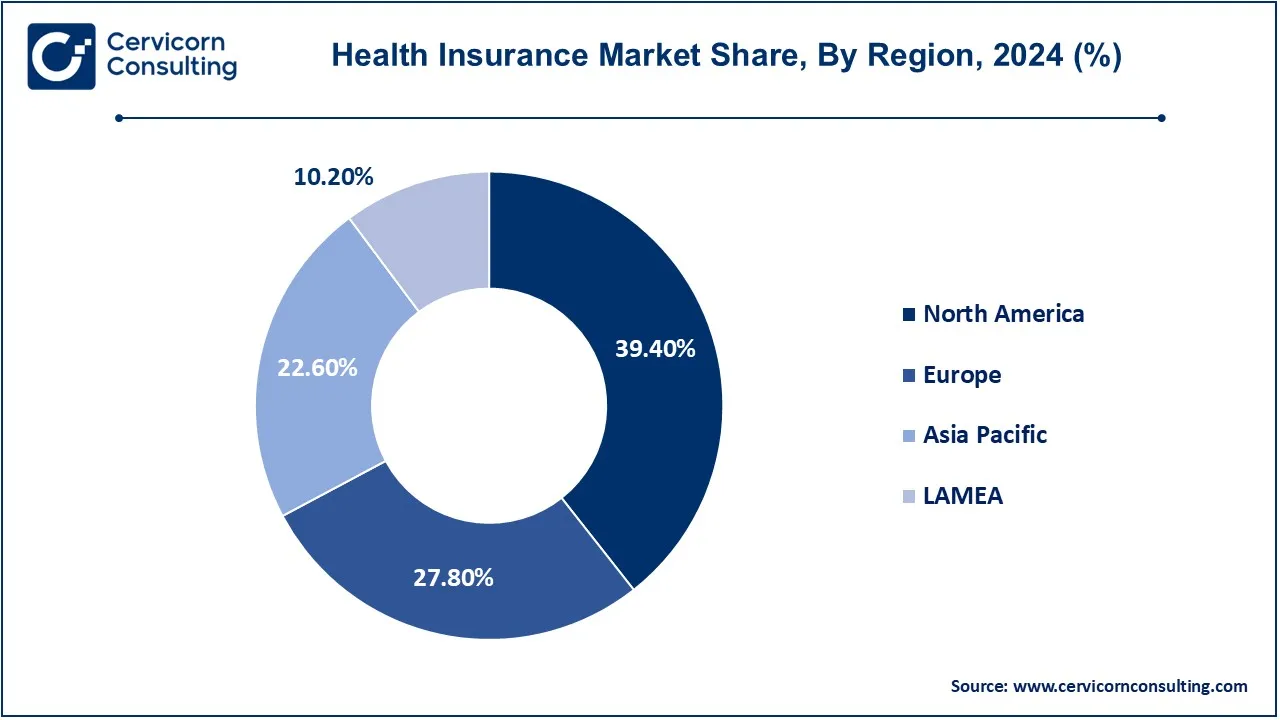
| Top-performing Region | North America |
| Highest Growth Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Insurance Type, Coverage, Type, Age Group, Distribution Channel, Level of Coverage, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Cigna Healthcare, Centene Corporation, Allianz Care, Aetna Inc., Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc., AXA, Broadstone Corporate Benefits Limited, Bupa, HealthCare International Global Network Ltd., HBF Health Limited, Now Health International, Oracle, UnitedHealth Group |
The health insurance market is segmented into insurance type, coverage, type, age group, distribution channel, level of coverage, end user and region. Based on insurance type, the market is segmented into private health insurance, family health insurance. Based on coverage, the market is segmented into preferred provider organizations (PPOS), point of service (POS), health maintenance organization (HMOS), exclusive provider organizations (EPOS). Based on type, the market is segmented into life-time coverage, term insurance. Based on age group, the market is segmented into senior citizens, adult, minors. Based on distribution channel, the market is segmented into direct sales, brokers/agent, banks, others. Based on level of coverage, the market is segmented as bronze, silver, gold, and platinum. Based on end user, the market is segmented into group and individual.
Private Health Insurance: It is sometimes known as individual health insurance plans, which are the cover given to a single individual who needs coverage for their medical expenses. The plans offer quite several benefits, including hospitalization, outpatient care, preventive services, and prescription medicines. One can make a choice that provides coverage tailored to meet one's specific health needs, meaning tailored to preferences based on age, health history, or budget. Normally, people can get these plans from the health insurance marketplaces or private insurers and employers as provided by their country. These individual plans are quite popular especially because of the option of flexibility in deductibles, premiums, and coverage limits for those preferring customized health care.
Health Insurance Market Share, By Insurance Type, 2024 (%)
| Insurance Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Private | 44% |
| Family | 56% |
Family Health Insurance: Family health insurance is made to enroll a family of members into one policy. In this way, such plans can provide generous medical coverage for spouses and children, in some cases extended family members. When multiple family members individually enroll for their policies, then purchasing them in family options can prove much less expensive. These often have a family deductible and fewer premiums per person. They also usually offer critical health cover, which covers preventive care, maternity, and pediatric care; so, all family members will hence be covered in terms of necessary medical treatment. A family health insurance program selection may make it easier to manage health care costs and facilitate easy access to services by all family members.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs offer a flexible network of healthcare providers, giving members several choices among doctors and specialists without requiring any referral. However, the member is free to see out-of-network providers; services from such providers typically cost more. Balanced between choice and cost, the popularity of PPOs remains since they offer many healthcare choices with little constraint.
Point of Service (POS): A POS plan has elements of HMO and PPO. Members have to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who then coordinates care and refers a member to a specialist, but members are permitted to receive services through providers out of the network - though at an additional cost after certain exclusions. In this package deal, flexibility in using different services is preserved; however, the use of network services is promoted as it appeals to those who prefer a level of personal control over decisions that are related to health care.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): In HMOs, members must first choose a primary care physician and obtain a referral from the physician to see any other specialists. Such a plan is more focused on prevention-based care, although premiums and out-of-pocket costs generally are lower than PPOs. However, the number of health professionals whom one can see through an HMO is, however, often more limited than in PPOs. HMOs still allow the necessary coordination and management of care through a more concentrated provider network, an entity that promotes better health outcomes and cost control for both the insurer and the patient.
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): EPOs are the same as PPOs, except for the fact that the enrollers agree to seek one designated network of providers to fill out the coverage instead of offering to pay for doctors outside the network unless it is an emergency. Generally, this kind of plan is said to be cheaper compared to the PPOs, and for those who just need basic yet affordable health care coverage with a broad range of health services, an EPO may deserve to be taken by them.
Senior Citizen: Other plans are specifically meant to cover chronic conditions, long-term care, and prescriptions. Such plans may provide wellness programs, preventive screenings, and even incorporate other benefits because of the increased need for healthcare for the elderly. Some are specified as only for older populations such as is the case with some U.S. plans called Medicare. Those plans provide them with much-needed health services, yet they also aim at curbing out-of-pocket expenditures among the elderly.
Adult: There are insurance coverages that exist for adults in the age range that come in several options to cope with lifestyles or health conditions. Younger adults who fall into the age range might be more concerned with preventive care, wellness, and more, whereas the same age group of older adults may favor chronic coverage. Adult health insurance is usually a type that weighs cost against flexibility in coverage, allowing the individual the liberty to choose plans that represent the personal nature of the health circumstances or financial situation.
Health Insurance Market Share, By Age Group, 2024 (%)
| Age Group | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Senior Citizens | 27% |
| Adult | 59% |
| Minors | 14% |
Minors: Health insurance for children would include, to a significant extent, coverage for preventive care, vaccinations, and other necessary medical services. These are typically offered by the child's parents or guardians. They ensure that children receive necessary medical care without overpaying money. An important focus of health insurance for children will be pediatric care; this is meant to provide good development and timely medical attention for all developmental problems or acute cases.
Direct Sales: Direct sales are sales of health insurance between the insurer and the consumer, with no intermediaries. Directly, consumers have the opportunity to research and buy insurance policies directly from the insurance company, mostly through the Internet platform. Direct sales result in a saving on costs for consumers since it eliminates the cost of brokers' fees, hence making the purchasing process more cost-effective as well as efficient.
Brokers/Agents: Intermediaries and agents are therefore crucial in the health insurance market as they help the consumer choose a suitable plan. They can provide valuable advice, compare various policies, and guide the applicant through the application process. Although they may be paid by insurers in terms of commissions, their acumen enhances the consumer's knowledge of the intricate insurance options.
Banks: Increasingly, banks are acting as channels for the distribution of health insurance products. In addition, they can sell them together with other financial products and services. A bank may provide HSAs or work insurance as part of an overall financial planning service. Selling directly through the existing relationship also offers a crucial advantage: ease for the consumer. It is convenient; they need not go elsewhere for everything.
Others: Other distribution channels include: online marketplaces, health providers, or, for instance, employer-sponsored insurance programs. Online marketplaces enable a customer to choose from and compare different health insurance plans. The healthcare provider might even sell insurance products as part of their services. For many people, especially employed, health insurance through the employer is the mainstay of insurance coverage.
The health insurance market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). North America has dominated the market in 2024.
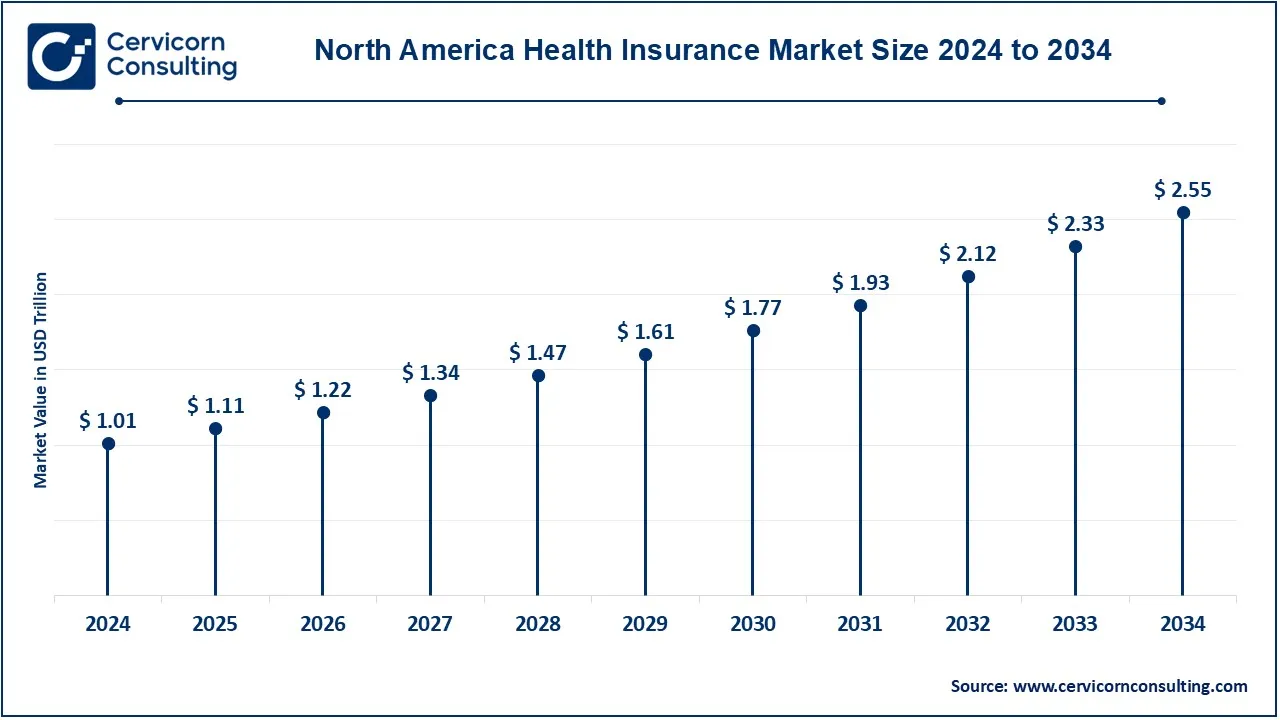
The North America health insurance market size was valued at USD 1.01 trillion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 2.55 trillion by 2034. The North American market is dominated by the United States and Canada. The U.S. has a rather complex health insurance system because it is a mix of public and private insurers, consisting of Medicare, Medicaid, and private employer-sponsored plans. All of these considerably impacted market dynamics because they increased access to insurance. The other features include that of a publicly funded healthcare system in Canada whereby coverage has been provided to all citizens through the provincial programs. However, private insurance is also used to supplement some of the care that one may require. Both countries are facing much stress for example in terms of high healthcare costs as well as assessing care.
The Europe health insurance market size was estimated at USD 0.71 trillion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 1.80 trillion by 2034. Europe has a very diverse landscape with regard to health coverage and different models are in place in different countries. For instance, the United Kingdom uses the model of the NHS that is based on taxation to cover everyone; Germany, conversely, uses a dual system where statutory and private insurance are used. In France, although the government bears the majority share of healthcare costs, private insurance fills in gaps. For instance, complete public medical care funded by taxes is offered by Nordic countries such as Sweden and Denmark. However, the sustainability issues in funding healthcare in these countries and the growing age of their populations remain the major wide-ranging challenges seen across the region.
The Asia-Pacific health insurance market size was accounted for USD 0.58 trillion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 1.46 trillion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region is comprised of rapidly growing markets and established systems. For example, India has a burgeoning private insurance market, although it remains the case that many rely on out-of-pocket expenses in part because public coverage is incomplete. Japan has a comprehensive healthcare system in which public and private insurance co-exist with high-quality care. Australia houses a mixed model with a publicly funded system of Medicare, aside from private insurance alternatives. In the remaining Southeast Asia, developing countries like Vietnam and Indonesia have a greater need for health insurance since their economic growth maximizes access to the available services, yet it remains grossly uneven.
The LAMEA health insurance market was valued at USD 0.26 trillion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 0.66 trillion by 2034. The health insurance landscape varies considerably in the LAMEA region. Examples like Brazil and Mexico can achieve universality through public programs in Latin America but would vary considerably depending on private insurance. System diversity prevails in the Middle East: While a country like the UAE boasts advanced private cover options alongside public services, others have limited access. In Africa, the scene is mixed: countries like South Africa have clear private markets, and many others are struggling with low coverage rates and high out-of-pocket spending levels. Overall, economic development and the growing need for health care in the LAMEA region encourage awareness and take-up of health insurance.
CEO Statements
David Cordani, CEO of Cigna Healthcare
Sarah London, CEO ofCentene Corporation
Tomas Kunzmann, CEO of Allianz Care
Market Segmentation
By Insurance Type
By Coverage
By Type
By Level of Coverage
By Age Group
By Distribution Channel
By End User
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Health Insurance
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Insurance Type Overview
2.2.2 By Coverage Overview
2.2.3 By Type Overview
2.2.4 By Level of Coverage Overview
2.2.5 By Age Group Overview
2.2.6 By Distribution Channel Overview
2.2.7 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Health Insurance Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Consumer Awareness
4.1.1.2 Product Innovation in Insurance
4.1.1.3 Global Health Initiatives
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Premium Costs
4.1.2.2 Regulatory Challenges
4.1.2.3 Lack of Knowledge
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Data Privacy Issues
4.1.3.2 Increasing Cost of Health Care
4.1.3.3 Adapt to Consumer Requirements
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Health Insurance Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Health Insurance Market, By Insurance Type
6.1 Global Health Insurance Market Snapshot, By Insurance Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Private Health Insurance
6.1.1.2 Family Health Insurance
6.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 7. Health Insurance Market, By Coverage
7.1 Global Health Insurance Market Snapshot, By Coverage
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOS)
7.1.1.2 Point of Service (POS)
7.1.1.3 Health Maintenance Organization (HMOS)
7.1.1.4 Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOS)
Chapter 8. Health Insurance Market, By Type
8.1 Global Health Insurance Market Snapshot, By Type
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Life-Time Coverage
8.1.1.2 Term Insurance
Chapter 9. Health Insurance Market, By Level of Coverage
9.1 Global Health Insurance Market Snapshot, By Level of Coverage
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Bronze
9.1.1.2 Silver
9.1.1.3 Gold
9.1.1.4 Platinum
Chapter 10. Health Insurance Market, By Age Group
10.1 Global Health Insurance Market Snapshot, By Age Group
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Senior Citizens
10.1.1.2 Adult
10.1.1.3 Minors
Chapter 11. Health Insurance Market, By Distribution Channel
11.1 Global Health Insurance Market Snapshot, By Distribution Channel
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
11.1.1.1 Direct Sales
11.1.1.2 Brokers/Agent
11.1.1.3 Banks
11.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 12. Health Insurance Market, By End User
12.1 Global Health Insurance Market Snapshot, By End User
12.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
12.1.1.1 Group
12.1.1.2 Individual
Chapter 13. Health Insurance Market, By Region
13.1 Overview
13.2 Health Insurance Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
13.3 Global Health Insurance Market, By Region
13.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
13.4 North America
13.4.1 North America Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.3 North America Health Insurance Market, By Country
13.4.4 U.S.
13.4.4.1 U.S. Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
13.4.5 Canada
13.4.5.1 Canada Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
13.4.6 Mexico
13.4.6.1 Mexico Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
13.5 Europe
13.5.1 Europe Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.3 Europe Health Insurance Market, By Country
13.5.4 UK
13.5.4.1 UK Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.5 France
13.5.5.1 France Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.6 Germany
13.5.6.1 Germany Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
13.5.7 Rest of Europe
13.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6 Asia Pacific
13.6.1 Asia Pacific Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.3 Asia Pacific Health Insurance Market, By Country
13.6.4 China
13.6.4.1 China Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.5 Japan
13.6.5.1 Japan Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.6 India
13.6.6.1 India Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.7 Australia
13.6.7.1 Australia Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
13.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7 LAMEA
13.7.1 LAMEA Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.3 LAMEA Health Insurance Market, By Country
13.7.4 GCC
13.7.4.1 GCC Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.5 Africa
13.7.5.1 Africa Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.6 Brazil
13.7.6.1 Brazil Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
13.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
13.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Health Insurance Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
13.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
13.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 14. Competitive Landscape
14.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
14.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
14.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
14.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
14.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 15. Company Profiles
15.1 Cigna Healthcare
15.1.1 Company Snapshot
15.1.2 Company and Business Overview
15.1.3 Financial KPIs
15.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
15.1.5 Strategic Growth
15.1.6 Global Footprints
15.1.7 Recent Development
15.1.8 SWOT Analysis
15.2 Centene Corporation
15.3 Allianz Care
15.4 Aetna Inc.
15.5 Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc.
15.6 AXA
15.7 Broadstone Corporate Benefits Limited
15.8 Bupa
15.9 HealthCare International Global Network Ltd.
15.10 HBF Health Limited
15.11 Now Health International
15.12 Oracle
15.13 UnitedHealth Group