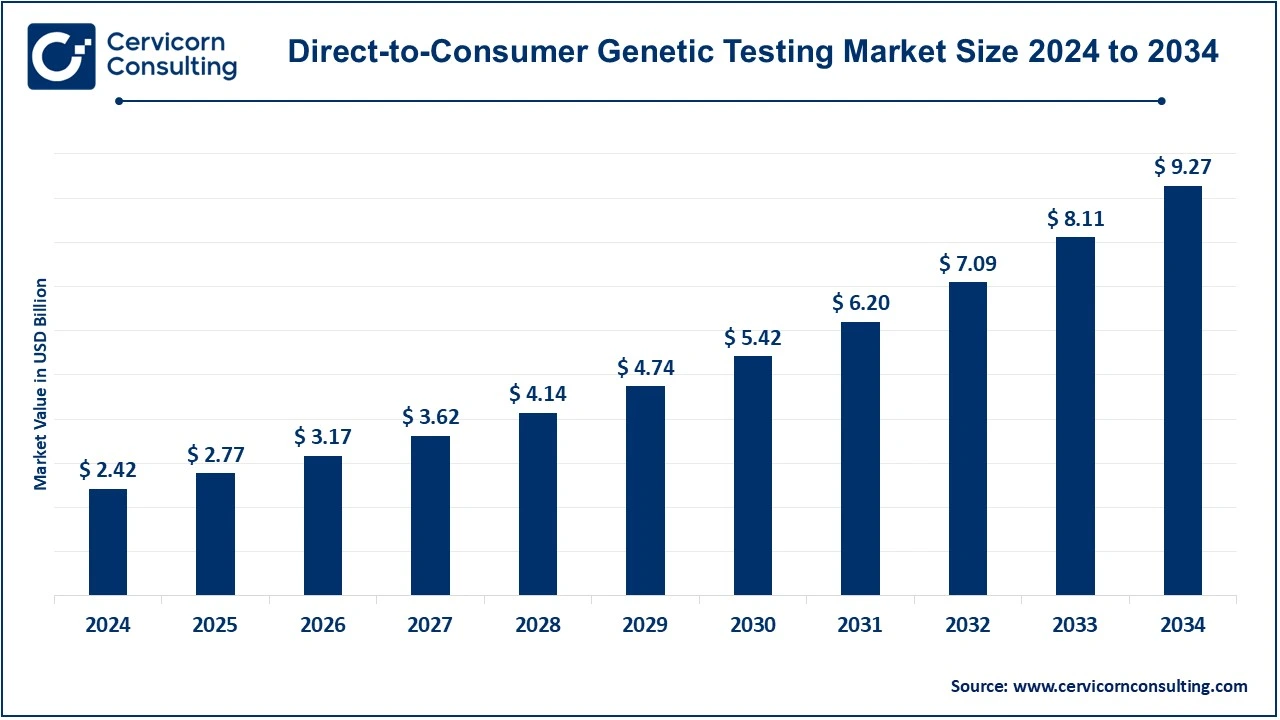
The global direct-to-consumer genetic testing market size was valued at USD 2.42 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 9.27 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.37% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The direct-to-consumer genetic testing market is driven by the increased interest among consumers in personalized healthcare, wellness, and ancestry insights. Genes keep attracting more interest in information concerning health as well as the in-taking control of one's health. An increased demand for in-home genetic tests is reported, and this is more so among millennials and health-conscious customers. Other factors that have also contributed to fueling this market size include the advances in genetic science and ready accessibility of non-costly, consumer-friendly testing kits. Growing awareness regarding the genetic predisposition to diseases or conditions is more and more encouraging people to join the market. With preventive health and data-driven decision-making around managing health being a larger social trend, this adoption supports it.
Direct-to-consumer genetic testing is a type of genetic test sold and marketed directly to a consumer with no engagement of health professionals or genetic counselors; the tests enable consumers to obtain a DNA sample, usually through a saliva or cheek swab kit that then has to be returned to a laboratory to be analyzed. Results may include ancestry, health risks, traits, or genetic predispositions and are usually directly communicated with the consumer via an online portal. Though such DTC genetic tests provide insight into genetics, concerns surrounding the privacy and security of data and results' interpretation without medical guidance continue to be a concern.
CEO Statements
Anne Wojcicki, CEO of 23andMe
Deborah Liu, CEO of Ancestry DNA
Othman Laraki, CEO of Color Genomics, Inc.
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.42 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 9.27 Billion |
| Expected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 14.37% |
| Leading Region | North America |
| Key Segments | Product, Sample, Technology, Distributional Channel, Region |
| Key Companies | 23andMe, Ancestry DNA, Color Genomics, Inc., Genetic Technology (EasyDNA), Full Genomes Corporation, Inc., Helix OpCo LLC, IDENTIGENE, LLC/ DNA Diagnostics Center, Living DNA Ltd, MyHeritage Ltd, Prenetics Limited, Family Tree DNA, Interleukin Genetics/orig3n, Counsyl/Myriad Genetics, Inc., Veritas Genetics, Fulgent Genomics |
The direct-to-consumer genetic testing market is segmented into product, sample, technology, distributional channel and region. Based on product, the market is classified into pharmacogenetics tests, carrier screening tests, genetic health risk (GHR) tests, cancer predisposition tests, low-risk general wellness tests, and ancestry tests. Based on sample, the market is classified into saliva, urine, and blood; Based on technology, the market is classified into whole genome sequencing, single nucleotide polymorphism chips, targeted analysis, and others. Based on distributional channel, the market is classified into online platform and OTC.
Pharmacogenetics Tests: Pharmacogenetic tests refer to how the genetic composition affects a person's response to a specific drug. Such testing aids in identifying the best and safest drugs for a person, as well as the appropriate dosages. Furthermore, through pharmacogenetic testing, risks of side effects arising from genetic variants may be revealed, which enables personal and tailored drug therapies. It is particularly applied in areas such as psychiatry, oncology, and cardiology, where drugs may have different responses in other people.
Carrier Screening Tests: Carrier screening tests assess whether a person carries a gene for a hereditary disease and yet does not exhibit symptoms of the disease. These tests are taken by those who are planning to have children, as they might themselves be genetic carriers of any such condition that would be passed on to their children. Such as beta-thalassemia; here, screening for cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia and Tay-Sachs disease is performed. This helps individuals make the right decision about reproductive planning and the chances of having a child suffering from specific genetic conditions.
Genetic Health Risk (GHR) Tests: The genetic health risk (GHR) test helps ascertain the individual's susceptibility to certain health conditions, for example, heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease, among many other chronic health conditions. While it is not a conclusive diagnosis but an important tool for lifestyle changes, additional screening, or preventative measures against these conditions.
Cancer Predisposition Tests: Cancer predisposition tests are examinations of an individual's DNA to find out whether they carry the genetic mutations associated with a higher risk of developing specific types of cancer, such as breast, ovarian, colorectal, or prostate cancer. Typically, predisposition tests test for cancer-predisposing genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2. These tests can provide preliminary insight into those who may have a family history of cancer or have concerns regarding the genetic propensity that may influence preventive strategies, more vigilant screening, or even lifestyle adjustments.
Low-Risk General Wellness Tests: These tests regarding general wellness would enlighten the user about their general health condition through the study of genes in association with sleep patterns, physical fitness, diet, and reaction to workouts. Tests would also include susceptibility to conditions such as lactose intolerance or sensitivity to caffeine. Most of these would not diagnose anything in medical terms but would allow those testing for their life choices to better judgment and then for decisions made afterward on how best to optimize for their health and well-being.
Ancestry Tests: Ancestry tests trace someone's genetic ancestry and reveal details regarding their ethnic origins as well as their origins. A comparative analysis of a person's DNA with databases is used to discover inherited genes from ancestors, trace family lineage, and locate potential distant relatives. Experts say that ancestry testing provides an exciting historical link while giving one a sense of identity. At the same time, it gives insights into some of the genetic traits inherited through generations.
Saliva: This is the most common mode of collection, applying saliva to collect samples for direct-to-consumer genetic testing. It is easy and painless because a collection tube may be facilitated by spitting into it and forwarding it to the testing laboratory. The DNA lives in the cells lining the mouth. Because this sample type is easily accessed and can be obtained at home, it is ideal for the convenience-loving and privacy-cherishing individual.
Urine: Urine genetic testing is not as common as saliva or blood genetic testing but it still applies there. Urine contains a range of compounds, including DNA, which can then be analyzed to check for certain health conditions or characteristics. Urine samples can further be used to diagnose, for example, certain inherited metabolic disorders or other specific genetic conditions. Although it is not as common of a sample type for direct-to-consumer genetic testing, urine can still be useful in giving information on specific genetic risks or predispositions to certain health problems.
Blood: It is perhaps the gold standard of many medical genetic tests because of the quality and large amount of DNA that may be isolated directly from blood cells. Although blood sampling is more invasive compared to saliva or urine samples, blood is used for a wide variety of genetic studies, including studies related to genetic predispositions to inherited diseases, cancer, and pharmacogenetics. Blood samples are the best sources for testing complex conditions, which require more detailed and accurate genetic information. Traditionally, one would have had to go through a healthcare provider or testing company, but today there are also direct-to-consumer services, using at-home collection kits that can be sent to a lab for analysis, offered by service companies.
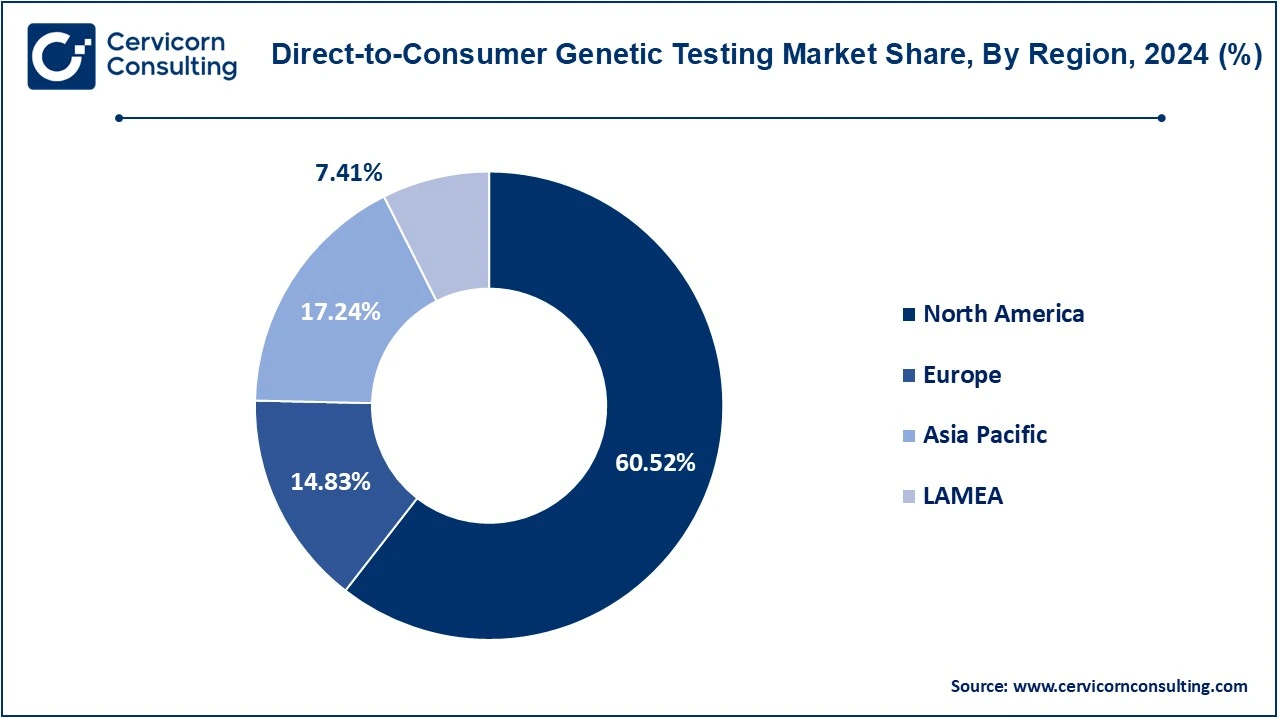
The direct-to-consumer genetic testing market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
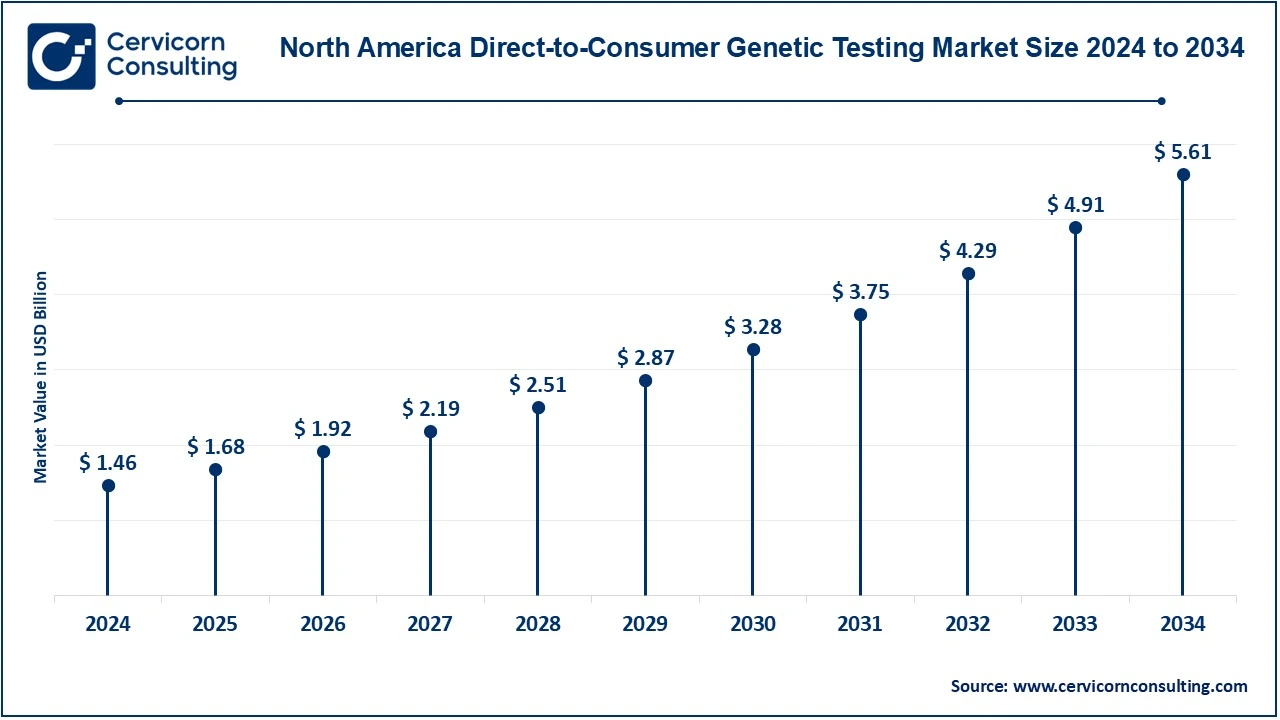
The North America direct-to-consumer genetic testing market size was valued at USD 1.46 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 5.61 billion by 2034. It is the largest and most mature market for DTC genetic testing. This is due to increased consumer awareness of the product, a well-developed structure of health care, and significant investment in biotechnology. The United States is considered the primary market where companies like 23andMe, AncestryDNA, and MyHeritage are offering direct-to-consumer genetic testing services. Although the market in Canada is smaller, interest in personal genomics is growing and testing services are being introduced more and more. Regulation also plays an important role in how the market will be shaped-for example, just as the U.S. FDA published regulations, such as those related to novel drugs. For example, in 2022, the FDA's CDER approved 37 novel drugs. Of these were 25 NMEs, and 12 new therapeutic biological products. These drugs received their first approvals through NDAs and BLAs, which means they are the first approvals for the active ingredients for use in the United States. Progress toward innovation for the treatment of disease is described by the continued development of novel therapeutics.
The Europe direct-to-consumer genetic testing market size was estimated at USD 0.36 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 1.37 billion by 2034. The DTC business is booming in Europe although its development is gradual and inhomogeneous relative to North American countries if considered given the national law within each country. Major markets include the UK, Germany, France, and Spain, considering health conditions, an interest in genetic information, and a necessity for specific personalized care. Such assertions are indicative of the reality that according to the guidelines given by the European Cancer Organization, at 75 years of age, 31% of males and 25% of females in the EU will have had a diagnosis of cancer. Genetic testing is a broad term that assumes ancestry features, while still considering health traits. Still, stiff data protection requirements confuse businesses as they try to understand what the regulations, such as GDPR, require in terms of collecting and handling genetic data.
The Asia-Pacific direct-to-consumer genetic testing market size was accounted for USD 0.42 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 1.60 billion by 2034. Direct-to-consumer genetic testing holds great growth prospects for the APAC region, majorly the key players being China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Growth in the country is also pretty fast, but there are some data privacy issues; this growth would be huge due to the middle class expanding rapidly and recent government investments in improving its healthcare infrastructure. There is an emerging trend of test adoption, mainly on health and wellness, in Japan and South Korea, promoted by next-generation sequencing and multiplex PCR. In Japan, genetic screening programs were conducted by CMIC in January 2024, including the HM-SCREEN-Japan project, to identify the gene mutations of patients with acute myeloid leukemia to discover drugs better.
The LAMEA direct-to-consumer genetic testing market size was valued at USD 0.18 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 0.69 billion by 2034. The LAMEA holds immense growth prospects due to growing consumer awareness, an increasing middle-class population, and easy access to digital technologies. Current demand drivers in Latin America are DTC Genetic tests, and this market is majorly taking place in Brazil. Economic and health access remain key challenges for this region. It is primarily the most youthful and technologically innovative population in the region which fuels demand for it across the Middle East of UAE and Saudi Arabia. There is growing interest in Africa, particularly in South Africa, but limited access, lack of regulation, and ethical concerns are likely to dampen further expansion in the market.
The key players that dominate the market are 23andMe, Ancestry DNA, Color Genomics, Inc., Genetic Technology (EasyDNA), Full Genomes Corporation, Inc., and Helix OpCo LLC, where the latest DNA sequencing technologies coupled with sophisticated data analytics and cutting-edge bioinformatics gives a clear insight into one's genetic makeup. Utilizing next-generation sequencing, or NGS, companies provide ancestry tracing, genetic health risk assessments, and even customized wellness recommendations, among many other services. Not to mention the collaborating agreements with health care providers, research entities, and technology companies that can ensure more valid, wide-ranging scope, and experience for the user to establish them in a premier position in the newly exploding market.
The products launched as well as strategic partnerships in the market are accelerating new-age business relationships among these key players such as 23andMe, Ancestry DNA, Color Genomics, Inc., Genetic Technologies (EasyDNA), Full Genomes Corporation, Inc., and Helix OpCo LLC. These companies have been taking up the new frontier for applications in personal health, ancestry study, and basic genetic research through new testing services being designed, improvements in the capacities of genetic analysis, and expanded offerings of these products. With cooperative works and novel technology adoption, they continue to advance accessibility with accuracy through genetic tests. They are increasingly being put into use in consumer health management as well as wellness programs, thus furthering genetic research. With this, the market becomes dynamic, hence promoting consumer engagement in genetics-related testing even more extensively with a whole range of genetic testing solutions.
Some notable examples of key developments in the market include:
Market Segmentation
By Product
By Sample
By Technology
By Distributional Channel
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Product Overview
2.2.2 By Technology Overview
2.2.3 By Sample Overview
2.2.4 By Distribution Channel Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Increasing Demand among Consumers
4.1.1.2 Global Health Trends
4.1.1.3 Older Population
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Privacy Issues
4.1.2.2 Limited Clinical Actionability
4.1.2.3 Regulatory Compliance
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Consumer Misunderstanding
4.1.3.2 Health Insurance Limitations
4.1.3.3 Legal and Regulatory Challenges
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Health and Well-being
4.1.4.2 Growing demand for ancestry testing from consumers
4.1.4.3 Integration with Digital Health Platforms
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Product
6.1 Global Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Snapshot, By Product
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Pharmacogenetics Tests
6.1.1.2 Carrier Screening Tests
6.1.1.3 Genetic Health Risk (GHR) Tests
6.1.1.4 Cancer Predisposition Tests
6.1.1.5 Low-Risk General Wellness Tests
6.1.1.6 Ancestry Tests
Chapter 7. Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Sample
7.1 Global Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Snapshot, By Sample
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Saliva
7.1.1.2 Urine
7.1.1.3 Blood
Chapter 8. Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Technology
8.1 Global Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Snapshot, By Technology
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Whole Genome Sequencing
8.1.1.2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Chips
8.1.1.3 Targeted Analysis
8.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 9. Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Distributional Channel
9.1 Global Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Snapshot, By Distributional Channel
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Online Platform
9.1.1.2 OTC
Chapter 10. Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
10.3 Global Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Region
10.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
10.4 North America
10.4.1 North America Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.3 North America Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Country
10.4.4 U.S.
10.4.4.1 U.S. Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.5 Canada
10.4.5.1 Canada Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.6 Mexico
10.4.6.1 Mexico Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
10.5 Europe
10.5.1 Europe Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.3 Europe Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Country
10.5.4 UK
10.5.4.1 UK Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.5 France
10.5.5.1 France Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.6 Germany
10.5.6.1 Germany Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.7 Rest of Europe
10.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6 Asia Pacific
10.6.1 Asia Pacific Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.3 Asia Pacific Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Country
10.6.4 China
10.6.4.1 China Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.5 Japan
10.6.5.1 Japan Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.6 India
10.6.6.1 India Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.7 Australia
10.6.7.1 Australia Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7 LAMEA
10.7.1 LAMEA Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.3 LAMEA Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market, By Country
10.7.4 GCC
10.7.4.1 GCC Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.5 Africa
10.7.5.1 Africa Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.6 Brazil
10.7.6.1 Brazil Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
10.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11. Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1 23andMe
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 Global Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 Ancestry DNA
12.3 Genetic Technology (EasyDNA)
12.4 Color Genomics, Inc.
12.5 Helix OpCo LLC
12.6 IDENTIGENE, LLC/ DNA Diagnostics Center
12.7 Living DNA Ltd
12.8 MyHeritage Ltd
12.9 Prenetics Limited
12.10 Family Tree DNA
12.11 Interleukin Genetics/orig3n
12.12 Counsyl/Myriad Genetics, Inc.
12.13 Veritas Genetics
12.14 Fulgent Genomics