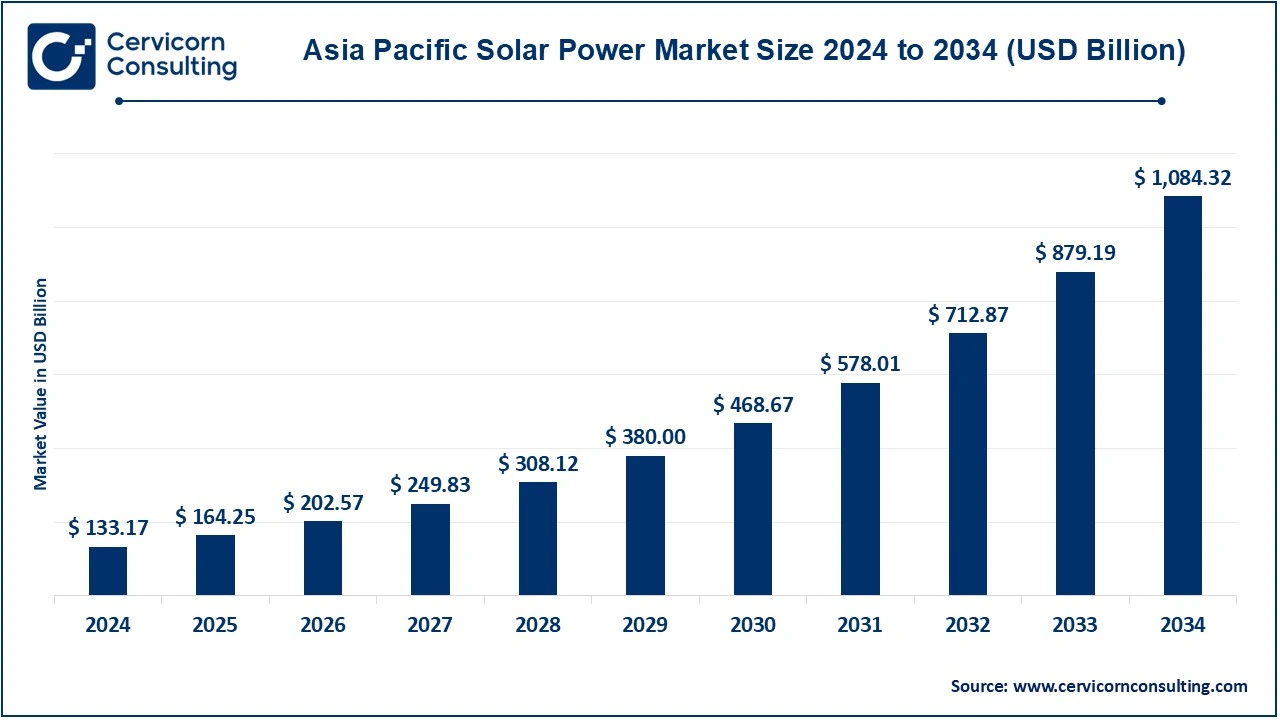
The Asia-Pacific solar power market size was valued at USD 133.17 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 1,084.32 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.31% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The solar power market is growing very fast due to the vast demand for renewable energy sources, driven by global concerns over climate change and the need for sustainable energy solutions. Key factors contributing to the growth include government incentives and subsidies, which promote solar energy adoption, as well as technological advancements that make solar power more efficient and affordable. Moreover, rising electricity prices and increased consumer awareness about environmental impact are further fueling the demand. Companies like First Solar, Tata Power Solar, and Adani Green Energy are capitalizing on these trends to expand their solar power capacities.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 164.25 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 1084.32 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 25.31% |
| Key Segments | Technology, Solar Module, Application |
| Key Companies | Trina Solar Limited, JinkoSolar, LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd., First Solar, Canadian Solar, Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd., JA Solar Technology Co., Ltd., Hanwha Q CELLS, REC Group, GCL-Poly Energy Holdings Limited, BYD Company Ltd., Sharp Corporation, Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd., LG Electronics, Suzlon Energy Limited |
Technological Innovation
Escalating Energy Prices
Electricity Demand Surge
Intermittency of Solar Energy
Grid Integration Challenges
High Initial Costs
Rural Electrification
Integration With Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Solar Microgrids
Intermittency of Solar Energy
Infrastructure Limitations
Land Scarcity for Large Projects
Solar Photovoltaic (PV): The solar PV segment has dominated the market with revenue share of 88% in 2024. Solar Photovoltaic (PV) technology dominates the Asia-Pacific solar power market due to its proficiency, cost-effective, and scalable set-up. Such PV systems use semiconductor materials to convert sunlight directly into electricity. In China, India, and Japan, PV systems are used widely for residential and commercial applications. Decreasing costs of PV modules, complemented with government incentives, have made solar power affordable and easily accessible. For instance, China has aggressively invested in PV technology and is the world's leading producer of solar panels, thus helping to push the region's market growth.
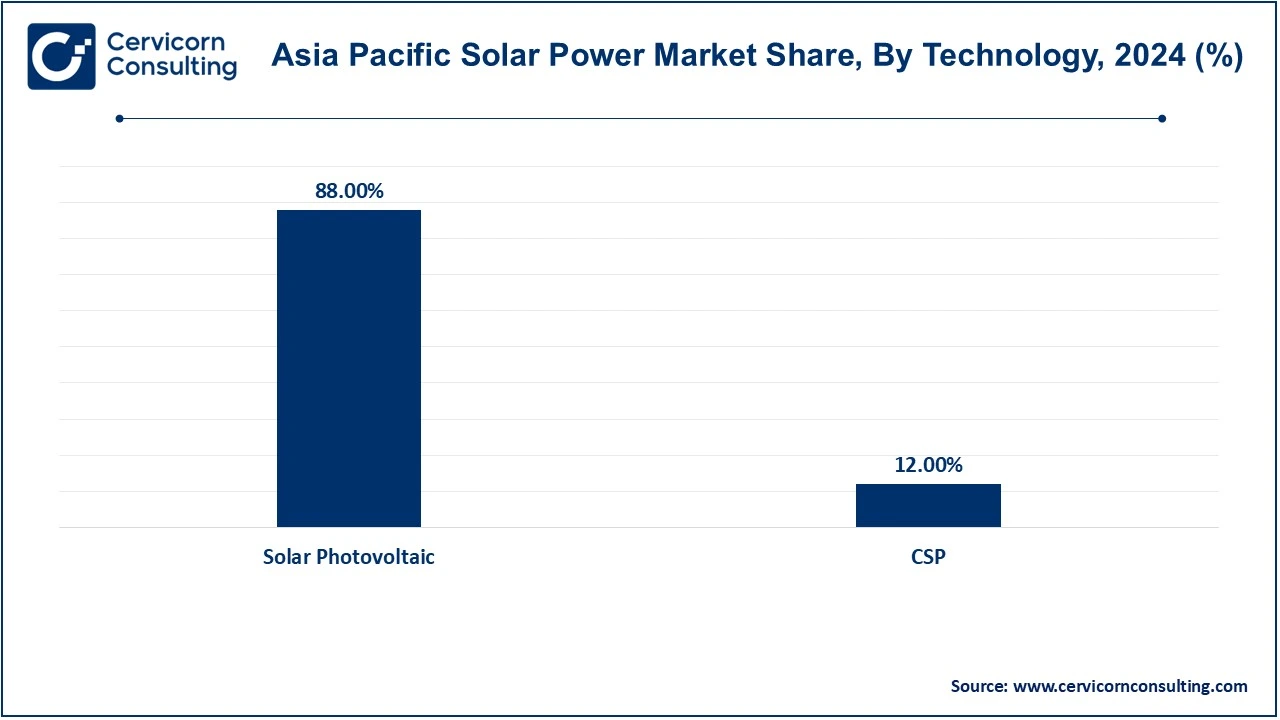
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): The CSP segment has captured revenue share of 12% in 2024. CSP technology utilizes mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area which uses the heat to drive a steam turbine for electricity generation. Though CSP is not as common as PV, it boasts a good potential for the APAC market especially in sun-rich regions like Australia and India. CSP stores heat in the form of energy and thus generates electricity even after sunset. This aspect of CSP makes it very suitable for large-scale solar power plants; one of the most well-known ones is the Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex in Morocco. While this will have its impact on ongoing initiatives in the region, it will change the outlook for CSP development.
Residential: Solar power generation, practically speaking, mostly happens in the residential sector through rooftop installations. Growing energy independence and the push for sustainability are making many residential solar systems supra appealing in some countries such as Australia, Japan, and India. Various incentives, subsidies, and net metering policies have made rooftop solar more affordable for homeowners. For instance, in Australia, rooftop solar is becoming more common, with over 2.5 million households having installed solar power systems. Residential solar power supplies clean energy at a lower price, thus greatly reducing dependence on the grid.
Non-residential: Non-residential solar power includes commercial, industrial, and institutional use. They are usually deployed for large-scale solar systems to meet the higher demands of energy units. This is being intertwined with the increased solar adoption in the Asia-Pacific, as businesses and industries seek to cut operational costs and attain their sustainability goals. An example is TATA Power of India, which has entered the commercial solar space with solar solutions for businesses. Countries such as Japan and South Korea are finally getting into solar in the commercial sector because, in such economic circumstances, expensive conventional energy sources make solar a feasible alternative.
Utility: Utility-scale solar power is major, large-scale solar farms which produce electricity for the grid. This sector of industry is growing rapidly within the Asian-Pacific region due to favorable governmental initiatives and increasing demand in Asia Pacific region for renewable energy, hence India, China and Australia, have developed large-sized projects, to meet their requirement as well as fulfill environment-oriented goals. India’s Bhadla Solar Park, the world’s largest solar park, exemplifies the potential of utility-scale solar projects. Utility-scale solar is increasingly seen as a reliable and cost-efficient solution to meet the energy needs of growing populations and industries across the region.
The new entrants in the solar power sector are employing technology to enhance energy efficiency, optimize performance, and reduce costs. By adopting advanced solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, integrated energy storage solutions, and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven grid management, these companies are positioning themselves as competitive players. For instance, newer players are utilizing cutting-edge solar panel manufacturing techniques, such as bifacial and tandem solar cells, to increase energy capture. Companies like Trina Solar and LONGi Green Energy are also exploring innovations in smart solar systems, incorporating IoT technology to monitor and optimize energy production in real-time. These technological advancements help them better meet the growing demand for clean and efficient energy solutions in regions like Asia-Pacific, where solar energy adoption is rapidly increasing.
CEO Statements
SunPower– Tom Werner, CEO
Ascent Solar– Jeffrey Max, CEO
Market Segmentation
By Technology
By Solar Module
By Application
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Solar Power
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Technology Overview
2.2.2 By Solar Module Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Technological Innovation
4.1.1.2 Escalating Energy Prices
4.1.1.3 Electricity Demand Surge
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Intermittency of Solar Energy
4.1.2.2 Grid Integration Challenges
4.1.2.3 High Initial Costs
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Intermittency of Solar Energy
4.1.3.2 Infrastructure Limitations
4.1.3.3 Land Scarcity for Large Projects
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Rural Electrification
4.1.4.2 Integration With Electric Vehicles (EVs)
4.1.4.3 Solar Microgrids
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Solar Power Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Solar Power Market, By Solar Module
6.1 Solar Power Market Snapshot, By Solar Module
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Monocrystalline Solar Panels
6.1.1.2 Polycrystalline Solar Panels
6.1.1.3 Thin-Film Solar Cells
6.1.1.4 Amorphous Silicon Solar Cell
6.1.1.5 Cadmium Telluride Solar Cell
6.1.1.6 Others
Chapter 7. Solar Power Market, By Technology
7.1 Solar Power Market Snapshot, By Technology
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Solar Photovoltaic
7.1.1.2 CSP
Chapter 8. Solar Power Market, By Application
8.1 Solar Power Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Residential
8.1.1.2 Non-Residential
8.1.1.3 Utility
Chapter 9. Solar Power Market, By APAC
9.1 Overview
9.2 Asia Pacific
9.2.1 Asia Pacific Solar Power Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.3 Asia Pacific Solar Power Market, By Country
9.2.4 China
9.2.4.1 China Solar Power Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.2.5 Japan
9.2.5.1 Japan Solar Power Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
9.2.6 India
9.2.6.1 India Solar Power Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.2.7 Australia
9.2.7.1 Australia Solar Power Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.2.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.2.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Solar Power Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 Trina Solar Limited
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 JinkoSolar
11.3 LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
11.4 First Solar
11.5 Canadian Solar
11.6 Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
11.7 JA Solar Technology Co., Ltd.
11.8 Hanwha Q CELLS
11.9 REC Group
11.10 GCL-Poly Energy Holdings Limited
11.11 BYD Company Ltd.
11.12 Sharp Corporation
11.13 Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd.