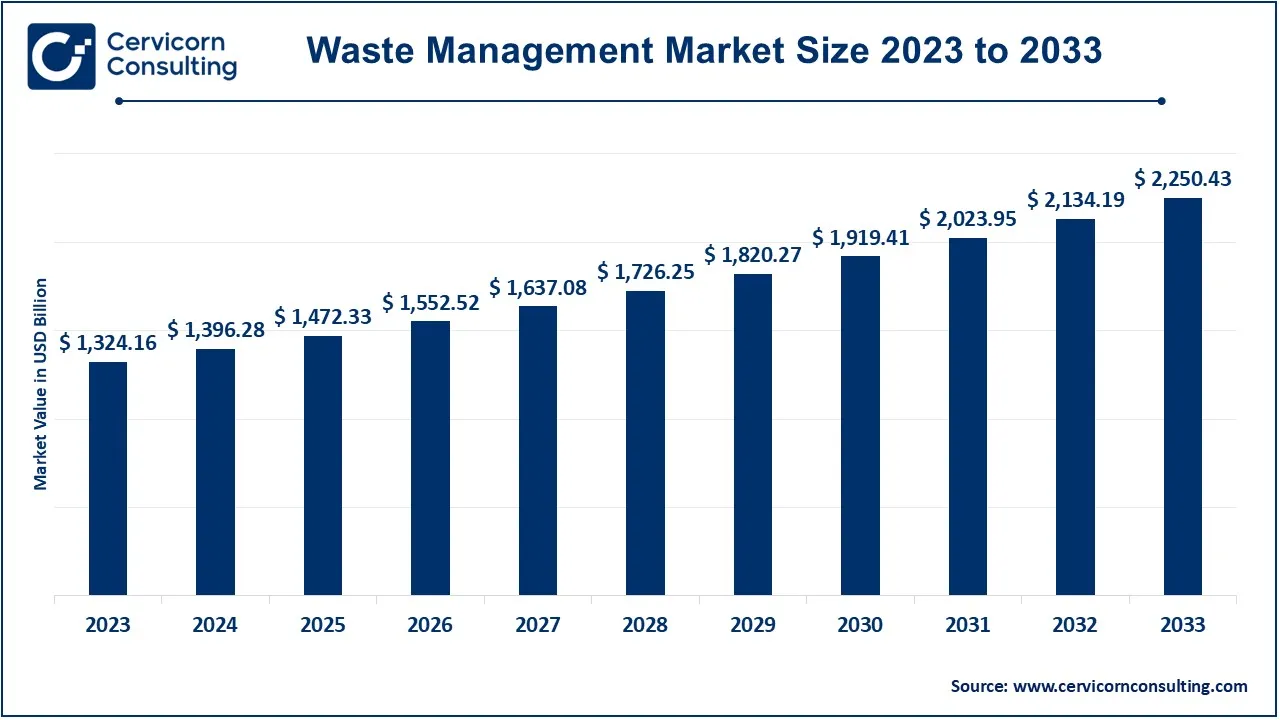
The global waste management market size was valued at USD 1,396.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 2,250.43 billion by 2033, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.44% from 2024 to 2033.
The waste management industry is expanding rapidly, driven by increased global waste generation and the need for sustainable solutions. Urbanization and industrialization are key contributors to the rise in waste volumes, creating demand for efficient waste collection, recycling, and disposal systems. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to tackle environmental pollution, which has encouraged the adoption of advanced waste management technologies. Regions like Asia-Pacific are witnessing significant growth due to population expansion and rapid industrial development. Countries such as India and China are focusing on improving their waste management infrastructure to handle rising waste levels. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are prioritizing circular economy models that emphasize recycling and resource recovery. The rise of smart waste management systems, including IoT-enabled solutions for tracking and optimizing waste collection, is also shaping the market. Waste Management (WM) company announced plans to invest USD 200 million in recycling infrastructure in 2022, totaling over USD 700 million since 2018. This investment aims to meet the rising demand for recycled materials and enhance recycling accessibility.
Waste management is the process of collecting, treating, and disposing of waste materials in a way that minimizes harm to the environment and public health. It involves various stages like segregation, recycling, composting, and safe disposal of non-recyclable waste. Waste can include household trash, industrial waste, electronic waste (e-waste), medical waste, and hazardous materials. Proper waste management is essential to reduce pollution, conserve resources, and protect ecosystems. Recycling helps transform waste into reusable materials, while composting turns organic waste into nutrient-rich fertilizer. Modern waste management systems also include technologies like waste-to-energy plants, where garbage is converted into electricity or fuel.
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1,472.33 Billion |
| Estimated Market Size (2033) | USD 2,250.43 Billion |
| Growth Rate (2024 to 2033) | 5.44% |
| Prime Region | North America |
| Fast-Developing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Waste Type, Service Type, End User, Region |
| Key Players | Waste Management Inc., Veolia Environnement S.A., Republic Services, Inc., Remondis AG & Co. Kg, Casella Waste Systems, Inc., Clean Harbors, Inc., Waste Connections, Inc., Covanta Holding Corporation, FCC Environment, Waste Industries, Renewi plc, Stericycle, Inc., Biffa Group Limited, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, China Everbright International Limited, URBASER, Daiseki Co., Ltd, Newater Technology, Inc., GFL Environmental Inc., Bingo Industries |
Increased Urbanization
Regulations Related to Waste Management
High Cost Associated with Waste Management
Implementation of Closed Loop Systems
Extended Producer Responsibility
Policies for Environmental Sustainability
Lack of Infrastructure for Recycling
Lack of Awareness
The waste management market is segmented into waste type, service type, end-user and region. Based on waste type, the market is classified into hazardous waste, E-waste, municipal waste, plastic waste, industrial waste, and others. Based on service type, the market is classified into collection, open dumping, incineration/combustion, landfill, and recycling. Based on end-user, the market is classified into residential, commercial, and industrial.
Industrial Waste: 9.2 billion tonnes of industrial waste is generated globally every year. These are wastes from industrial manufacturing processes, often a byproduct with no further use. They include everything from solid waste to chemical and liquid waste generated by factories, laboratories, construction sites engineering firms, mills, and plants. Growing industry and urbanization are two of the main causes of the increase in industrial waste production. Improper handling of industrial waste can harm plants and wildlife, as well as contaminate lakes and groundwater, hence it is essential to manage the industrial waste properly.
Hazardous Waste: Hazardous waste is toxic, corrosive, flammable, or reactive, and hence it poses a serious risk to both human health and the environment. It originates from many places, such as commercial endeavors, household goods, and industrial processes. To reduce risks and manage the waste effectively the waste must be identified and classified properly. Hazardous waste management is a critical environmental issue affecting public health, environmental sustainability, and the global economy. Proper handling, treatment, and disposal of hazardous waste is essential to prevent pollution, protect ecosystems, and safeguard human health.
E-Waste: E-waste or discarded electrical and electronic equipment poses significant environmental and health risks due to the toxic substances it contains. Recycling and disposal of e-waste properly is very essential for reducing the risk and guaranteeing sustainability. New and improved electronic products have been developed as a result of the rapid advancements in technology. The timely release of new electronic products and the need for updating of existing devices have led to an alarming increase in the generation of e-waste.
Municipal Waste: Solid or semi-solid commercial and residential waste produced in cities or other approved areas is referred to as municipal solid waste; treated biomedical waste is also included, however hazardous industrial waste is not considered as municipal waste. Globally, an estimated 2.01 billion tonnes of municipal solid waste (MSW) are produced each year.
Plastic Waste: Global production of plastic waste was estimated to be 367 million tonnes in 2020, and it is projected to grow significantly in the future. Reducing the initial generation of plastic waste is important, however, managing and disposing of the waste that has already been produced is equally important to address the plastic crisis. While preventing the generation of plastic waste overall is desirable, environmentally sound disposal of plastic waste once it is generated is essential to protect human health and the environment.
Others: The Others segment includes agricultural waste and organic waste. Agriculture, the backbone of our food supply chain, is also a significant waste generator. This category includes organic waste such as crop residues, animal manure, and agricultural byproducts. While some of this waste can be recycled as compost or biofuel, improper disposal methods can lead to soil degradation and water pollution. Organic waste is a broad term that includes all plant and animal materials that can decompose naturally. Food scraps, paper, yard waste, cardboard, and some kinds of plastic that are not harmful are included in this. Nutrient-rich soil is produced by composting organic waste that is suitable for planting new plants. Both the quality of the soil and the quantity of waste that ends up in landfills are improved by this process.
Collection: Collection is part of waste management that involves the transportation of waste from the point of use and disposal to the treatment point. Proper collection of solid waste is important for protecting public health, safety, and environmental quality. It is a labor-intensive activity that accounts for about three-quarters of the total cost of waste management.
Open Dumping: Open dumping being a cost-effective waste management option also has significant negative impacts on the environment and public health. Emissions such as dioxins, furans, mercury, and other hazardous substances, from the open dumpings, can lead to air, water, and soil pollution. Therefore, open dumping is prohibited in many places. An open dump is also defined as a landfill where solid waste is disposed of in a manner that does not protect the environment and can be openly burned.
Incineration/Combustion: Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves burning the substances contained in waste materials. Industrial waste incineration facilities are commonly referred to as waste incinerators. The waste streams that are commonly incinerated include municipal garbage, medical and infectious waste from medical facilities, sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants, hazardous waste streams from industrial processes, and materials from cleaning abandoned landfills.
Landfill: Disposing of waste in landfills reduces their impact on the environment and helps provide a sorting place for solid waste. Landfills have been around for quite some time, and their proven track record of effectively managing waste while minimizing risks to public health and the environment enables them to dominate the global market. The demand for composting and anaerobic digestion of waste is expected to grow significantly during the forecast period. The increasing emphasis on the use of waste-to-energy technologies is expected to help this segment gain more traction in the coming years.
Recycling: The process of turning waste materials into usable products is known as recycling. For creating new products, waste materials are first gathered, sorted, and then processed. Recycling helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the quantity of waste that ends up in landfills, and the use of natural resources. Recycling further helps in reducing the quantity of waste that ends up in landfills, which is one of the major sources of pollution. The landfills release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane, thereby contributing to climate change. Recycling helps to reduce this problem. Recycling is therefore an essential part of waste management since it helps conserve natural resources, reduces the amount of garbage that ends up in landfills and saves energy.
Industrial: The industrial segment has accounted revenue share of 69% in 2023. As the economy grows and industrial production increases, the generation of industrial waste is also increasing. Industrial waste generation is increasing in several sectors, including mining, construction, and manufacturing. Resource and waste recovery programs are becoming increasingly common across a variety of industries. These include efforts to reduce waste production, reuse materials, and recycle industrial byproducts. These initiatives could reduce waste management costs while making money from recycled materials.
Commercial: The commercial segment has generated revenue share of 22% in 2023.Rapidly increasing commercial activity and increasing use of commercial establishments make commercial waste the fastest-growing market segment. Rising consumer awareness about proper waste disposal and the adoption of corporate social responsibility initiatives by companies are also expected to help boost market growth in this segment in the long term.
Residential: The residential segment has captured revenue share of 9% in 2023. As the global population continues to grow, there are more households, increasing household waste. Increasing population density in cities and towns where households generate a lot of waste is a result of urbanization trends. Household waste management services need to be efficient. There has been an increased participation in household waste reduction and recycling programs due to the growing public awareness about recycling and environmental issues. Household waste management services are becoming more effective and efficient because of technologically advanced solutions such as smart waste collection systems and smartphone apps for scheduling pickups.
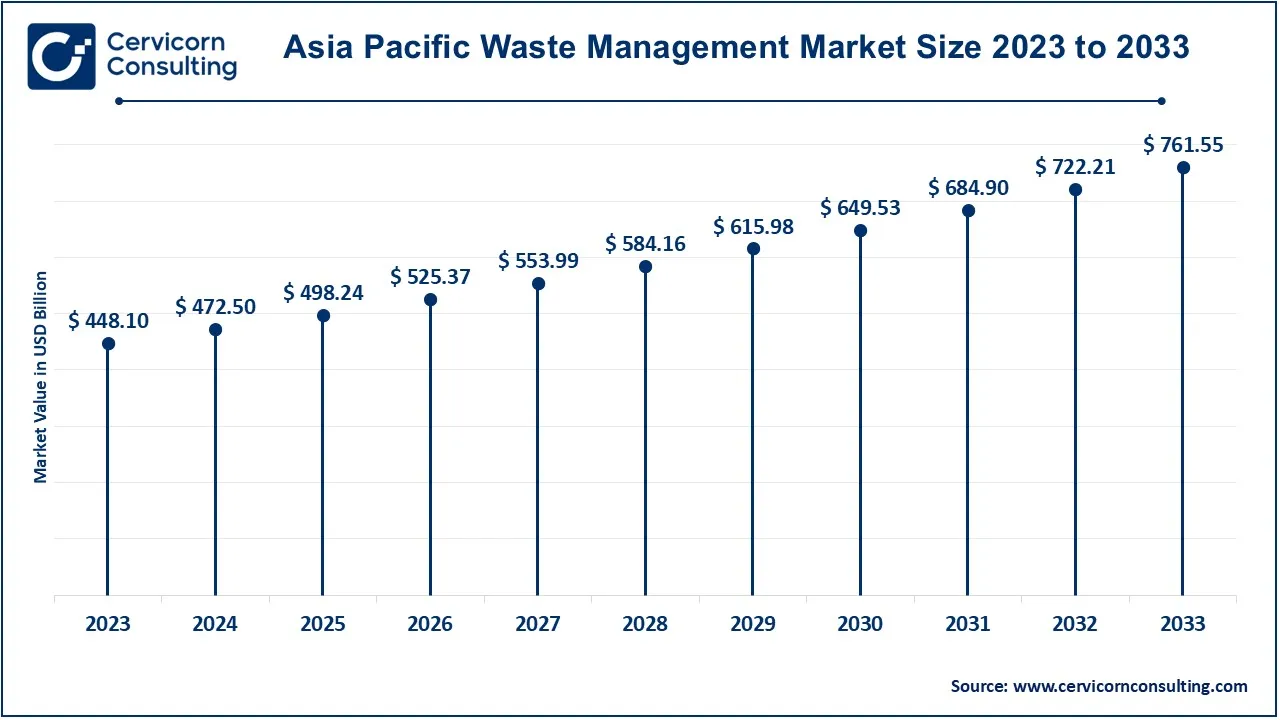
The Asia-Pacific waste management market size was accounted for USD 448.10 billion in 2023 and is predicted to surpass around USD 761.55 billion by 2033. As more and more people move from rural to urban areas across Asia Pacific, the amount of solid waste is projected to increase rapidly. Industrialization has increased urbanization in Asia Pacific through the migration of rural residents to urban areas and the expansion of towns into major cities.
The region's steady economic progress also provides customers in Asia Pacific with more money to spend, which has ultimately increased the demand for waste management services. The increasing understanding of the harmful environmental impacts of non-eco-friendly packaging such as plastic packaging and other plastic product components has significantly influenced the waste management business in this region.
The North America waste management market size was estimated at USD 324.95 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach around USD 552.26 billion by 2033. The North America market is driven by government regulations that require waste management across various industries and expanded infrastructure. The Resource Conservation and Recovery Act and the Waste Shipment Regulation are two government regulations that are expected to have a significant impact on the market. These regulations were enacted to improve service.
The Europe waste management market size was valued at USD 383.48 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 651.72 billion by 2033. Every year, the EU generates 2.2 billion tons of waste. More than a quarter of this is municipal waste: everyday garbage collected and treated by municipalities, mainly generated by households. Data shows that the amount of waste and the way it is managed varies greatly across EU countries, but there is a trend toward more recycling and less landfilling. To reduce waste and its impact on the environment, the EU has adopted ambitious recycling and landfilling targets and is working on packaging waste. The goal is to encourage the transition to a more sustainable model known as the circular economy.
The LAMEA waste management market was valued at USD 167.64 billion in 2023 and it is expanding to USD 284.90 billion by 2033. The LAMEA is growing due to significant urbanization and infrastructure development in the region which includes construction of buildings, roads, and other projects. This has in turn resulted in the generation of a significant amount of construction and demolition waste. The huge amount of waste generated and increasing environmental concerns towards waste recycling services are expected to boost the market growth in the region.
Moreover, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, and the UAE are among the countries with the highest amount of waste generation, which increases the adoption of waste management equipment and boosts the growth of the market. Moreover, the rise in residential and non-residential construction activities is promoting the use of waste management equipment in the construction industry. This factor is driving the growth of the market during the forecast period.
Many competitors in the smart waste management industry have chosen business expansion, agreements, acquisitions, and partnerships as their main development strategy to expand their service portfolio. In November 2023, Biffa Ltd, one of the leading companies in waste management, completed the acquisition of Hamilton Waste and Recycling Limited, currently the largest company in the UK providing construction and demolition waste services. In June 2023, Masterflex and REMONDIS entered into a partnership to build a circular economy for industrial products made of engineering plastics and implement it as an example in the hose and connection systems market.
CEO statements
Kevin Hull, CEO of Emergent Waste Solutions:
"We determined that if we're going to make an impact in this world, we've got to make being profitable (and) economically sustainable a part of the equation as well. And that's where we're unique in the whole field of environmental technologies."
Chris Gannon, President and CEO of 374Water Inc.:
"The economic and environmental benefits of waste destruction versus disposal are compelling, and our AirSCWO technology can bring these benefits to market at scale. This technology can deliver profoundly positive impacts to global water and waste management challenges for generations to come."
Key players in the waste management industry are pivotal in delivering a variety of innovative construction solutions, such as prefabrication techniques, sustainable materials, and advanced digital technologies. Some notable developments in the waste management sector include:
These advancements mark a notable expansion in the waste management market, driven by strategic acquisitions and innovative projects. The focus is on boosting sustainability, enhancing construction efficiency, and broadening product offerings to meet diverse building needs.
Market Segmentation
By Waste Type
By Service Type
By End-User
By Regions