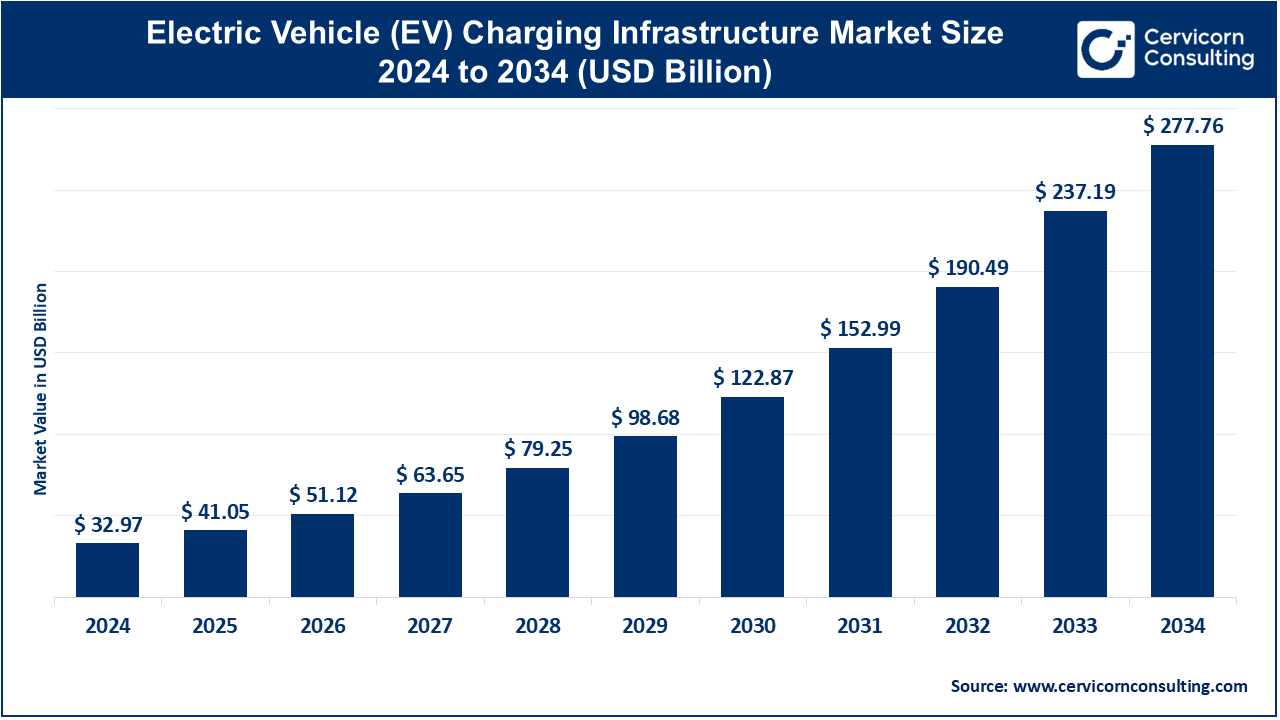
The global electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure market size was estimated at USD 32.97 billion in 2024 and is expected to surpass around USD 277.76 billion by 2034. It is growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.75% from 2025 to 2034.
The global electric vehicles (EV) charging infrastructure market has been experiencing significant growth due to the increasing demand for electric vehicles. Governments and private companies are investing heavily in expanding charging networks to support the adoption of EVs. The shift toward sustainable transportation, driven by environmental concerns and government incentives, has accelerated this growth. In addition, advancements in charging technology, such as fast-charging capabilities and wireless charging, are further enhancing the convenience of EV ownership. As EV sales continue to rise, the demand for charging stations is expected to increase, especially in urban areas and along major highways. The market is projected to grow at a strong pace, driven by the continued global push for reducing carbon emissions. India currently has approximately 200 electric vehicles per public charging point, highlighting the need for rapid expansion of charging infrastructure to support growing EV adoption.
EV charging infrastructure refers to the network of stations and devices that provide electricity to electric vehicles (EVs). This includes various types of chargers, from home chargers to public charging stations found in parking lots, highways, and commercial areas. The infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of EVs, as it ensures that electric vehicles can be charged conveniently and efficiently. EV chargers can vary in terms of charging speed, with Level 1 chargers being the slowest (using standard home outlets) and Level 3 chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, providing rapid charging for long trips. These charging stations are essential for reducing "range anxiety" and making electric vehicles a more practical option for everyday transportation.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size (2025 | USD 41.05 Billion |
| Market Size (2034) | USD 277.76 Billion |
| Projected CAGR | 23.75% |
| Largest Revenue Holder Region | Asia Pacific |
| Segments Covered | Charger Type, Application, Level, Installation Type, Deployment, Connector, Operation, Region |
| Top Companies | Tesla, Inc., ChargePoint, Inc., Blink Charging Co. ABB Ltd., BP Chargemaster, Siemens AG, EVgo Services LLC, Shell Recharge, Enel X, Electrify America, Daimler AG , Engie Schneider Electric, Greenlots (a Shell subsidiary), Eaton Corporation |
Regulatory Pressure
Corporate Sustainability Initiatives
High Initial Costs
Grid Capacity Limitations
Emerging Markets
Innovative Business Models
Interoperability Issues
Charging Speed Limitations
Fast: The fast charger segment has generated highest revenue share of 72.10% in 2024. The fast charging segment of the EV charging infrastructure market includes charging stations that are specifically designed for electric vehicles (EVs) to recharge within the shortest time possible. Often involving Level 3 Direct Current (DC) fast chargers, these telematics units are rated at power outputs range of 50 kW and 350 kW to cut down the charging time drastically in comparison to Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. Travel away from home for longer periods of time, are often fitted along roadways and within other facilities and deployment strategies, are called fast chargers.
Slow/Moderate: The slow charger segment has accounted revenue share of 27.90% in 2024. The implementation of slower charger/moderate charger segment of the market for electric vehicles (EVs) accessories infrastructure focuses on the provision of charging systems with less power ratings mainly level 1 and level 2 charging stations. While Level 1 chargers take the standard plugs used for household walls sockets and charge to extend ranges of 1-5 miles per hour ideal for per night house changed, Level two chargers are the fastest used for in houses/offices/public around 3-20 kW range which provides charge of approximately 10-30 miles range per hour. Such devices are also less expensive and more common but take relatively long to charge as compared to fast charge devices.
AC: The AC charging type segment has accounted revenue share of 40.90% in 2024. This segment of the market focuses on charging systems that employ Alternate Current (AC) power to recharge electric vehicles (EVs). These chargers are normally installed in Level 1 and Level 2 charging systems. In a charging process using AC, onboard the vehicle is an onboard charger which converts the alternating current (AC) of the mains to a direct current (DC) to let the vehicle’s battery to recharge. AC chargers are found in residences, offices, and public charging facilities; they provide moderate charging power. They are less expensive and easier to fix than DC fast chargers, ideal for use every day or overnight charging.
DC: The Direct Current (DC) charging peering market segment of EV charging infrastructure refers to charging systems which are high power and supply direct DC power to batteries without using onboard AC to DC converters. These chargers are also known as DC fast chargers or Level 3 chargers and they charge comparatively very fast charging speeds of 50kW-350kW capacities which enable EV to charge 80% of its battery in less than 30 minutes. Most of the DC chargers are located on highways, between public transportation sites, and businesses.
Fixed: The fixed installation segment has accounted highest revenue share in 2024. The fixed installation segment of the EV charging infrastructure market is comprised of dispensers that are installed and secured in a particular area, thus permanently affixed and functioning in nature. Such type of chargers enjoys widespread use at residences, offices, public parks, malls and gas stations along highways. Fixed installations consist of both AC Level 1 and Level 2 and DC fast chargers, depending on the installation site and the charging requirements. They are perfect for long term operations since they give stable and constant supply of electricity to electric vehicles (EVs).
Portable: The portable installation type segment has accounted revenue share of 23% in 2024. The portable installation segment of the EV charging infrastructure market incorporates chargers that are transportable and easy to carry for both vehicle owners and emergency purposes. These types of chargers are carried in small sizes so that the individual can plug it into a normal electricity socket (Level 1) or enhanced power source (Level 2) when required. Usual small portable chargers offer convenience to EV users who need a quick but temporary charging option especially in a place where there is no charging point. They are commonly used for towing services or for personal reserves.
CHAdeMO: The CHAdeMO connector segment has accounted highest revenue share in 2024. The CHAdeMO plug is a fast charging protocol and widely considered the first standardised connector in the charging infrastructure for electric vehicles (EV) targeted at high power DC charging systems. Developed in Japan, CHAdeMO which stands for CHAdeMO makes it possible to connect the battery of an electric vehicle to a power source and charge it in a range of power levels between 50 to 100 kW and future capabilities reach levels above 400 kW. It enables EVs to be charged to around 80 percent within half an hour. This specific connector is highly favoured by most Asian car manufacturers such as Nissan and Mitsubishi.
CCS: The CSS segment has accounted revenue share of 25% in 2024. The connector CCS (Combined Charging System) is one of the standards most commonly used in the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles and its main advantage is that it allows both standard AC and DC charging through one cable. Generally speaking, CCS connectors adopted in Europe and North America are high power DC fast charging capable connectors with power output range pitching in between 50kW and 350 kW assisting the electric vehicles to charge up to 80 % in 20 30 minutes. In this instance, the connector incorporates a regular Type 2 AC plug and two more DC pins for high power charging thus suiting slow medium and fast charging as well. Many major automobile manufacturers such as BMW, Volkswagen, and Ford support this connector type CCS which assists its growth expansion across the globe.
Others: The others segment has accounted revenue share of 33% in 2024. The section of the market for electric vehicle charging infrastructure referred to as ‘other connector’ comprises other standards of charging less prevalent than CHAdeMO and CCS. These include connectors such as that belonging to Tesla, which is used in the Tesla Supercharger, or the GB/T connector, which is prevalent in China. While Tesla’s connector enables both types of electrical charging delivering charging power at high levels, GB/T enables fast charging of Electric cars in China fitted with EVs. Furthermore, there exist some connectors which are in the trial stage or for specific regions or vehicle categories.
Level 1: Level 1 typically refers to the slowest mode of charge in the electric vehicles (EV) charging infrastructure and often employs a common standard wall 120V power supply in North America; 230V in most other regions. It ensures that power is supplied at a very slow tilt where overage charging within an hour range gives a maximum of about 2-5 miles. This kind of a charger does not need any sophisticated installation and hence is best suited for home use especially overnight where one can charge their vehicle. Nonetheless, the low speed makes going for any long-distance travel or using it for several days in a row rather impossible.
Level 2: Level 2 charging in the electric vehicle charging infrastructure market involves the charging of electric vehicles using 240V AC power in North America or 400V in Europe to provide maximum charge levels in less time compared to level 1 charging. Level 2 chargers typically deliver electric energy within a range of 3.3 kW to 22 kW typically giving a range of 10-60 miles of charging in an hour. These chargers are normally fitted in houses, offices and other public places like malls or even parking lots. They are relatively inexpensive, quite fast, and easy to use, thus they are suited for both private and semi-public charge applications.
Level 3: Level 3 charging is a DC fast charging station standard which connects the power source directly to the battery of the electric vehicle without going through any on-board charger. Level III charging generally requires an input in the range of 50 kW to over 350 kW allowing quick power delivery in a short time. Level 3 chargers are capable of charging an electric vehicle to about 80% within 20-30 minutes, thus making them fully support long distance journeys as well as located at bus terminals for easy access. These are mostly found in clusters or commercial buildings along highways or in travel centers. With the increasing growth of EV adoption, the market for such Level 3 Fast Charging infrastructural facilities is also increasing due to high demand for such fast& convenient charging facilities.
Non-connected Charging Stations: The non-connected charging stations mean those units that lack real-time network connection and sophisticated communication features. These stations are standalone units and do not require the use of any cloud-based systems or the internet. They are however able to perform the basic charging functions of delivery of power and charging sessions but will not be able to support remote management, payment systems, or any form of load control. Non-connected stations can however be proposed and installed in less cost and convenience than connected stations without functional guarantees of performance non-connected functional station. In this regard connected functional station provides better experience and management features.
Connected Charging Stations: Connected charging stations belonging to the EV charging infrastructure market are high-end units fitted with ainternet or any other networking device to provide an internet connection for the charging station thus creating a communication linkage between the charging station and the management system housed at the centre. Such stations can also be controlled from a distance so such functionalities as remote diagnostics, usage history, and management of loads can be exercised. They also incorporate a mobile app or an RFID card for payment transactions, user access management, and secured entry. Connected station systems can also work with smart grid systems and energy management systems to ensure maximization of charging functionality.
Mode 1: Mode 1 operation of the EV charging infrastructure market refers to a simplistic non-restrictive solution, which usually involves wheeling out a standard power socket from one’s home. When in this mode, an electric car (EV) is charged into a regular 120V or 230V wall socket without grounding, or rather, using the same idea as how household appliances are used. It supports slow charging – averagely 2-5 miles range has to be plugged in for an hour, and does not provide such important safety measures as, for example, compartment wiring, zoning ground fault, and overcurrent protection systems.
Mode 2: Mode 2 operation in the EV charging infrastructure market extends a little further to semi-regulated charging in which an electric vehicle (EV) is connected to a normal electrical socket via a special charging code with a built-in safety control unit. This box is essential because it has circuit protection, residual current circuit breakers, and overcurrent protection. Mode 2 charging considers 230V (European Union) or 120V (United States of America) power outlet, so it is average charging (7.4kW).
Mode 3: Mode 3 used in the context of electric vehicle charging infrastructure means a charging method, which is normally regulated, whereby the electric vehicle is cabled up to a dedicated charging unit using a fixed cable or plug. Here, safety is also guaranteed by an intermediary communication protocol that exists between the charging unit and the EV. It commonly runs on voltages of 230V (in Europe) or 120V (in North America) and integrates sophisticated communication networks within the vehicle and the station for power management, control and verification, and safety mechanisms.
Mode 4: Mode 4 operation in the EV charging infrastructure market indicates the extreme DC fast charging level whereby electric vehicles get direct current energy from a DC charging station. This method skips the Electric Vehicle AC-to-DC converter found in most cars, making it possible to charge a car at a speed of over 350KW. Fast Charging Equipment of Mode 4 is generally CCS or CHAdeMO fast charging standard equipment, and it is possible to charge the electric vehicle up to 80% within the range of 20 to 30 minutes.
Private: A private deployment of charging infrastructure for electric vehicles (EVs) is the placement of charging points for EVs within private premises such as residences, business entities, and office complexes. Such installations are for either unique or organizational use, offering dedicated and easy to access electric vehicle charging services in areas that are not open to the public. Private deployment usually includes Level 1 or Level 2 charging units which are more enhanced in terms of efficiency and safety. The increase in deployment of charging stations in this sector is as a result of the increasing rate of adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), government policies, and the need of the owners to have affordable individual charging solutions without frills.
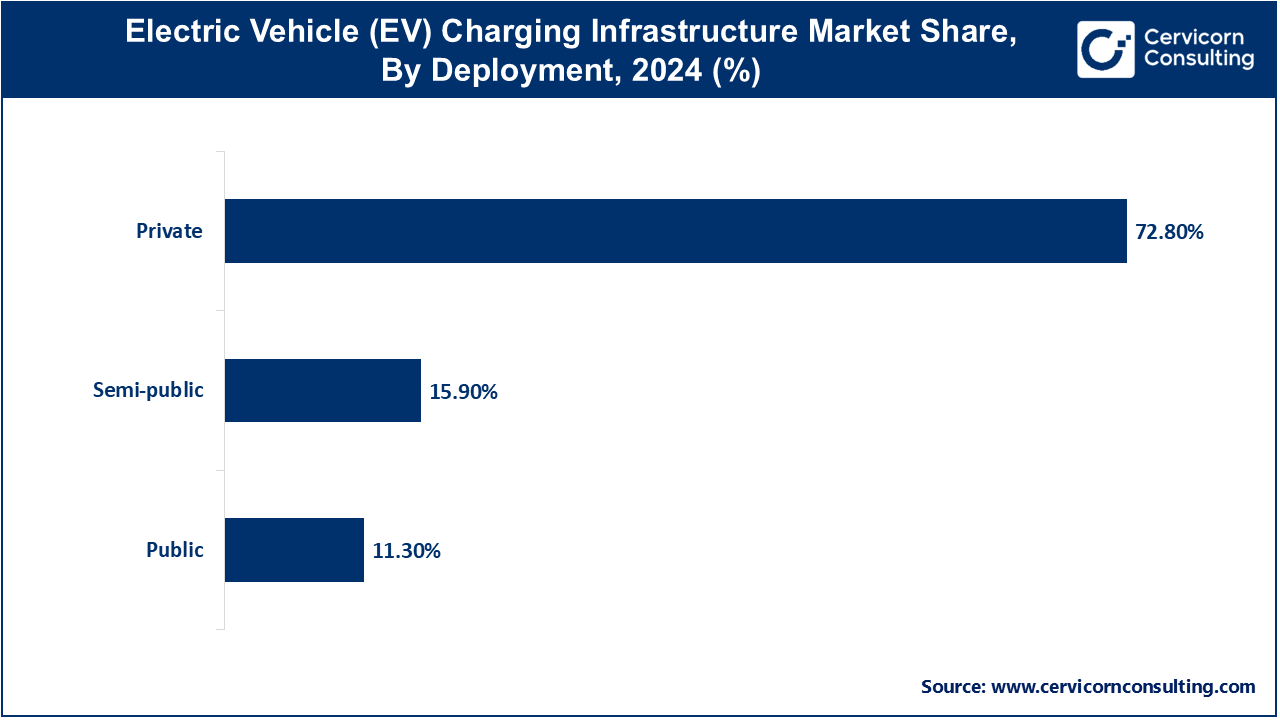
Semi-Public: The semi-public segment has accounted revenue share of 15.90% in 2024. Semi-public deployment of EV charging infrastructure refers to charging stations installed at locations that provide access to the general public, but which are also owned or operated by a non-public entity. In this case, charging stations may be found in many places like shopping malls, hotels, corporate buildings, and car park basements. Such stations provide service to some customers, employees, or visitors, who may not be permitted to the service without members’ or fees’ based acquisition. Semi-public deployments help in offering a plan that satisfies the residents while achieving their needs without hampering public interests.
Public: The public segment has accounted revenue share of 11.30% in 2024. Public deployment of EV charging infrastructure is described as installation of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations in places that can be found within the public reach like highways, city centers, parking areas, and bus stations. The stations are also made available to all EV owners and many of these charging networks are developed due to government funds or private investors. In public deployments, there are variations of available chargers that include Level 2 and DC fast chargers (level 3) as any long hauler or city user would find these very handy.
Commercial: The commercial segment has generated highest revenue share of in 2024. The commercial application of EV charging infrastructure pertains to the installation of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations in suitable business areas like retail shops, office premises, hotels, parking lots as well as fleet companies. These stations can serve customers, employees, or even commercial vehicle fleets in response to the increasing urban demand for EVs in buses and other businesses. Usually, commercial charging solutions encompass mixed types of Level 2 and DC fast electric car chargers in order to increase service speed and draw more customers. This benefits businesses through enhanced customers’ inflow in a sustainable manner.
Residential: The residential segment has accounted revenue share of 43% in 2024. Residential application of EV charging infrastructure implies the mounting of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations in private properties, commonly in cars’ garages, or on driveways. Such installations are mostly intended for personal use in charging of the EVs of the household. Such as standard (Level 1) which is the normal plug and more advanced 240V systems (Level 2). Residential charging brings both comfort and flexibility to the daily commute by allowing EV users to charge shoes overnight. With the rise of electric vehicles, the need for and hence, growth of residential charging solutions due to the availability of affordable and effective home charging systems to encourage eco-friendly transport is on the increase.
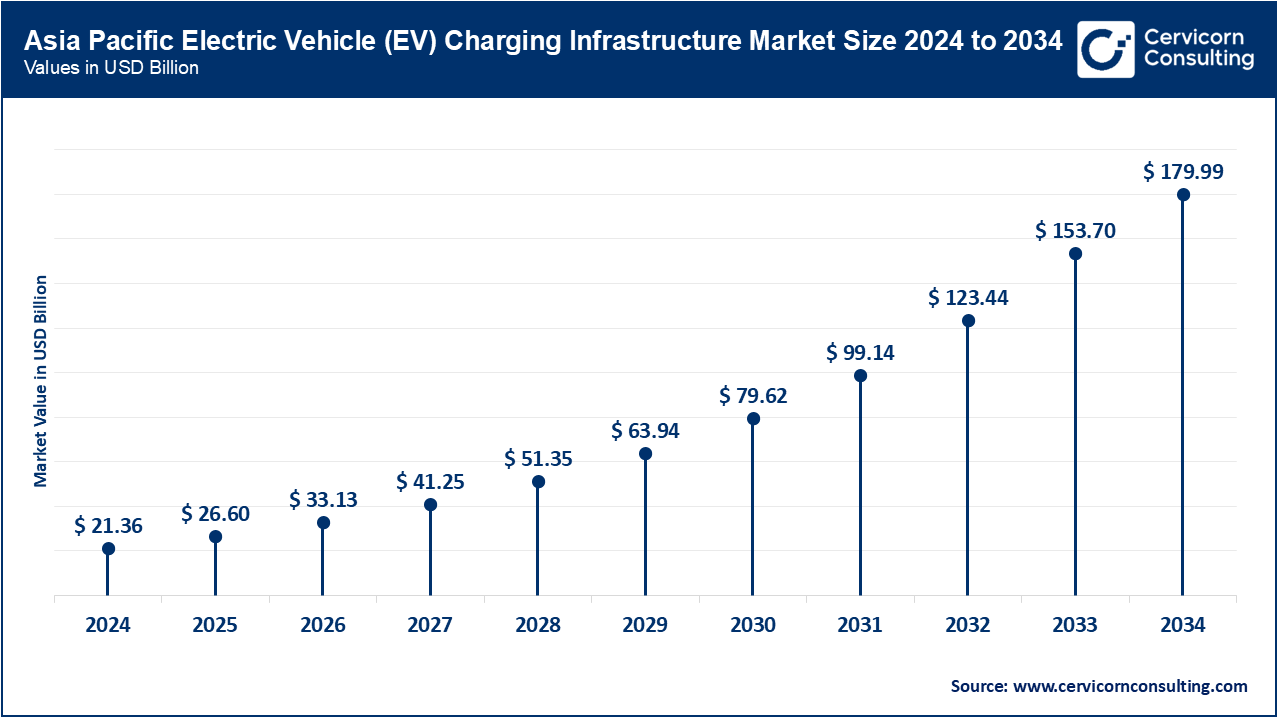
The Asia Pacific EV charging infrastructure market size was valued at USD 21.36 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to surpass around USD 179.99 billion by 2034 and expanding at a CAGR of 25.80% from 2025 to 2034. There is a significant surge in the growth of the EV charging infrastructure market in the Asia-Pacific region as electric vehicles are becoming popular in nations such as China, Japan, and South Korea. In particular, China is the primary market whose growth is aided by favorable government policies and investments in the development of public as well as private charging stations. The region is also working on creating a primary focus on fast charging infrastructure owing to the needs of the developing EV market. Other driving factors include urban development and ongoing smart city projects, which are leading to the erection of several charging stations in highly populated areas.
The Europe EV charging infrastructure market size was accounted for USD 4.42 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 37.22 billion by 2034. Europe is the most extensive area of the EV charging infrastructure market, owing to the enhanced measures put in place by the government such as tougher emission limits and policies made by the European Union on climate changes. For instance, in Germany, the Netherlands, and Norway extensive public and semi-public charging facilities have been installed. This area has also been advanced in the technologies of fast and ultra-fast charging in which public agencies and private sector have invested a lot of resources. On top of that, there is a growing inclination towards using renewable energy in charging stations, which is also in line with the vision of the continent.
The North America EV charging infrastructure market size was valued at USD 6 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 50.55 billion by 2034. North America hit notable growth in the market, primarily due to the immense government backing in the form of federal incentives and mandates aimed at directing every state to reduce carbon footprint levels. This is because the focus in the United States is purely on building a vast public charging network since a lot of funds are projectized under the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) initiatives. Furthermore, the existence of prominent automotive and technology firms is contributing to the advancement of charging technology. On the other hand, there is a growth of private and semi-private charging in the area, which also encouraged by their corporate’s sustainability strategies and as well as residential.
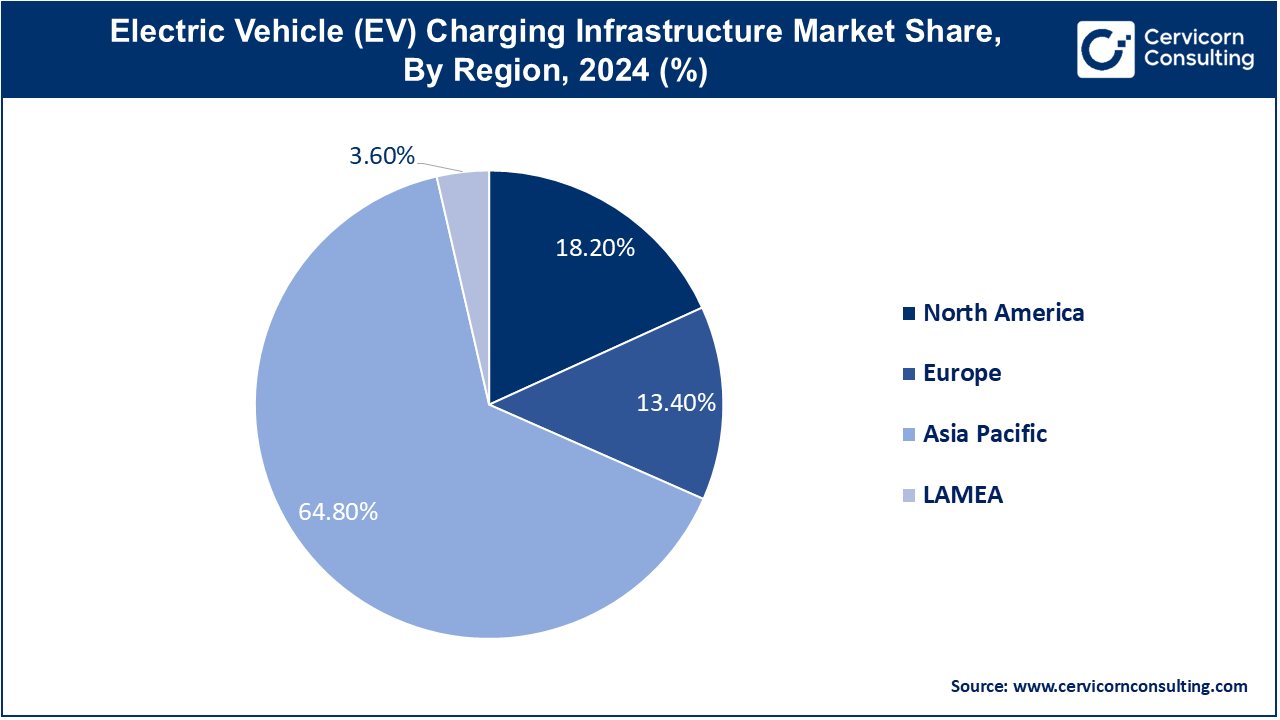
The LAMEA EV charging infrastructure market was valued at USD 1.19 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 10 billion by 2034. There are emerging markets for the EV charging infrastructure within LAMEA, where the market growth is mainly attributed to government initiatives and global investments. For the case of Latin America, it is Brazil and Chile that are at the forefront of electric vehicles in the region, therefore increasing the need for public charging facilities. LAMEA is showing interest in developing the EV market as well, with the exception of some areas like the UAE where it is being focused on more heavily. Nonetheless, the market is still depressed by issues such as low levels of EV adoption and poor grid systems but efforts are being made through specific programs and collaborations within the regions in question.
To turn up their innovative strategies towards charging infrastructure for the electric vehicles, new entrants such as Blink Charging Co. and Electrify America are achieving breakthroughs. While Blink Charging Co. is taking advantage of its own and existing public charging stations, Electrify America’s strategy emphasizes the establishment of a high-speed charging network across the country aimed at facilitating long haul journeys. Those who lead the charge include ChargePoint, Inc. and ABB Ltd. The ChargePoint solution is characterized by the ability to install many charging stations of varying power levels on the same destination in a very flexible manner. ABB sells a/k/a laminating and fastening systems and a/c systems with 3 phase supplies plus ancillary equipment. In addition, the responses claim that the companies partner and adopt other innovations such as incorporation of renewable energy resources and ultra-fast charging in order to improve their market share.
ChargePoint, Inc. – Pasquale Romano, CEO
“At ChargePoint, our mission is to deliver a seamless charging experience for every driver, everywhere. By expanding our network and investing in innovative technology, we are making EV charging more accessible and efficient, supporting the global shift towards sustainable transportation.”
Blink Charging Co. – Michael D. Farkas, CEO
“We are committed to accelerating the transition to electric vehicles by increasing the availability of our charging infrastructure. Our strategy involves deploying a comprehensive network of charging stations across key locations to provide convenient and reliable access for EV drivers.”
Electrify America – Giovanni Palazzo, CEO
“Electrify America is dedicated to building a robust and reliable network of fast chargers to support the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. Our focus is on innovation and expansion to ensure that our infrastructure meets the needs of EV owners nationwide.”
ABB Ltd. – Björn Rosengren, CEO
“ABB is driving the future of transportation with our advanced charging solutions. By integrating cutting-edge technology and sustainable practices, we are enhancing the efficiency of EV charging and supporting the global transition to cleaner energy sources.”
Shell Recharge – István Kapitány, EVP, Shell Retail
“Shell Recharge is at the forefront of transforming energy for mobility. We are investing in smart and scalable charging solutions that integrate seamlessly with our existing infrastructure, aiming to provide our customers with convenient and sustainable charging options.”
Enel X – Francesco Venturini, CEO
“Enel X is leading the way in smart and sustainable EV charging solutions. Our focus is on deploying innovative charging technologies and integrating them with renewable energy sources to provide a comprehensive and eco-friendly charging experience for all users.”
These CEO statements reflect a shared commitment to leveraging technology and personalized approaches in EV Charging Infrastructure, aiming to enhance employee health and productivity. Through innovation and comprehensive solutions, these key players are driving significant improvements in workplace well-being and performance.
Recent strategic partnerships and investments in the EV charging infrastructure reflect a strong commitment to advancing sustainable transportation. Key collaborations across Europe and South America are set to enhance charging networks, integrate innovative technologies, and expand the availability of renewable energy-powered charging solutions. Some notable examples of key developments in the EV Charging Infrastructure Market include:
These developments underscore a global drive to improve EV charging infrastructure through collaborative efforts and substantial investments. By addressing electrification challenges and expanding networks, these initiatives aim to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles and support a transition to cleaner, more efficient transportation system.
Market Segmentation
By Charger Type
By Application
By Level
By Charging Type
By Connector Type
By Installation Type
By Deployment
By Connectivity
By Operation
By Regional