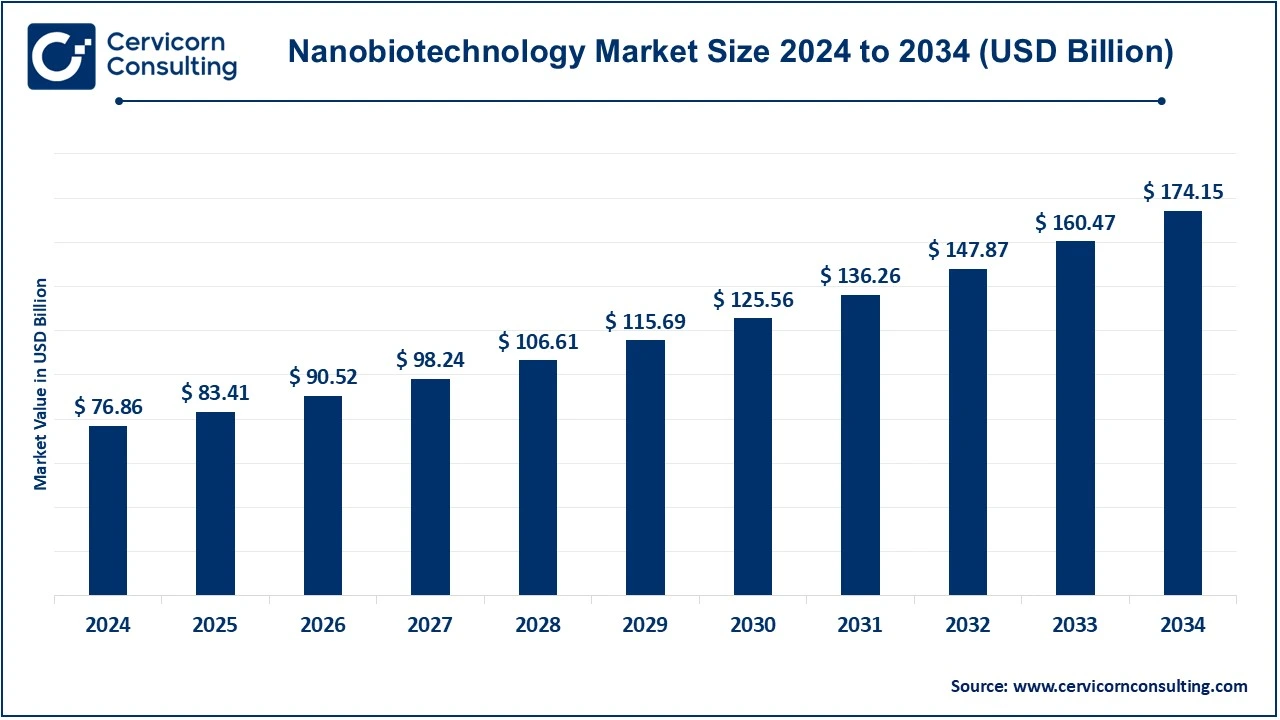
The global nanobiotechnology market size was valued at USD 76.86 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 174.15 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.5% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The nanobiotechnology market is fast-growing with the developments in advanced healthcare, electronics, energy, and materials science. Among the major drivers of these growths are greater demands for more efficient drug delivery systems, next-generation electronic devices, sustainable energy solutions, and innovations in manufacturing that are capable of making stronger, lighter, and more durable materials. Government investment and private sector research combine to accelerate the nanobiotech application's move into commercialization while growing awareness of a technology whose application can benefit in areas like environmental clean-up and food safety continue to build out the market.
Nanobiotechnology is an emerging interdisciplinary field of science, developed from nanobiotechnology and biotechnology, that delivers new applications at the nanoscale-from 1 to 100 nanometers-it generally involves manipulation and engineering of biological systems employing nanomaterials, nanoparticles, and nanodevices targeted at advanced fields such as medicine, diagnostics, drug delivery, environmental monitoring, and biosensors. In fact, adding nanoscale materials with specifically different biological properties mainly due to nanobiotechnology developments allows more specific, efficient, and targeted solutions in the health care sector as well as in agriculture and environmental sustainability.
CEO Statements
Xiuling Lu, CEO of Nami Therapeutics
"As we continue to explore the frontier of nanobiotechnology, we are witnessing its transformative potential to revolutionize medicine. Nanotechnology enables us to deliver therapeutics with unprecedented precision, enhancing the efficacy of treatments while minimizing side effects. At Nami Therapeutics, we are committed to harnessing the power of nanobiology to develop novel therapies that can address some of the most challenging diseases, ultimately improving patient outcomes and advancing healthcare globally.”
Mark Alles, CEO of Celgene Corporation
"At Celgene, we believe in the transformative potential of emerging technologies like nanobiotechnology, which holds promise for enhancing drug delivery systems, improving precision medicine, and advancing personalized treatments. Innovations in nanobiotechnology could ultimately lead to more effective therapies with fewer side effects, and we are committed to exploring these advancements as part of our ongoing efforts to revolutionize the treatment of serious diseases."
Jankowski, CEO of Nanophase Technologies Corporation
"At Nanophase Technologies, we are on the cutting edge of innovation, harnessing the power of nanotechnology to drive breakthroughs in nanobiotechnology. By integrating the precision of nanoscale materials with biological systems, we are opening new frontiers in medicine, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. Nanobiotechnology holds the potential to revolutionize drug delivery, diagnostics, and tissue engineering, offering highly targeted solutions that improve outcomes while minimizing side effects. As we continue to innovate, we remain committed to advancing the safe and responsible development of these technologies, unlocking new opportunities for human health and global well-being."
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 76.86 Billion |
| Estimated Market Size in 2034 | USD 174.15 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 8.52% |
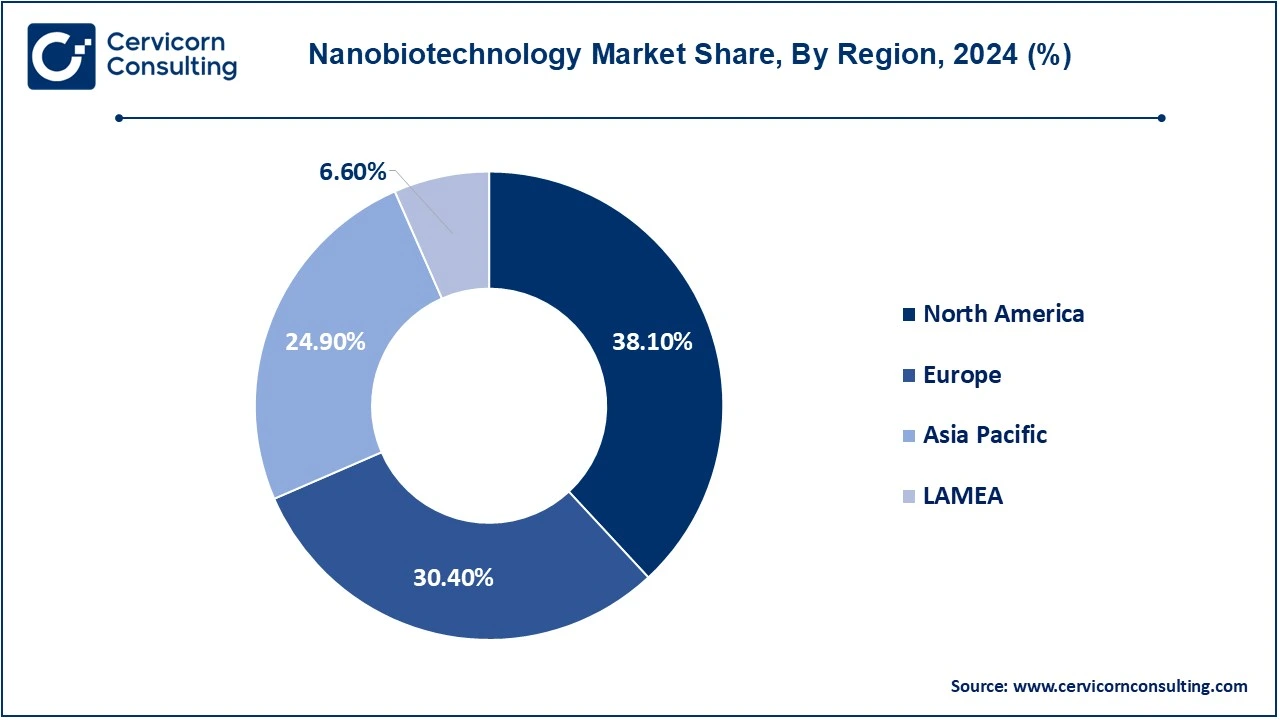
| High-impact Region | North America |
| Fast-Developing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Product, Type, Therapeutics, Technology, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Nami Therapeutics, Celgene Corporation, Nanophase Technologies Corporation, Sigma-Aldrich, Abbott Laboratories, Novartis AG, Ablynx, SkyePharma Pharmaceuticals, Nano Bridging Molecules SA, XanTecbioanalytics GmbH, Nanobiotix, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Riken Institute |
The nanobiotechnology market is segmented into product, type, therapeutics, technology, application, end user, and region. Based on product, the market is classified into nanomaterials, devices, and reagents. Based on type, the market is classified into 0-10 Nm and 10-100 Nm. Based on therapeutics, the market is classified into cancer, dental, cardiac, orthopaedic, others. Based on technology, the market is classified into nanocrystals, nanoparticles, liposomes, micelles, nanotubes, and others. Based on application, the market is classified into drug delivery, diagnostics, imaging, gene delivery, and tissue engineering. Based on end user, the market is classified into pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies, academic and research laboratories, and others.
Nano-materials: Nanomaterials are prepared at the nanoscale. The general features applied in their use include surface area, large reactivity, drug delivery, diagnostics, and tissue engineering. Among these, nanoparticles, nanorods, and nanowires have provided the essential material required for targeted therapy, improved bioavailability, and clearer diagnostics.
Devices: Those nanostructures are viewed as nanobiotechnology devices-biosensors, nanoscale delivery systems, and diagnostic tools. These devices rely on applications made by getting benefits from the unique properties of nanomaterials to enhance real-time monitoring as well as precise delivery and improved detection abilities.
Reagents: Reagents in nanobiotechnology represent chemicals or compounds used in laboratory tests, diagnostics, or therapy. Examples include nanoparticles, ligands, and enzymes that help facilitate the occurrence of specific reactions or molecular targeting for drug delivery, imaging, and diagnostics purposes.
Agriculture: Agriculture today fully relies on nanobiotechnology for crop protection, the elimination of pests, and high production of crops. Nanomaterials can be applied to provide effective delivery of pesticides by farmers and would minimize waste as well as pollution, which is otherwise adverse to the environment. Nanobiotechnology can also facilitate the release and supply of fertilizers and nutrients to plants only in the exact amounts required for their development and avoid resource waste. In addition, soil quality improvement through nanostructured materials enhances the resistance of plants to extreme environmental conditions. This, in turn, creates sustainable agricultural situations and thus food security.
Cancer Treatment: Nanobiotechnology has transformed targeted drug delivery in cancer treatment. The nanoparticles can even be fabricated to selectively target only cancerous cells such that chemotherapy or other therapeutic agents are directly delivered straight to the tumor. This targeted drug delivery system ensures that high concentrations of drugs reach the cancerous tissue without affecting the healthy cells, thus diluting side effects that follow traditional cancer treatments. Nanoparticles are also of great use in improving imaging and diagnostics so that cancer can be detected early and treatment results better monitored.
Diagnostics: Nanobiotechnology transforms medical diagnostics, mainly by facilitating the development of highly sensitive nanosensors and diagnostic devices. This allows biomarkers or pathogens to be identified at very low concentrations; hence, they can be diagnosed earlier and accurately. For example, nanoparticles can be functionalized in a way that they bind to specific markers of disease; the existence of these nanoparticles or their concentration can be measured by several techniques, including fluorescence or changes in optical behavior. This ability to detect disease at the molecular level forces earlier identification of infections, cancers, and other conditions; thus, early intervention reduces morbidity.
Drug Delivery: Improved drug delivery systems are amongst the most important breakthroughs of nanobiotechnology in that they enhance the accuracy and efficacy of drugs. Nanoparticles can encapsulate drugs and directly deliver them to targeted cells or tissues, including cancerous cells, thereby enhancing the efficacy of the drug by reducing damage to normal cells. Targeted delivery may also allow stepwise and controlled drug releases that may eventually have maximum therapeutic benefits with an accompanied reduction in toxicity. Nanocarriers include liposomes, dendrimers, nanoparticles, and many others; hence nanocarrier-based advancements enhance drug delivery where bioavailability is more improved, especially in diseases like cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
Environmental Monitoring: The application of nanobiotechnology impacts environmental monitoring because it utilizes high sensitivities, efficient, and cost-effective methods of identifying pollution through detection. Nanoparticles can be used in the detection of toxic contaminants in water, air, and soil that may contain dangerous metals, pesticides, and toxins. For instance, nanosensors can accurately detect traceable contents of pollutants in real-time and, therefore, allow a swift response to environmental hazards. Nanomaterials have been used to clean polluted places by the process of adsorption or neutralization of pollutants. In this regard, the use of nanobiotechnology helps in tracking one's health and in sustaining efforts aimed towards minimizing pollution and conserving ecosystems.
Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Companies: The companies are utilizing nanobiotechnology in drug delivery systems, diagnostics, and therapies developed using nanobiotechnology. While they improve designing drugs better, the nanomaterials do lie in aids to make the drugs effective, target-driven, and with minimum side effects.
Academic and research laboratories: Using nanobiotechnology, researchers engage in applications of experiments related to drug development, disease diagnosis, and genetic research. Handling nanoscale material allows scientists to make superb discoveries in the medical and biological sciences.
Nanobiotechnology Market Revenue Share, By End User, 2024 (%)
| End User | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Companies | 47.80% |
| Academic and Research Laboratories | 38.70% |
| Others | 13.50% |
Others: These include medical institutes, governmental organizations, and private agencies that employ nanobiotechnology as a tool for surveillance purposes, contaminant detections in food, or advanced biomaterials.
The nanobiotechnology market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
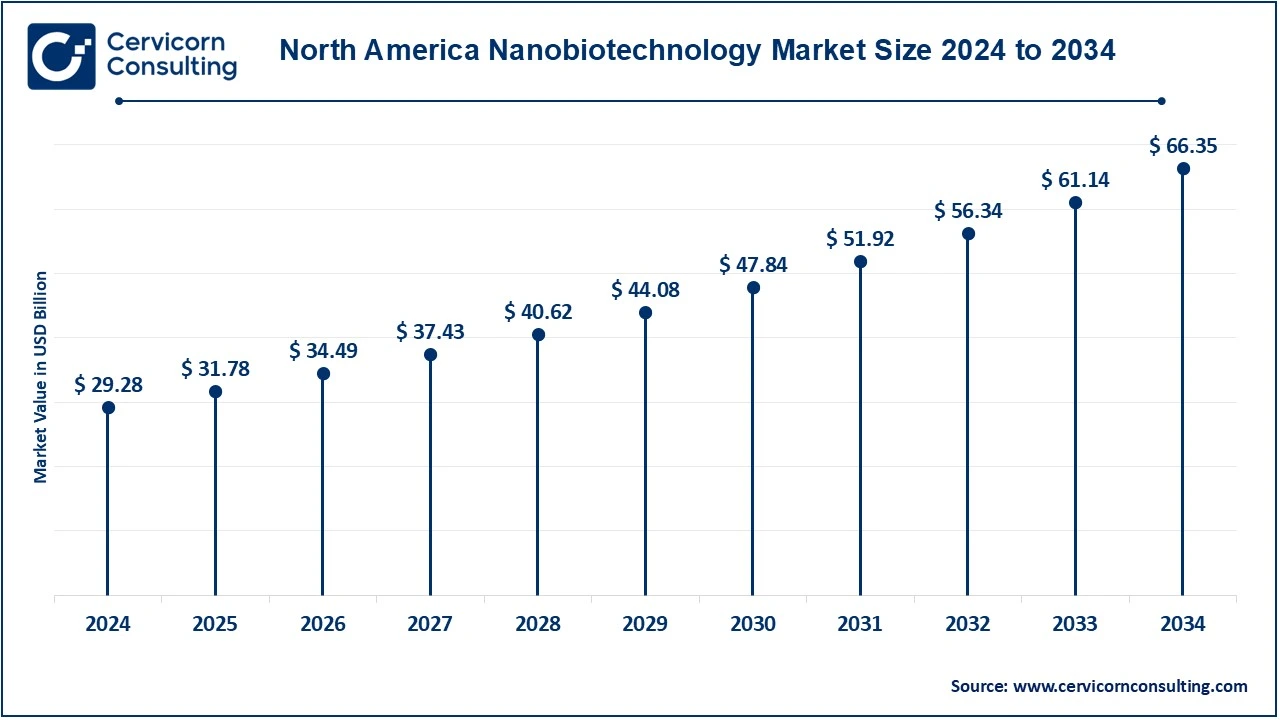
The North America nanobiotechnology market size was valued at USD 29.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 66.35 billion by 2034. North America hosts the United States as the greatest market player, due to its advanced research and development in biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and medical sectors. Canada is also a critical and growingly important contributor to nanobiotechnology innovations in agriculture and healthcare. For instance, Toronto is Canada's largest life sciences hub, with nearly 30,000 professionals in the biotech field contributing more than USD 2 billion to the local economy. Funding the sector also comes from the government in meaningful ways recently a USD 40 million investment from Ontario and USD 4 billion in global biomanufacturing investments are planned over the next three years. There is potential here in research, pharma, diagnostics, and medicine manufacturing this vibrant environment is the perfect place for education and biotechnology careers. Significant investment is made in scientific research, and leading industry players and academic institutions benefit from strong government funding and initiatives supporting nanobiotechnology efforts in the USA.
The Europe nanobiotechnology market size was estimated at USD 23.37 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 52.94 billion by 2034. Europe is a significant player in the market, inclusive of Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Switzerland, to name but a few. The point of fame concerning Germany happens to be its robust industrial base and superior research in pharmaceutical and health sectors. The U.K. These countries have invested quite heavily in drug-delivery nanobiotechnology and medical diagnostics. France has, meanwhile, biotech companies and research centers up to eyeballs working on nanomaterials and biotechnology. The European Union also propagates this sector through funding programs like Horizon Europe, collaborating with partners from various fields in research. For instance, nanobiotechnology is one of the key enabling technologies within Europe's push towards a knowledge-based economy. It encourages innovation in industry and academia. The European Commission has set nanobiotechnology leadership in line for major financial backing to projects that add value to European companies to become players in this high-growth global market. Investments are on scientific progress, economic value, responsible development, safety, and value delivered to society since nanobiotechnology triggers technological advances and economic growth.
The Asia-Pacific nanobiotechnology market size was accounted for USD 19.14 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 43.36 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region is likely to experience a very high growth rate, mainly due to China, Japan, India, and South Korea. Global leadership in nanobiotechnology research as well as production can be seen in China, which receives considerable support from the government and investments in the biotech as well as pharmaceutical sectors. The drug delivery systems and diagnostic tools have also had a long history of innovation in Japan. For instance, the nanotechnology market is growing due to an increased rate of adoption of nanobiotechnology in medical diagnostics and image processing, and technological advancement in nanobiotechnology devices. Additionally, government policy support, R&D funding, and expenditure increased by 2.6% in 2021 to 19.74 trillion yen. Self-powered nanobiotechnology devices will fuel the growth of the market. They would prefer to invest about 30 trillion yen in R&D of their own and a combined investment with the private sector to the tune of 120 trillion yen. India is in the process of becoming a hub for nanobiotechnology, with an area of focus being affordable healthcare solutions and the development of nanoscale materials for several medical applications. South Korea is also investing in nanobiotechnology research and commercialization, with a special focus on medical devices and biotechnology.
The LAMEA nanobiotechnology market was valued at USD 5.07 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 11.49 billion by 2034. The LAMEA region, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are still in the infancy stage when developing nanobiotechnology but are gradually seeing increased investments and research efforts. Latin American nations, for instance, have been upping their biotech research game, especially on agriculture and nanobiotechnological applications to the environment, across countries like Brazil and Mexico. For example, Israel has more than 80 companies engaged in nanobiotechnology, out of which 65 start-ups focus on nano-enabled innovations. Despite this development, Israel lags far behind China, which dominates 46% of the international market for nano-articles. Researchers from Tel Aviv University made a groundbreaking discovery by inventing a technique to grow ultra-long, ultra-narrow nanoribbons with semiconducting graphene properties. This ability to reproducibly manufacture hexagonal boron-nitride insulators can place Israel on the map in nanobiotech and can spur advancements in quantum computing and other realms. Advanced healthcare technology remains one focus of much in the Middle East, with Israel home to a high number of startups researching how best to apply nanobiotechnology to medicine. Nanobiotechnology will slowly be incorporated into the health and agriculture sectors of Africa by countries such as South Africa. Improved accessibility of medical treatments and productivity in agriculture remain the main objectives. In general, the market is still in its development stage, and problems like lack of funding, infrastructure, and regulatory framework define this region.
Recent product launches and innovations in the nanobiotechnology industry show very clearly a trend towards advancement at the cutting edge of advancement and strategic collaborations among the key players. These include giants such as Altair, NBX, Sanofi, Nami Therapeutics, Celgene Corporation, Nanophase Technologies, and Sigma-Aldrich leading respectively their niches: nanomedicine, drug delivery systems, and nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Such companies are using nanotechnology to find more effective, targeted drugs with fewer side effects, more advanced diagnostics, and innovative personalized medicine solutions. The company's emphasis on partnerships and mergers would accelerate the commercialization of leading-edge solutions, fueling further growth in the nanobiotech industry and its utility from drug discovery to therapeutics and diagnostics.
Some notable examples of the key developments in the Nanobiotechnology Market are:
Market Segmentation
By Product
By Type
By Therapeutics
By Technology
By Application
By End User
By Region