Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
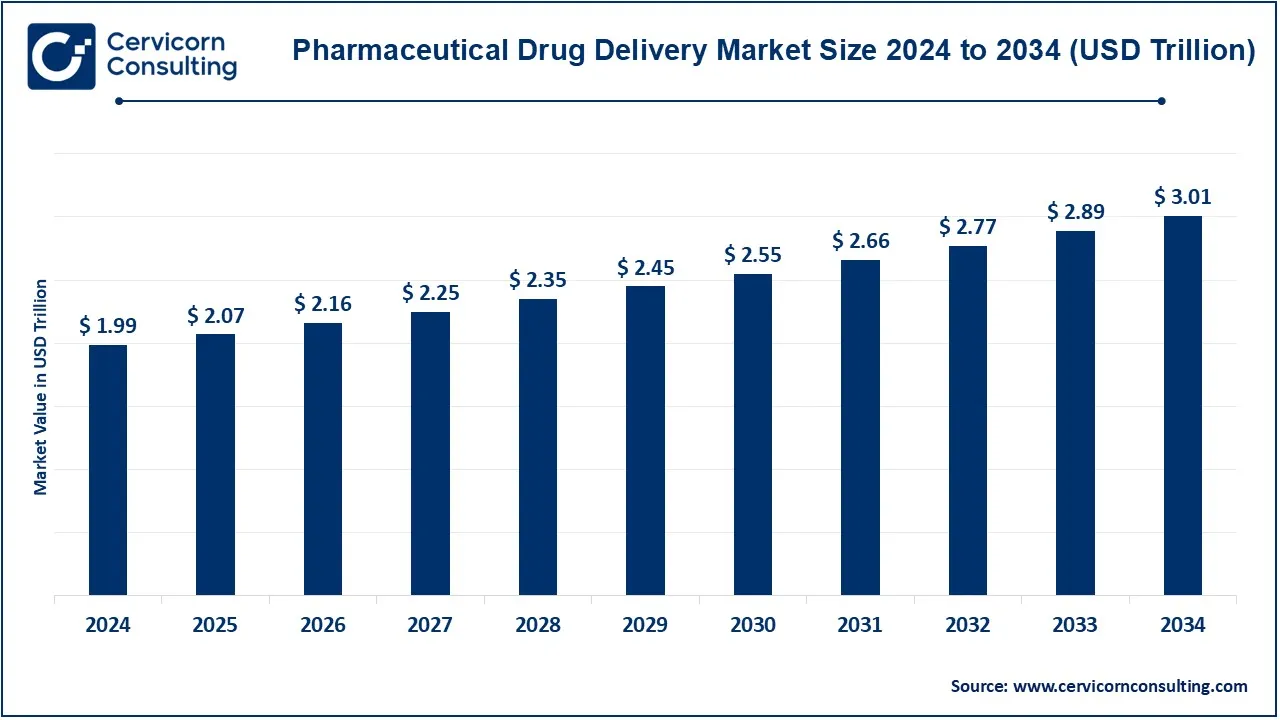
The global pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was valued at USD 1,993.22 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 3,011.50 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.24% from 2025 to 2034.
The pharmaceutical drug delivery market is expanding rapidly due to increasing demand for advanced treatments, rising chronic disease cases, and growing investments in research and development. Innovative drug delivery technologies, such as smart pills, implantable devices, and nanomedicine, are driving industry growth. Additionally, the shift towards patient-centric drug delivery solutions, including self-administered injections and wearable drug delivery devices, is boosting market demand. Regulatory approvals and the adoption of biologics further support the market's expansion.
Pharmaceutical drug delivery refers to the methods and technologies used to transport a drug into the body to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. It ensures that medications reach the right site in the body at the right time and in the right amount. Traditional drug delivery methods include oral tablets, injections, and topical creams. However, advancements in technology have led to innovative approaches such as nanotechnology-based drug carriers, controlled-release formulations, and targeted drug delivery systems. These modern techniques improve the effectiveness of drugs, reduce side effects, and enhance patient compliance. Drug delivery systems are crucial in treating chronic diseases like cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions by providing sustained and targeted medication release. The goal of pharmaceutical drug delivery is to optimize treatment outcomes, improve drug stability, and increase bioavailability while minimizing unwanted reactions.
Key Insights related to the Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery:
- Increased Adoption: The use of nanotechnology in drug delivery has improved drug efficacy by 40%-50% in clinical applications.
- Growing Investments: R&D spending in pharmaceutical drug delivery has increased by 20%-25% in the past five years.
- Chronic Disease Prevalence: Over 60% of the global population is affected by chronic diseases, boosting demand for advanced drug delivery methods.
- Biologic Drug Demand: The biologics segment in drug delivery is growing at a CAGR of over 10%, driven by personalized medicine.
- Technological Advancements: The market for smart drug delivery devices has seen a 30% increase in adoption due to patient-friendly innovations.
Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Report Highlights
- The U.S. pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was estimated at USD 621.88 billion in 2024.
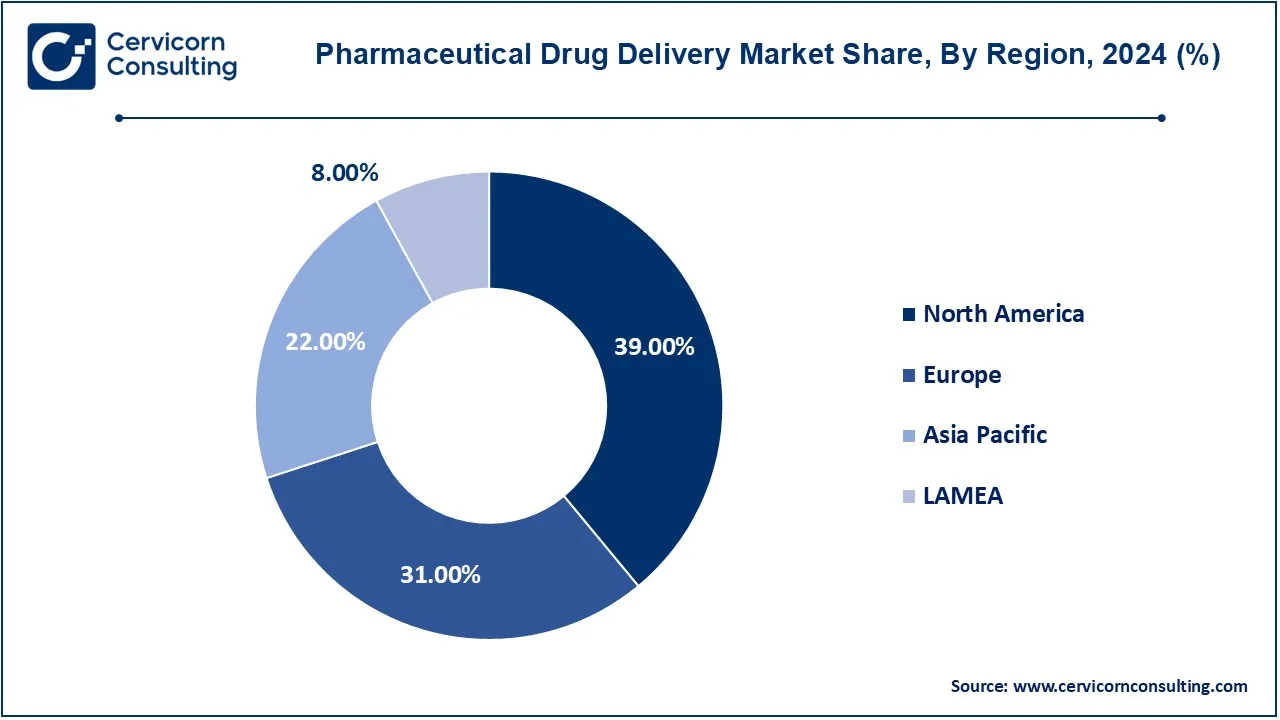
- North America region has lead the market in 2024 and recorded revenue share of 39%.
- Europe has recorded revenue share of 31% in 2024.
- By route of administration, the oral segment has dominated the market in 2024, however the topical segment is projected to hit a significant growth during the predicted timeframe.
- By application, the cancer companies segment has leading the market in 2024.
- By end user, the hospitals segment is expected to capture a significant market share during the forecast period.
Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Growth Factors
- Growing Pipeline for Biologics: There is a strong demand for advanced delivery systems that would maintain the efficacy and safety of the drug. With formulations such as injectables and European Union-targeted delivery systems, biological products necessitate special delivery solutions so as to ensure maximum absorption and efficiency. As more biologic drugs enter development, pharmaceutical companies are channeling their efforts into developing innovative modes of drug delivery that can accommodate these very complicated molecules, thus furthering expansion in drug delivery markets.
- An Emphasis on Patient Compliance: Patient compliance is extremely important to the success of treatment for chronic conditions; therefore, drug-delivery methods such as controlled-release formulations and transdermal patches may make dosing schedules easier for patients. Companies focus their investments on solutions that would minimize side effects, lower frequency of administration, or simply make a treatment more comfortable to adhere to. Once compliance is considered a factor for innovation, development would actually benefit further growth because healthcare providers and, of equal importance, patients are wanting any treatment that would deliver adherence to medication regimens.
- Health Infrastructure Development: Because the healthcare infrastructure is being markedly improved in developing regions, this lends the impetus for the respective new avenues for drug delivery systems. The very presence of such advanced treatment alternatives will bring the market to the reach of government subvention with superior health facilities. With the advancement of healthcare in emerging economies, the demand for modern drug-delivery systems will see a rise, consequently causing market growth resulting in a profit for larger patient populations.
- Innovation Regulatory Support for Drugs: Regulatory agencies are showing more confidence in supporting innovations in drug delivery systems that enhance drug efficacy and patient outcomes. The industry invests in accelerated approvals and supportive regulations of the innovations in drug delivery technologies. Such regulatory motivation aids to reduce the time taken for market entry into new systems while increasing patient access to cutting-edge therapies, which augments market growth for drug delivery systems.
- Cancer Prevalence Rise: The ongoing rise in global cancer incidence is creating demand for drug delivery solutions that are effective and targeted-action plans. Treatment of cancer requires highly precise delivery of drugs to prevalentally avoid damage to healthy cells, therefore targeted therapeutic drug delivery forms remain highly significant. Developing technological innovations like nanoparticles and ADCs promote better treatment outcomes. As the cancer incidence rises, such advanced drug delivery technologies are set to govern treatment modalities, hence thrusting growth in the pharmaceutical drug delivery market.
Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Trends
- Nanotechnology on the rise: Nanotechnology has revolutionized drug deliverance by enhancing precision and efficacious treatment. With the help of nanoparticles, drugs can be delivered to diseased cells or organs; drug wastage and side-effects on healthy tissues are minimal. This innovation is crucial for curing cancer and autoimmune diseases since targeted therapy improves the chances of patient recovery. The rising adoption of nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems is changing the face of pharmaceutical sciences by opening a new avenue for treating diseases.
- Rising interest in biodegradable polymers: The biodegradable nature of polymers in drug deliverance lends them to be sustainable and safe alternatives of natural degradation inside the body. Further, the use of such polymers promotes the controlled release of a drug over time and protects against toxicity while yielding a certain degree of patient safety. This technology is advantageous in hormone replacement therapies and pain management for chronic diseases. Biodegradable polymers in drug delivery systems are gaining popularity, buoyed by the rising awareness of environmental and patient health.
- Increasing self-administration: A largescale permitting of drug delivery systems including auto-injectors, inhalers, and small wearable devices for self-administration will facilitate home therapy for the management of chronic diseases. This will further support the traditional drive towards patient independence while lowering healthcare costs due to the requirement for continued disease control. Self-administration devices are designed for simplicity and efficiency, allowing the patient to follow a treatment regimen without requiring constant medical attention. Such trends undergird the ever-increasing demand for patient-centered health solutions, thereby further strengthening the drug delivery market.
- Growth of Oral Drug Delivery: Newer oral drug formulations seek to improve stability, absorption, and patient adherence. Oral drug delivery remains the preferred administration route as it is simply easy to use and, thus, for chronic conditions. Among the new formulations, for example, controlled-release tablets-have enabled constant therapeutic action and limited other doses that a drug might have taken under conventional dosage forms. This trend is propelled the increasing accent on patient comfort and compliance-up this line; drug companies have undertaken research activities into advanced oral drug delivery technologies, thereby reasserting the dominance of this method of delivery.
- Adoption of Smart Drug Delivery: Smart technonologies include implants with microchips that offer real-time monitoring and controlled release. This trend meets the requirements of precision in dosing and builds patient compliance, especially for long-term or chronic consecrations. Additional features that make drug delivery more patient-centric are to address just-in-time needs-based therapy. With the impetus of the digitalization of health care, smart drug delivery systems are expected to gain further momentum, offering novel platforms to improve patient care and reaffirm adherence.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 2.07 Trillion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 3.01 Trillion |
| Expected CAGR (2025 to 2034) |
4.24% |
| Flagship Region |
North America |
| Fast-Developing Region |
Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments |
Route of Administration, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies |
Novartis International AG, F.Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Pfizer Inc., Becton Dickinson & Company, GlaxoSmithKline PLC, Merck & Co Inc, Sanofi S.A., Bayer Medicine Products AG, 3M |
Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Dynamics
Drivers
- Growth of Chronic Diseases: The escalating worldwide incidence of chronic illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer has greatly increased drug delivery system devices. The treatment over periods that are in most cases years is imposition on the patient. It therefore follows that the need for advanced drug delivery technologies that increase drug efficacy and compliance is a key determinant in the administration of drugs. While these new-generation delivery systems enhance targeted administration, they reduce side effects and increase patient comfort. Taking into consideration the special needs posed by chronic conditions, companies will greatly increase the improvement of treatment outcomes that will drive growth in the drug delivery sector.
- Technological Advancements: Such as nanotechnology and target delivery systems, this field grew into a more exacting, efficient, and safer drug administration. Technology has made it increasingly easier for drugs to act to precisely target certain tissues or cells, minimizing side effects and enhancing range of applications. Coupled with the advances in biotechnology, these technologies now rapidly advance the development of new treatment modalities in biologics and personalized medicines that require special delivery methods. The rising adoption of advanced technologies drives the pharmaceutical companies to channel their R&D investments intodrug delivery, propelling rapid growth in the market.
- Emergence of Home Care Solutions: A surge of Homecare Solutions can be seen with the growing need for self-administered homecare drug delivery systems. Such systems include, among others, inhalers, transdermal patches, and auto-injectors patients can use. Treatment at home makes it possible for the patients to manage their conditions in their homes instead of going to the hospital, hence, reducing the costs incurred in healthcare. Devices for self-administration designed with safety and simplicity in mind get particularly useful when used by chronically ill patients, older persons, and those living in remote areas. This trend is encouraging the growth of the drug delivery market, and therefore companies are trying to come up with as many convenient home-based solutions as possible.
Restraints
- High development cost: Hefty costs involved in the development of advanced drug delivery systems including research, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals, renders the market inaccessible for many small companies. These high costs invariably lead to high-priced treatments, denying access to low-income parts of the world. Pharmaceutical companies undergo financial pressure to perform absolute sanity checks of innovation against affordability. Such tension is part and parcel of a wider hindrance to market accessibility. The development costs also affect profits that slow down the pace of innovation in drug delivery systems.
- Complexity of biologic delivery: Creating viable standards of biologic delivery is fraught with the greatest complexities due to the extremely delicate nature of biologics. The materials required are especially delicate and often most unstable. Storage, handling, and administration of the products are complicated-scalable. The complexity of delivering biologics may result in manufacturing costs and regulatory roadblocks that can render such treatments exceedingly expensive and difficult to produce at scale. Continued demand for biologics only hinders their accessibility into the market.
- Intellectual property hurdles: Patent protections and IPR often limit entry into the drug delivery market by new players. The established firms have extensive IP rights over various delivery technologies, a fact which curtails competition and slows innovation. Intellectual property barriers cause high licensing costs affecting small and emerging companies. Such barriers mean restricting and limiting the appearance of new and affordable drug delivery alternatives on the market.
Opportunity
- The demand is rising for biologics: The increasing occurrence of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders has triggered a demand for biologics such as monoclonal antibodies and gene therapy. Some opportunities lie in the development of drug delivery systems with biologics that are stable and capable of targeted delivery for maximum efficacy. Companies are now changing focus towards using advanced technologies such as liposomes and nanoparticles to address this issue while cashing in on personalized and precision medicine.
- Expansion of Injectable Drug Delivery: The rising global incidence of chronic conditions like diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis is boosting demand for injectable drug delivery systems, such as insulin pens and biologic injectors. These devices are convenient, accurate, and patient-friendly. Technological advancements, like prefilled syringes and auto-injectors, are adding further to compliance and safety. This growing reliance on injectable therapies represents a huge opportunity for manufacturers to provide innovative, user-centric delivery solutions for drugs that can be self-administered.
- Adoption of Smart Drug Delivery Systems: Smart drug delivery systems provide augmentations to human pharmaceuticals through IoT and wearable technologies. They make medication adherence tracking in real-time possible, dosage adjustments, and personalized treatment regimens that help patients follow their prescribed therapy. Examples like connected inhalers and smart patches are offering valuable data insights to both patients and healthcare providers. As digital health and patient-centric care solutions continue to grow in popularity, their adoption is steadily increasing over time.
Challenges
- Maintaining Drug Stability: Drug stability is defined as the maintaining of the drug balance. That has become an unrelenting challenge facing the world of drug delivery, particularly for advanced delivery systems such as injectables and implants. If this were not to happen, loss of efficacy and risk to safety arise, consequently inviting additional costs in storage and preservation solutions. The companies must develop delivery systems that keep drug integrity for long periods of time, especially when it comes to biologics that are sensitive to the slightest ecosystems of environmental factors. This is a key hurdle faced in relation to advanced drug delivery solutions since drug instability can hinder improved patient results and market acceptance process.
- Side effects: Side effects of any route of drug delivery, particularly invasively delivered drugs that come with a major concentration within the body, can act as discouragement to treatment. The same deters patients from completing their treatment regimens, which impairs overall efficacy and hackles the logistics of drug delivery.Aimed at balancing therapeutic efficacy with reduced side effects, patient comfort, and compliance, companies worldwide direct considerable time and effort into evolving systems to combat such issues. This has proven indispensable in boosting compliance with treatment.
- Interfacing with Digital Health: The interfacing of digital health platforms with drug delivery systems presents both positive opportunities and its own quandary. Aligning drug delivery with telemedicine and health monitoring platforms calls for a great deal of technological infrastructure and interoperability. Another challenge for ensuring the integration of digital health is secure data exchange and protection of patient privacy. This challenge is especially pertinent as digital health is coming into existence; companies will have to be certain that their drug delivery systems are interfaced in a manner that continues to comply with digital standards, risking patient confidentiality and compromising data integrity.
Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Segmental Analysis
The pharmaceutical drug delivery m arket is segmented into route of administration, application, end user and region. Based on application, the market is classified into infectious diseases, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory diseases, central nervous system disorders, autoimmune diseases and others. Based on route of administration, the market is classified into oral drug delivery, injectable drug delivery, self injection devices, topical & transdermal drug delivery, ocular drug delivery, pulmonary drug delivery, nasal drug delivery, transmucosal drug delivery, implantable drug delivery. Based on end user, the market is classified into hospitals, ambulatory surgery centers, home care settings, diagnostic centers and others.
Application Analysis
Infectious diseases: Drug delivery systems to fight infectious diseases strive to achieve efficacy in the eradication of infection while guarding against resistance-building mechanisms. Contact delivery routes include but are not limited to novel mechanisms for delivering orally, injectables, or inhalational forms of antibiotics, antivirals, and vaccines. Nanomedicine and various other technologies and approaches that are emerging, allow for the maximum utilization of drug delivery systems and remarkable immune response enhancement, which indicates the lack to potential treat diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV and COVID-19.
Cancer: Cancer drug delivery is focused on targeted therapies wherein nanoparticles and antibody-drug conjugates deliver chemotherapy or immunotherapy directly to tumors, ideally sparing healthy cells. Recent innovations in intravenous and transdermal systems provide extensive support for targeting, intended to ameliorate patient outcomes, combat side effects, and overcome challenges such as the development of drug resistance by tumors. This segment is undergoing a sea change conferred by precision medicine advances toward assuring therapeutic effectiveness and personalization.
Cardiovascular diseases: Cardiovascular drug delivery has in view the enhancement of bioavailability and controlled release of medicines like antihypertensives, anticoagulants, and statins. These systems include transdermal patches and controlled-release capsules, providing steady blood levels of a medicine in addition to improved patient compliance. Other approaches include brainstorming about nanoparticle-mediated delivery systems that might make a remarkable contribution, clinically enhancing the effectiveness of treatments or even decreasing required doses to respond to the high global burden associated with cardiovascular diseases.
Diabetes: Diabetes drug delivery encompasses sustained-release insulin preparations, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and antidiabetic agents with routes that involve injectables, transdermal patches, and inhalable systems. Drug delivery systems in alliance with continuous glucose monitoring recently brought tremendous advancements in the management of diabetes. The newer payloads are geared toward dispensing and administering drug therapy in new ways that are more user-friendly and patient-centric, thereby impacting the quality of life.
Respiratory Diseases: With regards to the treatment systems of respiratory diseases, the inhalation route is intended to improve the delivery of lung bronchodilators, corticosteroids and biologics to the lungs due to their local action in the lungs. Metered dose inhalers, dry powder inhaler and nebulizers have made it possible to target areas of diseases as with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations due to cystic fibrosis and its relief of the white mucus plugs of the bronchi. That, in turn, has fueled the impetus for increasing research into innovation for sustainable lung efficacy and reduced systemic exposure in patient medicine of new delivery systems for chronic respiratory diseases.
Central Nervous System Disorders: Drug delivery for CNS disorders addresses the challenge of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), presenting numerous inventive means of delivery using, for example, intranasal, liposome, and nanoparticle carriers needed for conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and epilepsy. Effective delivery is essential to treatment in neurologic disorders, as such, major regimens must achieve targeted superusefulness to mitigate side effects. Drug delivery enhancement for this route often explains advances obtained in conditions through BBB.
Autoimmune Diseases: The next generation of drug delivery systems for autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus directs the delivery of immunosuppressants and biologics to the targeted site. These include innovations in injectables, transdermal patches, and sustained-release formulations, making them crucial to initiating an immune-modulation response and reducing the frequency and intensity of side effects associated with these treatments. Targeted delivery approaches are thus vital in this area because they enhance the effective therapy while minimizing effects on surrounding, healthy tissues, overcoming chronicity and compliance issues in the management of autoimmune diseases.
Others: This segment covers less common conditions that still require specialized drug delivery solutions, such as metabolic, genetic, and hormonal disorders. These delivery systems may include implants, infusion pumps, or controlled-release oral formulations tailored for long-term management and optimized dosing. The “Others” segment is driven by the need for patient-centered solutions that offer consistent medication delivery with minimal side effects, addressing a variety of chronic and rare diseases.
End User Analysis
Hospitals: The major consumers of advanced drug delivery systems in critical areas such as critical care, oncology, and surgery. In such a situation, precisely controlled administration is executive in intravenous, injectable, and implantable drug delivery solutions, thought to administrate in most inpatient settings by infusion pumps and other devices. The drivers for reliability and safe drug delivery in hospitals see considerable innovation in controlled-release systems and smart devices, most relevant for improving patient outcomes, acute and special care.
Ambulatory Surgery Centers/Clinics: These institutions might also use available portable drug delivery systems and others with good recovery times, transdermal patches, and autoinjectors. More procedures are being performed in outpatient facilities ACC drug delivery solutions emphasize safety, usability, and rapid onset of action. Clinics act in their patients' best interests by demanding systems that give optimum performance and minimally invasive methods of treatment so the patient can return as soon as possible.
Home Care Settings: Drug delivery systems for home care focus on self-administration via inhalers, transdermal patches, and wearable infusion devices for diabetes and respiratory disease patients. The increased scope of the home care market is indicative of the patients' preferences for convenience and independence in systems that are easy to use and safe enough even outside clinical settings. All services are continuously moving the treatments to home settings; hence, user-friendly and effective drug delivery technology innovations are getting of the utmost importance.
Diagnostic Centers: This industry supplies drugs for administering contrast agents during imaging and radio-pharmaceuticals for diagnostic purposes. Among such drug delivery systems are those that may provide precise dosing and controlled release, with intravenous and injectable routes allowed in attaining the diagnostic agents at the precise area for clear imaging results. Drug delivery in the diagnostic centres must emphasise accuracy, speed, and comfort for the patient, leading to clear diagnoses and minimised side effects or risks with the diagnostic test.
Others: This segment includes home care setting configurations of rehabilitation, palliative care, and specialty-clinic types of care. Such entities would demand drug delivery systems that will provide chronic disease management, pain relief, and specialization therapy. The emphasis is on adaptable patient-centered delivery methods, such as long-acting injectables, implants, and infusion systems that could address different healthcare needs in diverse service environments outside traditional methods of care, i.e., hospital or outpatient care.
Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Regional Analysis
The pharmaceutical drug delivery market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). The North America has dominated the market in 2024.
Why is North America dominating in pharmaceutical drug delivery market?
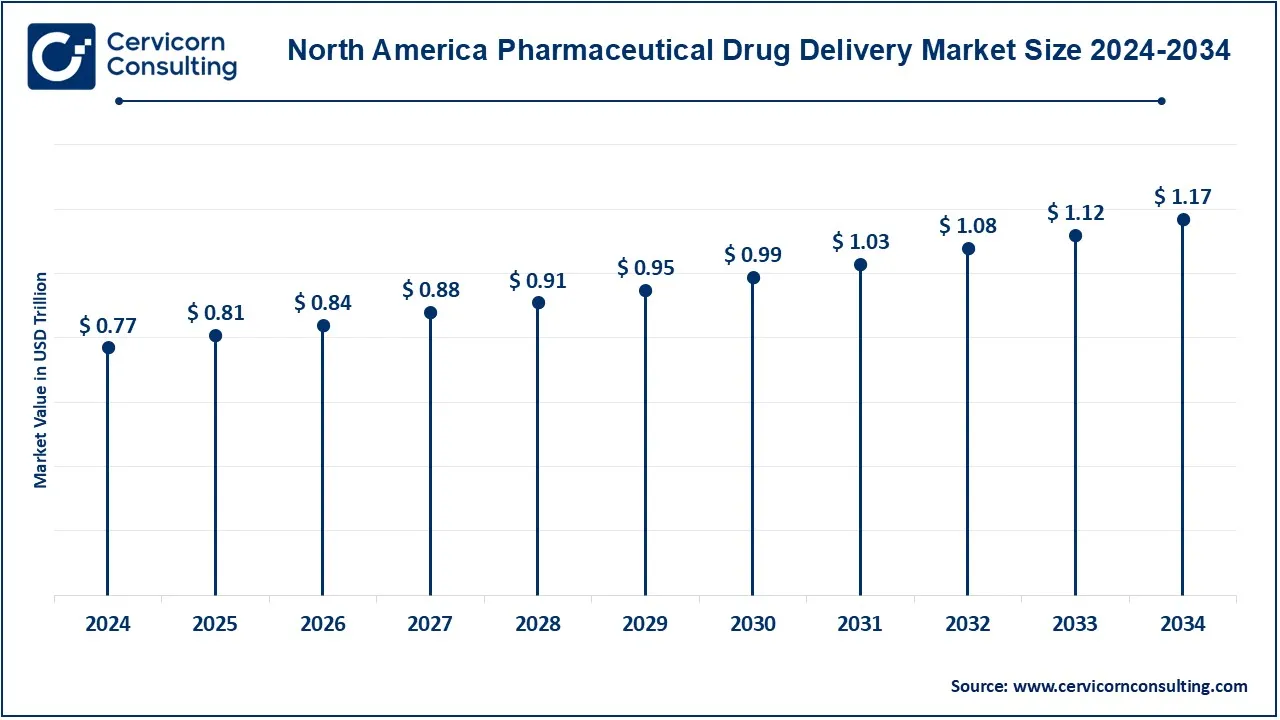
The North America pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was valued at USD 777.36 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 1,474.49 billion by 2034. This is the region under the leadership of the United States and Canada, which controls the market thanks to the advanced healthcare infrastructure, high investments in R&D, together with the rising demand for novel drug-delivery technologies. Particularly, the U.S. holds a salient position on account of the already-established pharmaceutical field and the continually rising prevalence of chronic diseases. The area also houses a favorable regulatory environment and is the first one to endorse advanced drug among its members, lending momentum to market growth.
What are the driving factors of Europe pharmaceutical drug delivery market?
The Europe pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was estimated at USD 617.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 933.57 billion by 2034. Europe, with Germany, France, and the UK as its key players, is a huge market due to favorable government policies that support innovation and healthcare improvements. The high awareness levels and spending on health drives demand for sophisticated drug delivery technologies. Germany leads in pharmaceutical R&D, while countries such as France and the United Kingdom place special emphasis on the accessibility of health care, thus becoming a very important frontrunner in the field of market expansion and the embrace of next-generation drug delivery.
Why is Asia-Pacific expected to witness strong growth in pharmaceutical drug delivery market?
The Asia-Pacific pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was valued at USD 438.51 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 662.53 billion by 2034. This is the rapidly growing market as a result of population increase, increasing expenditure on health care, and ever-increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in countries like China, Japan, India, and South Korea. In addition, China and India are among the largest manufacturers, whereas Japan and South Korea focus on advanced drug delivery systems. Backed by rising investments in healthcare infrastructure and other innovative initiatives, the rise in demand for both domestic and international pharmaceutical solutions in the Asia-Pacific region is further fostering market expansion.
LAMEA Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Growth
The LAMEA pharmaceutical drug delivery market was valued at USD 159.46 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 240.92 billion by 2034. These are Brazil, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa, all of which are becoming key markets in this region because of improved healthcare infrastructures, urbanization, and greater availability of healthcare access, respectively. Brazil is one of the frontline countries with an increasing pharmaceutical market, while Saudi Arabia proposes a modernization of the healthcare system. Although the penetration of the market is lower compared to the other regions, LAMEA is a potential area of high growth for the advances of pharmaceutical drug delivery as the healthcare systems evolve and the demand for the improved access to drugs rises.
Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Top Companies
CEO Statements
Bill Anderson, CEO of Bayer AG
- We are steering Bayer to focus on transformative innovation in oncology, cardiovascular health, and rare diseases, shifting resources to foster growth in these areas and away from others”
Christopher Boerner, CEO of Bristol Myers Squibb
- “Our journey has been transformational, expanding with Celgene’s acquisition and launching new medicines. We are committed to advancing therapies to improve patient outcomes”
Giuseppe Accogli, CEO of Chiesi Group
- “Our acquisition of Amryt Pharmaceuticals aligns with our strategic focus on rare diseases, where we see opportunities for significant impact and innovation in patient care”
Recent Developments
- In June 2022, Gufic Biosciences Ltd made history in India by launching Dual Chamber Bags, an innovative drug delivery system that offers an economical solution for effective medication delivery. This technology simplifies the process of mixing and administering intravenous drugs, enhancing patient safety and ease of use.
- In February 2022, the U.S. FDA approved TAKHZYRO (lanadelumab-flyo) injection in a single-dose prefilled syringe (PFS) format. This approval allows the treatment of hereditary angioedema (HAE) attacks in patients aged 12 and older, making it easier for patients to manage this rare condition.
Market Segmentation
By Route Of Administration
- Oral Drug Delivery
- Solid Oral Drug Formulation
- Tablets
- Oral Powders
- Capsules
- Oral Pills
- Liquid Oral Drug Formulation
- Oral Syrups
- Oral Emulsions
- Oral Solutions
- Oral Elixirs
- Semi Semi-solid oral Drug Formulation
- Injectable Drug Delivery
- By Device
- Conventional Injection Devices
- By Material
- By Product
- Fillable Syringes
- Prefilled Syringes
- By Usability
- Reusable Syringes
- Disposable Syringes
- Self Injection Devices
- Needle-Free Injectors
- Autoinjectors
- Pen Injectors
- Wearable Injectors
- Other Injection Devices
- Topical & Transdermal Drug Delivery
- Liquid Topical Drug Formulations
- Solutions
- Suspensions
- Emulsions
- Solid Topical Drug Formulations
- Semi-Solid Topical Drug Formulations
- Creams
- Gels
- Ointments
- Pastes
- Lotions
- Transdermal Drug Formulation
- Transdermal Patches
- Transdermal Gels
- Transdermal Sprays
- Ocular Drug Delivery
- Liquid Ocular Drug Formulations
- Semi-Solid Ocular Drug Formulations
- Ocular Devices
- Drug Coated Contact Lenses
- Ocular Inserts
- Pulmonary Drug Delivery
- Meterd Dose Inhalers
- Dry Powder Inhalers
- Nebulizers
- Jet Nebulizers
- Ultrasonic Nebulizers
- Soft Mist Nebulizers
- Nasal Drug Delivery
- Nasal Drops
- Nasal Sprays
- Nasal Powders
- Nasal Gels
- Transmucosal Drug Delivery
- Oral Transmucosal Formulations
- Buccal Drug Delivery
- Sublingual Drug Delivery
- Other Transmucosal Drug Delivery Technologies
- Rectal Transmucosal Drug Delivery
- Vaginal Transmucosal Drug Delivery
- Implantable Drug Delivery
By Application
- Infectious Diseases
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Diabetes
- Respiratory Diseases
- Central Nervous System Disorders
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgery Centers/Clinics
- Home Care Settings
- Diagnostic Centers
- Others
By Regions
- North America
- APAC
- Europe
- LAMEA
...
...


