The global quantum dot solar cells market size was valued at USD 910.49 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 3,550.03 million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.58% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The quantum dot solar cells market growth is driven by increasing global efforts to transition towards renewable energy sources and achieve sustainability goals. These solar cells are particularly attractive due to their ability to provide high efficiency, lightweight designs, and flexibility, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including rooftop installations, portable solar panels, and integration into electronic devices like laptops and smartphones. Additionally, the growing emphasis on advanced solar technologies with higher power conversion rates and adaptability to varying light conditions is further fueling the demand for quantum dot solar cells. The adoption of quantum dot solar cells is also benefiting from the rising investments in research and development by key players in the energy sector, along with government initiatives and subsidies promoting green technologies. Companies and research institutions are increasingly focusing on improving the scalability and stability of quantum dot solar cells to make them commercially viable.
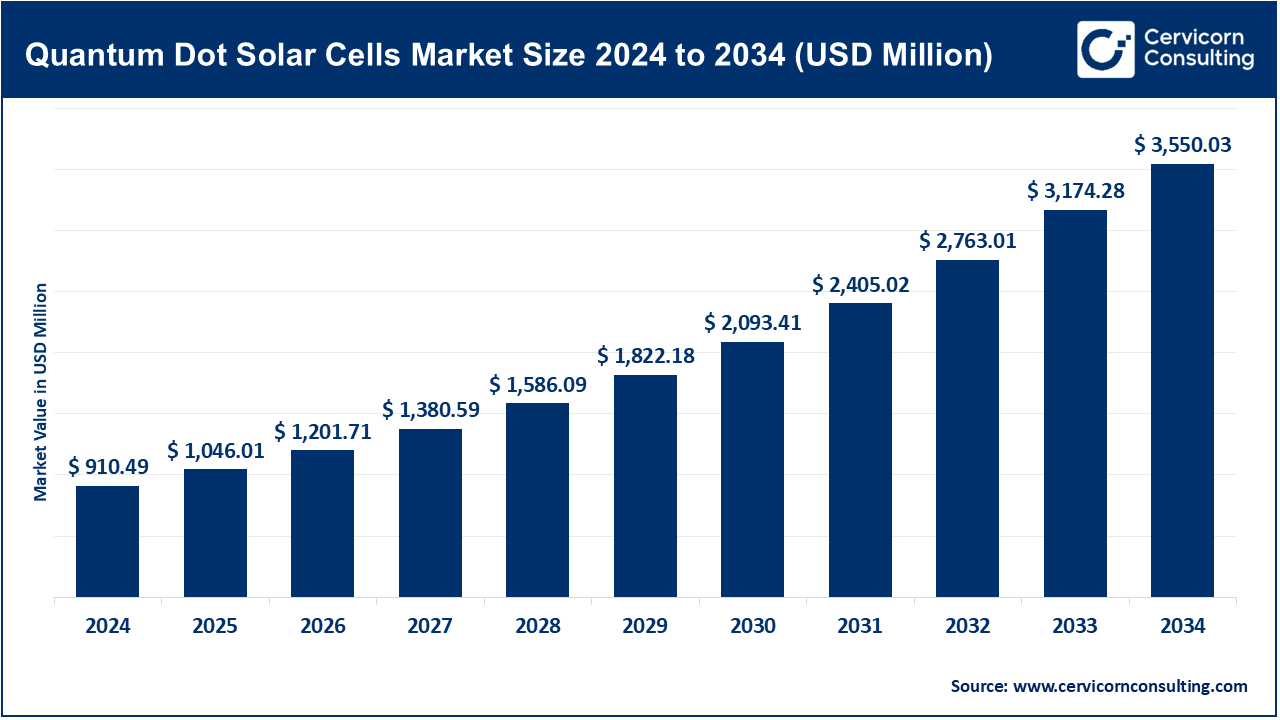
The market is driven by increasing demand for renewable energy and technological advancements in material science. Key applications include residential, commercial, and industrial solar installations. The market is growing due to innovations in quantum dot materials and improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
What are quantum dot solar cells?
Quantum dot solar cells are a cutting-edge photovoltaic technology that utilizes quantum dots nanometer-sized semiconductor particles to absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. These quantum dots have unique size-dependent optical and electronic properties, enabling them to absorb a broader spectrum of sunlight compared to traditional solar cells. By tailoring the size of quantum dots, researchers can optimize their light absorption efficiency. Quantum dot solar cells also exhibit enhanced photon-to-electron conversion efficiency due to quantum confinement effects, making them a promising alternative for next-generation solar technologies. Types of quantum dot solar cells include colloidal quantum dot solar cells, where quantum dots are dispersed in a solution, and solid-state quantum dot solar cells, which incorporate quantum dots in a solid medium. Emerging variations, such as perovskite-quantum dot hybrid solar cells, combine the strengths of both materials for improved efficiency and stability.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 910.49 Million |
| Market Growth Rate | CAGR of 14.58% from 2025 to 2034 |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 3,550.03 Million |
| North America Market Share | 36.8% in 2024 |
| APAC Market Share | 26.3% in 2024 |
Enhanced Efficiency and Performance:
Advancements in Manufacturing Techniques:
High Manufacturing Costs:
Limited Long-Term Stability:
Technological Integration and Hybrid Systems:
Innovations in Quantum Dot Materials:
Scaling Up Production:
Regulatory and Certification Hurdles:
Quantum Dot Solar Cells: Quantum dot solar cells use semiconductor nanocrystals to capture and convert sunlight into electricity. These cells offer enhanced efficiency due to their ability to absorb a broader spectrum of light. Trends include advancements in quantum dot materials, which improve performance and stability, and increased research focusing on cost reduction and scaling up production to make these cells commercially viable.
Quantum Dot Hybrid Solar Cells: Quantum dot hybrid solar cells combine quantum dots with traditional photovoltaic materials, such as silicon or organic semiconductors, to enhance light absorption and efficiency. Trends involve optimizing the interface between quantum dots and other materials, improving charge transfer, and integrating these hybrid cells into existing solar technologies to leverage the advantages of both components.
Quantum Dot With Nanowire in Solar Cells: Quantum dot with nanowire solar cells incorporate nanowires alongside quantum dots to create highly efficient photovoltaic cells. The nanowires improve charge transport and light absorption. Trends focus on refining nanowire fabrication techniques, enhancing the stability of these hybrid cells, and exploring their potential in high-efficiency, flexible, and lightweight solar technologies.
Cadmium Selenide: Cadmium Selenide (CdSe) is a prominent quantum dot material used in solar cells for its efficient light absorption and conversion properties. Trends include ongoing research to enhance CdSe quantum dot stability and efficiency, as well as efforts to reduce environmental concerns related to cadmium. CdSe remains a leading choice due to its high performance in capturing various light wavelengths.
Cadmium Sulfide: Cadmium Sulfide (CdS) is utilized in quantum dot solar cells for its role in forming p-n junctions and enhancing light absorption. Trends focus on improving the efficiency and environmental impact of CdS-based quantum dots. Advances aim to address toxicity issues and enhance material performance to make CdS a more viable option for commercial solar applications.
Cadmium Telluride: Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) is known for its high absorption coefficient and efficient light-to-electricity conversion. Trends include integrating CdTe with quantum dot technology to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Research is also focused on enhancing CdTe stability and exploring safer, less toxic alternatives while leveraging its high-performance characteristics in solar energy applications.
Zinc Sulfide: Zinc Sulfide (ZnS) is used in quantum dots to improve light absorption and electronic properties. It serves as a core or shell material in quantum dot structures. Trends involve enhancing ZnS quantum dot stability and efficiency, as well as exploring its use in tandem with other materials to boost overall performance in solar cells.
Indium: Indium-based quantum dots, such as Indium Phosphide (InP), offer high efficiency and stability. Trends focus on optimizing InP quantum dot performance and reducing material costs. Research is also directed toward developing scalable manufacturing processes and improving the sustainability of indium sources, which are critical for advancing quantum dot solar cell technologies.
Silicon: Silicon is a foundational material in solar technology, and its use in quantum dots aims to enhance efficiency and functionality. Trends include integrating silicon quantum dots with traditional silicon cells to improve performance and reduce costs. Advances focus on developing scalable processes and enhancing the efficiency of silicon-based quantum dot solar cells.
Others: The "Others" category includes emerging quantum dot materials like Lead Sulfide (PbS) and Lead Selenide (PbSe). Trends involve exploring new materials to enhance light absorption and energy conversion. Research focuses on discovering alternatives that offer better performance, reduced toxicity, and improved stability, expanding the range of materials used in quantum dot solar cells.
Single Junction Solar Cell: Single junction solar cells utilize a single layer of quantum dots to capture and convert sunlight into electricity. This simple design offers ease of manufacturing and integration. Trends indicate a focus on improving the efficiency of single junction cells through advanced quantum dot materials and enhanced light absorption, with ongoing research aimed at increasing their commercial viability and performance.
Multi-Junction Solar Cell: Multi-junction solar cells consist of multiple layers of quantum dots, each designed to capture different segments of the solar spectrum. This structure enhances overall efficiency by utilizing a broader range of wavelengths. Trends highlight significant advancements in multi-junction designs, aiming for higher efficiency and performance in energy conversion. These cells are increasingly used in specialized applications requiring high power output.
Roof Tiles: Quantum dot solar cells integrated into roof tiles offer an innovative approach to building-integrated photovoltaics. These tiles combine aesthetic appeal with energy generation. Trends include growing adoption in residential and commercial buildings, driven by advancements in tile durability and integration techniques. Research is focused on improving the efficiency and durability of solar roof tiles while maintaining their visual appeal.
Windows: Quantum dot solar cells embedded in windows provide a dual function of energy generation and light filtration. This application is expanding due to advances in transparent solar technology. Trends show increased development in enhancing the transparency and efficiency of window-integrated solar cells, with applications in smart buildings and energy-efficient architecture becoming more prevalent.
Walls: Quantum dot solar cells used in wall applications offer a novel method for incorporating solar power into building facades. This approach enhances energy generation potential without requiring additional space. Trends include innovation in the design of wall panels and coatings that integrate quantum dot technology, aiming to improve energy efficiency and aesthetic integration in urban environments.
Heat Sensors: Quantum dot solar cells applied in heat sensors utilize their sensitivity to light and temperature changes for advanced monitoring. This application is growing due to the benefits of quantum dots in detecting subtle changes. Trends focus on developing more precise and responsive heat sensors for applications in industrial monitoring and environmental control.
Others: The "Others" category includes diverse applications of quantum dot solar cells beyond conventional uses, such as in portable electronics, wearables, and advanced energy harvesting systems. Trends involve exploring novel applications where quantum dot technology can offer unique benefits, such as improved flexibility, lightweight properties, and enhanced energy conversion in specialized devices and systems.
Residential: Residential end-users utilize quantum dot solar cells for home energy solutions, aiming to reduce electricity costs and improve energy efficiency. Trends include growing consumer interest in advanced solar technologies, driven by increasing awareness of environmental benefits and the desire for higher energy yields. Innovations in quantum dot materials are making residential systems more feasible and attractive for homeowners seeking sustainable energy options.
Commercial: Commercial end-users deploy quantum dot solar cells for large-scale energy needs in businesses, offices, and industrial facilities. Trends show rising adoption due to the need for efficient and high-performance solar solutions that can meet substantial energy demands. Businesses are increasingly investing in cutting-edge technologies to enhance sustainability and reduce operational costs, with quantum dot solar cells offering improved efficiency and potential for significant energy savings.
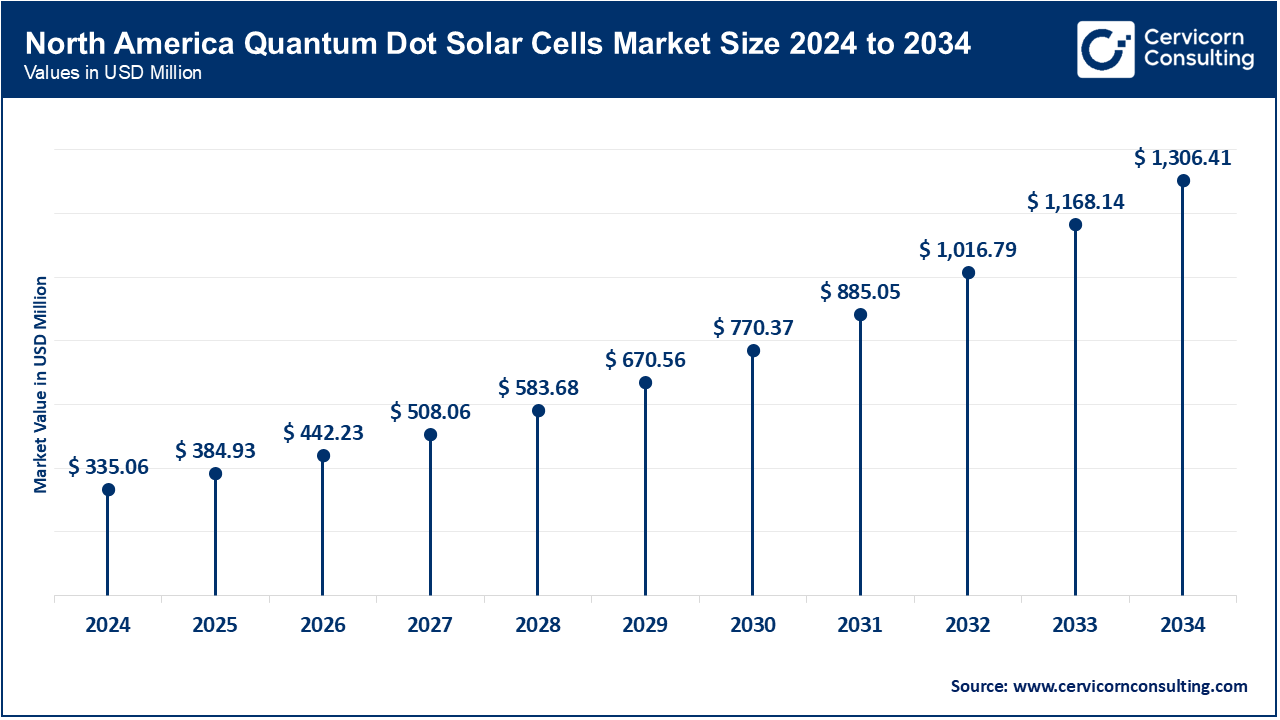
The North America market size was calculated at USD 335.06 million in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 1,306.41 million by 2034 increasing. North America region is leading due to increasing investments in renewable energy and advanced technologies. Trends include a rise in research and development activities, driven by tech hubs and academic institutions. The region is also seeing government incentives for innovative solar technologies and partnerships between technology firms and energy providers.
The Europe market size was calculated at USD 270.42 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 1,054.36 million by 2034. Europe market is driven by stringent environmental regulations and strong support for green energy initiatives. Trends include high adoption rates of advanced solar technologies, supported by EU policies and funding programs. European countries are leading in the commercialization and integration of quantum dot solar cells into existing solar infrastructure.
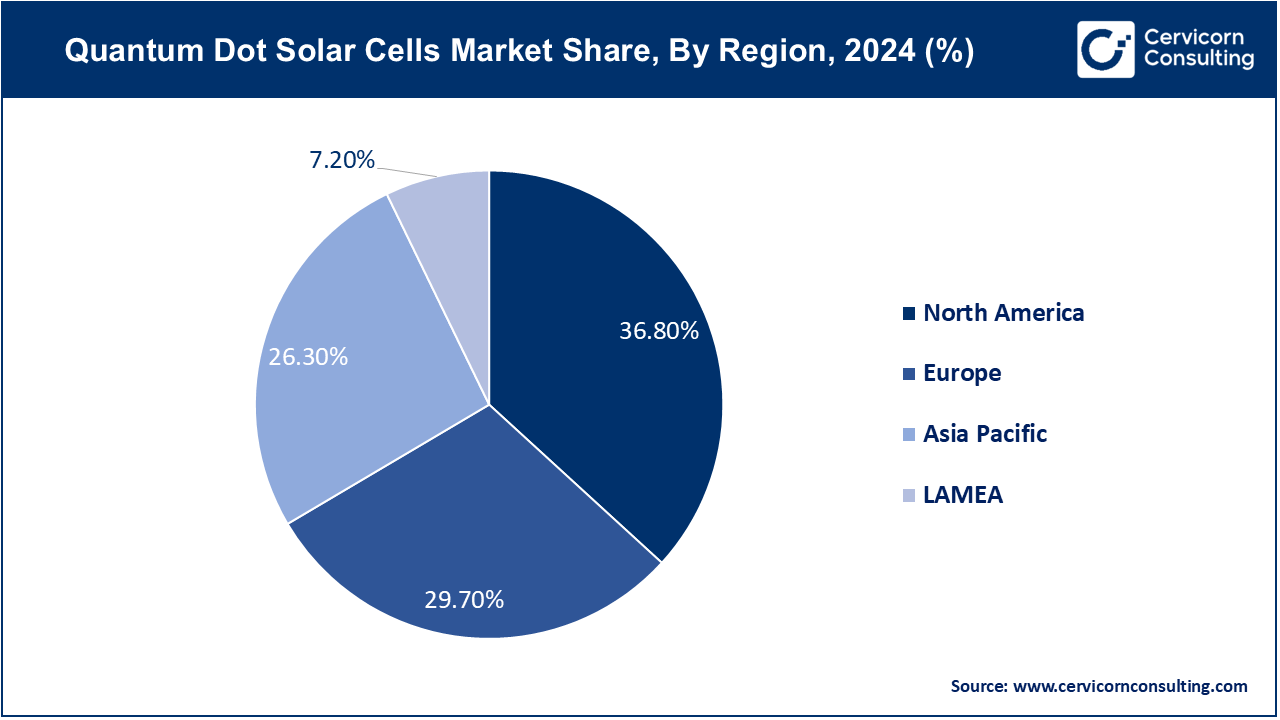
The Asia Pacific market size was valued at USD 239.46 million in 2024 and ispredicted to surpass around USD 933.66 million by 2034. Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid growth in the market, fueled by increasing energy demands and significant investments in renewable energy technologies. Trends include a surge in manufacturing capabilities and technology adoption in countries like China and Japan. The region is also focusing on scaling up production and expanding market reach through strategic partnerships and government-backed initiatives.
LAMEA is emerging as a growing market, with increasing interest in sustainable energy solutions. Trends include early-stage investments and pilot projects aimed at introducing advanced solar technologies. The region is exploring opportunities to leverage quantum dot technology for enhancing energy access and addressing energy challenges in remote and underserved areas.
New players like Nanosys Inc. and HelioGen Inc. are entering the Quantum Dot Solar Cells market by leveraging innovative technologies and advanced quantum dot materials to enhance efficiency and performance. These companies are focusing on breakthroughs in material science and scalable production methods. Dominant players such as STMicroelectronics N.V. and Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. are leading the market through extensive R&D, large-scale production capabilities, and established industry partnerships. Their dominance is reinforced by their technological expertise and ability to integrate quantum dot technology into broader solar and electronics applications.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
By Material
By Application
By End User
By Region
Chapter 1 Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Quantum Dot Solar Cells
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Product Type Overview
2.2.2 By Material Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.2.4 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3 Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4 Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Enhanced Efficiency and Performance
4.1.1.2 Advancements in Manufacturing Techniques
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Manufacturing Costs
4.1.2.2 Limited Long-Term Stability
4.1.3 Market Opportunities
4.1.3.1 Technological Integration and Hybrid Systems
4.1.3.2 Innovations in Quantum Dot Materials
4.1.4 Market Challenges
4.1.4.1 Scaling Up Production
4.1.4.2 Regulatory and Certification Hurdles
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5 Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Product Type
6.1 Global Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Snapshot, By Product Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2034
6.1.1.1 Quantum Dot Solar Cells
6.1.1.2 Quantum Dot Hybrid Solar Cells
6.1.1.3 Quantum Dot With Nanowire in Solar Cells
Chapter 7 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Material
7.1 Global Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Snapshot, By Material
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2034
7.1.1.1 Cadmium Selenide
7.1.1.2 Cadmium Sulfide
7.1.1.3 Cadmium Telluride
7.1.1.4 Zinc Sulfide
7.1.1.5 Indium
7.1.1.6 Silicon
7.1.1.7 Others
Chapter 8 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Application
8.1 Global Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2034
8.1.1.1 Single Junction Solar Cell
8.1.1.2 Multi-Junction Solar Cell
8.1.1.3 Roof Tiles
8.1.1.4 Windows
8.1.1.5 Walls
8.1.1.6 Heat Sensors
8.1.1.7 Others
Chapter 9 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By End User
9.1 Global Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Snapshot, By End User
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2034
9.1.1.1 Residential
9.1.1.2 Commercial
Chapter 10 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue Share, By Region 2023 (%)
10.3 Global Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Region
10.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
10.4 North America
10.4.1 North America Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.3 North America Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Country
10.4.4 U.S.
10.4.4.1 U.S. Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.5 Canada
10.4.5.1 Canada Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.6 Mexico
10.4.6.1 Mexico Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
10.5 Europe
10.5.1 Europe Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.3 Europe Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Country
10.5.4 UK
10.5.4.1 UK Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.4.3 UK Market Segmental Analysis
10.5.5 France
10.5.5.1 France Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.5.3 France Market Segmental Analysis
10.5.6 Germany
10.5.6.1 Germany Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.6.3 Germany Market Segmental Analysis
10.5.7 Rest of Europe
10.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.7.3 Rest of Europe Market Segmental Analysis
10.6 Asia Pacific
10.6.1 Asia Pacific Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.3 Asia Pacific Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Country
10.6.4 China
10.6.4.1 China Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.4.3 China Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.5 Japan
10.6.5.1 Japan Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.5.3 Japan Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.6 India
10.6.6.1 India Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.6.3 India Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.7 Australia
10.6.7.1 Australia Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.7.3 Australia Market Segmental Analysis
10.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.8.3 Rest of Asia Pacific Market Segmental Analysis
10.7 LAMEA
10.7.1 LAMEA Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.3 LAMEA Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market, By Country
10.7.4 GCC
10.7.4.1 GCC Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.4.3 GCC Market Segmental Analysis
10.7.5 Africa
10.7.5.1 Africa Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.5.3 Africa Market Segmental Analysis
10.7.6 Brazil
10.7.6.1 Brazil Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.6.3 Brazil Market Segmental Analysis
10.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
10.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Quantum Dot Solar Cells Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEA Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11 Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2021-2023
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2021-2023
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2023)
Chapter 12 Company Profiles
12.1 Nanosys Inc.
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 Global Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 QD Vision Inc.
12.3 Nano-Optoelectronics Research Group
12.4 Quantum Dot Corporation
12.5 Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE)
12.6 HelioGen Inc.
12.7 Solaris Nanosciences Corporation
12.8 Kurt J. Lesker Company
12.9 Altair Nanotechnologies Inc.
12.10 Nanoscale Components Inc.