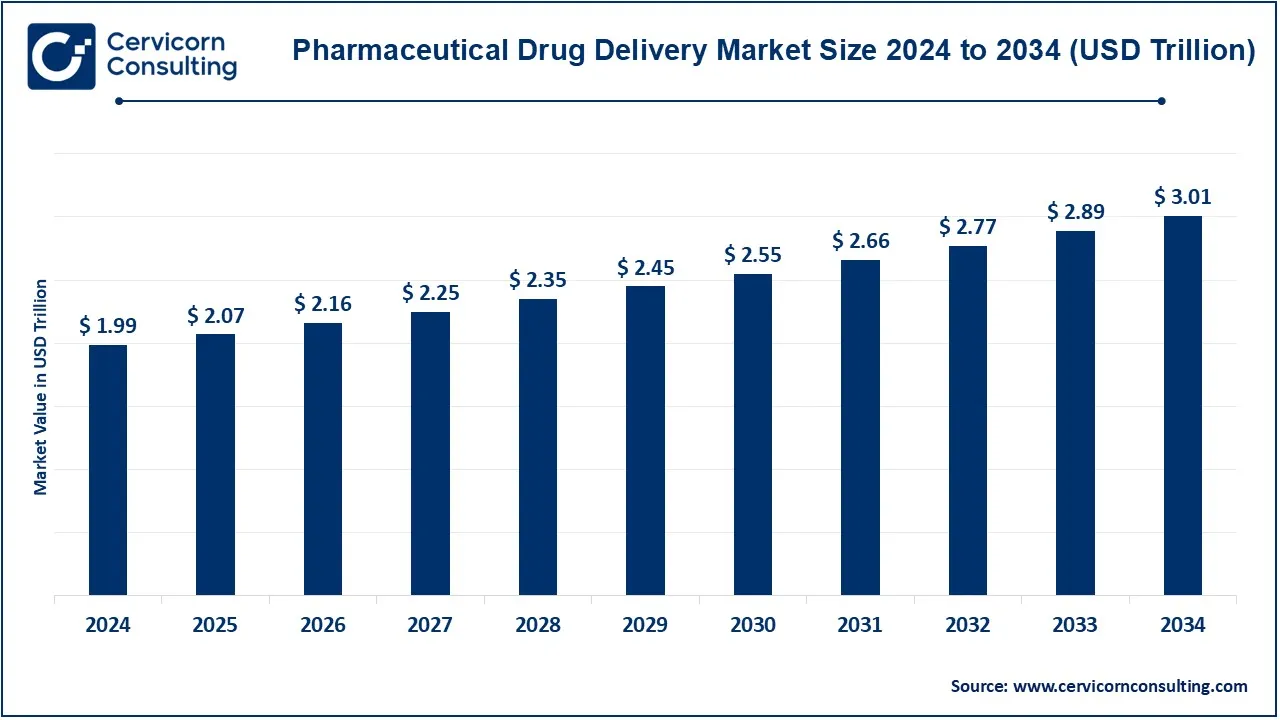
The global pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was valued at USD 1,993.22 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 3,011.50 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.24% from 2025 to 2034.
The pharmaceutical drug delivery market is expanding rapidly due to increasing demand for advanced treatments, rising chronic disease cases, and growing investments in research and development. Innovative drug delivery technologies, such as smart pills, implantable devices, and nanomedicine, are driving industry growth. Additionally, the shift towards patient-centric drug delivery solutions, including self-administered injections and wearable drug delivery devices, is boosting market demand. Regulatory approvals and the adoption of biologics further support the market's expansion.
Pharmaceutical drug delivery refers to the methods and technologies used to transport a drug into the body to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. It ensures that medications reach the right site in the body at the right time and in the right amount. Traditional drug delivery methods include oral tablets, injections, and topical creams. However, advancements in technology have led to innovative approaches such as nanotechnology-based drug carriers, controlled-release formulations, and targeted drug delivery systems. These modern techniques improve the effectiveness of drugs, reduce side effects, and enhance patient compliance. Drug delivery systems are crucial in treating chronic diseases like cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions by providing sustained and targeted medication release. The goal of pharmaceutical drug delivery is to optimize treatment outcomes, improve drug stability, and increase bioavailability while minimizing unwanted reactions.
Key Insights related to the Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery:
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.07 Trillion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 3.01 Trillion |
| Expected CAGR (2025 to 2034) | 4.24% |
| Flagship Region | North America |
| Fast-Developing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Route of Administration, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Novartis International AG, F.Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Pfizer Inc., Becton Dickinson & Company, GlaxoSmithKline PLC, Merck & Co Inc, Sanofi S.A., Bayer Medicine Products AG, 3M |
The pharmaceutical drug delivery m arket is segmented into route of administration, application, end user and region. Based on application, the market is classified into infectious diseases, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory diseases, central nervous system disorders, autoimmune diseases and others. Based on route of administration, the market is classified into oral drug delivery, injectable drug delivery, self injection devices, topical & transdermal drug delivery, ocular drug delivery, pulmonary drug delivery, nasal drug delivery, transmucosal drug delivery, implantable drug delivery. Based on end user, the market is classified into hospitals, ambulatory surgery centers, home care settings, diagnostic centers and others.
Infectious diseases: Drug delivery systems to fight infectious diseases strive to achieve efficacy in the eradication of infection while guarding against resistance-building mechanisms. Contact delivery routes include but are not limited to novel mechanisms for delivering orally, injectables, or inhalational forms of antibiotics, antivirals, and vaccines. Nanomedicine and various other technologies and approaches that are emerging, allow for the maximum utilization of drug delivery systems and remarkable immune response enhancement, which indicates the lack to potential treat diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV and COVID-19.
Cancer: Cancer drug delivery is focused on targeted therapies wherein nanoparticles and antibody-drug conjugates deliver chemotherapy or immunotherapy directly to tumors, ideally sparing healthy cells. Recent innovations in intravenous and transdermal systems provide extensive support for targeting, intended to ameliorate patient outcomes, combat side effects, and overcome challenges such as the development of drug resistance by tumors. This segment is undergoing a sea change conferred by precision medicine advances toward assuring therapeutic effectiveness and personalization.
Cardiovascular diseases: Cardiovascular drug delivery has in view the enhancement of bioavailability and controlled release of medicines like antihypertensives, anticoagulants, and statins. These systems include transdermal patches and controlled-release capsules, providing steady blood levels of a medicine in addition to improved patient compliance. Other approaches include brainstorming about nanoparticle-mediated delivery systems that might make a remarkable contribution, clinically enhancing the effectiveness of treatments or even decreasing required doses to respond to the high global burden associated with cardiovascular diseases.
Diabetes: Diabetes drug delivery encompasses sustained-release insulin preparations, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and antidiabetic agents with routes that involve injectables, transdermal patches, and inhalable systems. Drug delivery systems in alliance with continuous glucose monitoring recently brought tremendous advancements in the management of diabetes. The newer payloads are geared toward dispensing and administering drug therapy in new ways that are more user-friendly and patient-centric, thereby impacting the quality of life.
Respiratory Diseases: With regards to the treatment systems of respiratory diseases, the inhalation route is intended to improve the delivery of lung bronchodilators, corticosteroids and biologics to the lungs due to their local action in the lungs. Metered dose inhalers, dry powder inhaler and nebulizers have made it possible to target areas of diseases as with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations due to cystic fibrosis and its relief of the white mucus plugs of the bronchi. That, in turn, has fueled the impetus for increasing research into innovation for sustainable lung efficacy and reduced systemic exposure in patient medicine of new delivery systems for chronic respiratory diseases.
Central Nervous System Disorders: Drug delivery for CNS disorders addresses the challenge of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), presenting numerous inventive means of delivery using, for example, intranasal, liposome, and nanoparticle carriers needed for conditions like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and epilepsy. Effective delivery is essential to treatment in neurologic disorders, as such, major regimens must achieve targeted superusefulness to mitigate side effects. Drug delivery enhancement for this route often explains advances obtained in conditions through BBB.
Autoimmune Diseases: The next generation of drug delivery systems for autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus directs the delivery of immunosuppressants and biologics to the targeted site. These include innovations in injectables, transdermal patches, and sustained-release formulations, making them crucial to initiating an immune-modulation response and reducing the frequency and intensity of side effects associated with these treatments. Targeted delivery approaches are thus vital in this area because they enhance the effective therapy while minimizing effects on surrounding, healthy tissues, overcoming chronicity and compliance issues in the management of autoimmune diseases.
Others: This segment covers less common conditions that still require specialized drug delivery solutions, such as metabolic, genetic, and hormonal disorders. These delivery systems may include implants, infusion pumps, or controlled-release oral formulations tailored for long-term management and optimized dosing. The “Others” segment is driven by the need for patient-centered solutions that offer consistent medication delivery with minimal side effects, addressing a variety of chronic and rare diseases.
Hospitals: The major consumers of advanced drug delivery systems in critical areas such as critical care, oncology, and surgery. In such a situation, precisely controlled administration is executive in intravenous, injectable, and implantable drug delivery solutions, thought to administrate in most inpatient settings by infusion pumps and other devices. The drivers for reliability and safe drug delivery in hospitals see considerable innovation in controlled-release systems and smart devices, most relevant for improving patient outcomes, acute and special care.
Ambulatory Surgery Centers/Clinics: These institutions might also use available portable drug delivery systems and others with good recovery times, transdermal patches, and autoinjectors. More procedures are being performed in outpatient facilities ACC drug delivery solutions emphasize safety, usability, and rapid onset of action. Clinics act in their patients' best interests by demanding systems that give optimum performance and minimally invasive methods of treatment so the patient can return as soon as possible.
Home Care Settings: Drug delivery systems for home care focus on self-administration via inhalers, transdermal patches, and wearable infusion devices for diabetes and respiratory disease patients. The increased scope of the home care market is indicative of the patients' preferences for convenience and independence in systems that are easy to use and safe enough even outside clinical settings. All services are continuously moving the treatments to home settings; hence, user-friendly and effective drug delivery technology innovations are getting of the utmost importance.
Diagnostic Centers: This industry supplies drugs for administering contrast agents during imaging and radio-pharmaceuticals for diagnostic purposes. Among such drug delivery systems are those that may provide precise dosing and controlled release, with intravenous and injectable routes allowed in attaining the diagnostic agents at the precise area for clear imaging results. Drug delivery in the diagnostic centres must emphasise accuracy, speed, and comfort for the patient, leading to clear diagnoses and minimised side effects or risks with the diagnostic test.
Others: This segment includes home care setting configurations of rehabilitation, palliative care, and specialty-clinic types of care. Such entities would demand drug delivery systems that will provide chronic disease management, pain relief, and specialization therapy. The emphasis is on adaptable patient-centered delivery methods, such as long-acting injectables, implants, and infusion systems that could address different healthcare needs in diverse service environments outside traditional methods of care, i.e., hospital or outpatient care.
The pharmaceutical drug delivery market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). The North America has dominated the market in 2024.
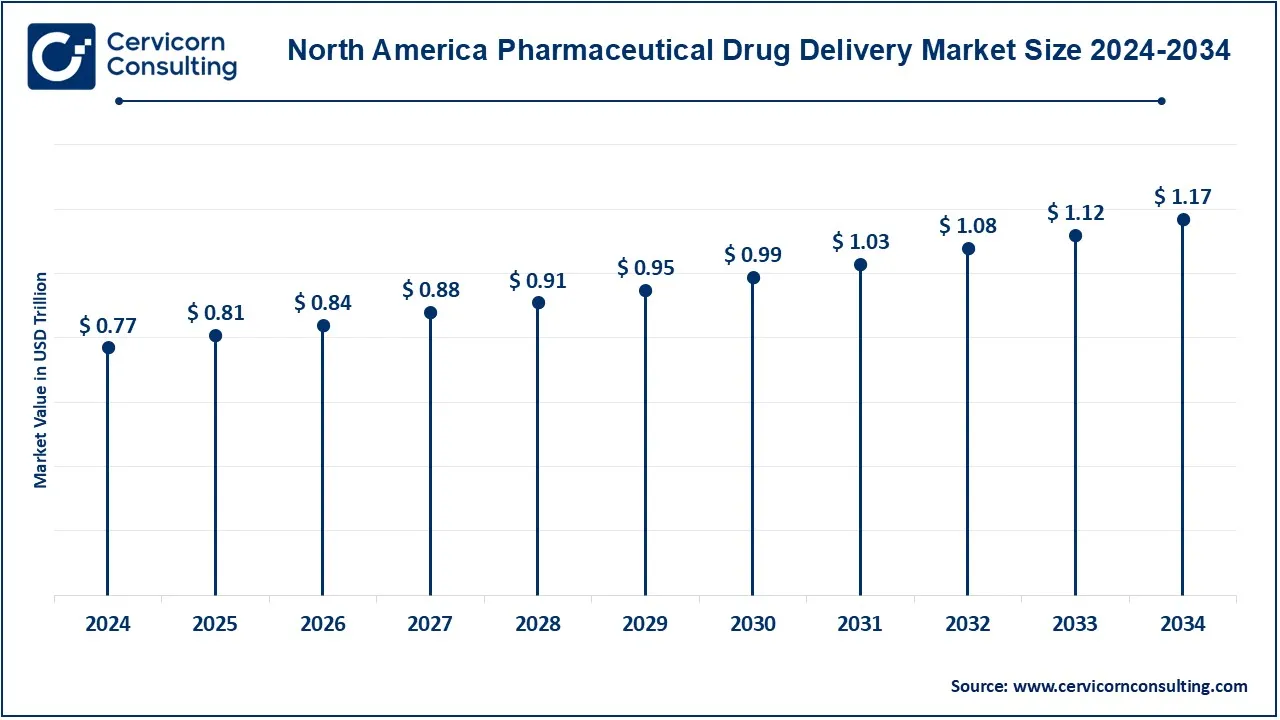
The North America pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was valued at USD 777.36 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 1,474.49 billion by 2034. This is the region under the leadership of the United States and Canada, which controls the market thanks to the advanced healthcare infrastructure, high investments in R&D, together with the rising demand for novel drug-delivery technologies. Particularly, the U.S. holds a salient position on account of the already-established pharmaceutical field and the continually rising prevalence of chronic diseases. The area also houses a favorable regulatory environment and is the first one to endorse advanced drug among its members, lending momentum to market growth.
The Europe pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was estimated at USD 617.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 933.57 billion by 2034. Europe, with Germany, France, and the UK as its key players, is a huge market due to favorable government policies that support innovation and healthcare improvements. The high awareness levels and spending on health drives demand for sophisticated drug delivery technologies. Germany leads in pharmaceutical R&D, while countries such as France and the United Kingdom place special emphasis on the accessibility of health care, thus becoming a very important frontrunner in the field of market expansion and the embrace of next-generation drug delivery.
The Asia-Pacific pharmaceutical drug delivery market size was valued at USD 438.51 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 662.53 billion by 2034. This is the rapidly growing market as a result of population increase, increasing expenditure on health care, and ever-increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in countries like China, Japan, India, and South Korea. In addition, China and India are among the largest manufacturers, whereas Japan and South Korea focus on advanced drug delivery systems. Backed by rising investments in healthcare infrastructure and other innovative initiatives, the rise in demand for both domestic and international pharmaceutical solutions in the Asia-Pacific region is further fostering market expansion.
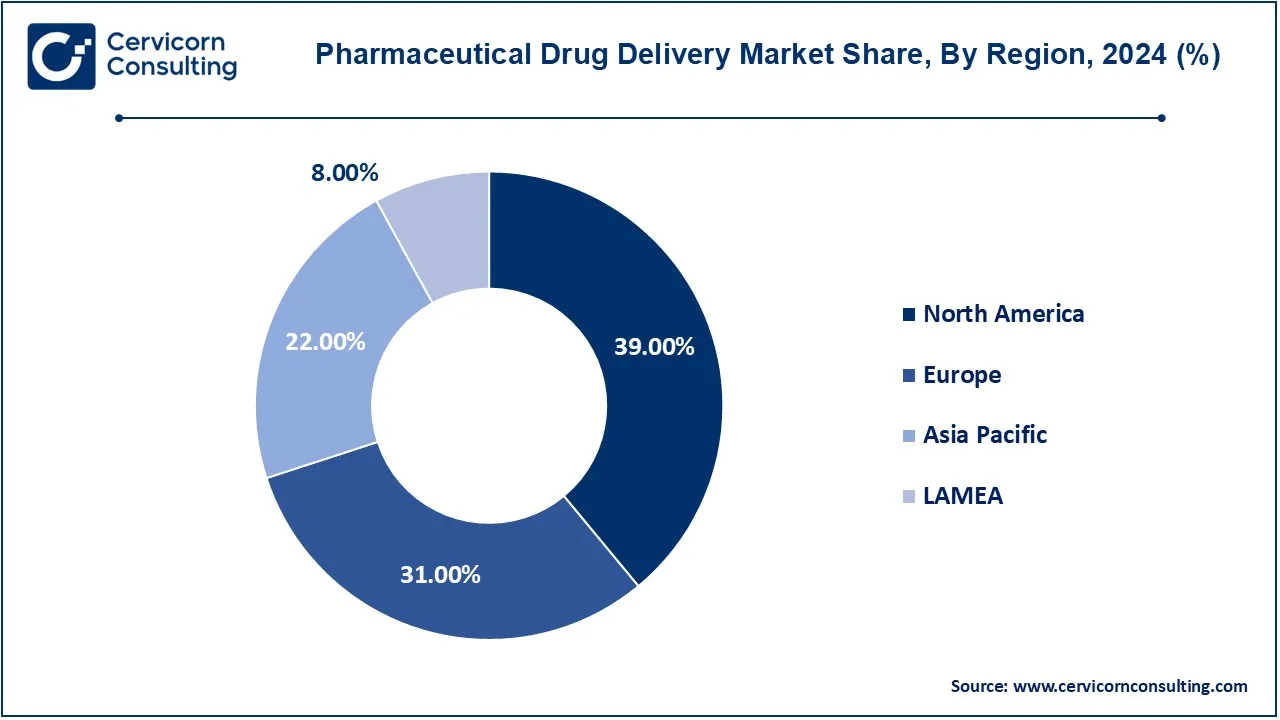
The LAMEA pharmaceutical drug delivery market was valued at USD 159.46 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 240.92 billion by 2034. These are Brazil, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa, all of which are becoming key markets in this region because of improved healthcare infrastructures, urbanization, and greater availability of healthcare access, respectively. Brazil is one of the frontline countries with an increasing pharmaceutical market, while Saudi Arabia proposes a modernization of the healthcare system. Although the penetration of the market is lower compared to the other regions, LAMEA is a potential area of high growth for the advances of pharmaceutical drug delivery as the healthcare systems evolve and the demand for the improved access to drugs rises.
CEO Statements
Bill Anderson, CEO of Bayer AG
Christopher Boerner, CEO of Bristol Myers Squibb
Giuseppe Accogli, CEO of Chiesi Group
Market Segmentation
By Route Of Administration
By Application
By End User
By Regions
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Route Of Administration Overview
2.2.2 By Application Overview
2.2.3 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Growth of Chronic Diseases
4.1.1.2 Technological Advancements
4.1.1.3 Emergence of Home Care Solutions
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High development cost
4.1.2.2 Complexity of biologic delivery
4.1.2.3 Intellectual property hurdles
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Maintaining Drug Stability
4.1.3.2 Side effects
4.1.3.3 Interfacing with Digital Health
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Application
6.1 Global Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Snapshot, By Application
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Infectious Diseases
6.1.1.2 Cancer
6.1.1.3 Cardiovascular Diseases
6.1.1.4 Diabetes
6.1.1.5 Respiratory Diseases
6.1.1.6 Central Nervous System Disorders
6.1.1.7 Autoimmune Diseases
6.1.1.8 Others
Chapter 7. Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Route Of Administration
7.1 Global Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Snapshot, By Route Of Administration
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Oral Drug Delivery
7.1.1.2 Injectable Drug Delivery
7.1.1.3 Self Injection Devices
7.1.1.4 Topical & Transdermal Drug Delivery
7.1.1.5 Ocular Drug Delivery
7.1.1.6 Pulmonary Drug Delivery
7.1.1.7 Nasal Drug Delivery
7.1.1.8 Transmucosal Drug Delivery
7.1.1.9 Implantable Drug Delivery
Chapter 8. Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By End User
8.1 Global Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Snapshot, By End User
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Hospitals
8.1.1.2 Ambulatory Surgery Centers/Clinics
8.1.1.3 Home Care Settings
8.1.1.4 Diagnostic Centers
8.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 9. Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
9.3 Global Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 Novartis International AG
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 F.Hoffmann-La Roche AG
11.3 Pfizer Inc.
11.4 Becton Dickinson & Company
11.5 GlaxoSmithKline PLC
11.6 Merck & Co Inc
11.7 Sanofi S.A.
11.8 Bayer Medicine Products AG
11.9 3M