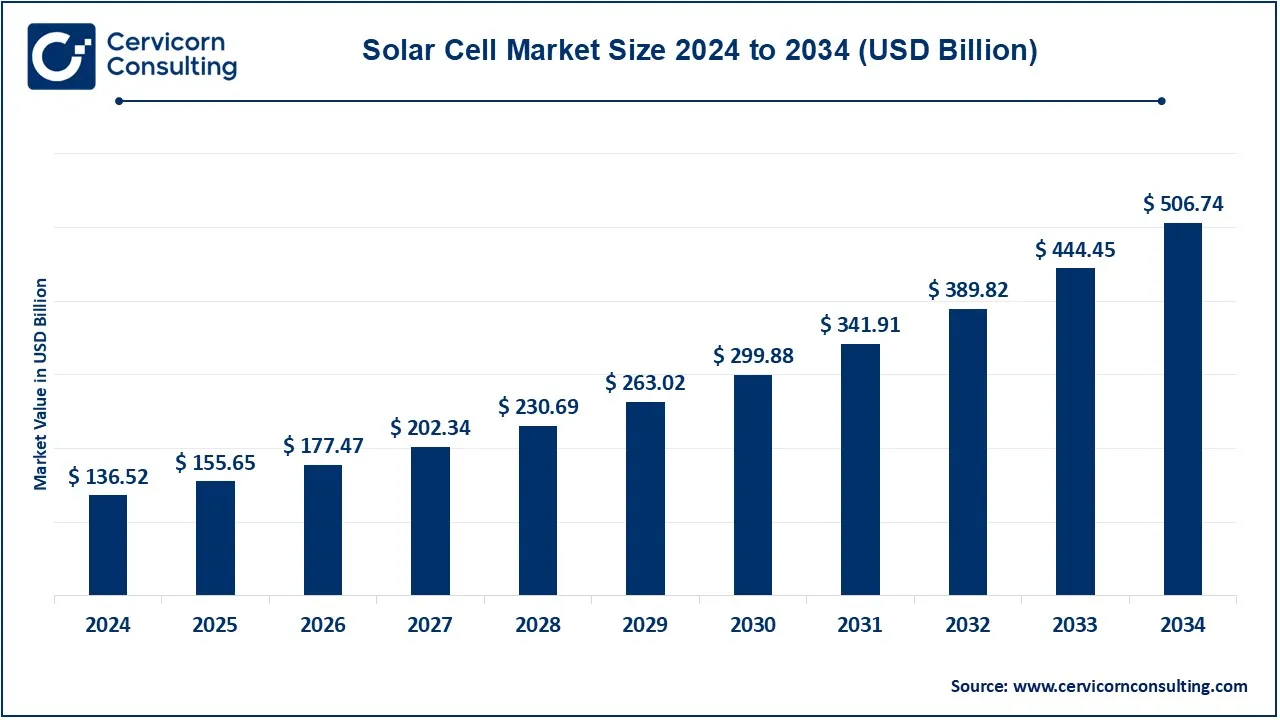
The global solar cell market size was reached at USD 136.52 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 506.74 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.83% from 2025 to 2034.
The solar cell market is experiencing rapid growth due to increasing demand for renewable energy, government incentives, and advancements in solar technology. Countries worldwide are investing in solar power to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and achieve net-zero emissions. The declining cost of solar panels and improvements in battery storage are further driving adoption. Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America are leading in solar energy deployment. With innovations in high-efficiency solar cells and floating solar farms, the industry is expanding into new sectors. The rise of solar-powered electric vehicles (EVs) and smart solar grids is expected to boost market demand in the coming years.
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) cell, is an electronic device that converts sunlight directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. It is made from semiconductor materials like silicon, which absorb sunlight and release electrons, creating an electric current. Solar cells are the building blocks of solar panels, which are widely used in homes, businesses, and industries to generate renewable energy. Solar cells are classified into different types, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar cells. Monocrystalline cells are the most efficient, while thin-film cells are lightweight and flexible. Solar technology is eco-friendly, reduces carbon emissions, and lowers electricity costs. With advancements in energy storage and solar efficiency, solar power is becoming a key part of global energy solutions.
Key Insights related to the Solar Cell:
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 136.52 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 506.74 Billion |
| Expected CAGR (2025 to 2034) | 15.83% |
| Most Prominent Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Type, Product, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd., Trina Solar Co., Ltd., Canadian Solar Inc., JA Solar Holdings Co., Ltd., Hanwha Q Cells Co. Ltd., LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd., First Solar, Inc., Yingli Green Energy Holding Company Limited, SunPower Corporation, Risen Energy Co., Ltd., GCL-Poly Energy Holdings Limited, LG Electronics Inc., REC Solar ASA |
The solar cell market is segmented into type, technology, product, installation type and region. Based on type, the market is classified into crystalline, thin film and others. Based on technology, the market is classified into monocrystalline, polycrystalline, cadmium telluride (CDTE), amorphous silicon (A-Si) and copper indium gallium diselenide. Based on product, the market is classified into BSF, PERC/PERL/PERT/TOPCON, HJT, IBC & MWT and others. Based on installation type, the market is classified into residential, commercial and utility-scale.
Crystalline (Multi-Si, Mono-Si): Multi-Si (Multi-Crystalline Silicon) consists of many silicon crystals. They are blue-speckled in appearance, less expensive, and slightly less efficient than mono-Si panels, but widely used due to their cost-effectiveness as well as reliability for performance. Mono-Si (Mono-Crystalline Silicon), panels consist of one single crystal structure. They appear sleek black and are generally more efficient. For the same power output, they take less space, thus ideal for areas with limited roof space. Generally, it is more expensive but efficient and durable.
Thin film (CdTe, a-Si, CI(G)S): Cadmium Telluride employs a thin layer of cadmium telluride that absorbs sunlight. CdTe panels are less efficient than crystalline panels but cheaper to manufacture and may be more efficient in low light. Utility-scale installations utilize this. a-Si (Amorphous Silicon) does not form a crystalline structure and, hence is flexible and light. These panels have lower efficiency but could be used where weight and flexibility are important aspects, like building-integrated photovoltaics. CI(G)S (Copper Indium Gallium Selenide), is a technology that combines multiple materials to fabricate a thin-film layer with efficiency other than options of thin-film performance. CIGS panels are flexible and lightweight, making them fit for many applications including rooftops and building materials.
Solar Cell Market Revenue Share, By Type, 2024 (%)
| Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Crystalline (Multi-Si, Mono-Si) | 46% |
| Thin film (CdTe, a-Si, CI(G)S | 32% |
| Others | 22% |
Others: Organic photovoltaics and perovskite solar cells are another in this category which is still under development or low-level production. These technologies do have a high promise towards efficiency but lower production costs, yet very challenging toward stability and scalability.
Residential: These systems are for homes and small buildings. They are normally installed on rooftops or in yards, and their sizes vary depending on the homeowner's energy needs and budget. Residences qualify often to get incentives and net metering options installed.
Commercial: These are huge systems that a business, school, or government building can use. They may be mounted on the roof or the ground and will offset a high percentage of the facility's energy use. These types of systems are much more complex and generally take advantage of scale incentives.
Solar Cell Market Revenue Share, By Installation Type, 2024 (%)
| Installation Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Residential | 26% |
| Commercial | 31% |
| Utility-Scale | 43% |
Utility-Scale: Utility-scale solar farms are great electricity-generating installations for a power grid. They encompass large land areas and could operate using different panel technologies to yield a lot of energy. Such projects often come from energy companies suggesting them as part of their portfolio to transition the nation or region to renewable sources.
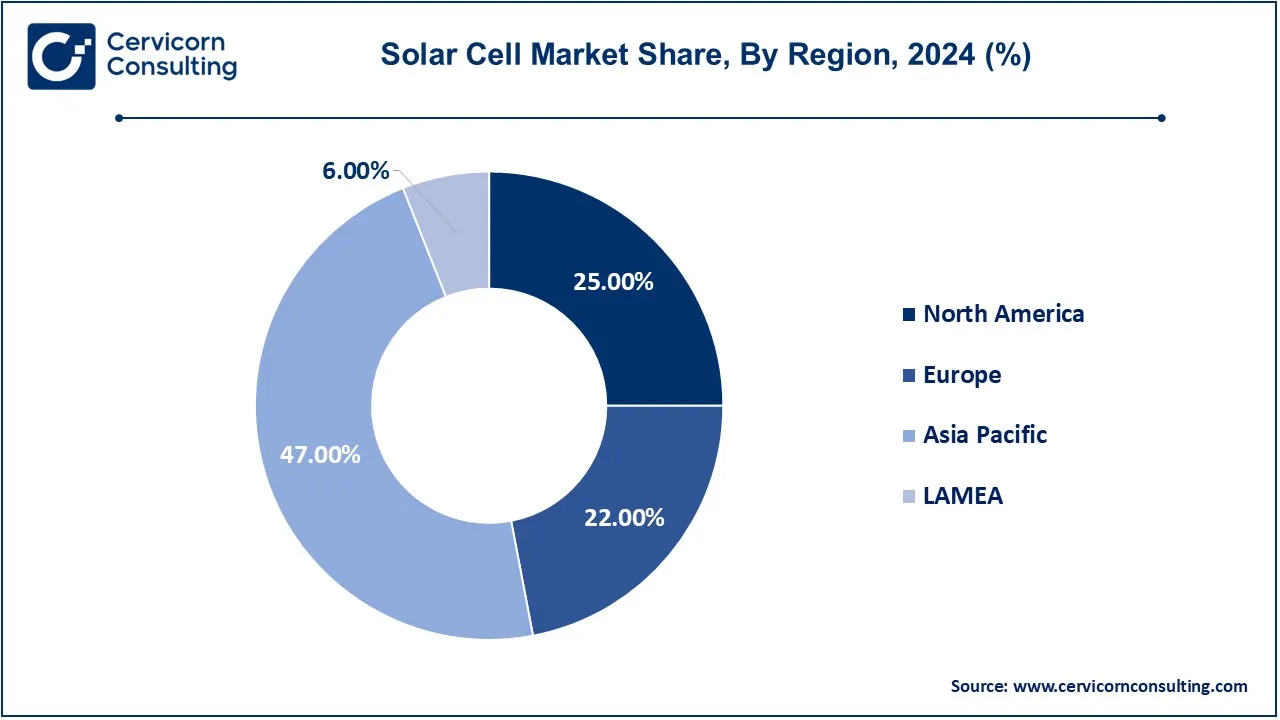
The solar cell market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). The Asia-Pacific region has dominated the market in 2024.
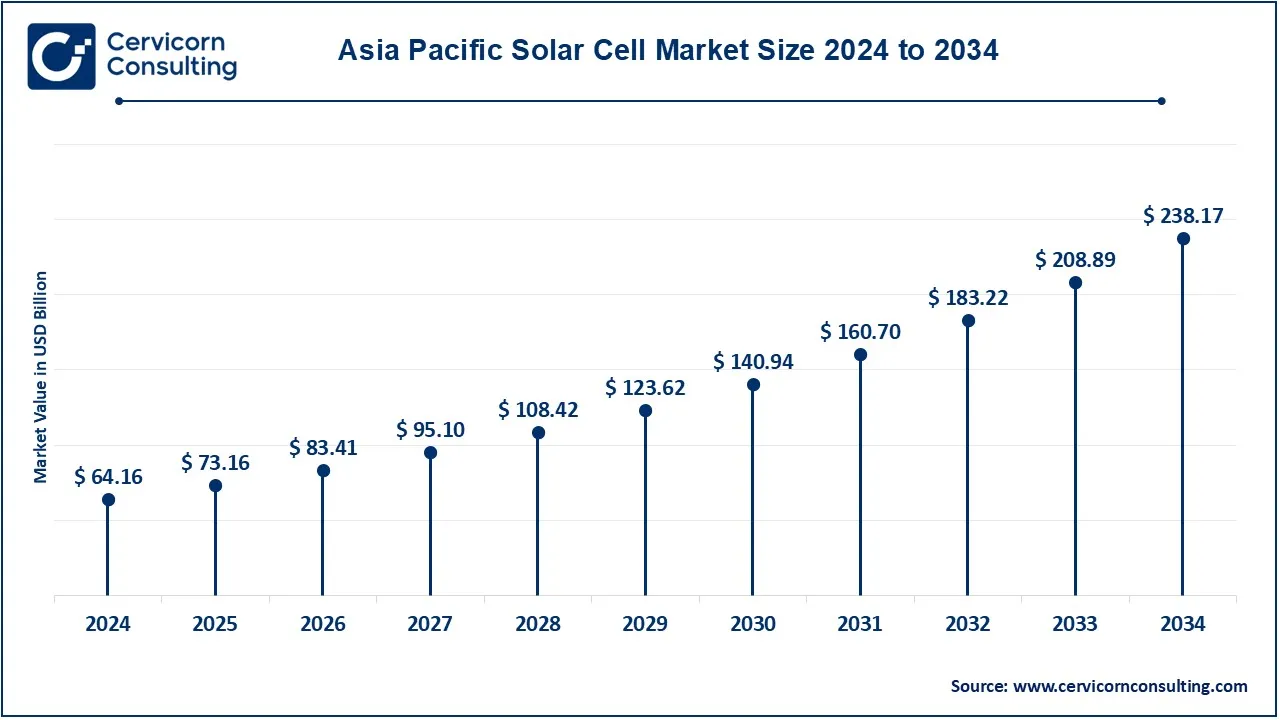
The Asia-Pacific solar cell market size was accounted for USD 64.16 billion in 2024 and is projected to surpass around USD 238.17 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing exponential growth; China is the leading entity. China not only accounts for the largest share of global solar panel manufacturing but is also one of the global leaders in terms of capacities for solar installations. India is rapidly increasing its solar infrastructure, and government initiatives have been a major driver for pursuing ambitious renewable energy targets. Other countries in the region are Japan and Australia, which are making great strides in solar adoption, with residential installations as well as integration of solar with battery storage solutions.
The North America solar cell market size was valued at USD 34.13 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 126.69 billion by 2034. The North America market is dominated mainly by the US and Canada. Although economic incentives-the federal government and states with tax credits and rebates- have significantly contributed to the increase in solar energy usage in the United States, the largest solar installations were seen in California, followed closely by Texas and Florida. Canada is committing more to solar technologies, mainly in areas that embrace projects of renewable energy, such as Ontario and Alberta, and incentives for home and commercial solar systems.
The Europe solar cell market size was estimated at USD 30.03 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 111.48 billion by 2034. Europe remains the world leader when it comes to countries putting up solar energy. Germany heads the list for having laws favoring the installation of both rooftop and large-scale solar farm installation, while aggressive renewable energy targets of France bring this nation toward increasing solar capacity, and advantageous legislation also helped Spain revive its solar business. Italy and the Netherlands are now getting ready for their future solar policies by developing and adding more solar solutions to their existing structural designs.
The LAMEA solar cell market was valued at USD 8.19 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 30.40 billion by 2034. Emergence in the LAMEA region is witnessed in the market, spearheaded by Brazil and South Africa. The policies in Brazil are becoming friendly to solar projects, especially in rural areas, while in South Africa, the number of solar installations has increased sharply within its Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme. In the Middle East, for example, countries such as the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia invest in heavy solar projects to ensure diversity in their energy sources by tapping the abundant sun to meet soaring energy demands. African countries such as Kenya and Morocco are also aware of the solar energy prospect as a way of helping solve the shortage of energy and increase access.
Leading competitors include JinkoSolar, Trina Solar, Canadian Solar, JA Solar, and Hanwha Q Cells. They employ advanced technologies and the most developed manufacturing processes that yield an inexpensive but efficient output. The companies have heavily invested in research and development to make their solar panels better performing and more durable. They increase their global footprint through strategic partnerships and acquisitions. Diversified product lines- from monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels to sustainable practices and supply chain optimization all of them well positioned to deal with the high demand in a clean energy solution-driven market.
CEO Statements
Xiande Li, CEO of JinkoSolar
Jifan Gao, CEO ofTrina Solar
Shawn (Xiaohua) Qu, CEO of Canadian Solar
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Technology
By Product
By Installation Type
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Solar Cell
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Tyre Overview
2.2.2 By Technology Overview
2.2.3 By Product Overview
2.2.4 By Installation Type Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Solar Cell Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 The Government Policies
4.1.1.2 Energy Transition Goals
4.1.1.3 Growing Electric Vehicle Market
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Initial Cost
4.1.2.2 Infrastructure Challenges
4.1.2.3 Regulatory Barriers
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Funding and Finance
4.1.3.2 Policy stability
4.1.3.3 Skill Gaps
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Solar Cell Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Solar Cell Market, By Type
6.1 Global Solar Cell Market Snapshot, By Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Crystalline (Multi-Si, Mono-Si)
6.1.1.2 Thin film (CdTe, a-Si, CI(G)S)
6.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 7. Solar Cell Market, By Technology
7.1 Global Solar Cell Market Snapshot, By Technology
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Monocrystalline
7.1.1.2 Polycrystalline
7.1.1.3 Cadmium Telluride (CDTE)
7.1.1.4 Amorphous Silicon (A-Si)
7.1.1.5 Copper Indium Gallium Diselenide
Chapter 8. Solar Cell Market, By Product
8.1 Global Solar Cell Market Snapshot, By Product
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 BSF
8.1.1.2 PERC/PERL/PERT/TOPCON
8.1.1.3 HJT
8.1.1.4 IBC & MWT
8.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 9. Solar Cell Market, By Installation Type
9.1 Global Solar Cell Market Snapshot, By Installation Type
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Residential
9.1.1.2 Commercial
9.1.1.3 Utility-Scale
Chapter 10. Solar Cell Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 Solar Cell Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
10.3 Global Solar Cell Market, By Region
10.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
10.4 North America
10.4.1 North America Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.3 North America Solar Cell Market, By Country
10.4.4 U.S.
10.4.4.1 U.S. Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.5 Canada
10.4.5.1 Canada Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.6 Mexico
10.4.6.1 Mexico Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
10.5 Europe
10.5.1 Europe Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.3 Europe Solar Cell Market, By Country
10.5.4 UK
10.5.4.1 UK Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.5 France
10.5.5.1 France Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.6 Germany
10.5.6.1 Germany Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.7 Rest of Europe
10.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6 Asia Pacific
10.6.1 Asia Pacific Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.3 Asia Pacific Solar Cell Market, By Country
10.6.4 China
10.6.4.1 China Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.5 Japan
10.6.5.1 Japan Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.6 India
10.6.6.1 India Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.7 Australia
10.6.7.1 Australia Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7 LAMEA
10.7.1 LAMEA Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.3 LAMEA Solar Cell Market, By Country
10.7.4 GCC
10.7.4.1 GCC Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.5 Africa
10.7.5.1 Africa Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.6 Brazil
10.7.6.1 Brazil Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
10.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Solar Cell Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11. Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1 JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd.
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 Global Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 Trina Solar Co., Ltd.
12.3 Canadian Solar Inc.
12.4 JA Solar Holdings Co., Ltd.
12.5 Hanwha Q Cells Co. Ltd.
12.6 LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
12.7 First Solar, Inc.
12.8 Yingli Green Energy Holding Company Limited
12.9 SunPower Corporation
12.10 Risen Energy Co., Ltd.
12.11 GCL-Poly Energy Holdings Limited
12.12 LG Electronics Inc.
12.13 REC Solar ASA