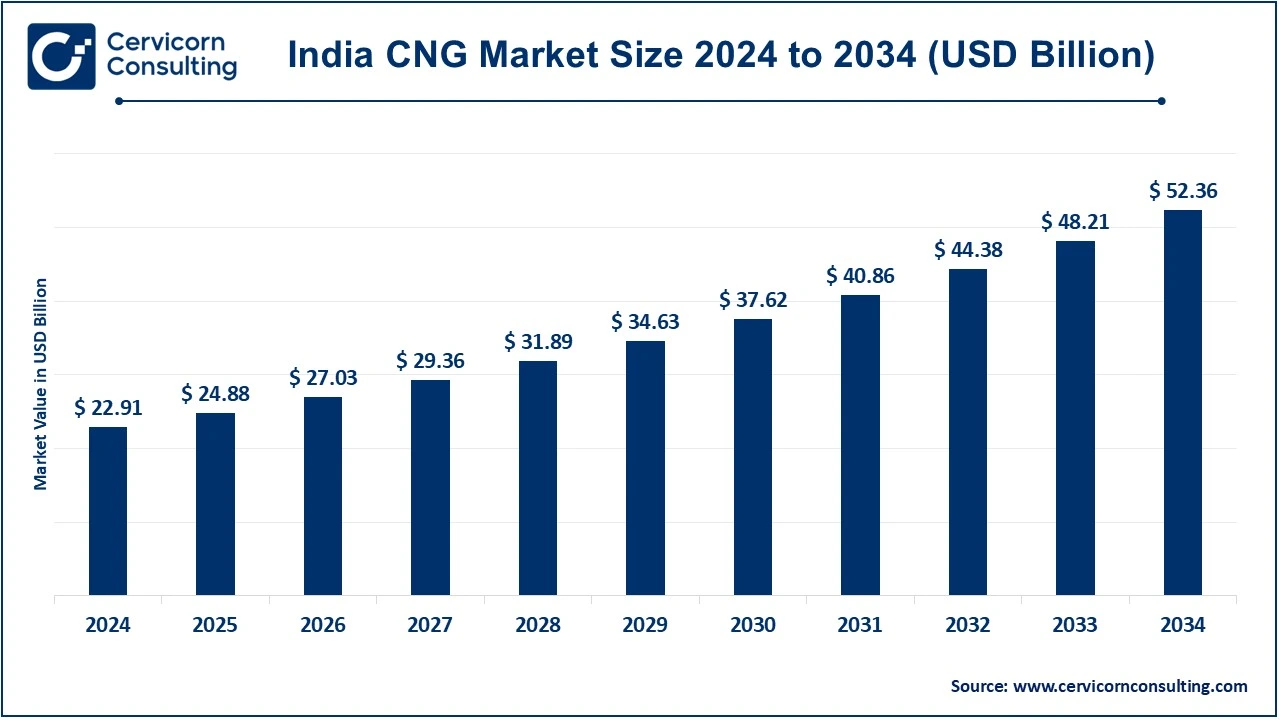
The India CNG market size was valued at USD 22.91 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 52.36 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.61% over the forecast 2025 to 2034.
The market for CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) is growing very fast due to the vast demand for cleaner, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional fuels. CNG offers lower emissions compared to gasoline and diesel, making it an attractive option for industries focused on reducing their carbon footprint. Additionally, the rise in government incentives and regulations promoting sustainable energy solutions, coupled with the growing adoption of CNG vehicles and infrastructure development, further supports its rapid market growth.
CEO Statements
Adani Total Gas Ltd (ATGL) – Suresh P Manglani, CEO
VE Commercial Vehicles- Vinod Aggarwal, CEO
The India CNG market is segmented into source, end user, and application. Based on source, the market is classified into associated gas, non-associated gas, unconventional sources. Based on end user, the market is classified into light duty vehicles, medium/heavy duty buses, medium/heavy duty trucks, and others. Based on application, the market is classified into residential, chemical, industrial, auto gas, refinery, and others.
Associated Gas: Associated gas is a natural gas found in association with crude oil. It is liberated when oil is produced; if not collected, it is often flared. In the Indian context, associated gas has great importance as a resource for producing CNG especially in areas where oil exploration is carried out. Increasingly, the companies, Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) and Indian Oil Corporation (IOC), have been tapping associated gas to cater to the growing demand for CNG. Hence, associated gas is available in a practical sense and is important for expanding the CNG infrastructure of the country.
Non-associated gas: Non-associated gas is extracted independently of crude oil production from its dedicated gas fields. In India, non-associated gas constitutes a huge part of the CNG supplies, with its sources being largely domestic fields such as the Krishna-Godavari basin and imported liquefied natural gas (LNG). Companies like GAIL (India) Limited and Reliance Industries are heavily working towards the exploration and delivery of non-associated gas, catering CNG to meet the ever-growing demand for cleaner alternative energy solutions for transport.
Unconventional sources: Unconventional sources of natural gas, such as shale gas and CBM, are attracting attention as a possible source of CNG in India. While these resources have not been fully tapped in India, their development is growing. Companies like Cairn Oil & Gas (a subsidiary of Vedanta) are exploring the development of the unconventional sources of energy in order to diversify the supply of natural gas in the country to ease supply constraints and reduce dependence on ever-increasing imports of LNG. Development of these sources can strengthen India's energy security as well as CNG market growth.
Light Duty Vehicles: Light-duty vehicles are the major consumers of CNG in India. Passenger cars or smaller commercial vehicles have an advantage as their price is reduced because of CNG, and also their emissions are lower. A number of best-selling car models are now being offered as factory-fitted CNG systems. Companies such as Maruti Suzuki and Hyundai have CNG versions of their best-selling products in the market to assist the general public in saving on fuel expenses and switching to cleaner fuel options. The penetration and rising acceptance of CNG-powered LDVs is one of the most influencing factors in putting CNG on the market for consideration.
Medium/Heavy-duty buses: Medium/Heavy-duty buses using CNG have now become a common sight in Indian cities, especially as far as public transport is concerned. Government fleets in Delhi and Mumbai are operating these buses to combat air pollution and cut down on fuel costs. Tata Motors and Ashok Leyland, among others supply CNG-powered buses to various state transport corporations that are hugely investing in cleaner vehicles targeting the aspirations of the increasingly growing urban populations for green public transport options.
Medium/Heavy-duty trucks: Medium/Heavy-duty trucks are the lifeblood of India's logistics and freight movement. The increasing cost of fuels and the rising demand for cleaner alternatives have seen many fleet owners moving to CNG trucks. Many manufacturers, including Eicher Motors and Tata Motors, among others, have brought out various models of CNG trucks to meet this demand with choices that are both economical in their operational costs and comparatively eco-friendly when juxtaposed with diesel-powered trucks. With increasing concerns about sustainability, CNG trucks will play a larger role in contributing to climate management in the logistics sector in times to come by reducing emissions and operational costs.
Other applications: CNG can also be used as industrial fuels, and other purposes in generating power. Some industrial states use the cleaner fuel CNG for boilers and furnaces which in the long run, usually consume coal or oil for energy purposes. Fuel consumption by the power plant is now under investigation particularly in countries which have installed a natural gas network. Companies like GAIL and Indian Oil Corporation are busy exploring more avenues for CNG in the non-automotive sectors, as this clean fuel can be used for so many things.
Recent strategic collaborations in the India CNG market reflect a strong commitment to expanding infrastructure, improving fuel accessibility, and promoting sustainable energy solutions. These partnerships often focus on setting up new refueling stations, increasing CNG production capacity, and enhancing distribution networks, thereby supporting the growing demand for cleaner energy alternatives. Companies aim to strengthen their foothold in both urban and rural areas to meet the evolving needs of consumers and businesses. By aligning with government initiatives and leveraging technological advancements, these collaborations also contribute to reducing the carbon footprint and enhancing environmental sustainability in the transportation sector. Some notable examples of key developments in the CNG industry include:
Market Segmentation
By Source
By End User
By Application
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of CNG
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Source Overview
2.2.2 By End User Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. India Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on CNG Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: India Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: India Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting India Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Pollution Control
4.1.1.2 Increased demand for CNG
4.1.1.3 Commercial asset transformation continues
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Infrastructure Limitation
4.1.2.2 Initial Conversion Costs
4.1.2.3 Competition with Electric Vehicles
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Regulatory Compliance
4.1.3.2 Fuel Supply Issues
4.1.3.3 High Conversion Costs
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Infrastructure Development
4.1.4.2 CNG Storage Innovations
4.1.4.3 Hybrid CNG Cars
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 India CNG Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. CNG Market, By Source
6.1 India CNG Market Snapshot, By Source
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Associated Gas
6.1.1.2 Non-Associated Gas
6.1.1.3 Unconventional Sources
Chapter 7. CNG Market, By End User
7.1 India CNG Market Snapshot, By End User
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Light Duty Vehicles
7.1.1.2 Medium/Heavy Duty Buses
7.1.1.3 Medium/Heavy Duty Trucks
7.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 8. CNG Market, By Application
8.1 India CNG Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Residential/Commercial
8.1.1.2 Chemical
8.1.1.3 Industrial
8.1.1.4 Auto Gas
8.1.1.5 Refinery
8.1.1.6 Others
Chapter 9. CNG Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 CNG Market Revenue Share, By India 2024 (%)
9.3 India CNG Market, By States
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.3.2 Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited
11.3 AG&P
11.4 Gujarat Gas Ltd
11.5 MGL
11.6 Adani Group
11.7 THINK Gas Distribution Pvt. Ltd
11.8 Central U.P. Gas Limited
11.9 GAIL (India) Limited
11.10 Sabarmati Gas Limited