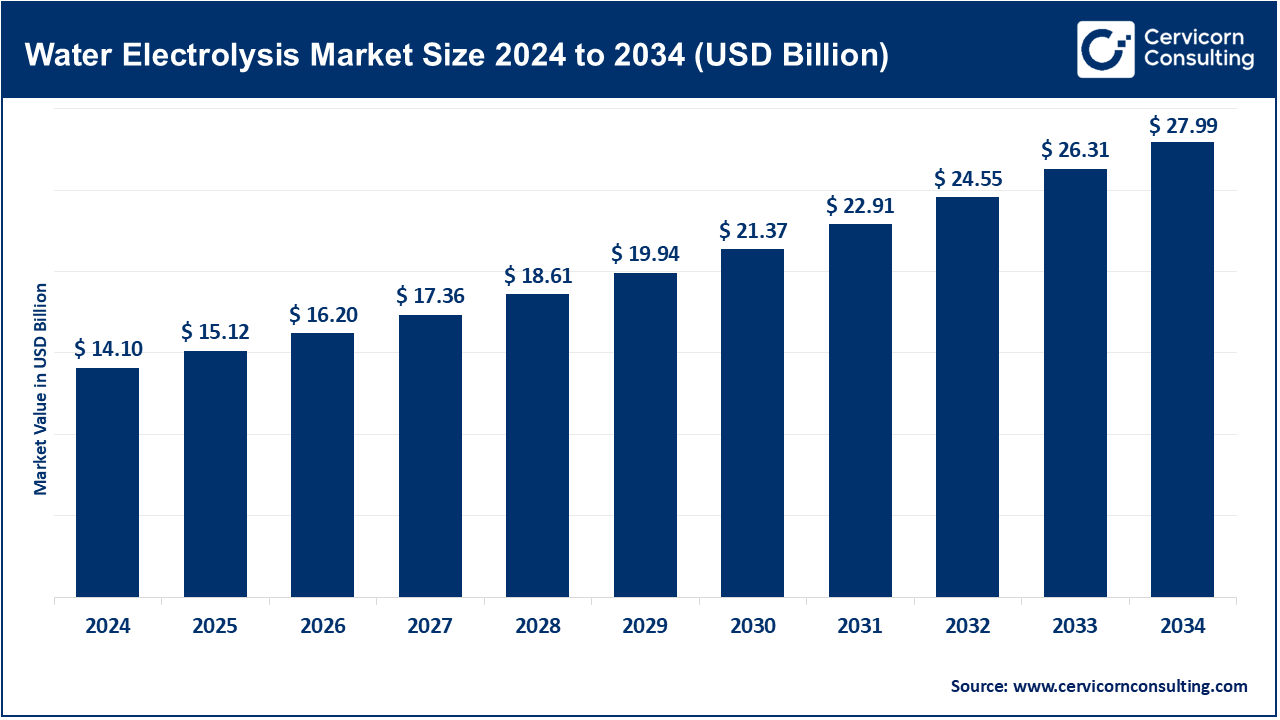
The global water electrolysis market size was surpassed at USD 14.10 billion in 2024 and is predicted to reach around USD 27.99 billion by 2034 increasing from USD 15.12 billion in 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.09% from 2025 to 2034.
The water electrolysis market involves the process of using electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, a method essential for producing green hydrogen. This process occurs in an electrolyzer, where water is broken down in the presence of an electric current. The water electrolysis market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing demand for clean hydrogen production, driven by the transition to renewable energy and decarbonization efforts. Hydrogen is a crucial element in energy storage, industrial applications, and transportation. With the global shift towards sustainable practices, the market for water electrolysis is expected to expand rapidly in the coming years. Government incentives, technological advancements, and the decreasing cost of renewable energy sources like wind and solar are further accelerating the adoption of water electrolysis technologies, making it a key player in the global hydrogen economy.
Key technologies include alkaline, proton exchange membrane (PEM), and solid oxide electrolysis. Alkaline electrolysis uses a liquid alkaline solution, PEM electrolysis utilizes a solid polymer electrolyte, and SOE operates at high temperatures and offers high efficiency. Each type has distinct advantages, with PEM electrolysis being highly efficient and suitable for variable renewable energy sources, while alkaline electrolysis is more cost-effective for large-scale production. Applications span various sectors, including power generation, transportation, chemical manufacturing, and industrial processes. Major growth drivers include the push for decarbonization, the integration of renewable energy sources, and the development of hydrogen infrastructure across regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 15.12 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 27.99 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.09% from 2025 to 2034 |
| Largest Region | Europe |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Segment Covered | By Technology, Application, End User, Region |
Rising Corporate Sustainability Goals:
Increasing Hydrogen Fuel Cell Adoption:
High Initial Capital Costs:
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs:
Collaboration with Emerging Technologies:
Expansion into Developing Markets:
Limited Availability of High-Purity Water:
Integration with Existing Energy Systems:
Alkaline Water Electrolysis (AWE): In 2024, the AWE segment has accounted market share of 31.2%. Alkaline Water Electrolysis (AWE) is a mature technology that uses an alkaline electrolyte (such as potassium hydroxide) to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. It’s known for its reliability and cost-effectiveness. Trends include increasing efficiency and scaling up for large-scale hydrogen production, driven by the need for sustainable energy solutions and decreasing costs of materials and systems.
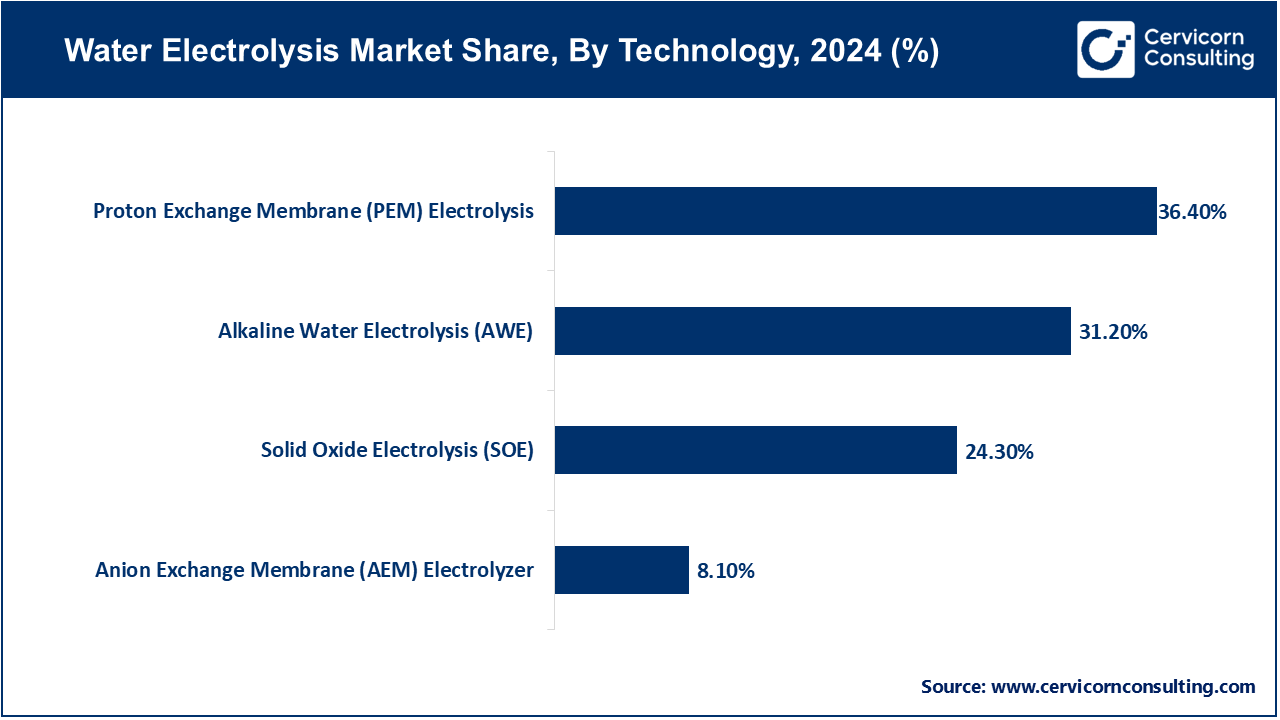
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis: The PEM Electrolysis segment has accounted market share of 36.4% in 2024. Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolysis uses a solid polymer membrane as an electrolyte, offering high efficiency and fast response times. It’s suited for applications requiring high purity hydrogen and integration with renewable energy sources. Current trends involve advancements in membrane technology, enhancing performance and durability, and expanding use in decentralized and small-scale hydrogen production systems to support renewable energy integration.
Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOE): The SOE segment has generated market share of 24.3% in 2024. Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOE) operates at high temperatures using a solid oxide electrolyte, enabling high-efficiency hydrogen production. It is particularly effective for industrial applications and energy storage. Trends include improvements in material durability and system integration, with a focus on increasing operational stability and efficiency. SOE is gaining attention for its potential in large-scale and high-temperature hydrogen production processes.
Power Plants: Water electrolysis in power plants focuses on producing hydrogen as a clean energy carrier. This hydrogen can be used for energy storage, balancing grid demand, and generating electricity. Trends include increasing integration with renewable energy sources to utilize surplus power and enhance grid stability. The technology is advancing to improve efficiency and scalability, driving growth in the market.
Chemical Industry: In the chemical industry, water electrolysis is used to produce hydrogen for various processes, including ammonia synthesis and methanol production. The trend is toward adopting green hydrogen to reduce carbon emissions and align with sustainability goals. Innovations in electrolysis technology aim to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, making green hydrogen a more attractive option for chemical manufacturing.
Petroleum Industry: The petroleum industry uses hydrogen from water electrolysis for refining processes, such as hydrocracking and desulfurization. Trends include a shift towards green hydrogen to decrease the carbon footprint of refining operations and meet regulatory requirements. Technological advancements are focused on improving hydrogen production efficiency and integrating electrolysis systems with existing infrastructure in the petroleum sector.
Electronics and Semiconductors: Water electrolysis provides high-purity hydrogen essential for electronics and semiconductor manufacturing, used in processes like chemical vapor deposition. The trend is towards increased adoption of green hydrogen to meet environmental regulations and improve sustainability. Advances in electrolysis technology are enhancing purity and efficiency, addressing the high-quality hydrogen needs of the electronics industry.
Steel Production: In steel production, hydrogen from water electrolysis is utilized as a reducing agent to replace carbon-intensive processes. The trend is towards adopting green hydrogen to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and meet industry decarbonization targets. Innovations in electrolysis technology are focused on scaling up production and reducing costs to support the steel industry’s transition to cleaner methods.
Others: Other applications of water electrolysis include hydrogen production for fuel cells, backup power systems, and various industrial uses. The trend is towards expanding the use of green hydrogen in diverse applications to support sustainability and energy transition goals. Technological advancements are improving electrolysis efficiency and reducing costs, driving growth in these additional sectors.
Industrial: In the industrial sector, water electrolysis produces hydrogen used as a feedstock for chemicals and refining processes. Trends include increasing adoption for ammonia and methanol production and efforts to decarbonize heavy industries. Innovations in electrolysis technology aim to improve efficiency and reduce costs, supporting the shift toward more sustainable industrial practices and fostering growth in this segment.
Transportation: Water electrolysis is used to generate hydrogen for fuel cells in vehicles, including buses, trucks, and cars. The transportation sector is seeing a rise in hydrogen-powered vehicles as part of the transition to cleaner fuels. Trends include expanding refueling infrastructure and advancements in fuel cell technology, which are driving increased adoption and investment in hydrogen-powered transport solutions.
Energy: In the energy sector, water electrolysis provides a method for storing and utilizing excess renewable energy by converting it into hydrogen. Trends involve the integration of electrolysis with wind and solar power to enhance grid stability and energy storage. As renewable energy sources grow, so does the role of electrolysis in balancing energy supply and supporting a sustainable energy infrastructure.
Commercial: Water electrolysis in the commercial sector focuses on providing hydrogen for various applications, including backup power systems and heating. Trends include growing interest in hydrogen as a clean energy solution for commercial buildings and facilities, driven by sustainability goals and energy efficiency improvements. This segment is expanding as businesses seek to reduce carbon footprints and adopt cleaner energy technologies.
Others: The "Others" segment encompasses niche applications of water electrolysis, such as in aerospace for propulsion systems or in specialized manufacturing processes. Trends include research and development into novel applications and technologies that leverage hydrogen for unique use cases. This segment reflects emerging opportunities and innovative uses of electrolysis technology across diverse and specialized fields.
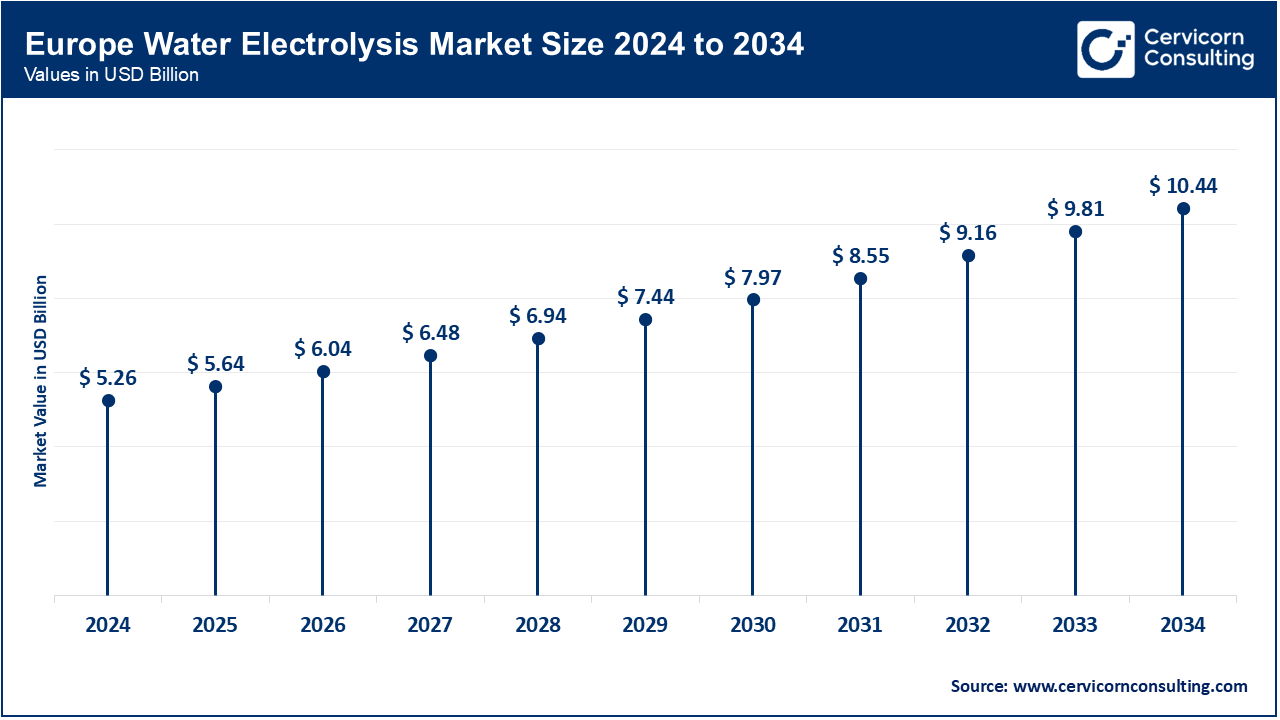
The Europe water electrolysis market size is expected to hit around USD 10.44 billion by 2034 and growing at a CAGR of 7.10% from 2025 to 2034 driven by ambitious climate goals and a strong commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The trend in Europe involves substantial public and private investments in hydrogen infrastructure, with a focus on integrating electrolysis with renewable energy sources and advancing hydrogen fuel cell technology for various applications, including transportation and industry.
The North America water electrolysis market size was valued at USD 4.4 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 8.73 billion by 2034, driven by substantial investments in green hydrogen projects and research. The trend is focused on integrating electrolysis with large-scale renewable energy projects and advancing hydrogen infrastructure. There is significant support from government policies and incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and fostering clean energy technologies, particularly in the U.S. and Canada.
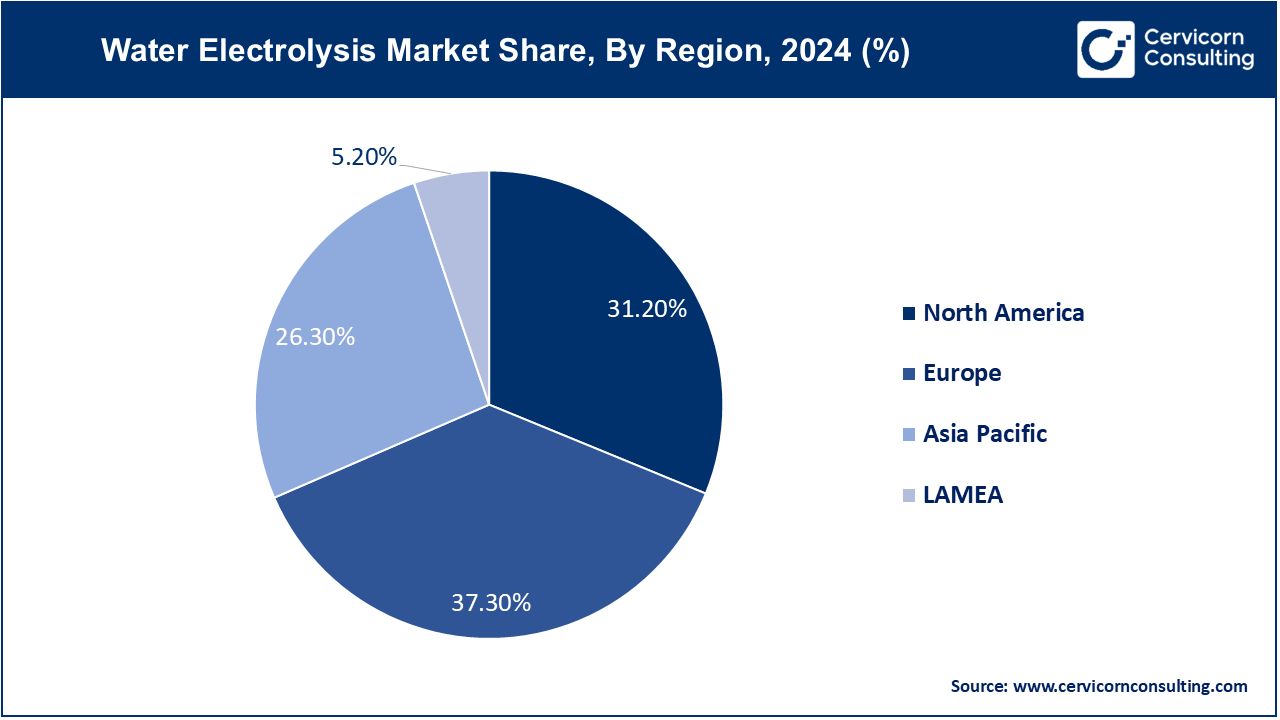
The Asia-Pacific water electrolysis market size was valued at USD 3.71 billion in 2024 and is poise to reach around USD 7.36 billion by 2034, experiencing rapid growth (CAGR of 7.23%) due to increasing industrialization and energy demands. Trends include significant investments in hydrogen production technologies and initiatives to develop hydrogen infrastructure, particularly in countries like Japan, South Korea, and China. The region is focusing on integrating water electrolysis with renewable energy sources to address energy security and environmental concerns.
In the LAMEA region, the water electrolysis market is emerging with opportunities driven by growing interest in sustainable energy solutions and industrial applications. Trends include the development of pilot projects and partnerships to explore hydrogen production potential, especially in the Middle East, which has abundant renewable energy resources. In Latin America and Africa, there is a focus on leveraging electrolysis for energy access and industrial development, although the market is still in early stages.
New players such as Green Hydrogen Systems and H2B2 Electrolysis Technologies are adopting innovative approaches like modular systems and advanced electrolyzer designs to enter the market. Nel Hydrogen, ITM Power, and Siemens Energy dominate the market due to their extensive experience, broad technology portfolios, and significant investments in R&D. These key players leverage their advanced technology, strong global presence, and established infrastructure to lead in hydrogen production, driving advancements and scaling up electrolyzer capabilities to meet growing demand.
Market Segmentation
By Technology
By Application
By End User
By Region