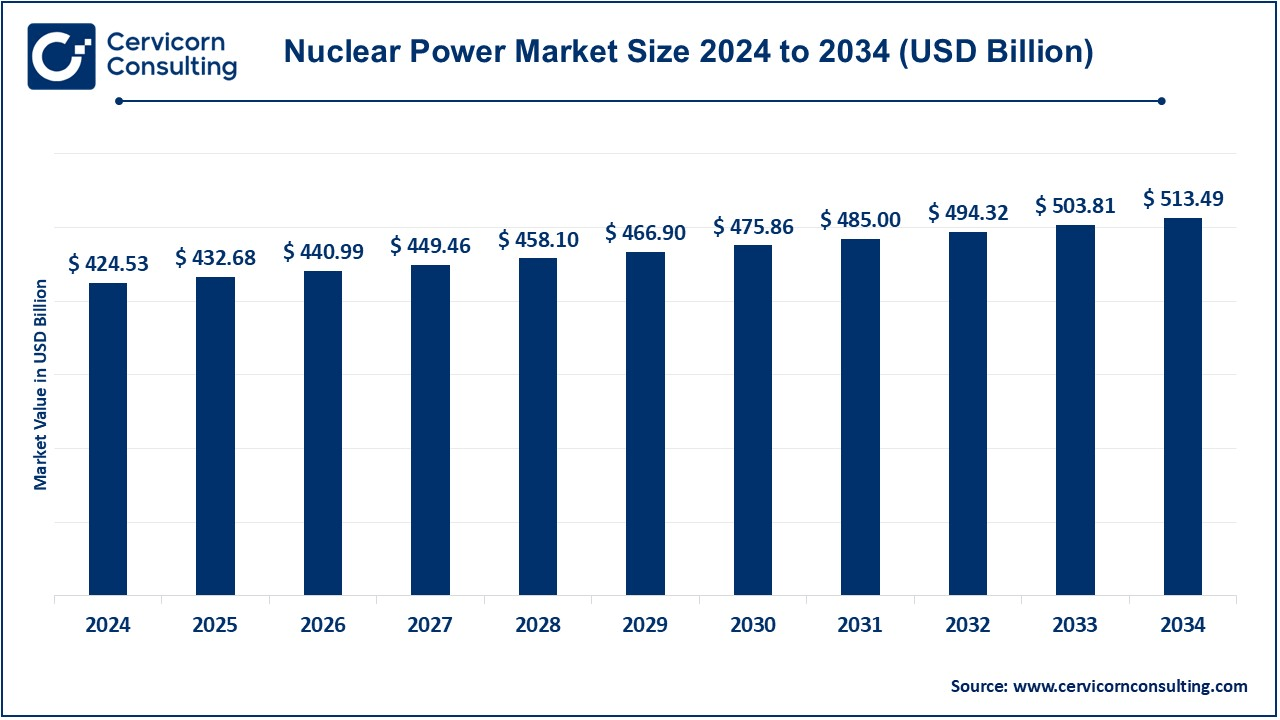
The global nuclear power market size was valued at USD 424.53 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 513.49 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.92% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The nuclear power market has witnessed solid growth in response to the escalating global demand for clean and sustainable resources, nuclear technological advancements, and surging investments in nuclear infrastructure. Initiatives among governments aimed at cutting carbon emissions, and energy security, are other crucial factors bottoming this ostensible hike in nuclear power. Growing advanced reactors and well-engineered nuclear waste management are likely to supplement market growth, with the continued push toward diversification of energy resources contributing most as a driving force tome markets overall.
Nuclear power refers to the use of nuclear reactions, primarily fission, in the generation of electricity. This involves controlling the reaction with the correct moderation and cooling to extract the heat released in fission reactions between heavy atomic nuclei, for example, uranium or plutonium, within a nuclear reactor. Nuclear energy is considered a low-carbon source of energy, which could serve as a viable substitute for fossil fuels. The industry is concentrating on safety, efficiency, and sustainability, while at the same time contributing to inquiries relating to wastes and nuclear proliferation.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 432.68 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 513.49 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 1.92% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Applications, Type, Connectivity, Capacity, Plant Lifecycle Stage, Region |
| Key Companies | BHP Billiton, Paladin Energy, Bulgarian Energy Holding, Electrabel, Electronuclear, Uranium One, Bruce Power, New Brunswick Power, China Guangdong Nuclear Power Group, Fortum, Areva, EDF, Nukem Energy GmbH, PreussenElektra GmbH, Dominion Resources, RWE AG, Nuclear Power Corporation of India, Ansaldo Energia |
The nuclear power market is segmented into applications, type, connectivity, capacity, plant lifecycle stage and region. Based on applications, the market is classified into energy, defense and others. Based on type, the market is classified into nuclear power plants and small modular reactors. Based on connectivity, the market is classified into off-grid and grid-connected. Based on capacity, the market is classified into small (Less Than 500 MW), medium (500-1000 MW) and large (Above 1000 MW). Based on plant lifecycle stage, the market is classified into EPC, maintenance and operation services and decommissions.
Energy: Nuclear reactors are essential for energy production- a low-carbon source of electricity. Electricity is generated through steam turbines by capturing the heat produced from a nuclear fission process. This makes the energy crucial for application both in large-scale power grids and off-grid systems reliable for base load. Nuclear energy is considered one of the most appropriate options available to fulfill rising energy demand worldwide and lower emission compared to fossil fuel burning.
Defense: Nuclear reactors have defense applications, mainly in the production of materials like plutonium and enriched uranium that are used to produce weapons. In naval defense, nuclear reactors power submarines and aircraft carriers, which stay at sea for extended periods without needing to return to shore for refueling. Some use nuclear reactors to conduct their research and development in military technology; this covers propulsion systems, weaponry, and strategic deterrence, forming a crucial element of the national security policy in some nations.
Others: Beyond energy and defense, nuclear reactors have many applications in the industries of medicine, space, and industry. For example, reactors are used to make medical isotopes, that play a very important role in imaging diagnostics and as treatments for cancer. Nuclear reactors are also used in powering small deep-space missions and even to provide long-duration energy supplies for spacecraft. Industrially, nuclear reactors are used for research, testing materials under extreme conditions, and for specific advanced manufacturing processes that require high temperatures and neutron sources.
Pressurized Water Reactor and Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor: The most popular reactors of the world, globally are PWRs or PHWRs. A pressurized water reactor uses regular water both as coolant as well as neutron moderator while heavy water deuterium oxide serves the function in case of pressurized heavy water reactor. A key benefit to those countries that have not possessed natural uranium enrichment facility, is that a natural uranium fuelled pressurized heavy water reactor has been advantageous. Both of these reactor types are characterized by stability, safety, and high efficiency in energy production.
Boiling Water Reactor: The Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) utilises water as a coolant and moderator that directly boils in the reactor core for the production of steam, which then drives turbines mounted onto generators, producing electricity. BWRs are simpler compared to PWRs since they are not required to have secondary loops for steam production, but this design releases the radio steam directly through the system of turbines, leading to some strange operational and safety issues. BWRs are also the most widely used types of nuclear power plants all over the world.
High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor: High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor is designed to operate at far higher temperatures than other types of reactors, usually with the use of helium gas as the coolant. These reactors have a positive edge in that they generate excellent quality heat which, except for electricity production, is useful for applications such as hydrogen production and desalination. They are safer because they provide inherent safety systems that will prevent overheating and ensure that accidents never happen at any extreme condition, hence highly promising for energy in the future.
Liquid Metal Fast Breeder Reactor: Liquid Metal Fast Breeder Reactors (LMFBRs) are reactors designed to breed more fuel than they consume by converting fertile material, such as uranium-238, into fissile material, such as plutonium-239, through nuclear reactions. Liquid metals, like sodium, can be used in the coolants to get high operating temperatures and increased efficiency. LMFBRs are considered to be the future direction for sustainable long-term development in nuclear energy. LMFBRs are going to make use of readily available depleted uranium but have material and safety related complexities, which must overcome.
Other Types of reactors: There are a very large number of other types of reactors, either under development or just niche applications. Molten Salt Reactors for instance is using a liquid salt that serves both as a fuel and as coolant. Once again they have a very efficient high thermal efficiency with various intrinsic safety features. Fusion reactors are still very much in their experimental phases but promise clean, nearly limitless energy production. Additionally, Small Modular Reactors, or SMRs, will offer scaleable designs with flexibility suitable for generation at smaller or remote locations. Advanced reactor types aim at overcoming many of the limitations currently inherent to traditional reactors with safer and more efficient sources of energy.
The nuclear power market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
North America: North America is a key player in the global nuclear power market, primarily due to the United States. The country has the highest number of nuclear reactors globally. The U.S. accounts for nearly a third of global nuclear energy generation. For example, in August 2024, The United States has become the world's leading producer of nuclear power as it produces about 30% of the nuclear electricity globally, with its reactors producing 772 TWh in the year 2022 which constitutes 18% of all electrical output. In fact, the Inflation Reduction Act, passed in August 2022, endorses nuclear development by increasing investment and tax incentives for nuclear. Despite low natural gas prices that reduce the economic viability of new projects, the industry continues to invest significantly in maintenance and upgrades in order to be able to sustain its role in providing nearly 20% of the nation's electricity and over 55% of its carbon-free energy. Another country with a major share is Canada, particularly due to its advanced CANDU reactors, which are moderated and cooled by heavy water. The two nations are investing in nuclear technology to ensure energy security while reducing carbon emissions. In Mexico, the nuclear capacity is smaller, but still, it continues to be part of its energy mix.
Europe: Europe is home to some of the world's most mature nuclear energy markets, with France, the United Kingdom, and Germany leading the pack. Nuclear energy produces about 70% of electricity in France, which depends heavily on its nuclear fleet for both domestic and export energy needs. For instance, as of December 2024, France is so dependent on nuclear energy, whose share in electricity generation is approximated to be about 70%. The government, at one point had planned to reduce the nuclear share to 50% by 2025, the target was then pushed all the way to 2035, and finally was abolished in 2023. In response to callings for energy, it launched plans to build six new reactors; eight more are also reported to be possible. France is the world's largest net exporter of electricity, mainly due to low generation costs and the fact that a good chunk of its electricity is made from recycled nuclear fuel. The UK operates several nuclear plants, including new builds in the country's energy transition. The country of Germany has hosted a significant nuclear fleet in the past but is planning to get out of that business as part of the policy in the country, which, in essence, means that it is transitioning to a way of generating energy. Other nuclear-dependent countries include Russia and Ukraine, as well as Sweden, among others.
Asia-Pacific: Asia-Pacific is one of the most rapidly growing regions for nuclear power, mainly due to the fast development of China, Japan, and South Korea. China is very fast expanding its nuclear capacity to decrease dependence on coal and tackle environmental issues. The State Council has already sanctioned five nuclear power projects to be ready by August 2024, which include 11 new reactors to be constructed. Notably, the Xuwei Phase I project will combine with the world's first-of-its-kind combination between a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor and a pressurized water reactor into one plant that could help provide both industrial heating and electricity. The initiative is expected to lessen coal usage and carbon emissions, and overall, this approval would reflect China's continuous engagement in expanding its nuclear energy capacity, with 56 operable reactors it and 30 under construction. After the Fukushima disaster, Japan restarted its reactors and, now, is again the big player in the nuclear market. South Korea stands for its advanced nuclear technology with a considerable nuclear fleet and a significant portion of this country's energy is covered. India is expanding its nuclear energy capacities and attempts to reduce carbon footprints and cover the growing demand in this field.
LAMEA: The LAMEA region has a more diversified nuclear landscape, with countries at every stage of nuclear development. In Latin America, Brazil and Argentina stand out as the main participants, with both countries already operating nuclear plants and adding to their nuclear capacities in the near future. Mexico hosts a nuclear plant but plays a less active role than its regional peers do. In the Middle East, countries like the United Arab Emirates have recently entered the nuclear power sector, and an operational Barakah nuclear plant is seen here. Other nations like Saudi Arabia are also interested in nuclear energy for future power generation. Africa, except South Africa, boasts no working nuclear power station at all; however, various countries in this continent continue to deliberate over establishing nuclear energy as long-term energy sources like Egypt and Kenya.
The new entrants in the nuclear power market are using cutting-edge technologies like small modular reactors (SMRs), which provide scalability, improved safety, and shorter construction times compared to conventional large reactors. It also integrates advanced digital tools, including AI-driven monitoring systems, predictive maintenance, and real-time data analytics, to optimize operations and improve efficiency. Further, they are now concentrating on sustainability by using innovative materials and techniques that will help them reduce waste and carbon emissions and address public concerns over safety and environmental impact through a nuclear energy solution that is more reliable and environmentally friendly.
Nuclear power recently fervently energized strategic partnerships and investments in advancing the industry. A lot has improved for next-generation reactors, including safety and environment improvements, under the cooperation for the last five years among the governments, the private sector companies, and institutes of research. This supported innovations, including SMRs, and research into energy from fusion that eventually led to the nucleus for power becoming one of the advantageous positions in attaining the global energy goals imagined. This eventually led to giving more attention to nuclear power as one of the reliable sources of low-carbon energy currently.
These developments push the global nuclear power sector toward greater efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Countries are striving toward ambitious climate goals while reducing their dependence on fossil fuels; therefore, there is a great interest in advanced nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors and next-gen fusion reactors. Innovation, along with the big investments in strategic partnerships, breaks traditional barriers in nuclear energy by driving innovation to the points of waste management and security. This is what can place nuclear power in critical use in the new path toward a cleaner and much more reliable global energy system.
Market Segmentation
By Applications
By Type
By Connectivity
By Capacity
By Plant Lifecycle Stage
By Region