The logistics industry is witnessing high growth rates owing to the growing need for effective supply chain solutions, rising e-commerce market, and innovation in automation and digitalization. The growth of omnichannel retailing, last-mile delivery technologies, and route optimization using AI is transforming logistics operations, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
In addition, the convergence of IoT, blockchain, and predictive analytics is enhancing real-time monitoring, inventory management, and fraud detection. Increasing global trade, the growth of free trade agreements, and the increasing demand for cold chain logistics in pharmaceuticals and perishables are also fueling the market. Sustainability programs, including electric delivery trucks and carbon-neutral warehouses, are also picking up pace, further cementing industry transformation.
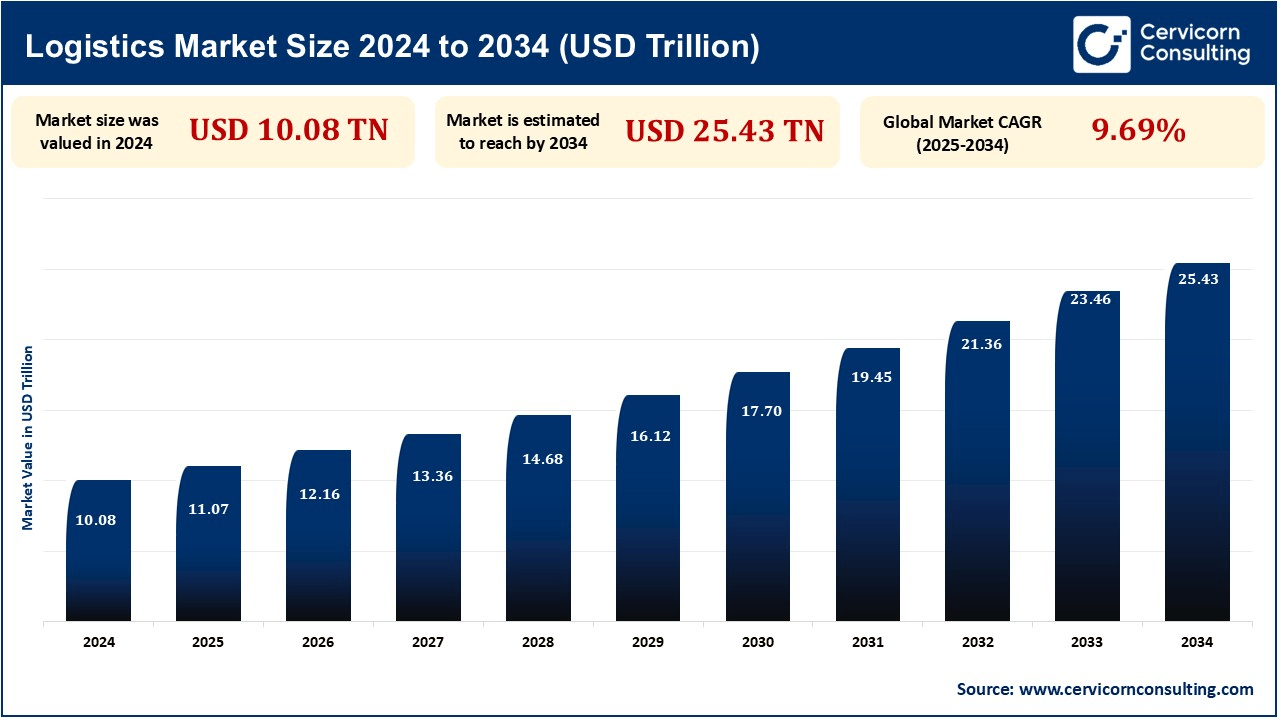
The global logistics market size was reached at USD 10.081 trillion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 25.43 trillion by 2034, exhibiting at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.69% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The online growth is transforming logistics operations, with focuses on quicker delivery, improved warehouse management, and last-mile connectivity. Amazon, Alibaba, and Flipkart are some e-commerce platforms that are investing in sophisticated logistics solutions, such as automated fulfillment centers, micro-warehouses, and drones for delivery. Omnichannel logistics is part of physical stores, online stores, and mobile commerce, which enable consumers to select convenient delivery options. Demand for same-day and next-day delivery has compelled the players in the logistics sector to expand fleets and streamline supply chains. Technology drivers such as real-time tracking, digital freight matching, and AI-based demand forecasting also drive the trend as these increase efficiency as well as consumerization of e-commerce logistics. For instance, Global e-commerce sales reached $5.8 trillion in 2023, and are expected to surpass $7.4 trillion by 2025, driving demand for faster logistics solutions.
Cold chain logistics is expanding rapidly with the rise in demand for temperature-controlled transportation and warehousing in pharmaceuticals, food, and biotechnology. With more and more biologics, vaccines, and perishable foods being manufactured in greater volumes, it is essential to maintain their integrity during transportation. The COVID-19 pandemic made the focus anew on advanced cold storage solutions, particularly vaccine distribution. Companies are investing in smart refrigeration technology, Internet of Things temperature tracking, and blockchain traceability. Moreover, green cold chain solutions such as solar-powered refrigeration units and COâ‚‚-cooling systems are being adopted in an effort to meet environmental imperatives. Expansion of global food trade and pharma supply chains continues to drive the need for effective and secure cold chain logistics. For instance, the global spending in biopharma cold chain logistics from 2020 to 2024. In 2024, biopharma cold chain logistics spending is expected to amount to 21.3 billion U.S. dollars.
While automation and AI have several benefits, the significant initial investment required for robotic warehouses, AI-driven logistics software, and IoT connection is a barrier. Small and medium-sized logistics organizations struggle to adopt these technologies due to budgetary constraints and implementation costs. The deployment of autonomous vehicles, smart warehouses, and AI-driven analytics requires substantial infrastructure upgrades. Additionally, ongoing maintenance, cybersecurity measures, and workforce training add to operational expenses. Although large corporations can afford these investments, smaller players face difficulties in competing with tech-driven logistics giants. The return on investment (ROI) for AI implementation often takes time, making it a major barrier for widespread adoption in the industry. For example, Amazon spent over $300 million to automate its warehouses with Kiva robots, improving efficiency but increasing capital costs.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing logistics by improving decision-making, supply chain optimization, and eliminating inefficiencies. Predictive analytics enables demand fluctuation forecasting, route optimization, and inventory management improvement. AI-based automation in warehouses automates order fulfillment, minimizes processing time, and eliminates errors. Logistics companies are using machine learning algorithms to detect fraud, assess risk, and clear customs automatically. Chatbots are also improving customer service through AI by providing real-time updates of shipments and answering questions in an effective way. The use of deep learning models and AI-based fleet management platforms is expected to enhance the responsiveness and agility of supply chains in the future. For instance, FedEx uses AI-powered analytics, which has reduced delivery errors by 25% and improved fuel efficiency by 10% through smart route optimization.
| Attributes | Details |
| Logistics Market Size in 2025 | USD 11.07 Trillion |
| Logistics Market CAGR | 9.69% from 2025 to 2034 |
| Key Players |
|
| By Model |
|
| By Mode of Transport |
|
| By End Use |
|
| By Region |
|
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing logistics market as a result of rapid industrialization, urbanization, and booming e-commerce. Key players are China, India, Japan, and the Southeast Asian economies, with investments being high on infrastructure, upgrading ports, and smart logistics solutions. The sector in the region is supported by massive production in large volumes, increasing middle-class consumers, and an aggressive need for quick and efficient delivery service.
Business establishments are embracing automation, robots, and blockchain for more supply chain visibility. However, there are impediments such as scattered logistics networks, regulatory divergence, and geopolitical tensions that could influence market efficiency and trade movement. For instance, in 2022 alone, the Transport Department of China allocated over USD 3.4 billion to bolster road transport infrastructure. Looking ahead, the National Development and Reform Commission, along with the Ministry of Transport, has set an ambitious goal: expanding the national road network to encompass 299,000 km of highways and 162,000 km of expressways by 2035.
North America has a very well-developed logistics sector, propelled by advanced infrastructure, sound manufacturing, and the presence of global logistics giants. The United States leads the continent, fueled by increased road, rail, and air freight infrastructure, with a sound e-commerce foundation. Technology is also revolutionizing the logistics sector through innovations like automation, supply chain management through artificial intelligence, and self-driving trucks. Canada and Mexico are crucial as well, as cross-border trade under free trade agreements such as the USMCA increases regional logistical productivity. Expansion, however, faces constraints in labor shortages, fuel price increases, and regulatory restrictions.
Manufacturing logistics involves the movement, storage, and delivery of raw materials, parts, and finished products between production plants and markets. Effective logistics management provides minimal downtime and efficient supply chain operations. JIT and lean manufacturing concepts demand accurate inventory management and on-time deliveries to prevent production stoppages. With globalization, manufacturers increasingly use multimodal transport solutions to minimize costs and lead times. Further, automation advancements and AI-powered predictive analytics are boosting the efficiency of freight transport and warehouse management. Logistics is the key to mitigating wastage, operational effectiveness, and staying competitive.
Second-party logistics (2PL) providers deliver transportation and warehousing services to companies. They own fleets of trucks, ships, or warehouses and provide required logistics services. Businesses employ 2PL firms to arrange the transportation of freight without involving themselves in end-to-end supply chain management. Examples are shipping firms, freight firms, and warehouse firms. The model provides businesses with specialized logistics service but maintains control of supply chain strategy.
Road transport is the most prevalent logistics mode because of its flexibility, large network, and cost-effectiveness for short- to medium-distance deliveries. It is critical for last-mile delivery, allowing door-to-door transportation without any hiccups. Road freight is vital for retail, FMCG, and agriculture industries, providing timely restocking of goods. The growth in e-commerce has enormously increased the demand for road logistics, as companies are spending in fleet management, route planning, and electric trucks to make their operations efficient. But there are challenges in operational effectiveness arising from traffic congestion, regulatory hindrances, and volatility in fuel prices.
Empower your strategy with expert insights, purchase this premium research@ https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/buy-now/2316
Ask here for more details@ sales@cervicornconsulting.com