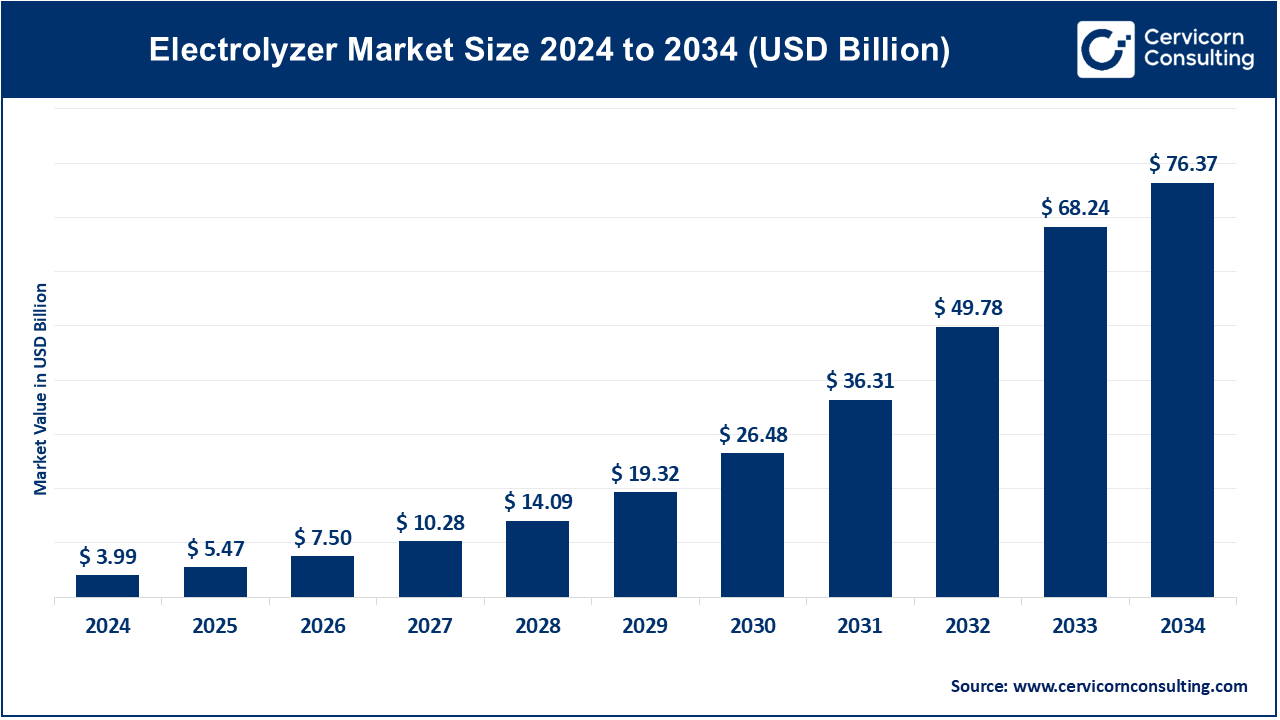
The global electrolyzer market size was accounted for USD 3.99 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 76.37 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34.34% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The electrolyzers market is growing rapidly, driven by the increasing demand for clean hydrogen production as part of the global transition to renewable energy sources. The rise in hydrogen applications in sectors such as transportation, industrial processes, and energy storage is expected to drive market growth. With governments and industries investing heavily in hydrogen technologies to reduce carbon emissions, the electrolyzer market is expected to grow significantly over the next decade. The growth is further supported by technological advancements, cost reductions, and the scaling up of production capacity, making electrolyzers more cost-competitive and commercially viable in the near future.
The electrolyzer market involves technologies that use electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, crucial for hydrogen production. Key applications include renewable energy storage, industrial processes like steel production, and fuel cells for clean energy solutions. The market is driven by increasing global focus on sustainable energy solutions, government initiatives promoting hydrogen economy, and advancements in electrolysis technology. Key players are innovating in electrolyzer types like alkaline, PEM, and SOEC to enhance efficiency and scalability. Challenges include high initial costs and technological barriers, but growth opportunities lie in expanding applications across industries and integrating electrolyzers with renewable energy sources.
“According to Indian government data, the first phase of the National Hydrogen Mission aims to establish 1.5 gigawatts (GW) of electrolyzer manufacturing capacity, with an initial 0.3 GW capacity set to be operational soon”.
“The Adani Group is advancing its clean energy goals by developing in-house electrolyzer technology with a planned annual capacity of up to 5 gigawatts (GW). This initiative underscores Adani's commitment to green hydrogen integration, supporting projects in green ammonia, urea, and methanol production as part of their broader decarbonization strategy.”
What is electrolyzer?
An electrolyzer is a device that uses electricity to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction, particularly electrolysis, to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. There are several types of electrolyzers, the most common being alkaline electrolyzers (AEL), proton exchange membrane electrolyzers (PEM), and solid oxide electrolyzers (SOE). AELs are the most mature technology, typically used in industrial-scale hydrogen production due to their lower cost and durability. PEM electrolyzers are gaining popularity due to their efficiency and ability to operate at variable power inputs, making them suitable for renewable energy applications. SOE electrolyzers, which operate at high temperatures, are still under development but have the potential to offer greater efficiency in hydrogen production.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 5.47 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 76.37 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate | CAGR of 34.34% from 2025 to 2034 |
| Largest Region | Asia Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region | North America |
| Segment Covered | Type, Capacity, Application, Region |
Industrial Decarbonization Initiatives:
Industries face increasing pressure to decarbonize operations to meet environmental regulations and sustainability targets. Electrolyzers enable industries such as steel, chemicals, and refining to produce green hydrogen, reducing carbon emissions from traditionally high-emission processes. This adoption supports industry efforts to achieve carbon neutrality and enhances their competitiveness in a carbon-constrained future.
Investment in Hydrogen Infrastructure:
Governments, energy companies, and automotive manufacturers are making substantial investments in hydrogen infrastructure, including refueling stations and distribution networks. These investments are critical for scaling up hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and ensuring adequate hydrogen supply. Electrolyzers play a pivotal role in supplying green hydrogen to these infrastructure developments, driving market growth and supporting the transition to a hydrogen economy.
High Capital Costs and Initial Investments:
The high upfront capital costs associated with electrolyzer installation and operation present a significant barrier to market entry and widespread adoption. Despite potential long-term cost savings from renewable hydrogen production, the initial investment required for electrolyzer projects can be prohibitive for many potential buyers and investors.
Grid Integration Challenges:
Integrating electrolyzers into existing electricity grids poses technical challenges, particularly regarding grid stability and compatibility with fluctuating renewable energy sources. Electrolyzers require consistent and reliable electricity supply to operate efficiently, and grid infrastructure may need upgrades to accommodate the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation, adding complexity and costs to electrolyzer deployment.
Hydrogen Export and International Trade:
There is a growing opportunity for electrolyzer manufacturers and hydrogen producers to participate in international hydrogen trade. Countries with abundant renewable energy resources can produce green hydrogen at competitive prices and export it to regions with high demand for clean energy solutions, fostering global partnerships and economic growth.
Electrolyzers in Energy Storage Systems:
Electrolyzers can play a crucial role in energy storage systems by converting surplus renewable electricity into hydrogen during periods of low demand or excess generation. This stored hydrogen can then be used for power generation, heating, or transportation when renewable energy production is insufficient, enhancing grid stability and reliability while maximizing renewable energy utilization. Integrating electrolyzers into energy storage solutions presents a significant opportunity to support grid flexibility and resilience.
Supply Chain Constraints:
The electrolyzer market faces challenges related to the global supply chain, including sourcing critical materials and components required for electrolyzer manufacturing. Supply chain disruptions, geopolitical factors, and limited availability of specialized components can impact production timelines, increase costs, and hinder market growth.
Performance and Efficiency Improvements:
Despite technological advancements, electrolyzer efficiency and performance metrics such as durability, hydrogen purity, and operational reliability remain critical challenges. Achieving higher efficiency levels, improving electrolyzer lifespan, and reducing maintenance requirements are ongoing priorities for manufacturers to enhance competitiveness and meet evolving market demands.
Alkaline Electrolyzer: Alkaline electrolyzers segment has captured share revenue of 19% in 2024. Alkaline electrolyzers use an alkaline electrolyte (usually potassium hydroxide) to conduct electricity and split water into hydrogen and oxygen. They are known for their efficiency in industrial applications and have been widely used for decades, although advancements in other types are shifting market preferences.
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolyzer: PEM electrolyzers segment has accounted second highest revenue share of 38% in 2024. PEM electrolyzers use a solid polymer electrolyte membrane to facilitate the electrochemical reaction, producing high-purity hydrogen suitable for various applications including fuel cells. They offer fast response times, high efficiency, and compact size, making them ideal for applications requiring intermittent operation and precise control.
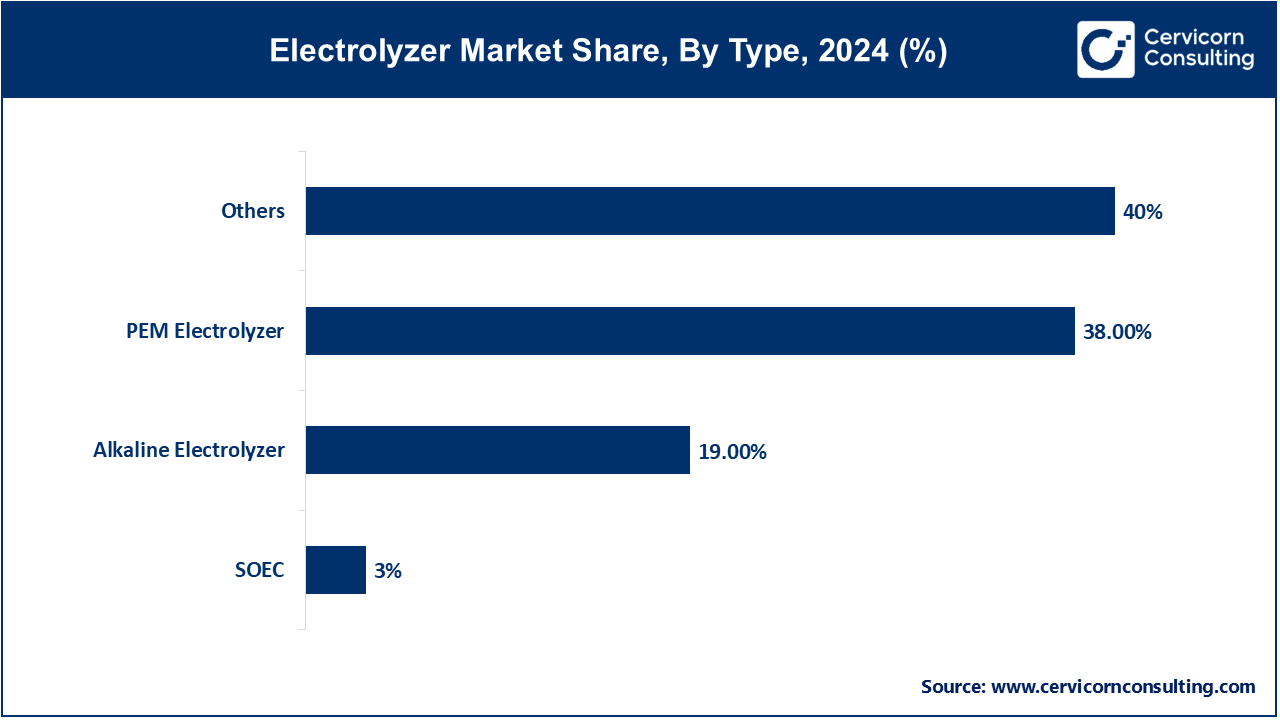
Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Cell (SOEC): In 2024, the solid oxide electrolyzer cell (SOEC) segment has held revenue share of 3%. SOECs operate at high temperatures (typically above 600°C) and use a solid oxide ceramic electrolyte to convert steam into hydrogen and oxygen. They can also operate in reverse to produce syngas or other chemicals from CO2 and water, offering potential versatility in industrial processes and energy storage systems.
Others: The other segment dominates the electrolyzer market with revenue share of 40% in 2024. This category includes emerging electrolyzer technologies such as polymer electrolyte membrane electrolyzers (PEMECs) and high-temperature alkaline electrolyzers (HTAEs), which are under development or niche applications. These technologies aim to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and expand electrolyzer applications across various sectors.
≤ 500 kW: The ≤ 500 kW segment has measured second highest revenue share of 31% in 2024. ≤ 500 kW typically have a lower power output, suitable for decentralized applications like off-grid hydrogen production for fueling stations or small industrial processes. Trends include advancements in compact design, integration with renewable energy sources, and applications in remote areas lacking grid connectivity.
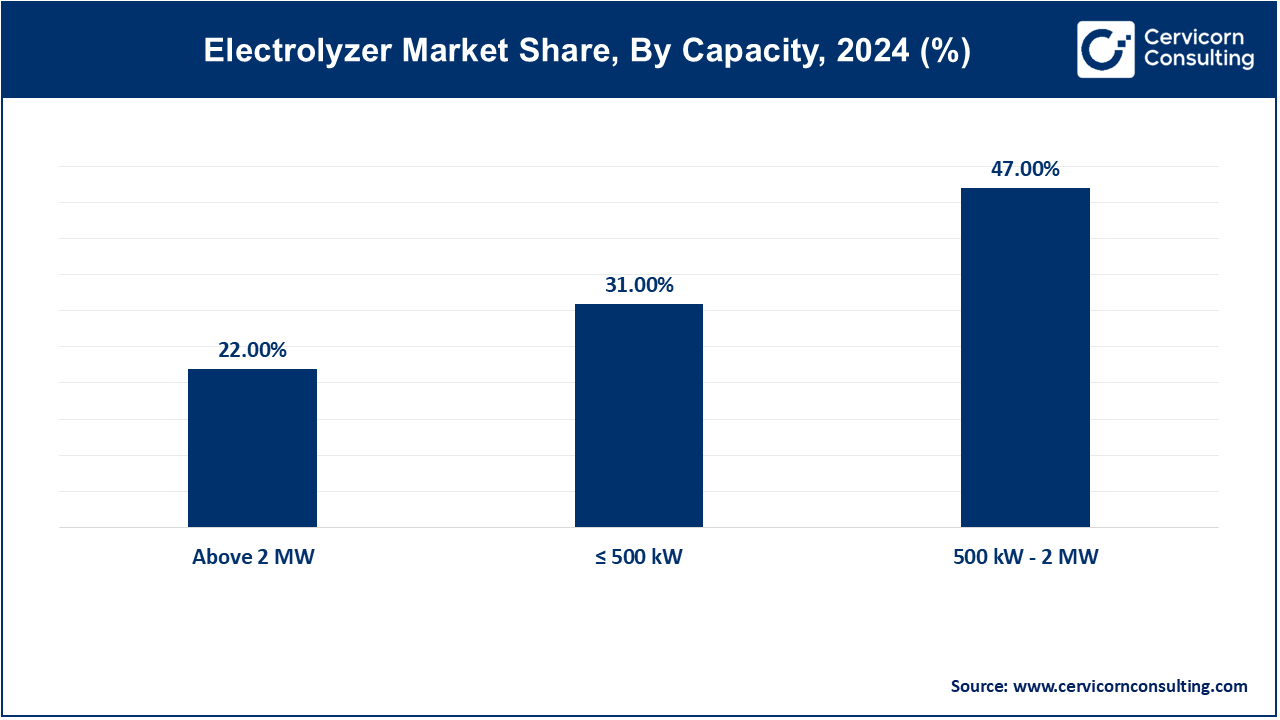
500 kW - 2 MW: The 500 kW - 2 MW segment has calculated highest revenue share of 47% in 2024. 500 kW - 2 MW offer moderate power output, catering to industrial applications such as chemical manufacturing and renewable energy storage. Trends focus on efficiency improvements, cost reduction through economies of scale, and integration with grid-balancing services and large-scale renewable energy projects.
Above 2 MW: The above 2 MW segment has covered revenue of 22% in 2024. Above 2 MW provide high power output for industrial hydrogen production, energy storage, and large-scale grid integration. Trends include advancements in electrolysis efficiency, scalability for megawatt-scale projects, and deployment in hydrogen refueling stations and energy-intensive industries like steel production and ammonia manufacturing.
Power Plants: Electrolyzers in power plants play a crucial role in the production of green hydrogen from surplus renewable energy. This hydrogen can be stored and utilized for grid balancing, peak shaving, and backup power generation, enhancing grid stability and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources.
Steel Industry: Electrolyzers are pivotal in the steel industry's transition to greener production methods. By utilizing hydrogen produced via electrolysis instead of coking coal in direct reduction processes, electrolyzers help reduce carbon emissions significantly, supporting sustainability goals and enhancing operational efficiency.
Electronics & Semiconductor Industry: Hydrogen produced by electrolyzers is essential for semiconductor manufacturing processes, where it is used as a carrier gas and in deposition processes to ensure high purity and quality of semiconductor materials, meeting stringent industry standards for cleanroom environments.
Pharmaceuticals: Electrolyzers provide hydrogen for pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, ensuring the purity and consistency required for chemical reactions and synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds. This application supports efficiency in production while reducing environmental impact compared to traditional chemical synthesis methods.
Chemical Industry: Electrolyzers are increasingly adopted in the chemical industry for producing hydrogen as a feedstock and reducing agent in various chemical processes. This enables the production of chemicals with lower carbon footprints and enhances the industry's sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Others: Beyond these sectors, electrolyzers find applications in transportation, where hydrogen serves as a clean fuel for fuel cell vehicles, and in heating applications for residential and commercial buildings. Agricultural applications include hydrogen for ammonia production and fertilizer synthesis, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices and reducing reliance on conventional fertilizers.
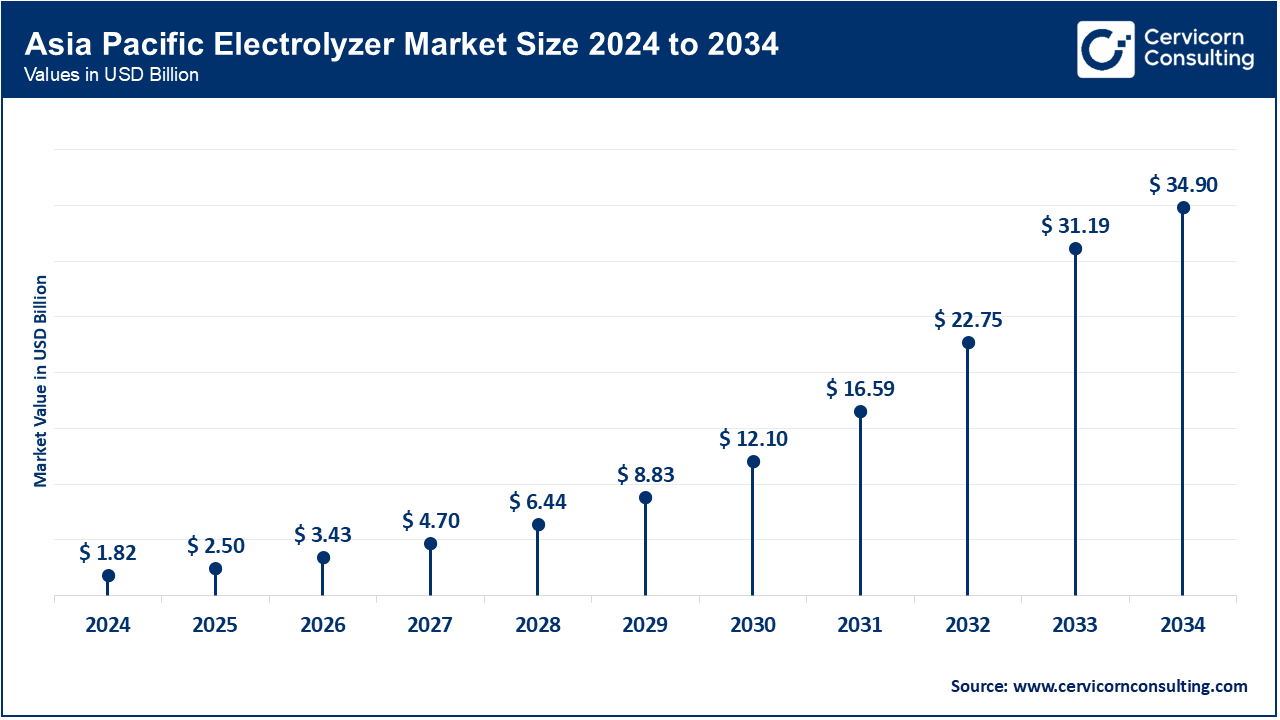
The Asia-Pacific electrolyzer market size is calculated at USD 1.82 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 34.9 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific market is driven by rapid industrialization and increasing adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy alternative. Trends include government investments in hydrogen infrastructure, partnerships for technology transfer and localization of electrolyzer manufacturing, and the integration of electrolyzers with renewable energy projects to support energy security and sustainability goals.
The North America electrolyzer market size was valued at USD 0.75 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 14.36 billion by 2034. In North America, the market is driven by ambitious renewable energy targets and strong government support for hydrogen initiatives. Key trends include increasing investments in electrolyzer projects for renewable hydrogen production, partnerships between energy companies and technology providers, and the development of hydrogen infrastructure to support regional energy transition goals.
The Europe electrolyzer market size was valued at USD 1.03 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow around USD 19.78 billion by 2034. Europe leads in electrolyzer deployment with robust policies promoting green hydrogen as a cornerstone of the European Green Deal. Trends include rapid expansion of electrolyzer capacity, advancements in electrolyzer technology to improve efficiency and scalability, and collaborations across sectors to develop hydrogen value chains integrating renewable energy sources.
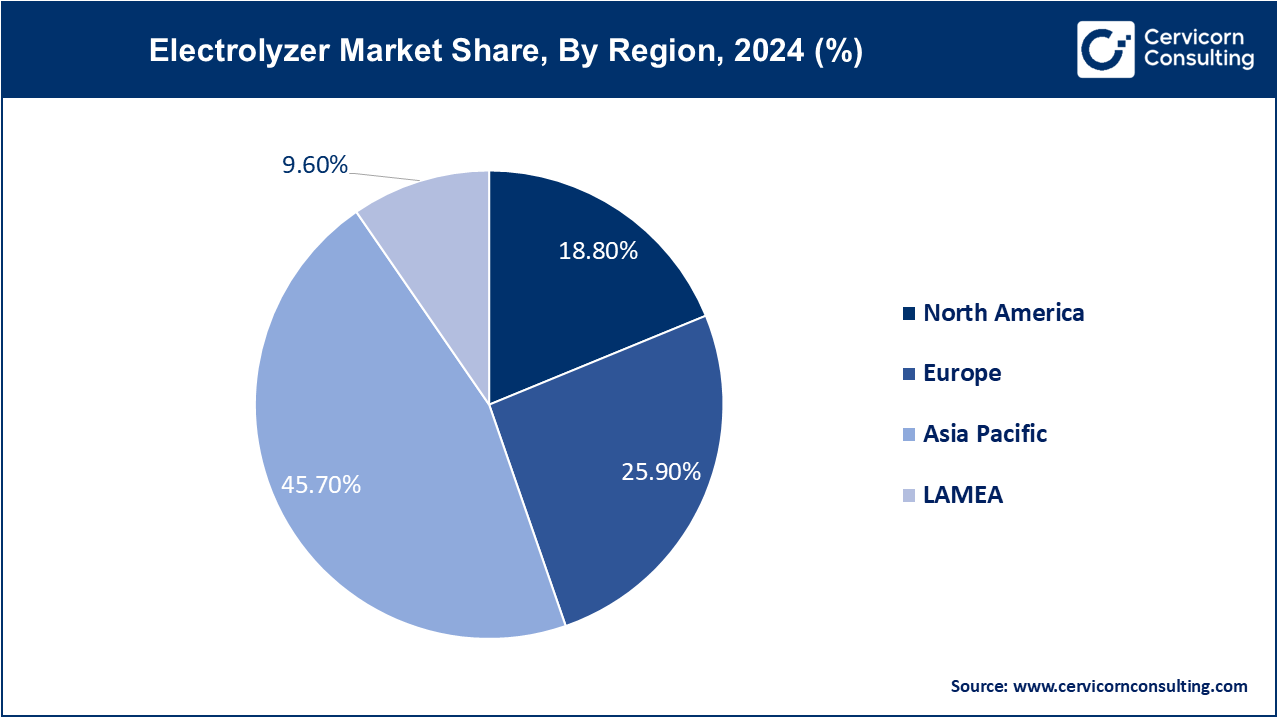
LAMEA regions are exploring electrolyzer technologies to diversify energy sources and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Trends include pilot projects for electrolyzer installations in renewable energy-rich areas, collaborations between international and local stakeholders to develop hydrogen ecosystems, and government initiatives to leverage hydrogen for economic diversification and sustainable development.
Innovative new players entering the electrolyzer market include companies like Enapter AG and Green Hydrogen Systems, focusing on compact, modular electrolyzer solutions for decentralized hydrogen production. These firms emphasize scalability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness to cater to emerging applications in various industries. Dominant key players in the market include Nel ASA, ITM Power plc, and McPhy Energy S.A., leveraging extensive R&D investments and strategic partnerships to maintain market leadership. They lead through established global presence, large-scale electrolyzer deployments, and technological advancements driving efficiency improvements and cost reductions, solidifying their market dominance.
Market Segmentation
By Type
By Capacity
By Application
By Region
Chapter 1 Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Electrolyzer
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Type Overview
2.2.2 By Capacity Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3 Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Electrolyzer Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4 Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Industrial Decarbonization Initiatives
4.1.1.2 Investment in Hydrogen Infrastructure
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Capital Costs and Initial Investments
4.1.2.2 Grid Integration Challenges
4.1.3 Market Opportunity
4.1.3.1 Hydrogen Export and International Trade
4.1.3.2 Electrolyzers in Energy StorType Systems
4.1.4 Market Challenges
4.1.4.1 Supply Chain Constraints
4.1.4.2 Performance and Efficiency Improvements
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5 Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Electrolyzer Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6 Electrolyzer Market, By Type
6.1 Global Electrolyzer Market Snapshot, By Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2034
6.1.1.1 Alkaline Electrolyzer
6.1.1.2 Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Electrolyzer
6.1.1.3 Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Cell (SOEC)
6.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 7 Electrolyzer Market, By Capacity
7.1 Global Electrolyzer Market Snapshot, By Capacity
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2034
7.1.1.1 ≤ 500 kW
7.1.1.2 500 kW - 2 MW
7.1.1.3 Above 2 MW
Chapter 8 Electrolyzer Market, By Application
8.1 Global Electrolyzer Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2034
8.1.1.1 Power Plants
8.1.1.2 Steel Industry
8.1.1.3 Electronics & Semiconductor Industry
8.1.1.4 Pharmaceuticals
8.1.1.5 Chemical Industry
8.1.1.6 Energy Storage or Fueling for FCEVs
8.1.1.7 Power to Gas
8.1.1.8 Others
Chapter 9 Electrolyzer Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 Electrolyzer Market Revenue Share, By Region 2023 (%)
9.3 Global Electrolyzer Market, By Region
9.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
9.4 North America
9.4.1 North America Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.3 North America Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.4.4 U.S.
9.4.4.1 U.S. Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.5 Canada
9.4.5.1 Canada Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
9.4.6 Mexico
9.4.6.1 Mexico Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
9.5 Europe
9.5.1 Europe Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.3 Europe Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.5.4 UK
9.5.4.1 UK Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.4.3 UK Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.5 France
9.5.5.1 France Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.5.3 France Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.6 Germany
9.5.6.1 Germany Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.6.3 Germany Market Segmental Analysis
9.5.7 Rest of Europe
9.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.5.7.3 Rest of Europe Market Segmental Analysis
9.6 Asia Pacific
9.6.1 Asia Pacific Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.3 Asia Pacific Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.6.4 China
9.6.4.1 China Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.4.3 China Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.5 Japan
9.6.5.1 Japan Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.5.3 Japan Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.6 India
9.6.6.1 India Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.6.3 India Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.7 Australia
9.6.7.1 Australia Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.7.3 Australia Market Segmental Analysis
9.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
9.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.6.8.3 Rest of Asia Pacific Market Segmental Analysis
9.7 LAMEA
9.7.1 LAMEA Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.3 LAMEA Electrolyzer Market, By Country
9.7.4 GCC
9.7.4.1 GCC Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.4.3 GCC Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.5 Africa
9.7.5.1 Africa Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.5.3 Africa Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.6 Brazil
9.7.6.1 Brazil Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.6.3 Brazil Market Segmental Analysis
9.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
9.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Electrolyzer Market Revenue, 2021-2034 ($Billion)
9.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEA Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10 Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2021-2023
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2021-2023
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2023)
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
11.1 Nel ASA
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 ITM Power plc
11.3 McPhy Energy S.A.
11.4 Siemens Energy AG
11.5 Hydrogenics Corporation (now part of Cummins Inc.)
11.6 Plug Power Inc.
11.7 Ballard Power Systems Inc.
11.8 Proton OnSite (Nel Hydrogen)
11.9 Giner ELX
11.10 Green Hydrogen Systems