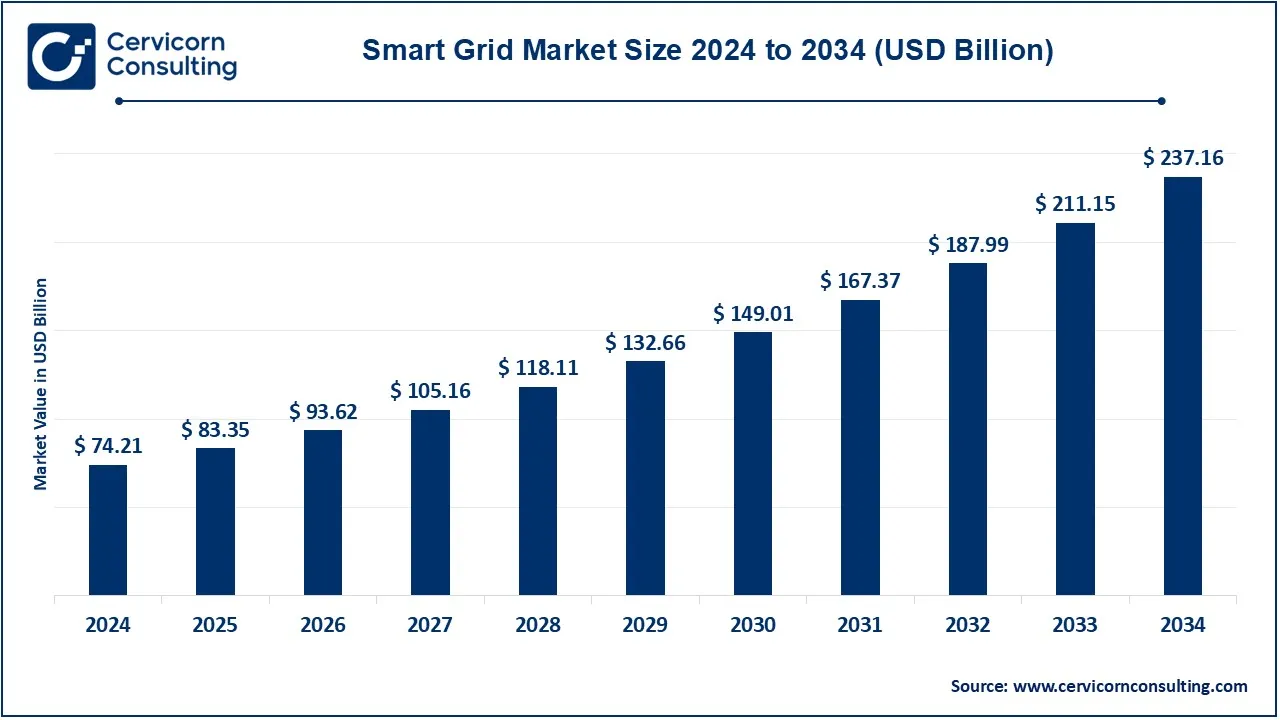
The global smart grid market size was valued at USD 74.21 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 237.16 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.20% from 2025 to 2034.
The need for energy has grown as a result of urbanization, rising living standards, and technological developments. Cities account for 80 percent of greenhouse gas emissions and use between 75 and 80 percent of all energy. This is concerning for the preservation of the ecosystem worldwide as well as for the supply of renewable energy. Efficient energy use and dependence on renewable resources will also help reduce the carbon footprint of humanity. The power grid in its current form is unreliable, has high transmission losses and poor power quality, is prone to brownouts and blackouts, provides inadequate power, and prevents the integration of distributed energy sources. There is a lack of monitoring and real-time control in the traditional non-smart systems, which poses a challenge for smart grids to act as real-time solutions.
The electricity utility industry is going through massive changes. The power grid has been around for a long time and it shows. It is costly, ineffective, and untrustworthy. Smart grids are becoming more and more necessary worldwide, and power companies must prioritize cost-effectiveness, smarter storage, and cleaner energy. With the use of cutting-edge automation, control, IT, and Internet of Things technology, the smart grid concept aims to improve the power grid by allowing for real-time monitoring and management of the electrical flow from generation to consumption. Among the many technologies it encompasses are energy storage systems (ESS), AI and ML tools, and advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), also known as smart meters. Power generation is optimized, distribution efficiency is increased, and educated consumer choices are supported by these technologies.
Among the drivers propelling the smart grid market's expansion are growing environmental protection concerns and the growing use of smart grid technology to increase energy conservation and consumption efficiency. Furthermore, some of the key elements propelling the market expansion include encouraging government laws and policies regarding the use of smart meters as well as rising expenditures in digital power infrastructure. However, it is anticipated that the market's expansion will be hampered by a lack of standards and growing privacy and security concerns. In addition, the growing number of electric cars on the road and the impending smart city initiatives in developing nations are anticipated to present significant market expansion prospects in the years to come.
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 74.21 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 237.16 Billion |
| Projected CAGR (2025 to 2034) | 17.40% |
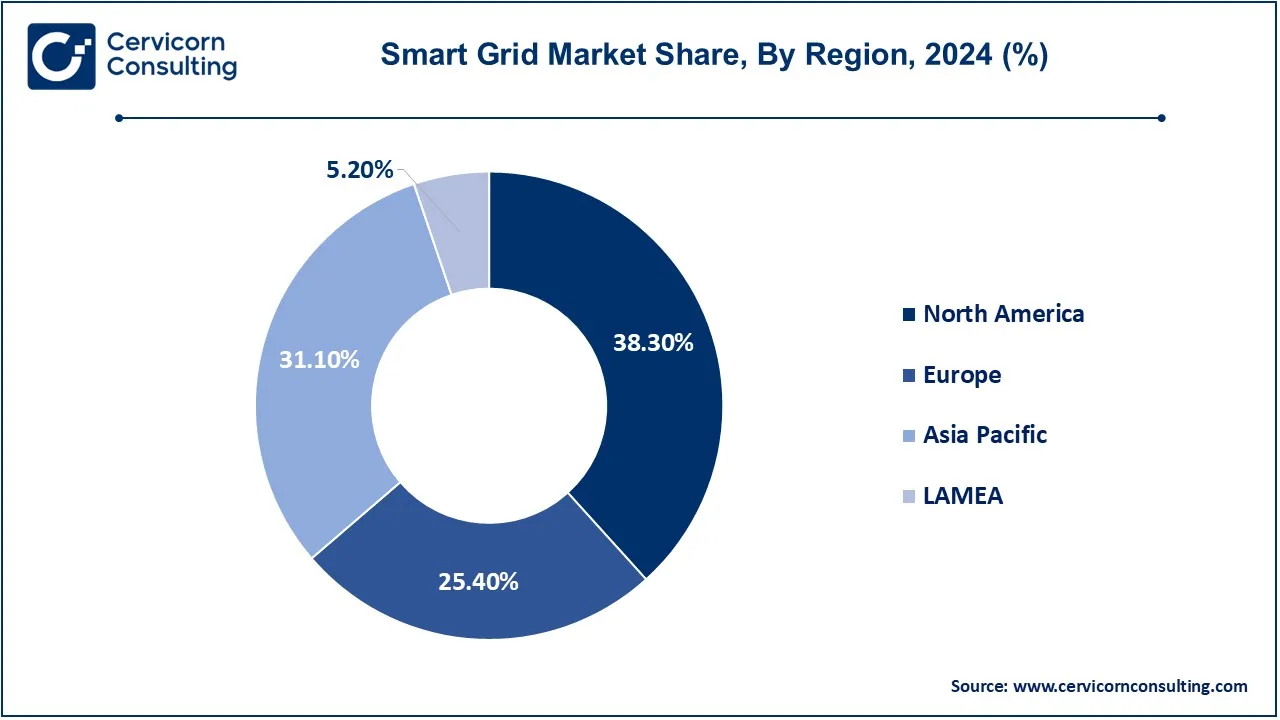
| Leading Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Application, Solution, Technology, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Wipro Ltd, IBM Corporations, Schneider Electric SA, Landis+Gyr Group AG, Honeywell International Inc., Open Systems International Inc, Oracle Corporations, Trilliant Holdings Inc., Elster Group GmbH, General Electric Company, S&C Electric Company, ABB Ltd, Fujitsu Limited, Itron Inc, Cisco Systems Inc, Toshiba Corporation, Eaton Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Echelon Corporation, Siemens AG, Aclara Technologies LLC |
Increased Government Support
Growing Demand for EMS
High Cost of Implementing a Smart Grid
Lack of Standards
Growing Research Numbers
Adoption of Blockchain Technology
Security Issues
Technological Complexity
The smart grid market is segmented in to component, application, solution, technology, end user and region. Based on component, the market is classified into hardware, software and services, Based on application, the market is classified into generation, transmission, distribution, consumption. Based on solution, the market is classified into advanced metering infrastructure, smart grid distribution management, smart grid communications, smart grid network management, substation automation, smart grid security and thers; Based on end use, the market is classified into residential, utility & industrial and commercial. Based on technology, the market is classified into wired and wireless.
Software: Advanced software solutions are becoming essential for managing grids, data analytics, and predictive maintenance because of the increasing complications associated with the grids as a result of the integration of multiple energy sources. Further, this software also assists companies in optimizing energy distribution, integrating renewable resources effectively, and improving consumer engagement through the utilization of real-time data knowledge and insight. In addition, the governments have also increased the spending on advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) which is likely to spur market growth. For instance, to develop and implement smart grid technology, the Energy Independence and Security Act was approved by the US government in 2007.
Smart Grid Market Revenue Share, By Component, 2024 (%)
| Component | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Hardware | 38.20% |
| Software | 49.50% |
| Service | 12.30% |
Hardware: Smart meters, sensors, and controllers are required to facilitate real-time monitoring and energy management. The development of sophisticated hardware is necessary for helping in the integration of the smart grid with renewable energy sources. Various governments of different countries have also been leading the charge in the process of installing smart electricity meters. For instance, the Australian Energy Market Commission initiated an independent rule to review electricity meters in December 2020 to install smart electricity meters all over the country further encouraging the adoption of smart grids.
Services: For the operation of the smart grids the services sector allows applications including the installation and integration of various modules. Therefore, companies opt for these services to make the integration and deployment process smooth and reduce costs. Services include consulting, installation, support, and maintenance services which are critical for the successful deployment and operation of smart grids. The complexity of smart grid systems requires specialized expertise, which increases the demand for skilled professionals who can manage these complex networks.
Residential: Growing populations, especially in developing countries, are increasingly demanding energy. There is a higher demand for energy from residential customers to better control costs and consumption. Homeowners are becoming more aware of the benefits of energy saving and are adopting smart grid technologies to optimize electricity consumption, reduce bills, and contribute to environmental sustainability. Furthermore, smart homes that are equipped with Internet of Things devices that need effective energy management are becoming highly popular among the population. Home management systems and smart meters (HEMS) are examples of smart grid technologies that give owners real-time control and monitoring over their day-to-day energy usage.
Utilities and Industry: The use of grid technologies is increasing worldwide. Governments of underdeveloped and emerging countries are also recognizing these technologies as strategic infrastructure investments that will help achieve carbon emission targets. In addition, growing populations, industrialization, and increasing environmental concerns due to fossil fuel power plants are forcing the government to plan regulatory standards related to carbon emissions. The industrial sector is further anticipated to grow significantly because of many favorable policies and tax incentives passed by the government.
Commercial: The increasing need for genuine and efficient energy management in different businesses and public institutions is one of the reasons driving the commercial segment. Malls, hospitals, and offices are among the commercial facilities that are implementing smart grid technologies to reduce operating costs, thereby ensuring a consistent supply of electricity, and improving operational sustainability. The commercial sector is encouraged to use renewable energy sources due to the mounting regulatory pressure of reducing carbon emissions which has also positively affected market expansion. Further, there is a growing number of commercial buildings that are utilizing advanced metering infrastructure and energy management systems for controlling load in a better manner and predictive maintenance is leading to market growth.
The smart grid market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. The North America has dominated the market in 2024.
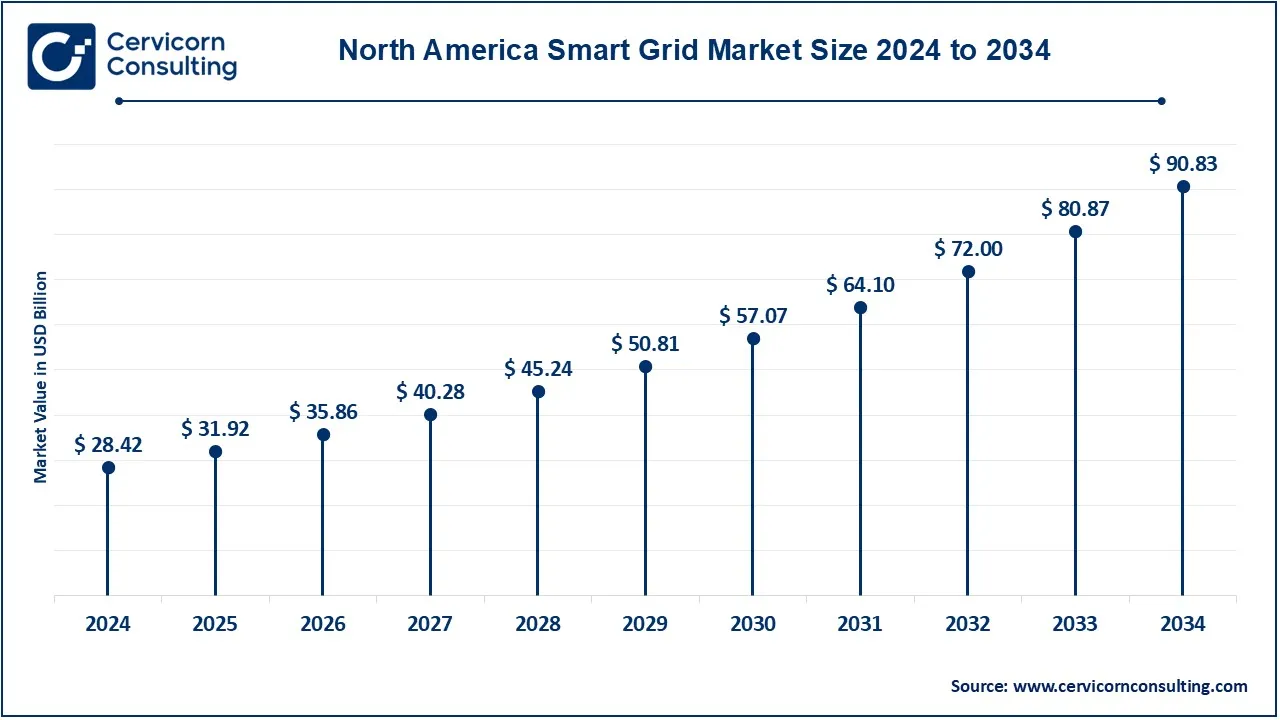
The North America smart grid market size was valued at USD 28.42 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 90.83 billion by 2034. The growth of the smart grid market in North America is attributed to the adoption of electric vehicles and large investments by private and public as well as government entities in this region. The region has a strong regulatory framework that supports the development of smart grids, including incentives and policies that encourage the use of smart technologies. There is also a growing demand for improved grid reliability and efficiency, especially in the face of extreme weather events. Moreover, the high penetration of advanced metering infrastructure and the drive for energy independence are further stimulating the market in the region.
The Europe smart grid market size was estimated at USD 18.85 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 60.24 billion by 2034. Europe is expected to grow owing to the encouraging government initiatives towards clean power generation in the region. The UK, France, and Germany are among the countries in Europe that hold a significant market share. Also, the increasing demand for energy efficiency in power supply is likely to drive the regional outlook. The growing investments in distribution automation and the increasing complexity of power distribution infrastructure are expected to enhance the market outlook. For example, the smart metering implementation program launched by the UK government in May 2020 resulted in a total of 26.6 million electricity meters being operated by major energy suppliers in residential homes across the UK.
The Asia-Pacific smart grid market size was valued at USD 23.08 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 73.76 billion by 2034. Asia Pacific holds a significant market position due to the wide adoption of these technologies and a strong focus on renewable energy growth. For example, in February 2020, the Indian government announced the installation of 1 million smart meters across the country under the Smart Meter National Program (SMNP). The region's major growth is coming from countries like China, India, Japan, Australia, and South Korea, with China being the most promising frontrunner in adopting these technologies. In addition, the growing smart city development programs in the region are expected to boost market growth.
The LAMEA smart grid market size was valued at USD 3.86 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 12.33 billion by 2034. Latin America is also expected to witness significant growth due to the large demand from Brazil and Mexico to support the increasing industrialization in the region. For example, in February 2021, Brazilian energy utility Amazonas Energia selected Landis+Gyr to implement an advanced metering infrastructure project in the Brazilian state of Amazonas. Landis+Gyr will provide the utility with its SGP+M Mesh IP smart central metering solution to serve around 100,000 customers. In the Middle East and Africa, high adoption of solutions to minimize outages and revenue losses and provide enhanced control with low disruption is expected to drive market growth. With the new projects to utilize various conventional and non-conventional energy resources, the region is expected to witness steady growth in the coming years.
Most companies are actively conducting research and development, believing that this will enable them to develop the next generation of active electronic component products that can generate even more energy than previous generations. In October 2022, Eaton announced the launch of its new advanced energy storage system, the EnergyAware UPS. This cutting-edge system helps consumers save money and increase power reliability by intelligently storing and delivering energy during times of high demand. It's easy to integrate Eaton's current energy management technologies. In June 2021, Schneider Electric said they would work together to encourage microgrids to help people and communities affected by climate and weather disasters. The company has deployed more than 170 kWh of mobile battery storage and more than 45 kW of mobile solar power to support more than 100 disaster relief and recovery missions, providing emergency electricity to Americans. Siemens is a major European industrial manufacturing company that specializes in several industries, such as infrastructure, transportation, and healthcare.
CEO Statements
James Aein, CEO of ENERZA
P Raja Manickam, CEO of Tata Electronics OSAT
Key players in the smart grid market are pivotal in delivering a variety of innovative construction solutions, such as prefabrication techniques, sustainable materials, and advanced digital technologies.
These advancements mark a notable expansion in the smart grid market, driven by strategic acquisitions and innovative projects. The focus is on boosting sustainability, enhancing construction efficiency, and broadening product offerings to meet diverse building needs.
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Application
By Solution
By Technology
By End Use
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Smart Grid
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Component Overview
2.2.2 By Solution Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.2.4 By Technology Overview
2.2.5 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Smart Grid Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Increased Government Support
4.1.1.2 Growing Demand for EMS
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Cost of Implementing a Smart Grid
4.1.2.2 Lack of Standards
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Security Issues
4.1.3.2 Technological Complexity
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Growing Research Numbers
4.1.4.2 Adoption of Blockchain Technology
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Smart Grid Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Smart Grid Market, By Component
6.1 Global Smart Grid Market Snapshot, By Component
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Hardware
6.1.1.2 Software
6.1.1.3 Services
Chapter 7. Smart Grid Market, By Material
7.1 Global Smart Grid Market Snapshot, By Material
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Advanced Metering Infrastructure
7.1.1.2 Smart Grid Distribution Management
7.1.1.3 Smart Grid Communications
7.1.1.4 Smart Grid Network Management
7.1.1.5 Substation Automation
7.1.1.6 Smart Grid Security
7.1.1.7 Others
Chapter 8. Smart Grid Market, By Application
8.1 Global Smart Grid Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Generation
8.1.1.2 Transmission
8.1.1.3 Distribution
8.1.1.4 Consumption/End Use
Chapter 9. Smart Grid Market, By Technology
9.1 Global Smart Grid Market Snapshot, By Technology
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Wired
9.1.1.2 Wireless
Chapter 10. Smart Grid Market, By End Use
10.1 Global Smart Grid Market Snapshot, By End Use
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Residential
10.1.1.2 Utility & Industrial
10.1.1.3 Commercial
Chapter 11. Smart Grid Market, By Region
11.1 Overview
11.2 Smart Grid Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
11.3 Global Smart Grid Market, By Region
11.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
11.4 North America
11.4.1 North America Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.3 North America Smart Grid Market, By Country
11.4.4 U.S.
11.4.4.1 U.S. Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.5 Canada
11.4.5.1 Canada Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.6 Mexico
11.4.6.1 Mexico Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
11.5 Europe
11.5.1 Europe Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.3 Europe Smart Grid Market, By Country
11.5.4 UK
11.5.4.1 UK Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.5 France
11.5.5.1 France Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.6 Germany
11.5.6.1 Germany Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.7 Rest of Europe
11.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6 Asia Pacific
11.6.1 Asia Pacific Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.3 Asia Pacific Smart Grid Market, By Country
11.6.4 China
11.6.4.1 China Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.5 Japan
11.6.5.1 Japan Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.6 India
11.6.6.1 India Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.7 Australia
11.6.7.1 Australia Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
11.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7 LAMEA
11.7.1 LAMEA Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.3 LAMEA Smart Grid Market, By Country
11.7.4 GCC
11.7.4.1 GCC Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.5 Africa
11.7.5.1 Africa Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.6 Brazil
11.7.6.1 Brazil Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
11.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Smart Grid Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 12. Competitive Landscape
12.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
12.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
12.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
12.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
12.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1 Wipro Ltd
13.1.1 Company Snapshot
13.1.2 Company and Business Overview
13.1.3 Financial KPIs
13.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
13.1.5 Strategic Growth
13.1.6 Global Footprints
13.1.7 Recent Development
13.1.8 SWOT Analysis
13.2 IBM Corporations
13.3 Schneider Electric SA
13.4 Landis+Gyr Group AG
13.5 Honeywell International Inc.
13.6 Open Systems International Inc
13.7 Oracle Corporations
13.8 Trilliant Holdings Inc.
13.9 Elster Group GmbH
13.10 General Electric Company
13.11 S&C Electric Company
13.12 ABB Ltd
13.13 Fujitsu Limited
13.14 Itron Inc
13.15 Cisco Systems Inc
13.16 Toshiba Corporation
13.17 Eaton Corporation
13.18 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
13.19 Echelon Corporation
13.20 Siemens AG
13.21 Aclara Technologies LLC