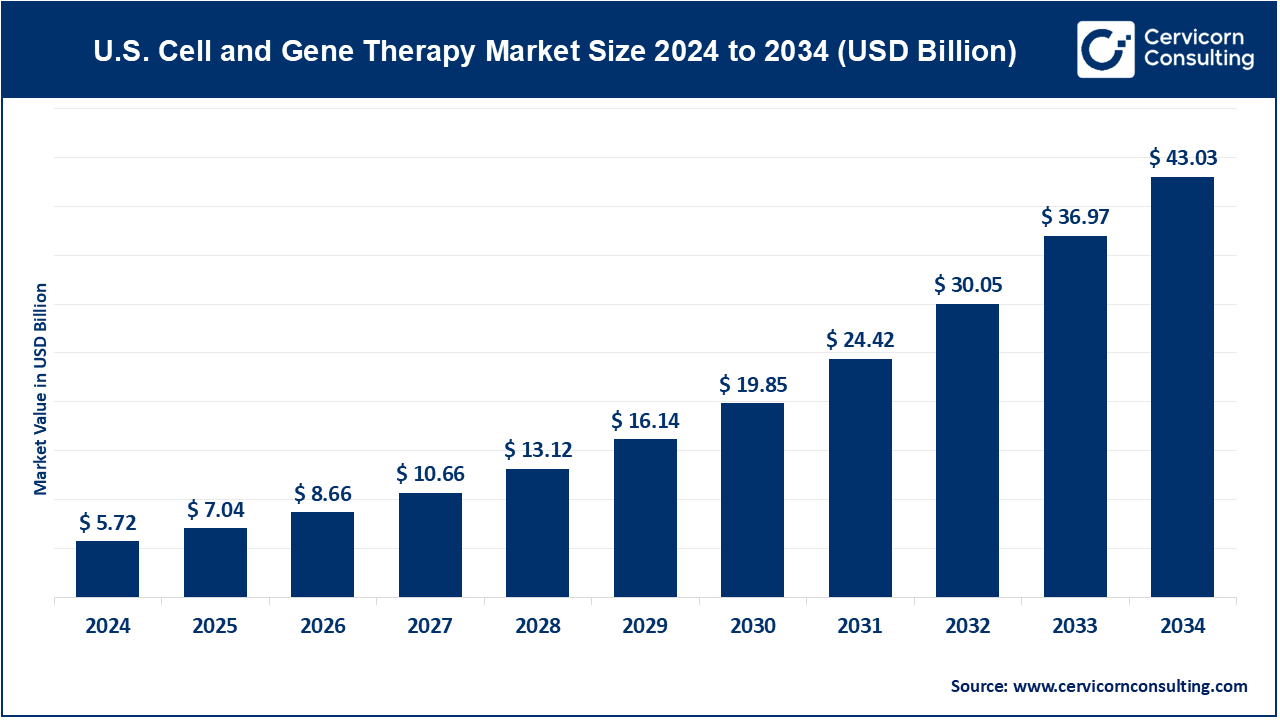
The U.S. cell and gene therapy market size was valued at USD 5.72 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 43.03 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Growth in the cell and gene therapy market would mainly be fueled by advancements in biotechnology, increased incidences of genetic disorders, and a rise in personalized medicine. Major drivers involve the technological advancement of tools used in gene editing, improved mechanisms of delivery, and increasing regulatory support. The soaring number of clinical trials, increasing investment in both the public and private sectors and exciting results from early-stage therapies further support market growth with new treatments that could potentially cure previously untreatable conditions.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.04 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 43.03 Billion |
| CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 23% |
| Key Segments | Therapy Type, Therapeutic Class, Delivery Method, End User |
| Key Companies | Bluebird Bio, Sangamo Therapeutics, Editas Medicine, AveXis (a Novartis company), Gilead Sciences (Kite Pharma), Fate Therapeutics, Bellicum Pharmaceuticals, Legend Biotech, Allogene Therapeutics, Poseida Therapeutics, Rocket Pharmaceuticals |
The U.S. cell and gene therapy market is segmented into therapy type, therapeutic class, delivery method and end users. Based on therapy type, the market is classified into cell therapy, and gene therapy. Based on therapeutic class, the market is classified into cardiovascular disease, cancer, genetic disorder, rare diseases, oncology, hematology, ophthalmology, infectious disease, neurological disorders and others. Based on delivery method, the market is classified into in vivo and ex vivo. Based on end-users, the market is classified into hospitals, cancer care centers, wound care centers and others.
Cell Therapy: Cell therapy is a form of medical treatment involving living cells used to prevent or treat disease. Cells are autologous (the patient's cells) or allogeneic (a donor's cells) and may be engineered in the lab before administration to the patient. Cell therapies are mainly used in regenerative medicine to repair or replace damaged tissues and cells, including conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. This approach has attracted much attention because it can offer more personalized and targeted treatments.
Gene Therapy: Gene therapy is the introduction or alteration of genetic material within a patient's cells to treat or prevent disease. This can be done by replacing bad genes, correcting mutations, or adding new genes that can help in combating the disease. Gene therapy has proven to be promising for treating genetic disorders, cancers, and other complex diseases based on their etiologic causes. Gene therapy is becoming a new hallmark of personalized medicine due to its potential to specifically address genetic abnormalities. It aims to cure conditions based on research, and such techniques are being developed for other medical conditions as well.
Cardiovascular Disease: Cardiovascular disease refers to a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Cell and gene therapies have shown promise in addressing cardiovascular conditions by promoting tissue regeneration, repairing damaged blood vessels, or correcting genetic mutations that predispose individuals to heart disease. These therapies are indeed exciting, ongoing areas of medical research aiming to target the underlying causes at a cellular and genetic level, which enhance heart function, reduce symptoms, and hopefully even reverse some elements of cardiovascular disease.
Cancer: Cancer involves many different diseases of uncontrolled cell growth and spread. Cell and gene therapies in oncology attempt to target and treat cancer cells by modifying the patient's immune system or tumor cells. Gene therapies can introduce genes that make cancer cells more susceptible to treatment, whereas cell therapies may consist of a re-engineering process for the use of engineered immune cells, such as T-cells, that identify and destroy cancer. These innovative treatments are paving the way for more precise, individualized therapies that have the potential to improve survival rates and reduce side effects compared to traditional treatments.
Genetic Disorder: Genetic disorders are diseases caused by abnormalities in an individual's DNA, often inherited from parents. Cell and gene therapies hold immense potential in treating genetic disorders by targeting the genetic root causes. Gene therapy can be used for the replacement of defective genes, repair of mutations, and introduction of new genetic material to correct the disease. Such therapies are being developed in the treatment of inherited diseases such as cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and sickle cell disease. These are the hopes of long-term and even permanent cures to the disorder by addressing the genetic mutation that causes it, changing the treatment scenarios of genetic diseases.
Rarity Diseases: Rare diseases are, by definition, conditions that affect a small percentage of the population. Such diseases pose challenges because they have limited treatment options and less research conducted on them. Most rare diseases have a genetic origin; hence, cell and gene therapies are promising in such cases. The correction or replacement of genetic mutations causing rare diseases is what gene therapy promises to make possible in the treatment process. In some instances, cell therapy can also restore or even replace damaged tissues. The challenges associated with high prices and bureaucratic red tape exist, but research continues to reveal potential treatments for rare diseases, which heretofore could not be treated effectively.
Oncology: Oncothery is an area that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer through the discovery of new theories in cellular and gene therapeutics. Gene therapy can manipulate the genetic content of the cells within cancers, so these are also used, making cancerous cells much more susceptible to treatments involving chemotherapy or radiation. Most applications of cell therapies in oncology involve altering a patient's immune cells, most typically their T-cells, for better identification of the cancers. These therapies form part of the very new, growing immuno-oncology arena, thereby bringing hope for patients to combat cancers resistant to traditional therapy, as well as widen possibilities for the personalizing of treatment.
Hematology: Hematology is medicine focused on disorders involving the blood and bone marrow. Hematology ranges from simple bleeding disorders or clotting to complex cancerous conditions. Cell and gene therapies in hematology are directed at the underlying causes of these diseases, which in most cases involve modification of blood cells or genes to correct a defect. For instance, gene therapy can be applied in the treatment of genetic blood disorders such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia by correcting defective genes that cause abnormal hemoglobin production. Cell therapies, including stem cell transplants, play an important role in restoring the blood supply in the body after treatments for blood cancers. These developments are a major stride toward individualized treatments in hematology.
Ophthalmology: Ophthalmology is a specialty concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases in the eye. In ophthalmology, cell and gene therapies are being developed for a wide range of disorders, such as macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa, and other inherited retinal disorders. Gene therapies can be given to deliver healthy copies of defective genes to restore or improve vision. Cell therapies may be done through the transplantation of retinal cells or stem cells to replace damaged tissues that offer hope for restoring a person's sight who suffers from previously untreatable conditions. These new approaches may help stop or reverse vision loss, changing the course for people with eye diseases.
Infectious Disease: Infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi continue to be a global health problem. Cell and gene therapies are emerging as potential treatments for some infectious diseases, particularly those caused by viruses. For example, gene therapy can modify the genetic makeup of immune cells to increase their effectiveness in combating infections, while cell therapies may give patients immune cells that can target infectious agents. More gene-editing technologies, including CRISPR, which can target and modify the DNA of pathogens directly, open new avenues in the fight against infectious diseases, including antibiotic-resistant infections.
Neurological Disorders: Neurological disorders include Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis, which result from the degeneration of the nervous system with limited treatments available. Cell and gene therapies may hold the promise of breakthroughs in treating such conditions. Gene therapy involves introducing therapeutic genes into the brain to correct or replace faulty genes responsible for neurological dysfunction. Cell therapy might involve stem cell transplantation or other cell types that can replace damaged neurons or tissues. These are emerging therapies but seem promising for treating complex and debilitating neurological conditions.
In Vivo: In vivo delivery can be described as the introduction of therapeutic cells or gene therapies straight into a patient's body. In this method, therapeutic cells or genetic materials are introduced into the body to target disease sites from inside the patient's body. For gene therapy, methods employed in vivo include delivering genes via vectors, mostly viruses, directly into the cells of the patient. For cell therapy, usually, cells are injected or infused into the bloodstream, hence traveling to the area to be treated. In vivo, therapies offer the benefits of targeting a particular tissue or organ, so they are accurate and very effective in most diseases.
Ex Vivo: Ex vivo delivery involves cell manipulation or engineering outside the patient's body for later introduction into the body to affect treatment. This involves harvesting cells from the patient, known as autologous, or from a donor, which is allogeneic, modifying or treating the cells in a laboratory, and then transplanting or infusing them back into the patient. Gene therapy might include editing the genes of those cells to correct mutations, while cell therapy could be expanding or reprogramming stem cells for therapeutic use. Ex vivo therapies highlighted the future possibilities of stem cell treatments and immunotherapies that create highly customized and target-directed treatments for different diseases.
Hospitals: Hospitals are the primary delivery sites of advanced cell and gene therapies. Hospitals are centers of medical expertise and infrastructure where all the equipment, well-trained medical staff, and monitoring systems to support these complicated therapies are available. Gene or cell therapies usually require high-intensity procedures, from pre-treatment screening to preparation, administration, and post-treatment follow-up care. Hospitals are well-stocked for these high-risk treatments, especially in specialized units like oncology, hematology, and cardiology. Cell and gene therapies are also very dynamic; hence, hospitals are fundamental for clinical trials and are providing the latest treatments possible to patients.
Cancer Care Centers: Cancer care centers are specialized facilities committed to diagnosing, treating, and managing cancer. They are important for delivering targeted cancer therapies, such as cutting-edge cell and gene therapies. Specialized treatments, such as CAR-T cell therapy, where a patient's T-cells are genetically modified to fight cancer, are offered in cancer care centers. Gene therapy is also being pursued in cancer care centers for the administration of targeted therapies that might affect cancer cells or boost immune responses. Such centers play a very crucial role in offering tailored cancer care, as often access to the latest therapies under clinical trials and established treatments tailored to individual patient needs is possible.
Newcomers in the cell and gene therapy industry focus their attention on innovative, next-generation therapies that seek to bridge unmet medical needs with diverse diseases. These companies aim at innovative methods, such as CRISPR-Cas9 techniques, which correct genetic mutations in an even more precise level; as well as pioneering cell-based therapies that are aimed to regenerate damaged tissues or even enhance immune responses. New entrants are looking at the accessibility, scalability, and affordability of therapies. They are working with big biopharma companies as well as academic institutions to speed up their clinical development and commercialization. The innovation flood stimulates competition and leads to rapid breakthroughs in the field.
CEO Statements
Andrew Obenshain, CEO of Bluebird Bio:
Gilmore O'Neill, CEO of Editas Medicine:
Bob Valamehr, CEO of Fate Therapeutics:
Market Segmentation
By Therapy Type
By Therapeutic Class
By Delivery Method
By End-Users
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Cell and Gene Therapy
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Therapy Type Overview
2.2.2 By Therapeutic Class Overview
2.2.3 By Delivery Method Overview
2.2.4 By End Use Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. U.S. Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: U.S. Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting U.S. Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 The increasing incidence of genetic disorders
4.1.1.2 Supportive Government Initiatives
4.1.1.3 Breakthrough Clinical Results
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Extremely High treatment costs
4.1.2.2 Regulatory Obstacles
4.1.2.3 Limited Reimbursement Models
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 High Development and Production Costs
4.1.3.2 Regulatory Approval Delay
4.1.3.3 Patient and Physician Resistance
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Expansion into Rare Disease Treatments
4.1.4.2 Gene Therapy for Age-related Diseases
4.1.4.3 Emerging opportunity Combination Therapies
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Cell and Gene Therapy Market, By Therapy Type
6.1 U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Snapshot, By Therapy Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Cell Therapy
6.1.1.2 Gene Therapy
Chapter 7. Cell and Gene Therapy Market, By Therapeutic Class
7.1 U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Snapshot, By Therapeutic Class
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Cardiovascular Disease
7.1.1.2 Cancer
7.1.1.3 Genetic Disorder
7.1.1.4 Rare Diseases
7.1.1.5 Oncology
7.1.1.6 Hematology
7.1.1.7 Ophthalmology
7.1.1.8 Infectious Disease
7.1.1.9 Neurological Disorders
7.1.1.10 Others
Chapter 8. Cell and Gene Therapy Market, By Delivery Method
8.1 U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Snapshot, By Delivery Method
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 In Vivo
8.1.1.2 Ex vivo
Chapter 9. Cell and Gene Therapy Market, By End Use
9.1 U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Snapshot, By End Use
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Hospitals
9.1.1.2 Cancer Care Centers
9.1.1.3 Wound Care Centers
9.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 10. Cell and Gene Therapy Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.3 Market Size and Forecast
10.4. U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11. Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1 Bluebird Bio
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 U.S. Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 Sangamo Therapeutics
12.3 Editas Medicine
12.4 AveXis (a Novartis company)
12.5 Gilead Sciences (Kite Pharma)
12.6 Fate Therapeutics
12.7 Bellicum Pharmaceuticals
12.8 Legend Biotech
12.9 Allogene Therapeutics
12.10 Poseida Therapeutics
12.11 Rocket Pharmaceuticals