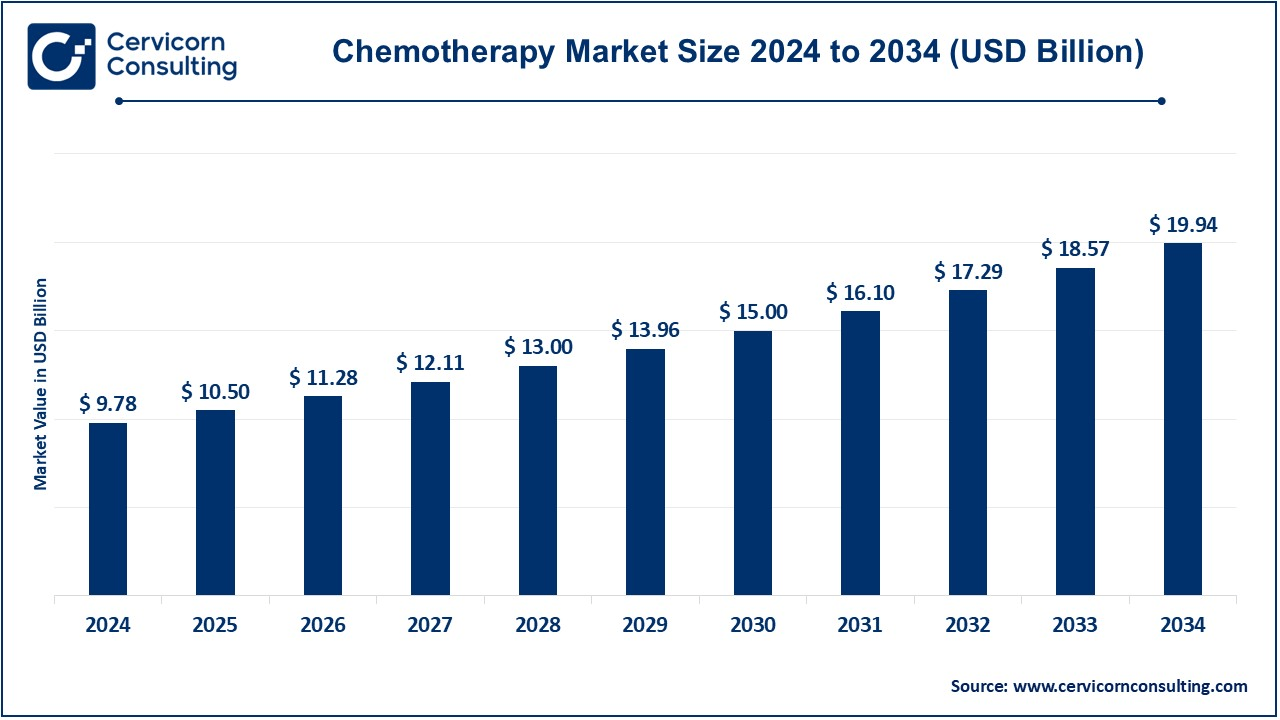
The global chemotherapy market size was valued at USD 9.78 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 19.94 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.38% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
The chemotherapy market is growing largely due to an increase in cancer cases worldwide. The more cancers there are, the more treatments are needed. Improved medical research has led to better chemotherapy methods that have made it possible for patients to enjoy improved outcomes. Increased awareness of cancer and early diagnosis help identify patients who would benefit from chemotherapy, further expanding the market. Governments and healthcare organizations are investing in cancer treatment infrastructure, thereby making chemotherapy accessible to a large population. The advancement of personalized medicine and targeted therapies also ensures that chemotherapy is becoming more efficient in its performance, thus increasing the accessibility to other types of cancer. All these factors are driving the growth of the chemotherapy market because patients and healthcare providers are increasingly resorting to chemotherapy as a necessary part of cancer treatment.
The chemotherapy market is fueled by the growing incidence of cancer around the world, and an estimated 1.9 million new cases are projected in the U.S. by 2025. Chemotherapy is an important aspect of the treatment of cancer either to cure, prolong life, or improve quality of life. Approximately 650,000 patients undergo chemotherapy each year in the U.S. The advancement in drug development has resulted in more effective chemotherapy agents with fewer side effects, such as personalized therapies targeting specific types of cancer. The global chemotherapy market is expected to increase multifold in the next decade with innovation in drug formulation and delivery methods. The regulatory agencies also welcome the introduction of new therapies for better patient outcomes. However, the high cost of treatments, side effects, and variability in response to treatment continue to be some of the important challenges that need to be overcome to ensure that chemotherapy overall becomes the best option.
The NCI and American Cancer Society predict 2,001,140 new cases of cancer in the United States in 2024, while an estimated 611,720 individuals will die of cancer. Treatment advancement will raise the number of cancer survivors from 18.1 million in 2022 to 22.5 million in 2032. 40.5% of all men and women will develop cancer sometime in their lifetime. Besides, 14,910 children and adolescents in the U.S. are likely to be diagnosed with cancer in 2024, out of which 1,590 are expected to die due to cancer. The U.S. cancer care cost Was at USD 208.9 billion for 2020, and with an aging population and more costly treatments, there is a likelihood of an increase. Worldwide, death due to this disease remains on the list as one of the top causes of death. An estimated 20 million new cases and 9.7 million deaths in 2022 are expected to reach 29.9 million cases and 15.3 million deaths by 2040.
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 10.50 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 19.94 Billion |
| Expected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 7.38% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| High-growth Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Drug Type, Cancer Type, Administration Route, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Saint-Gobain, Owens Corning, Johns Manville (a Berkshire Hathaway company), Rockwool International, Knauf Insulation, Kingspan Group, Dow Inc., Basf SE, Mineral Wool (Wool), Nitto Denko Corporation, Celotex (a Saint-Gobain brand), Sika AG, GAF Materials Corporation, Jushi Group, Haley & Aldrich Inc. |
Increasing cancer cases and aging population
Advancement in Drug Development of Chemotherapy Drugs
Limited Efficacy Against Certain Cancer Types
Low Access in Resource-Poor Situations
Increasing Access to Chemotherapy in Developing Countries
Advances in Targeted Therapies
High Treatment Costs
Side Effects and Patient Tolerance
The chemotherapy market is segments into drug type, cancer type, administration route and region. Based on drug type, the market is classified into alkylating agents, antimetabolites, mitotic inhibitors, topoisomerase inhibitors and Other. Based on cancer type, the market is classified into breast cancer, lung cancer, leukemia, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer and others. Based on administration route, the market is classified into oral chemotherapy, intravenous chemotherapy, intramuscular chemotherapy and subcutaneous chemotherapy. Based on end user, the market is classified into hospitals, research institutes and others.
Alkylating Agents: The alkylating agents has dominated the market in 2024. Alkylating agents are a class of chemotherapy drugs that work by adding alkyl groups to the DNA of cancer cells, leading to DNA damage, which prevents replication and cell division. These drugs are effective in treating a wide range of cancers, including leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. Common alkylating agents include cyclophosphamide, melphalan, and cisplatin. These agents significantly slow down or completely halt the advancement of cancerous cells; however, they have side effects such as nausea and vomiting, suppression of the bone marrow, and even the risk of secondary cancers due to the long time they take in the body. They are commonly combined with other drugs in chemotherapy to be more effective.
Antimetabolites: The drug functions by interfering with the synthesis of nucleic acids, a process that cancer cells need for replication. They can resemble naturally occurring substances the body uses to create DNA and RNA, therefore inhibiting cancer cells from multiplying and spreading. Examples include methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), and gemcitabine. These types of agents are commonly used in cancer types such as leukemia, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer. Though they are effective, they can cause mouth sores, nausea, and liver toxicity. The most commonly used antimetabolites are in combination with other drugs to enhance their effect and overcome drug resistance.
Mitotic Inhibitors: The mitotic inhibitors are also referred to as spindle poisons. This poisons the cancer cells from dividing by disrupting the microtubules that form the mitotic spindle. It is an essential component for cell division. Examples of such drugs are paclitaxel, docetaxel, and vincristine, which have been used for the treatment of breast, ovarian, and lung cancers. They are important drugs in targeted therapies of refractory tumors to other chemotherapy agents. Their use is however associated with side effects such as neuropathy, hair loss, and gastrointestinal problems. They are used together with other chemotherapy drugs for enhanced effectiveness.
Topoisomerase Inhibitors: These are the enzyme inhibitors that help unwind DNA strands during replication. Topoisomerase I and II inhibitors include drugs like irinotecan and etoposide, among others. Since they break double-stranded DNA, cell death occurs. It forms a drug against many cancers - colorectal cancers, small-cell lung cancers, and leukemia to name a few. Although so potent, diarrhea and myelosuppression, among other adverse effects, may frequently be involved, even nausea in extreme cases. Such drugs are sometimes used in conjunction with other chemotherapy regimens to enhance treatment effectiveness and improve the patient's prognosis.
Other Chemotherapy Drugs: This is the category of chemotherapy drugs that have unique mechanisms of action or are applied specifically for types of cancer. These drugs include platinum-based compounds like carboplatin, hormone therapy drugs for breast and prostate cancer (e.g., tamoxifen), and monoclonal antibodies like rituximab for lymphomas. They provide a variety of treatments for cancers that are not responsive to conventional chemotherapies. Their management may vary for the different cancers, stages of the tumor, and genetic background of the patient, but they also lead to side effects such as immunosuppression or allergic reactions.
Leukemia: The leukemia segment has dominated the market in 2024. Treatment varies based on the kind of leukemia being acute or chronic. In the case of acute leukemias, aggressive chemotherapy protocols are implemented like cytarabine and anthracyclines (for instance, daunorubicin). Targeted therapy, for chronic leukemias like CML, is being added to chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is rapidly aimed at lowering leukemia cell counts with maintenance therapy occurring afterward as most may relapse once the drugs wear off. Supporting therapy alleviates myelosuppression, infection, and some bleeding complications, among other symptoms.
Breast Cancer: Chemotherapy is an integral part of both early and advanced breast cancer. It is used in conjunction with other therapies like hormone therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy to enhance results. The drugs include doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and cyclophosphamide. They are used in breast cancer treatment, especially when the tumors are hormone receptor-negative or HER2-positive. Chemotherapy is used following surgery as adjuvant therapy to help get rid of cancer cells. Among the many side effects that can be associated with these drugs, side effects include hair loss, fatigue, and nausea; however, measures are also taken through supportive care to minimize such effects.
Lung Cancer: Chemotherapy is given to non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). The major drugs for NSCLC are cisplatin, carboplatin, and pemetrexed with other targeted therapies like EGFR inhibitors. For SCLC, chemotherapy treatment protocols like EP (etoposide and cisplatin) are conducted since this cancer is highly aggressive. Chemotherapy for lung cancer may be done as the primary treatment or with a combination of other therapies, such as radiation or surgery, depending on the extent of the cancer. The common side effects include weakness, nausea, and respiratory difficulties.
Prostate Cancer: Ordinarily chemotherapy has been employed with the advancement of hormone-refractory prostate cases in which some other therapy fails such as hormone therapy. Standard drugs utilized with the chemotherapy are largely docetaxel and cabazitaxel. There are times the chemotherapy has also been used, with hormone therapy, to prevent the growth of carcinoma prostate. While it is not a common treatment for the prostate, as such, it proves to be very useful in advanced stages when survival is at stake. The most common complications include fatigue and hair loss accompanying gastrointestinal problems.
Colorectal Cancer: The mainstay of treatment for colorectal cancer is adjuvant chemotherapy following surgery and in metastatic disease. Medicated drugs used include 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), oxaliplatin, leucovorin, and several combinations, including FOLFOX (5-FU, leucovorin, oxaliplatin). These treatments aim to reduce the size of tumors, recurrences, and metastasis. Nausea and vomiting, fatigue, and neuropathy are potential side effects. Chemotherapy is also given in combination with targeted therapies for patients diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Ovarian Cancer: Paclitaxel and carboplatin-based chemotherapy regimens are the most commonly used for high-grade serous ovarian cancers. Chemotherapy is generally given after surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible and to lower the risk of recurrence. Maintenance therapy with PARP inhibitors is increasingly used in the treatment of ovarian cancer. Chemotherapy is one of the best options but creates side effects that include tiredness, queasiness, and ovarian function lowering, which jeopardizes a patient's fertility.
Other Cancers: Other cancers include pancreatic, liver, kidney, and bladder cancers and most of the time require treatment through chemotherapy. For instance, gemcitabine is used as chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer patients while cisplatin is administered as chemotherapy for bladder cancer. Chemotherapy regimens differ greatly with cancer type, and in some instances, personalized medicine determines the best course of treatment. In some cases, chemotherapy use is also combined with radiation therapy, surgery, and targeted therapies depending on the stage and type of cancer.
Oral Chemotherapy: Oral chemotherapy is very convenient and increasingly used for outpatient care, thus allowing the patient to take their drugs at home. The drugs include oral chemotherapy agents, such as capecitabine, temozolomide, and cyclophosphamide. The route is good for long-term therapy, mainly in cancers like colorectal and breast cancer. However, the convenience aspect can be problematic for patient compliance. Side effects are common and may include gastrointestinal discomfort, mouth sores, and fatigue. Follow-up visits have to be scheduled closely; the patient has to receive proper education on the treatment so it can work effectively and reduce risks.
IV Chemotherapy: IV chemotherapy is the most common form of chemotherapy. It injects medication directly into the bloodstream, so it works quickly in reaching the body in its entirety. IV chemotherapy is applied to aggressive cancers, such as breast, lung, and colorectal cancers, and it is usually administered in a hospital or outpatient infusion center. The administration of drugs through the veins allows for a higher dose, which is sometimes necessary for the treatment of advanced cancers. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, and an increased risk of infection due to the suppression of the immune system. Patients are closely watched for any reaction during and following the infusion.
Intramuscular Chemotherapy: Intramuscular chemotherapy requires injecting the medication into a muscle, where it is absorbed gradually. This type of chemotherapy is less frequently performed than IV injection but may be used when a localized therapy is needed or in cases where a patient cannot get an IV line. For instance, methotrexate can be administered intramuscularly for particular types of cancers or autoimmune disorders. This route does not necessitate a central IV line but is painful and absorption varies. Pain at the injection site, muscle stiffness, and systemic symptoms like fever are common side effects.
Subcutaneous Chemotherapy: This refers to the subcutaneous injection of chemotherapy under the skin. This is less invasive than intravenous injections and is used for drugs such as cytarabine in the treatment of some leukemias. Subcutaneous injections are usually given at home or in a clinic, giving the patient more mobility. The absorption rate is slower compared to intravenous chemotherapy, but it can be more comfortable for patients. It may cause localized redness or swelling at the site of injection and can bring about some systemic reactions such as fatigue and even gastrointestinal issues.
The chemotherapy market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
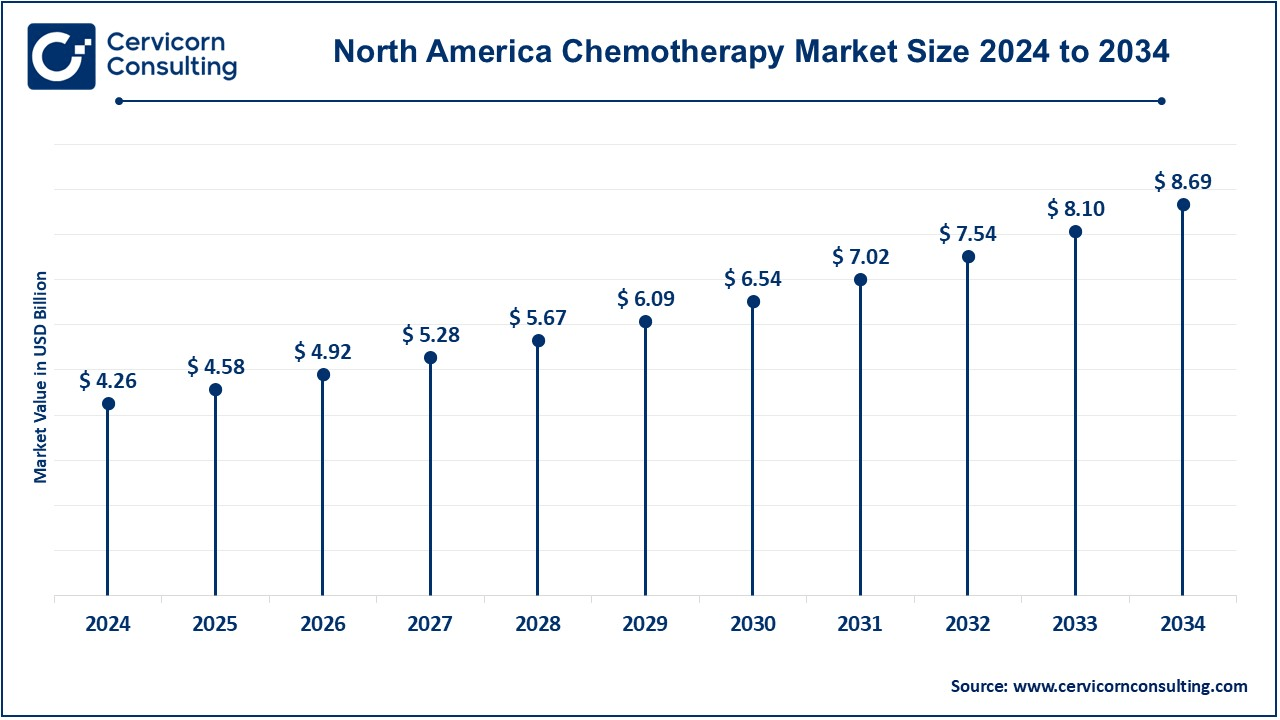
The North America chemotherapy market size was valued at USD 4.26 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 8.69 billion by 2034. In North America, due to the higher incidence of cancer and more developed medical infrastructure, this is the largest market for chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapy drugs have been developed by leading pharmaceuticals like Pfizer, Merck, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Furthermore, the use of advanced therapies and supportive care systems such as oncology specialists and research facilities also drives the market growth of chemotherapy drugs. Increased adoption of customized medicines and newer drug therapy increases the use of chemotherapy drugs. The major constraint, however, is the cost of treatment that patients have to incur, especially those without health insurance.
The Europe chemotherapy market size was estimated at USD 2.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow around USD 5.40 billion by 2034. High healthcare standards in the region, well-established healthcare systems, and public health initiatives contribute to strong chemotherapy drug use. Major contributors to the market are countries like Germany, France, the UK, and Italy. European regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) ensure that chemotherapy drugs are safe and effective. The use of chemotherapy in combination with personalized medicine and immunotherapies is on the rise, especially at advanced stages of cancer. However, disparities in healthcare access between Western and Eastern Europe create a challenge for market expansion.
The Asia-Pacific chemotherapy market size was accounted for USD 2.27 billion in 2024 and is predicted to hit around USD 4.63 billion by 2034. The chemotherapy market in the Asia Pacific region is growing rapidly due to a large population base, increasing incidence of cancer, and improvement in healthcare infrastructure. The key markets are China, Japan, and India, where the demand for chemotherapy drugs is increasing due to better awareness of cancer treatments. The region also has a growing middle class with better access to healthcare, which is driving market expansion. The challenges include inaccessibility due to unaffordability and variation in rural areas. However, the local production of generics and increasing research in cancer has assisted in the growth of the market.
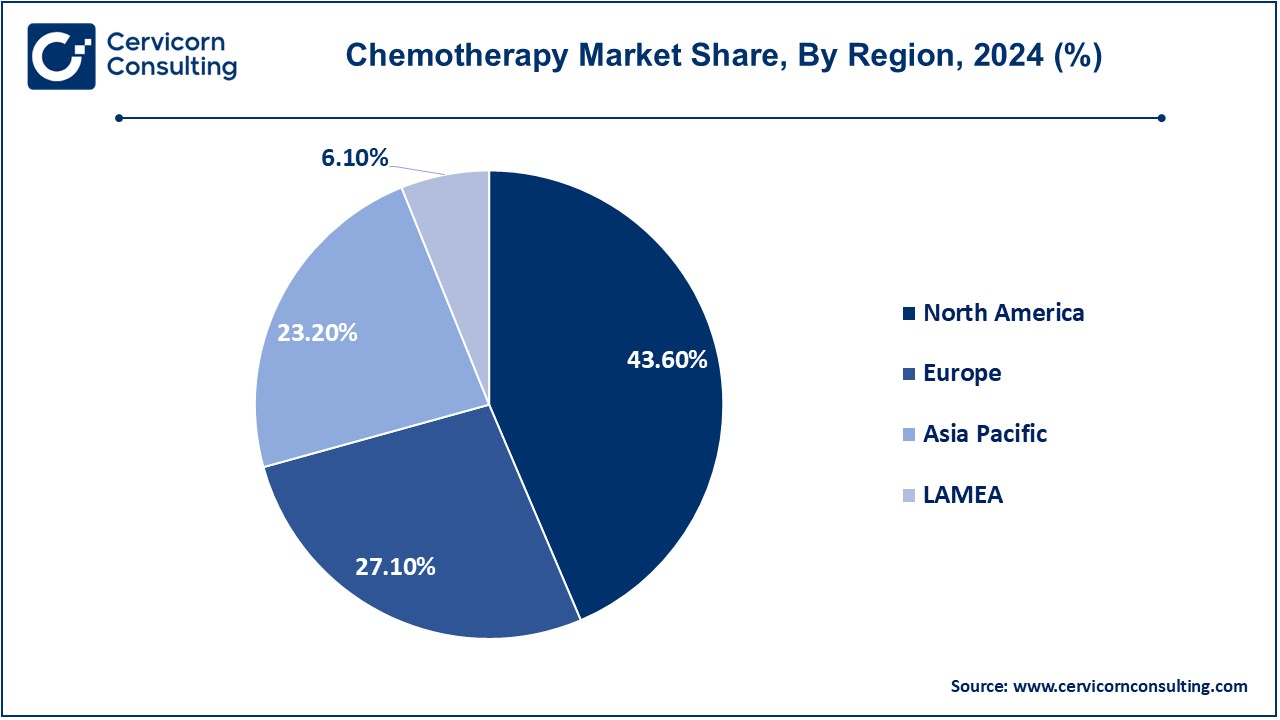
The LAMEA chemotherapy market was valued at USD 0.60 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1.22 billion by 2034. The chemotherapy market in LAMEA is still developing. The issues related to this market are the weak health infrastructure, especially in rural areas, as well as less access to highly advanced treatments in some regions. Although improvement in the healthcare systems in Latin America and the Middle East is noted, with increasing importance on cancer care, the market for chemotherapy drugs remains relatively less promising. Chemotherapy drugs remain expensive in Africa and continue to have issues with accessibility, though a better healthcare system will bring improvement in this segment as well, due to a rising burden of cancer in these regions. Support from the government and international collaborations can be a great catalyst for enhancing the availability of chemotherapy.
Market Segmentation
By Drug Type
By Cancer Type
By Administration Route
By End User
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Chemotherapy
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Drug Type Overview
2.2.2 By Cancer Type Overview
2.2.3 By Administration Route Overview
2.2.4 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Increasing cancer cases and aging population
4.1.1.2 Advancement in Drug Development of Chemotherapy Drugs
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Limited Efficacy Against Certain Cancer Types
4.1.2.2 Low Access in Resource-Poor Situations
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 High Treatment Costs
4.1.3.2 Side Effects and Patient Tolerance
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Increasing Access to Chemotherapy in Developing Countries
4.1.4.2 Advances in Targeted Therapies
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Chemotherapy Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Chemotherapy Market, By Drug Type
6.1 Global Chemotherapy Market Snapshot, By Drug Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Alkylating Agents
6.1.1.2 Antimetabolites
6.1.1.3 Mitotic Inhibitors
6.1.1.4 Topoisomerase Inhibitors
6.1.1.5 Others
Chapter 7. Chemotherapy Market, By Cancer Type
7.1 Global Chemotherapy Market Snapshot, By Cancer Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Breast Cancer
7.1.1.2 Lung Cancer
7.1.1.3 Leukemia
7.1.1.4 Prostate Cancer
7.1.1.5 Colorectal Cancer
7.1.1.6 Ovarian Cancer
7.1.1.7 Others
Chapter 8. Chemotherapy Market, By Administration Route
8.1 Global Chemotherapy Market Snapshot, By Administration Route
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Oral Chemotherapy
8.1.1.2 Intravenous Chemotherapy
8.1.1.3 Intramuscular Chemotherapy
8.1.1.4 Subcutaneous Chemotherapy
Chapter 9. Chemotherapy Market, By End-User
9.1 Global Chemotherapy Market Snapshot, By End-User
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Hospitals
9.1.1.2 Research institutes
9.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 10. Chemotherapy Market, By Region
10.1 Overview
10.2 Chemotherapy Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
10.3 Global Chemotherapy Market, By Region
10.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
10.4 North America
10.4.1 North America Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.3 North America Chemotherapy Market, By Country
10.4.4 U.S.
10.4.4.1 U.S. Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.5 Canada
10.4.5.1 Canada Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
10.4.6 Mexico
10.4.6.1 Mexico Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
10.5 Europe
10.5.1 Europe Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.3 Europe Chemotherapy Market, By Country
10.5.4 UK
10.5.4.1 UK Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.5 France
10.5.5.1 France Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.6 Germany
10.5.6.1 Germany Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
10.5.7 Rest of Europe
10.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6 Asia Pacific
10.6.1 Asia Pacific Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.3 Asia Pacific Chemotherapy Market, By Country
10.6.4 China
10.6.4.1 China Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.5 Japan
10.6.5.1 Japan Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.6 India
10.6.6.1 India Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.7 Australia
10.6.7.1 Australia Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7 LAMEA
10.7.1 LAMEA Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.3 LAMEA Chemotherapy Market, By Country
10.7.4 GCC
10.7.4.1 GCC Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.5 Africa
10.7.5.1 Africa Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.6 Brazil
10.7.6.1 Brazil Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
10.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
10.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Chemotherapy Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
10.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
10.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 11. Competitive Landscape
11.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
11.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
11.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
11.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
11.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 12. Company Profiles
12.1 Saint-Gobain
12.1.1 Company Snapshot
12.1.2 Company and Business Overview
12.1.3 Financial KPIs
12.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
12.1.5 Strategic Growth
12.1.6 Global Footprints
12.1.7 Recent Development
12.1.8 SWOT Analysis
12.2 Owens Corning
12.3 Johns Manville (a Berkshire Hathaway company)
12.4 Rockwool International
12.5 Knauf Insulation
12.6 Kingspan Group
12.7 Dow Inc.
12.8 Basf SE
12.9 Mineral Wool (Wool)
12.10 Nitto Denko Corporation
12.11 Celotex (a Saint-Gobain brand)
12.12 Sika AG
12.13 GAF Materials Corporation
12.14 Jushi Group
12.15 Haley & Aldrich Inc.