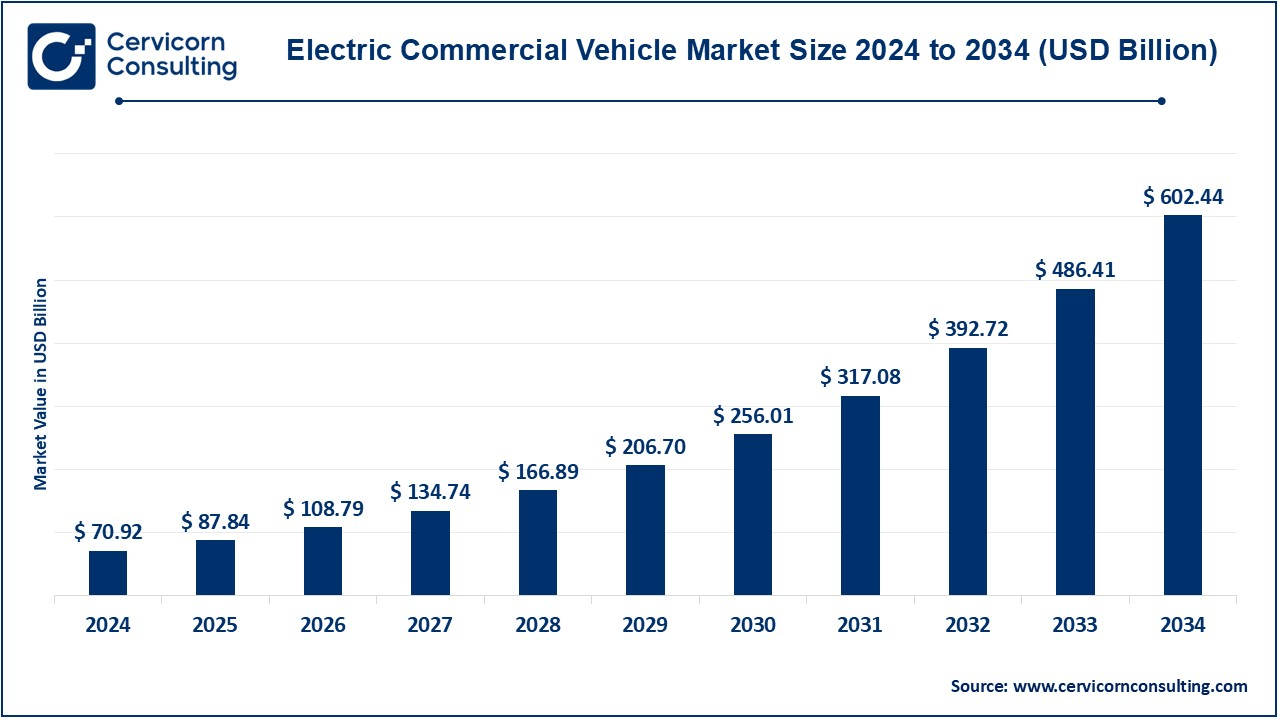
The global electric commercial vehicle market size was estimated at USD 70.92 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 602.44 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.85% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Report Highlights
With the escalating environmental regulations worldwide for sustainability, the electric commercial vehicle market will keep on picking up. Strict emission standards on governments' agendas minimize pollution levels and combat climatic changes by reducing fossil fuels. Regulations push firms into opting for clean technologies, in which electric commercial vehicles (EVs) are some means that are helpful for corporations in achieving environment-related goals in the directions governments lead towards. Another addition is the low-emission zones implemented in many cities, which encourage using electric commercial vehicles. Businesses, especially in urban and regional transportation, are changing their ways to electric vehicles to protect against fines by abiding by the new regulation.
Electric commercial vehicles, on the other hand, is a commercial vehicle that runs not on fossil but on electricity, which includes commercial buses, vans, trucks, and other services used for either transporting goods or providing services to the public. ECVs are important, as they enable sustainable transportation methods, reducing gas emissions and at the same time reducing operational expenses compared to conventional engines. The ECV market is always increasing and is an overt move toward more environmentally friendly transport. Data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration, EIA, reveals that the electricity consumption by light-duty electric vehicles has risen smoothly since 2018 to the date. For instance, the amount of electricity that the BEVs and PHEVs used increased from 1,581,706 MWh in 2018 to 7,595,513 MWh in 2023, meaning that use is growing. This is propelled by a trend such as better battery technology, greater developments of charging points, and governmental stipulations to improve carbon emissions. The future for the ECV market seems promising as growth will continue to rise because of advancements in battery technologies, greater availability of charging stations, and investments by both the public and private sectors. As the regulatory framework for emissions gets tougher and stricter, this would push the shift for an increasing number of electric commercial vehicles. Thus, by the end of the decade, the ECV market would have gained substantial market valuations, wherein electric vehicles were one of the popular solutions in sustainable transportation solutions.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 87.84 Billion |
| Estimated Market Size in 2034 | USD 602.44 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 23.85% |
| Dominant Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Vehicle Type, Range, Propulsion, Battery Type, Battery Capacity, Power Output, Body Construction, Component, Application, Region |
| Key Companies | Volvo Group, Daimler AG, Traton Group, BYD, Nikola Motor, Tesla, DAF Trucks, Rivian, Ford Motor Group, General Motors, Tata Motors, Mahindra Electric, Ashok Leyland, Ather Energy, Ola Electric Mobility |
Technological Advancements
Government policies and laws
High Initial Investment Costs
Limited charging infrastructure
Growing Demand for Sustainable Transportation
Expansion of charging infrastructure
High Initial Costs
The electric commercial vehicle market is segmented into vehicle type, range, propulsion, battery type, battery capacity, power output, body construction, component, application, region. Based on vehicle type, the market is classified into electric trucks, electric vans, electric buses and electric light commercial vehicles. Based on range, the market is classified into short-range electric vehicles, medium-range electric vehicles and long-range electric vehicles. Based on propulsion, the market is classified into BEVS and FCEVS. Based on battery type, the market is classified into NMC batteries, LFP batteries, solid-state battery and others. Based on battery capacity, the market is classified into less Than 60KWH, 60-120 KWH, 121-200 KWH, 201-300 KWH, 301-500 KWH and 501-1000 KWH. Based on power output, the market is classified into less than 100 KW, 100-250 KW, and above 250 KW. Based on body construction, the market is classified into integrated, semi-integrated and full-sized. Based on component, the market is classified into battery pack, onboard charger, electric motors, inverters and fuel cell stacks. Based on application, the market is classified into logistics and freight, public transport, construction and mining and last-mile delivery.
Electric Trucks: Electric trucks are increasingly being used these days for the transportation of goods over varying distances. Light-duty trucks are used for short, urban delivery routes, and medium to heavy-duty trucks are used for a larger distance and heavier payload. Even big logistics players like UPS and FedEx have now started embracing electric trucks in a big way as a means of reducing emissions. The trend of producing electric trucks revolves around increasing the size of the batteries to have heavy payloads and overlong routes. As this technology advances, it can replace diesel trucking for freight movement between towns and cities for a majority of sustainability objectives.
Electric Vans: Electric vans are being popularized for urban delivery last mile needs because of their small size and low emissions, with cheaper operating costs. They are ideal for city-based logistics companies like Amazon, FedEx, and DHL that experience congested roads. Low maintenance requirements, government incentives, and the growing e-commerce sector accelerate the fast-paced adoption of electric vans. Additionally, developments in battery technology increase range and charge options for logistics needs and drive the electric van market.
Electric Buses: Electric buses are used globally because they eliminate pollution in cities, save money on their maintenance, and consume less energy. They are deployed in city public transportation, intercity, and school routes. Cities like London, Paris, and Los Angeles have promised to convert to electric buses as part of their overall efforts toward sustainability. Government funding also makes electric buses affordable for municipal transit authorities to adopt. Operationally, electric buses also help reduce noise pollution and reduce lifetime maintenance costs.
Electric Light Commercial Vehicles: These include the small delivery vans, electric pickup trucks, and others of their ilk that are vital for the movement of goods within an urban setup. The business saves fuel in these and are smaller, low-emitting vehicles, which are ideal for city roads. LCVs are being more and more used by small and medium-sized businesses for local deliveries. The demand for electric LCVs is expected to grow as more businesses seek efficient solutions for their fleets while aligning with sustainability goals. Some manufacturers such as Rivian and Ford invest in these types of vehicles and thus make them available and even cheaper.
Short-Range Electric Vehicles: These electric vehicles are developed for short-range operations within an urban setting or smaller-scale application. It ranges below 150 miles. These can be used in short local trips or commutations around the city or last-mile delivery operations. Since they are relatively small in terms of battery size, their cost is cheaper compared to long-range vehicles, hence suitable for small businesses and delivery services. Electric short-range vehicles have more demand in heavily trafficked cities with shorter distances between delivery points. Their ranges are also shorter which makes their recharging faster hence suitable for frequent stops and fast turnaround times.
Medium-Range Electric Vehicles: They will be able to range between 150 and 300 miles per charge, ideal for regional transportation requirements. They then become popular among logistics companies, regional delivery services, and businesses with moderate-distance travel requirements. They have bigger batteries so that they can drive on their daily routes comfortably while maintaining an inexpensive status relative to long-range vehicles. The range therefore makes feasible the trade-off between operational costs, efficiency, and sustainability. Electric trucks and vans from medium ranges therefore offer a way through which fleet owners can reduce their emissions considerably without losing out on their freight performance.
Long-Range Electric Vehicles: Over 300 miles on a single charge, the electric vehicles serve the requirement of long-distance haul distance freight movement. Ultra-long-range electric vehicles cater to the needs of companies that move state-to-state lines to implement cross-country deliveries and transportation interstate. The long-range feature reduces stops to charge further helps improve operational efficiency and saves time. Long-range electric vehicles cost more because more capacity is needed in the batteries. Companies adopting this type of vehicle will have to invest in infrastructure, but the overall benefits, like fuel cost and emission reduction, make it worthwhile to spend the amount on the purchase of the long-haul electric vehicle.
Logistics and Freight: The top big area is Logistics and Freight with the major of adopting electric commercial vehicles. Such fleets help logistic companies save fuel, achieve emission targets, and lessen noise pollution due to electric trucks and vans. Companies like DHL and UPS are testing or adding electric vehicles on their diesel lines, especially at the last leg of delivery through towns or cities. In the case of electric vehicles, several models may fit cargo transportation, especially short-distance urban operations or more regional routes. Logistics companies have taken sustainability into great focus, and are finding solutions that help optimize the supply chain efficiency as well as reduce the impact on the environment.
Public Transport: The use of electric buses is a major component of shifting towards cleaner public transport. Cities are implementing electric buses slowly to achieve set air quality targets as well as low operating costs. The top countries of electric public transport are China, the U.K., and India. Electric buses produce less noise and fewer greenhouse gases as well as need less maintenance compared to traditional diesel buses. Not only city buses but electric buses are also being employed for intercity and even school transport. Governments offer financial benefits for using such vehicles. These vehicles are connected to long-term savings and align with climate change mitigation.
Construction and Mining: Electric commercial vehicles are being gradually replaced with diesel-powered equipment in the construction and mining industries. Electric bulldozers, excavators, and haul trucks emit lower carbon content and are more efficient, thus fitting perfectly for workspaces that value workers' safety and sound reduction. Though adoption is slower in these industries than in urban transport, companies are increasingly drawn to the long-term environmental and economic benefits. Industry players are focusing on improving the capabilities of these machines, such as longer battery life and higher performance, for more demanding tasks in remote or construction sites, with growing interest in electric solutions.
Last-Mile Delivery: Last-mile delivery is one of the fastest-growing segments. e-Commerce boom is the reason behind it. Electric vans and small trucks are suitable vehicles for delivering products to consumers living in cities. Electric propulsion systems have reduced environmental impacts in delivering frequently. Cars are more diminutive, agile, and less pricey, so they appeal to various clients. In addition, most last-mile delivery activities involve short routes, and electric cars are ideal for such operations. Therefore, e-commerce increases, customers demand faster deliveries, and companies begin to scale up electric vehicles to meet their sustainability commitments and realize delivery savings.
The electric commercial market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
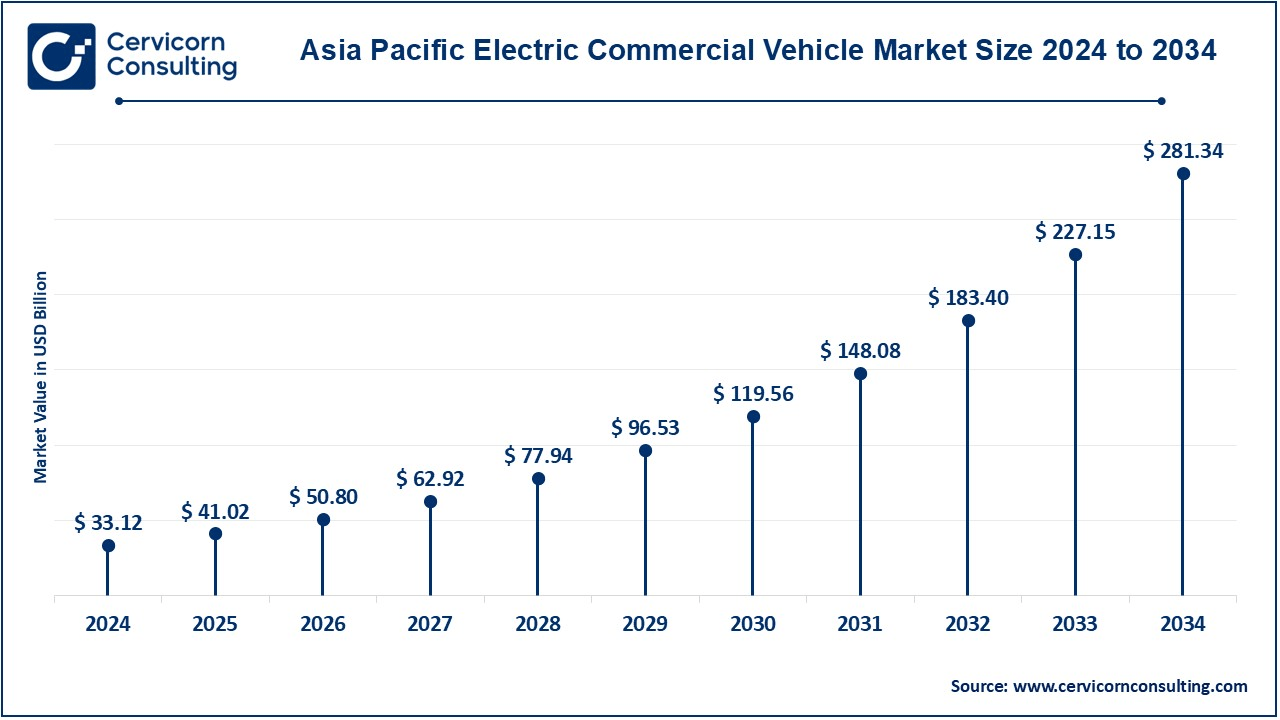
The Asia-Pacific electric commercial vehicle market size was accounted for USD 33.12 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 281.34 billion by 2034. The Asia Pacific region, yet again led by China, is the market with the biggest demand for e-commercial vehicles. China is at the top in the adoption and production of electric trucks, buses, and vans with great government support in incentives and infrastructural settings. The adoption of electric commercial vehicles is increasing in countries committed to clean energy and emissions reduction. Other countries including Japan and India have gradually been embracing electric vehicles. India is targeting bus electrification, and Japan is developing electric freight solutions to meet sustainability objectives.
The North America electric commercial vehicle market size was reached at USD 14.61 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow around USD 124.10 billion by 2034. In North America, the U.S. and Canada are on the advanced side of electric commercial vehicle implementation, mainly because of positive government policies, incentives, and infrastructure development. The increasing trend towards zero-emission transportation solutions and carbon emissions regulations push fleet operators to place electric trucks and vans in service. Cities such as Los Angeles and New York are now found to be at the forefront of adopting electric buses and last-mile delivery vehicles. More so, US-based companies like Tesla and Rivian are also experiencing massive success in the market. Electric buses and vans are being taken up by Canada in urban cities through government grants and clean energy.
The Europe electric commercial vehicle market size was valued at USD 20.21 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 171.70 billion by 2034. Europe has been the forerunner in electric commercial vehicles as the emission rules are quite stringent, and most governments encourage that kind of usage through incentives. Norway, the Netherlands, and the UK have led. Ambitious targets have been set by the companies in adopting electric vehicles. The companies target cities, especially for adaptation to electric vehicles. In Europe, urban centers are among the growing markets where cities have adopted renewable transport through electric buses. Companies such as Volvo and Daimler have invested quite seriously in the manufacturing of electric trucks. More recently, the European Union's Green Deal and more are accelerating e-vehicle migration on the continent; hence making Europe a key growth centre for electric commercial vehicles.
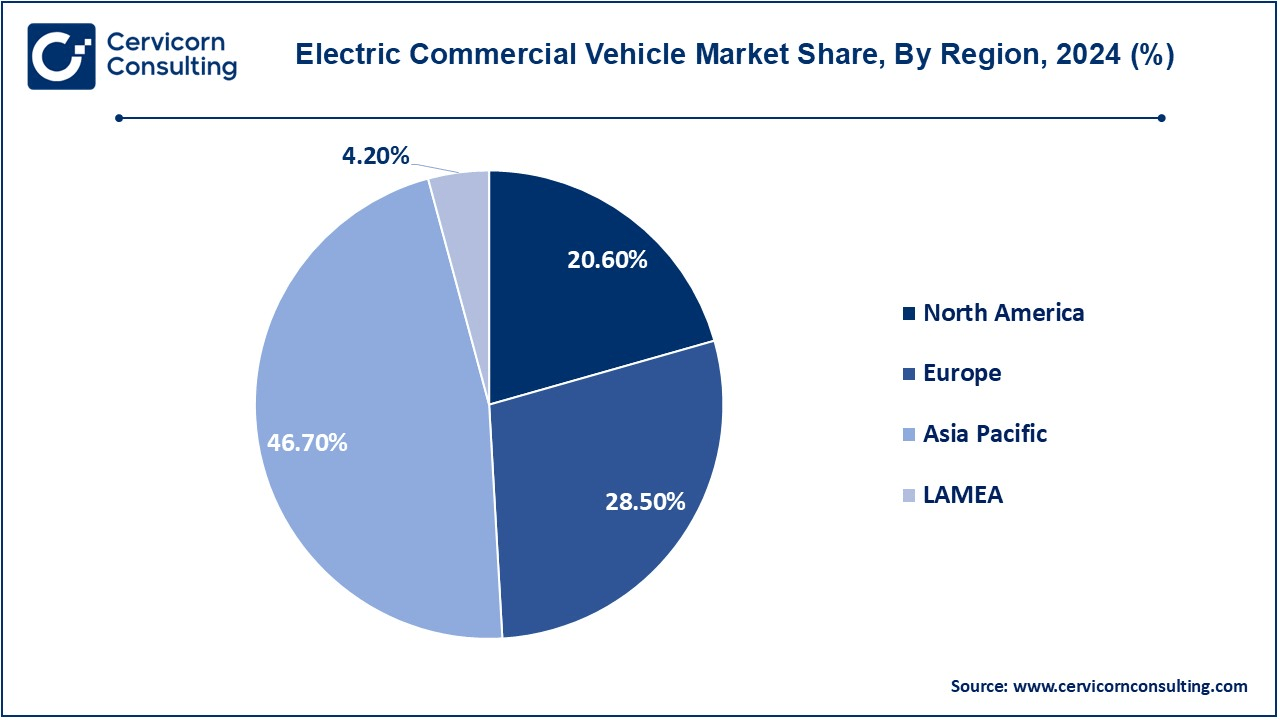
The LAMEA electric commercial vehicle market was valued at USD 2.98 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 25.30 billion by 2034. The adoption rate is slower in regions such as Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East but is increasing gradually. For instance, Brazil and Mexico are investing in electric vehicle infrastructure, and the government offers subsidies to encourage adoption. However, disadvantages are still seen in the insufficient charging infrastructure and the higher price of vehicles. Electric buses are being introduced in some African cities to curb air pollution. The Middle East is promising electric commercial vehicles in the UAE and Saudi Arabia to reduce dependence on traditional energy sources and lessen emissions.
CEO Statements
Thierry Dombreval, CEO of Renault Trucks
Ola Källenius, CEO of Mercedes-Benz Group AG
Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type
By Range
By Propulsion
By Battery Type
By Battery Capacity
By Power Output
By Body Construction
By Component
By Application
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Electric Commercial Vehicle
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Vehicle Type Overview
2.2.2 By Power Output Overview
2.2.3 By Battery Capacity Overview
2.2.4 By Battery Type Overview
2.2.5 By Propulsion Overview
2.2.6 By Range Overview
2.2.7 By Body Construction Overview
2.2.8 By Application Overview
2.2.9 By Component Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Technological Advancements
4.1.1.2 Government policies and laws
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Initial Investment Costs
4.1.2.2 Limited charging infrastructure
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 High Initial Costs
4.1.3.2 Limits of Charging Infrastructure
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Growing Demand for Sustainable Transportation
4.1.4.2 Expansion of charging infrastructure
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Vehicle Type
6.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Vehicle Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Electric Trucks
6.1.1.2 Electric Vans
6.1.1.3 Electric Buses
6.1.1.4 Electric Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs)
Chapter 7. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Power Output
7.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Power Output
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Less Than 100 KW
7.1.1.2 100-250 KW
7.1.1.3 Above 250 KW
Chapter 8. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Range
8.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Range
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Short-range Electric Vehicles
8.1.1.2 Medium-range Electric Vehicles
8.1.1.3 Long-range Electric Vehicles
Chapter 9. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Propulsion
9.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Propulsion
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 BEVS
9.1.1.2 FCEVS
Chapter 10. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Battery Type
10.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Battery Type
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 NMC Batteries
10.1.1.2 LFP Batteries
10.1.1.3 Solid-State Battery
10.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 11. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Battery Capacity
11.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Battery Capacity
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
11.1.1.1 Less Than 60KWH
11.1.1.2 60-120 KWH
11.1.1.3 121-200 KWH
11.1.1.4 201-300 KWH
11.1.1.5 301-500 KWH
11.1.1.6 501-1000 KWH
Chapter 12. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Body Construction
12.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Body Construction
12.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
12.1.1.1 Integrated
12.1.1.2 Semi-Integrated
12.1.1.3 Full-Sized
Chapter 13. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Application
13.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By Application
13.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
13.1.1.1 Logistics and Freight
13.1.1.2 Public Transport
13.1.1.3 Construction and Mining
13.1.1.4 Last-Mile Delivery
Chapter 14. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Component
14.1 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Snapshot, By End-User
14.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
14.1.1.1 Battery Pack
14.1.1.2 Onboard Charger
14.1.1.3 Electric Motors
14.1.1.4 Inverters
14.1.1.5 Fuel Cell Stacks
Chapter 15. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Region
15.1 Overview
15.2 Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
15.3 Global Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Region
15.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
15.4 North America
15.4.1 North America Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.4.3 North America Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Country
15.4.4 U.S.
15.4.4.1 U.S. Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
15.4.5 Canada
15.4.5.1 Canada Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
15.4.6 Mexico
15.4.6.1 Mexico Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
15.5 Europe
15.5.1 Europe Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.5.3 Europe Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Country
15.5.4 UK
15.5.4.1 UK Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
15.5.5 France
15.5.5.1 France Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
15.5.6 Germany
15.5.6.1 Germany Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
15.5.7 Rest of Europe
15.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
15.6 Asia Pacific
15.6.1 Asia Pacific Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.6.3 Asia Pacific Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Country
15.6.4 China
15.6.4.1 China Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
15.6.5 Japan
15.6.5.1 Japan Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
15.6.6 India
15.6.6.1 India Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
15.6.7 Australia
15.6.7.1 Australia Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
15.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
15.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
15.7 LAMEA
15.7.1 LAMEA Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.7.3 LAMEA Electric Commercial Vehicle Market, By Country
15.7.4 GCC
15.7.4.1 GCC Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
15.7.5 Africa
15.7.5.1 Africa Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
15.7.6 Brazil
15.7.6.1 Brazil Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
15.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
15.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Electric Commercial Vehicle Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
15.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
15.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 16. Competitive Landscape
16.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
16.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
16.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
16.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
16.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 17. Company Profiles
17.1 Volvo Group
17.1.1 Company Snapshot
17.1.2 Company and Business Overview
17.1.3 Financial KPIs
17.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
17.1.5 Strategic Growth
17.1.6 Global Footprints
17.1.7 Recent Development
17.1.8 SWOT Analysis
17.2 Daimler AG
17.3 Traton Group
17.4 BYD
17.5 Nikola Motor
17.6 Tesla
17.7 DAF Trucks
17.8 Rivian
17.9 Ford Motor Group
17.10 General Motors
17.11 Tata Motors
17.12 Mahindra Electric
17.13 Ashok Leyland
17.14 Ather Energy
17.15 Ola Electric Mobility