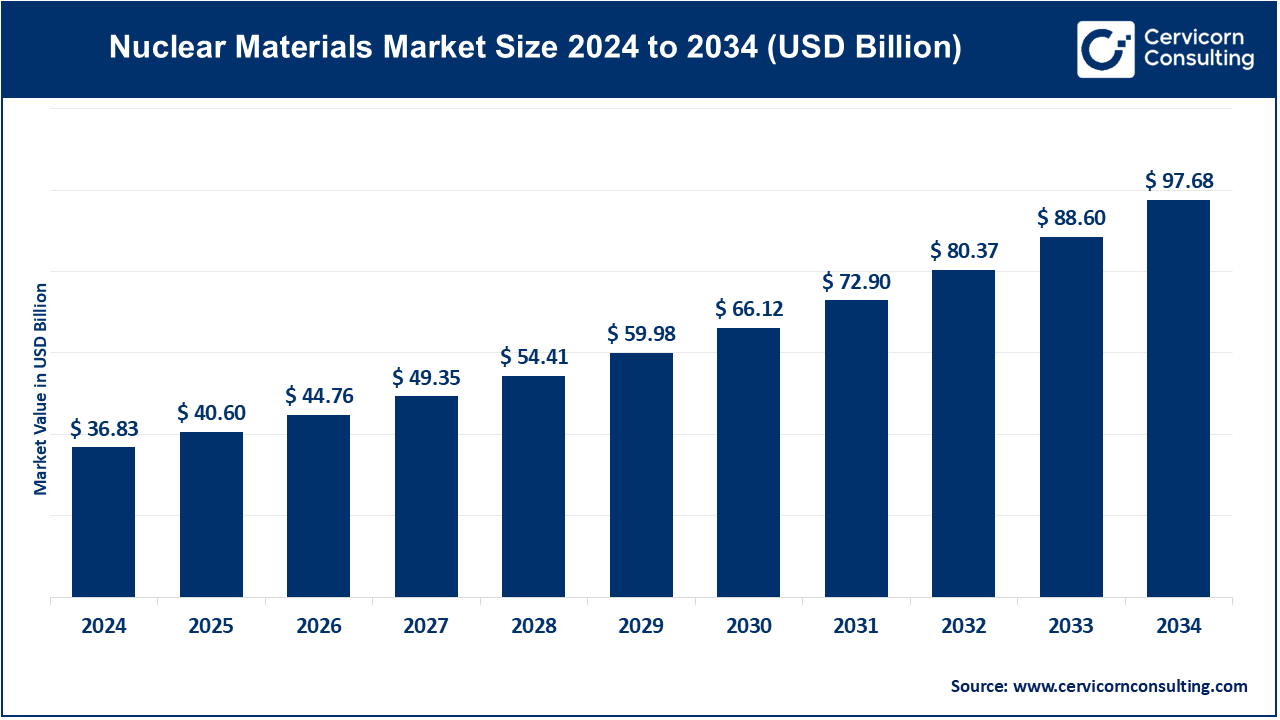
The global nuclear materials market size was valued at USD 36.83 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 97.68 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.24% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The growth of the nuclear materials market can be attributed to the demand for nuclear energy on the rise globally as more and more governments are looking to reduce carbon emissions. The growing demand for advanced nuclear fuels along with materials for nuclear reactors-in particular zirconium alloys and uranium-is another driver for growth in this sector. Besides, investments in R&D for next-generation nuclear reactors-small modular reactors ( SMRs)-air another aspect lighting market growth. Increased concerns regarding nuclear waste management as well as the needs for advanced high radiation-absorption materials are further fueling the growth of the sector.
A nuclear material is a substance in the production of nuclear energy. Specifically, these would be uranium, thorium, plutonium, or other radioisotopes. Such materials are critical in nuclear reactors in their fission for heating and electrical generation. Nuclear materials also find ubiquitous applications in medicine, industry, and the defense establishment wherein they are used for radiography, cancer treatments, and nuclear weapons. With such, safeguards regarding the safety, security, and handling of nuclear materials would minimize risks related to radiation exposure, environmental contamination, and nuclear proliferation.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 40.60 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 97.68 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 10.24% |
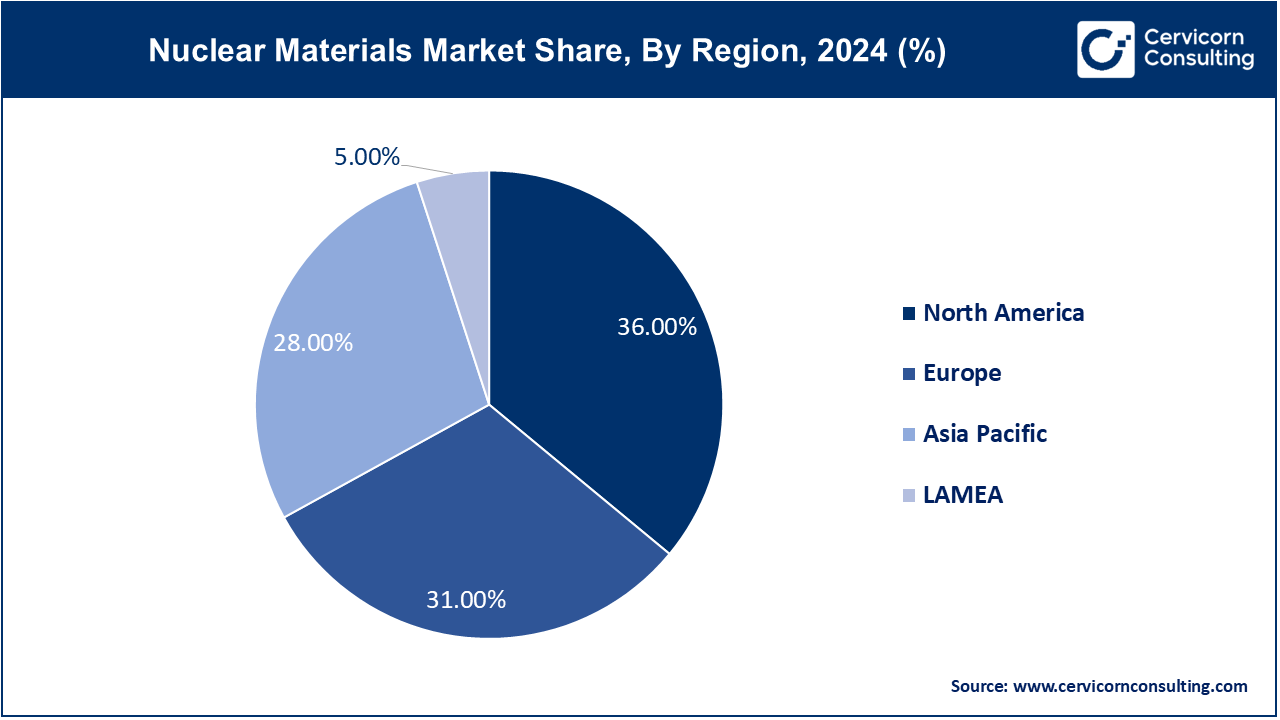
| Dominant Area | North America |
| Fastest Growing Area | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Special Nuclear Material Type, End User, Region |
| Key Companies | Kazatompron, Cameco, Orana, Uranium One, ARMZ Uranium Holding, China Nuclear National Corporation, New Brunswick Power Corporation, Uranium Corporation of India, United States Enrichment Corporation, GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy |
Special Nuclear Material
Source Material
Product Material
Medicine: Nuclear materials have been used very widely in medicine both as diagnostic and for therapeutic purposes. Radioisotopes, like iodine-131 and technetium-99m, are applied in imaging procedures with the intention of detecting cancer or other diseases. In addition, nuclear medicine is highly regarded in the use of cancer treatment through radiation therapy where isotopes such as cobalt-60 are applied to cancerous cells. In this regard, it is the medical sector that remains the demand supplier of nuclear materials due to its use of the improved statuses of nuclear technologies.
Agriculture: In agriculture, nuclear technologies are used on food irradiation, pest control, and soil analysis. Crop yield increases when radioisotopes eradicate pests and diseases, and the irradiation of food to extend shelf life is radiation. Isotopic methods are used for crop breeding. Crop breeding focuses on producing higher strength varieties by using isotopic techniques. The growth of the global population fuels the nuclear agriculture industry, but sustainability in farmlands was a tad more significant compared to previous decades.
Energy and Power: The Energy and Power segment dominated the market in 2024. Nuclear energy is the largest source of low-carbon power in the global energy market. Uranium-235 and plutonium-239 are the fuel used in nuclear reactors that produce electricity by fission reaction under control. Nuclear energy is therefore playing a very crucial role in providing stable and reliable power as the world seeks ways of meeting increasing energy demand while at the same time reducing greenhouse gas emissions, especially in countries committed to clean energy transitions.
Marines: Nuclear materials play a very critical role in the marine sector. They provide a source of power used for propulsion purposes in naval applications, namely compact, long-duration nuclear reactors used by nuclear-powered submarines and aircraft carriers. These types of vessels can stay underwater for extended periods without needing to refuel, making them even more strategically relevant. Many countries depend on nuclear materials as part of their national defense and deterrence.
Aerospace: Nuclear materials can serve as a principal source of energy for space exploration in aerospace. RTGs provided with the power of Plutonium 238 power space craft and rovers to work beyond sun rays, when only solar power is insufficient. These materials warrant rovers working for tens of years on Mars and planetary probes far from Earth working long after their collection of solar or battery power is depleted.
Industrial: There are many industrial applications that require the use of nuclear materials. They are applied in radiography, material testing, and industrial gauging. Radiographic examination, which employs radioactive isotopes such as cobalt-60, enables the detection of welds, pipes, and structural parts of items without causing damage that might have flaws or defects that exist within them. Such applications are of critical importance in industries such as the oil and gas business, construction industry, and manufacturing, where the integrity of materials and structures is crucial to provide safety and better performance. This contributes to widespread industrial demand for nuclear materials.
The nuclear materials market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). Here’s an in-depth look at each region
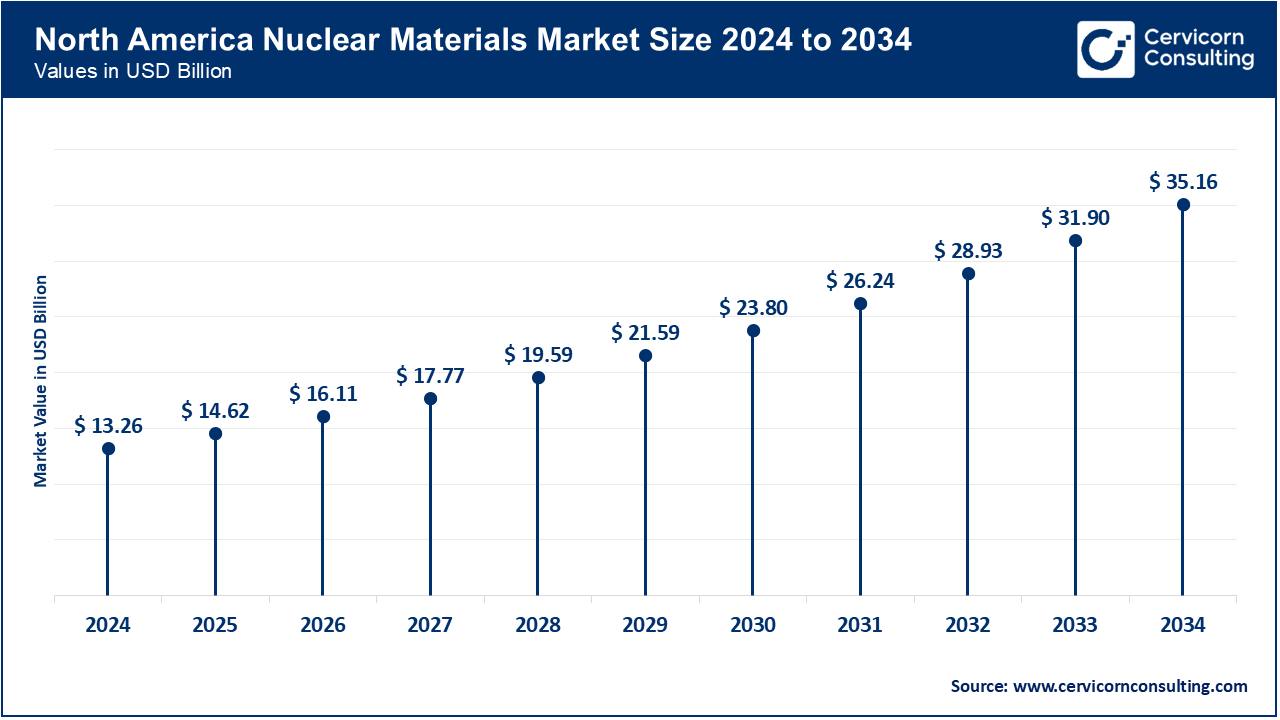
The North America nuclear materials market size was reached at USD 13.26 billion in 2024 and is predicted to hit around USD 35.16 billion by 2034. The United States possesses hundreds of operating nuclear reactors; this has established the United States as the largest producer of nuclear electricity globally. For example, from the United States Environmental Protection Agency, it has been known that nuclear reactors account for nearly 20 percent of all the electricity produced in the United States. Uranium is the fuel most widely used in nuclear reactors at power plants. Nuclear energy is produced when uranium atoms are split in a process called fission.
The Europe nuclear materials market size was estimated at USD 11.42 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 30.28 billion by 2034. Europe boasts of the largest share of world-leading market, dominated by France, the UK, and Russia. In the case of France, around 70% of its electricity comes from nuclear energy, and similarly, Russia has also focused efforts on nuclear construction. Countries like Germany, which are now phasing out nuclear, continue to play important roles in nuclear technology and waste management. For example, as of 2022, Germany is decommissioning nuclear power. Only three reactors are currently in operation, with plans to close them at the end of 2022. Of the reactors, 26 are decommissioned while four have been taken offline. The country's energy policy focuses on the transition towards renewable sources; it has plans to increase its renewable energy percentage to 65% by 2030 and be greenhouse gas neutral by 2045, among other sustainable and secure energy supply commitments. It is also one of the bases for nuclear innovation in Europe with several ongoing research projects on advanced reactors.
The Asia-Pacific nuclear materials market size was accounted for USD 10.31 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow around USD 27.35 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific region, which includes China, India, and Japan, is one of the world's fastest-growing markets for nuclear materials. China is rapidly increasing its nuclear capacity to meet its ever-growing energy needs, and India is investigating thorium reactors as a more sustainable future source of power. For example, in January 2023, the Sasakawa Peace Foundation reported that China is exponentially expanding its nuclear arms capabilities and aims to level with the U.S. In Kansu Province, China is constructing two plutonium reprocessing plants that are scheduled to be operational in 2025 and 2030. It is also working on a program involving fast breeder reactors (FBRs), which can possibly produce large amounts of weapons-grade plutonium. Then China's nuclear arsenal may grow to exceed 1,000 warheads by 2030, leaving the rest of the world with serious concerns about proliferation. Japan has committed itself to nuclear power, investing in reactor safety and fuel reprocessing technologies despite setbacks at Fukushima. Clean energy demands drive nuclear power and materials growth in the region.
The LAMEA nuclear materials market was valued at USD 1.84 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to surpass around USD 4.88 billion by 2034. LAMEA is emerging as a growing market, among others such as Brazil, South Africa, and the United Arab Emirates. Brazil possesses considerable uranium reserves; additionally, it is developing its nuclear energy capacity. South Africa operates the only nuclear power plant in Africa. The United Arab Emirates is building nuclear reactors. One of its nuclear power plants at Barakah is operational. The region's emphasis on energy diversification and sustainability increases demand for nuclear energy and associated materials. For example, according to World Nuclear Association in September 2024, The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has developed a nuclear power program with significant public support, constructing four reactors at Barakah, expected to produce 25% of the country's electricity. The first unit was inaugurated in April 2021 and the subsequent units were commissioned in 2022 and 2023. The UAE Emirate has a strategic plan by 2050 to target half of energy through nuclear power and renewable sources that make it efficient for energy security and sustainability.
CEO Statements
Meirzhan Yussupov, CEO of Kazatompron
"At Kazatomprom, we are committed to being a global leader in the sustainable production and responsible management of nuclear materials. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and maintaining the highest safety standards, we are not only meeting the world’s growing energy demands but also contributing to a cleaner, more secure energy future. Our focus is on expanding the use of uranium, improving supply chain resilience, and ensuring the safe, long-term use of nuclear energy."
Tim Gitzel, CEO of Cameco
"At Cameco, we are at the forefront of providing clean, reliable, and sustainable nuclear fuel to meet the world’s growing energy needs. Nuclear energy is a critical part of the global solution to addressing climate change, and as demand for low-carbon energy increases, we are committed to supporting the transition to a cleaner future through responsible uranium production and innovation in the nuclear sector."
Eduards Smirnovs, CEO of Uranium One
"At Uranium One, we are committed to providing the world with the clean energy needed for a sustainable future. As a leading producer of uranium, we understand the vital role nuclear energy plays in reducing carbon emissions and ensuring energy security. Our focus is on responsible resource extraction, innovation, and meeting the growing global demand for uranium to fuel the nuclear power plants of tomorrow."
Market Segmentation
By Special Nuclear Material Type
By End User
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Nuclear Materials
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Special Nuclear Material Type Overview
2.2.2 By End User Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.2 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Technology Innovation in reactor design
4.1.1.2 Government Subsidies
4.1.1.3 Cost Escalation in Fossil Fuels
4.1.1.4 Nuclear Fuel Supply Security
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High initial capital
4.1.2.2 Longer Development Timelines
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Frequent changes in the Regulation
4.1.3.2 Competition from Renewable Energy
4.1.3.3 Bureaucratic Approval Process Taking a Long Time
4.1.4 Market Opportunities
4.1.4.1 Extension of SMR Technology
4.1.4.2 Global Nuclear Power Revival
4.1.4.3 Production of Nuclear Hydrogen
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Nuclear Materials Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Nuclear Materials Market, By Special Nuclear Material Type
6.1 Global Nuclear Materials Market Snapshot, By Special Nuclear Material Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Special Nuclear Material
6.1.1.2 Source Material
6.1.1.3 Product Material
Chapter 7. Nuclear Materials Market, By End-User
7.1 Global Nuclear Materials Market Snapshot, By End-User
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Medicine
7.1.1.2 Agriculture
7.1.1.3 Energy and Power
7.1.1.4 Marines
7.1.1.5 Aerospace
7.1.1.6 Industrial
Chapter 8. Nuclear Materials Market, By Region
8.1 Overview
8.2 Nuclear Materials Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
8.3 Global Nuclear Materials Market, By Region
8.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
8.4 North America
8.4.1 North America Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.4.3 North America Nuclear Materials Market, By Country
8.4.4 U.S.
8.4.4.1 U.S. Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
8.4.5 Canada
8.4.5.1 Canada Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
8.4.6 Mexico
8.4.6.1 Mexico Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
8.5 Europe
8.5.1 Europe Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.5.3 Europe Nuclear Materials Market, By Country
8.5.4 UK
8.5.4.1 UK Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
8.5.5 France
8.5.5.1 France Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
8.5.6 Germany
8.5.6.1 Germany Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
8.5.7 Rest of Europe
8.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
8.6 Asia Pacific
8.6.1 Asia Pacific Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.6.3 Asia Pacific Nuclear Materials Market, By Country
8.6.4 China
8.6.4.1 China Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
8.6.5 Japan
8.6.5.1 Japan Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
8.6.6 India
8.6.6.1 India Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
8.6.7 Australia
8.6.7.1 Australia Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
8.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
8.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
8.7 LAMEA
8.7.1 LAMEA Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.7.3 LAMEA Nuclear Materials Market, By Country
8.7.4 GCC
8.7.4.1 GCC Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
8.7.5 Africa
8.7.5.1 Africa Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
8.7.6 Brazil
8.7.6.1 Brazil Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
8.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
8.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Nuclear Materials Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
8.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
8.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 9. Competitive Landscape
9.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
9.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
9.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
9.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
9.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 10. Company Profiles
10.1 Kazatompron
10.1.1 Company Snapshot
10.1.2 Company and Business Overview
10.1.3 Financial KPIs
10.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
10.1.5 Strategic Growth
10.1.6 Global Footprints
10.1.7 Recent Development
10.1.8 SWOT Analysis
10.2 Cameco
10.3 Orana
10.4 Uranium One
10.5 ARMZ Uranium Holding
10.6 China Nuclear National Corporation
10.7 New Brunswick Power Corporation
10.8 Uranium Corporation of India
10.9 United States Enrichment Corporation
10.10 GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy