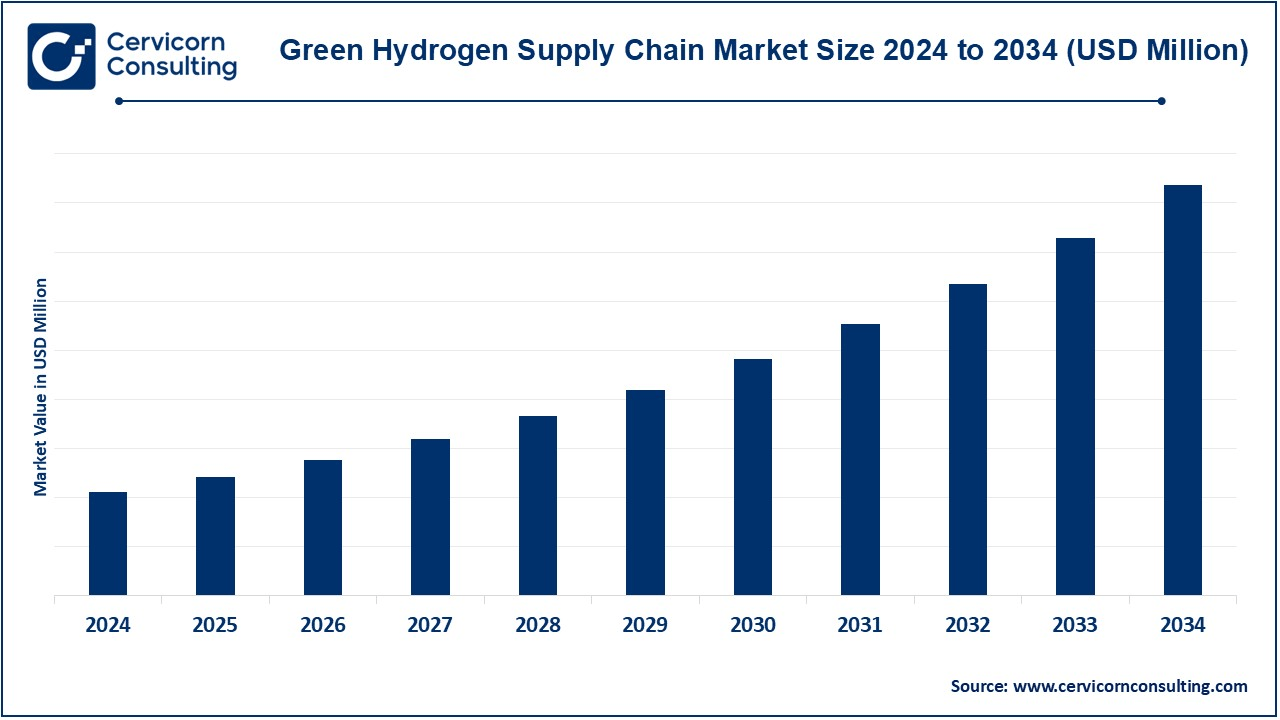
The green hydrogen supply chain market is experiencing significant growth driven by the global push toward clean energy and decarbonization. Industries worldwide are adopting green hydrogen as a sustainable energy source to reduce carbon emissions and achieve net-zero goals. This growth is supported by advancements in hydrogen production technologies, increasing investments in infrastructure, and supportive government policies promoting renewable energy. The demand spans across various sectors, including transportation, energy storage, and industrial applications, as companies explore hydrogen's versatility as a clean alternative to fossil fuels. However, challenges like high production costs, storage complexities, and infrastructure development are being actively addressed through innovation and collaboration, fueling optimism for the market's future.
What is a Green Hydrogen Supply Chain?
The green hydrogen supply chain refers to the series of processes, infrastructure, and systems involved in the production, storage, transportation, and utilization of green hydrogen. Green hydrogen is produced through the electrolysis of water using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, making it a sustainable and carbon-free energy carrier. This supply chain ensures the efficient flow of green hydrogen from production to end-use across various industries, such as transportation, power generation, and industrial applications.
Key Elements of the Green Hydrogen Supply Chain
1. Production
2. Storage
3. Transportation
4. Infrastructure
5. Distribution
6. Utilization
7. Integration with Renewables
Key Highlights
The green hydrogen supply chain market is segmented into technology, production source, storage type, transportation mode, end user and region. Based on technology, the market is classified into electrolysis, photolysis, biomass gasification and others. Based on production source, the market is classified into solar energy, wind energy, hydropower and others. Based on storage type, the market is classified into compressed gas storage, liquid hydrogen storage and solid-state storage. Based on transportation mode, the market is classified into pipelines, compressed gas trailers, liquid hydrogen tankers and hydrogen carriers. Based on end-use, the market is classified into transportation, power generation, industrial sector, residential & commercial and others.
Electrolysis is the most commonly used method for producing green hydrogen. It splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable electricity. As renewable energy sources like wind and solar are becoming more cost-competitive, electrolysis has seen substantial growth. It also offers scalability and versatility, making it a preferred choice for large-scale green hydrogen production. Electrolysis is supported by government policies and incentives aimed at decarbonization, which further propels its dominance.
Biomass gasification is growing rapidly due to increasing interest in utilizing organic waste materials for hydrogen production. Biomass gasification not only provides a renewable source of hydrogen but also contributes to waste management. With the push for circular economies and sustainable waste-to-energy solutions, biomass gasification is gaining momentum, especially in areas with abundant agricultural or forestry waste.
Wind energy has become one of the most cost-effective renewable sources for generating electricity. As wind farms become more widespread and efficient, they are increasingly used to power electrolysis for green hydrogen production. Regions like Europe and North America are investing heavily in wind-to-hydrogen projects, making wind energy the dominant production source for green hydrogen.
The combination of declining solar panel costs and the ability to scale solar energy production rapidly makes solar energy the fastest-growing source for green hydrogen production. Countries like India, Australia, and the Middle East are developing large-scale solar hydrogen projects, which are expected to dramatically increase solar’s contribution to the green hydrogen supply chain.
Compressed gas storage is the most widely used storage method for hydrogen, as it is a well-established technology. Hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks, making it a reliable and cost-effective option for large-scale distribution. This method is particularly preferred for transportation and refueling stations, and its infrastructure is already in place across many regions.
Liquid hydrogen storage is gaining popularity as it enables higher-density storage, making it ideal for large-scale hydrogen transport. As green hydrogen demand increases, particularly for long-distance transportation, liquid hydrogen storage is growing rapidly. The key challenge is the energy required to cool hydrogen to its liquid state, but technological advancements in cryogenic storage systems are improving its viability.
Pipelines are the most efficient and cost-effective method for transporting hydrogen over large distances. They are commonly used in regions with established hydrogen infrastructure, such as Europe. As hydrogen demand grows, pipelines will remain the dominant transportation method for long-term and large-scale distribution.
Hydrogen carriers, such as ammonia and liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHC), are emerging as an efficient means to transport hydrogen over long distances. These carriers allow hydrogen to be stored and transported more easily than in its gaseous or liquid state, addressing some of the logistical challenges of hydrogen transportation. As international trade in hydrogen grows, the use of hydrogen carriers will increase rapidly.
The transportation sector is one of the largest consumers of green hydrogen, particularly in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) for buses, trucks, and trains. With global governments encouraging the adoption of clean transportation, green hydrogen offers a feasible solution for zero-emission vehicles, especially in heavy-duty applications. Companies like Hyundai, Toyota, and Nikola are driving the growth of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
Green hydrogen is increasingly being used in power generation, particularly for peak-load power plants and as a backup power source for renewable energy systems. Hydrogen fuel cells and turbines can be used to generate electricity with zero emissions. As the grid becomes more decentralized and renewable energy penetration increases, the use of green hydrogen in power generation is growing rapidly.
Europe is a leading region in developing and adopting green hydrogen technologies, with several countries implementing ambitious hydrogen strategies. Germany is at the forefront of Europe’s green hydrogen supply chain market, having introduced its National Hydrogen Strategy in 2020, which includes heavy investments in hydrogen production, infrastructure, and research. Companies such as Siemens Energy, Uniper, and RWE are contributing to the growth of hydrogen projects, especially in the field of electrolysis. France and Netherlands are also heavily investing in hydrogen as part of their decarbonization plans. The European Commission has allocated over €10 billion for hydrogen projects, supporting initiatives like the H2-Industries project, which aims to produce hydrogen from renewable sources. The EU’s Green Deal and Fit for 55 climate package emphasize hydrogen as a critical solution for reducing carbon emissions, particularly in the hard-to-abate industrial sectors like steel and chemicals.
The APAC region is the fastest-growing market for green hydrogen supply chain due to its large-scale industrial base, government policies, and rapidly growing demand for clean energy solutions. Countries like Japan, South Korea, and China are leading the region’s efforts in green hydrogen development. Japan has been particularly proactive, with companies like Toyota and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries investing in hydrogen infrastructure and fuel cell technologies. The Japanese Hydrogen Roadmap aims to deploy hydrogen as a cornerstone for its energy strategy, including hydrogen-powered transportation and industrial use. South Korea’s Green New Deal focuses on hydrogen as a central pillar for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. China, with its massive manufacturing sector and growing energy needs, is also rapidly adopting hydrogen for industrial applications and transportation.
North America, particularly the United States and Canada, is a key player in the green hydrogen supply chain market. The region benefits from strong government support, including investments and incentives aimed at fostering clean energy technologies. The U.S. government, through initiatives like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and Clean Hydrogen Production Standard, has committed billions of dollars to support hydrogen production. Additionally, companies like Plug Power, Air Products, and Nel Hydrogen are heavily investing in developing hydrogen infrastructure and scaling up production capacity. The U.S. is one of the largest investors in hydrogen production technologies, particularly focusing on electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources. Canada has made significant strides with its hydrogen strategy, setting a target to become a global leader in clean hydrogen production. Furthermore, North America's geographical advantages, including access to abundant renewable energy sources like wind and solar, make it a strong contender in the global market.
LAMEA is witnessing a growing interest in green hydrogen, driven by an abundance of renewable energy resources such as solar and wind. Saudi Arabia is making significant strides in this market, with its Neom Hydrogen Project aimed at producing 650 tons of green hydrogen per day, making it one of the largest green hydrogen projects globally. The country is also investing heavily in hydrogen production and export capabilities to become a key player in the global hydrogen market. South Africa is exploring green hydrogen as part of its efforts to reduce its dependence on coal and boost clean energy production. Chile is positioning itself as a key green hydrogen producer in Latin America, leveraging its massive solar energy potential, and it has already attracted investments from companies like Enel and Siemens Energy.
The green hydrogen supply chain market is supported by key players involved in various stages, including hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and distribution. These companies span across industries such as energy, manufacturing, and technology, driving innovation and large-scale investments in green hydrogen infrastructure. The market is highly dynamic, with companies focused on advancing electrolysis, improving hydrogen storage solutions, and scaling up production to meet the growing demand for clean energy.
Several factors influence the market dynamics for these companies, including government incentives, partnerships, and research & development (R&D) investments. Furthermore, the competition among players is intensifying as the global shift toward decarbonization accelerates. The growing demand for sustainable energy, combined with regulatory mandates to reduce carbon emissions, is creating a favorable environment for companies to expand their operations in the green hydrogen space.
Key Companies in the Green Hydrogen Supply Chain Market:
Market Segmentations
By Technology
By Production Source
By Storage Type
By Transportation Mode
By End-Use Industry
By Region