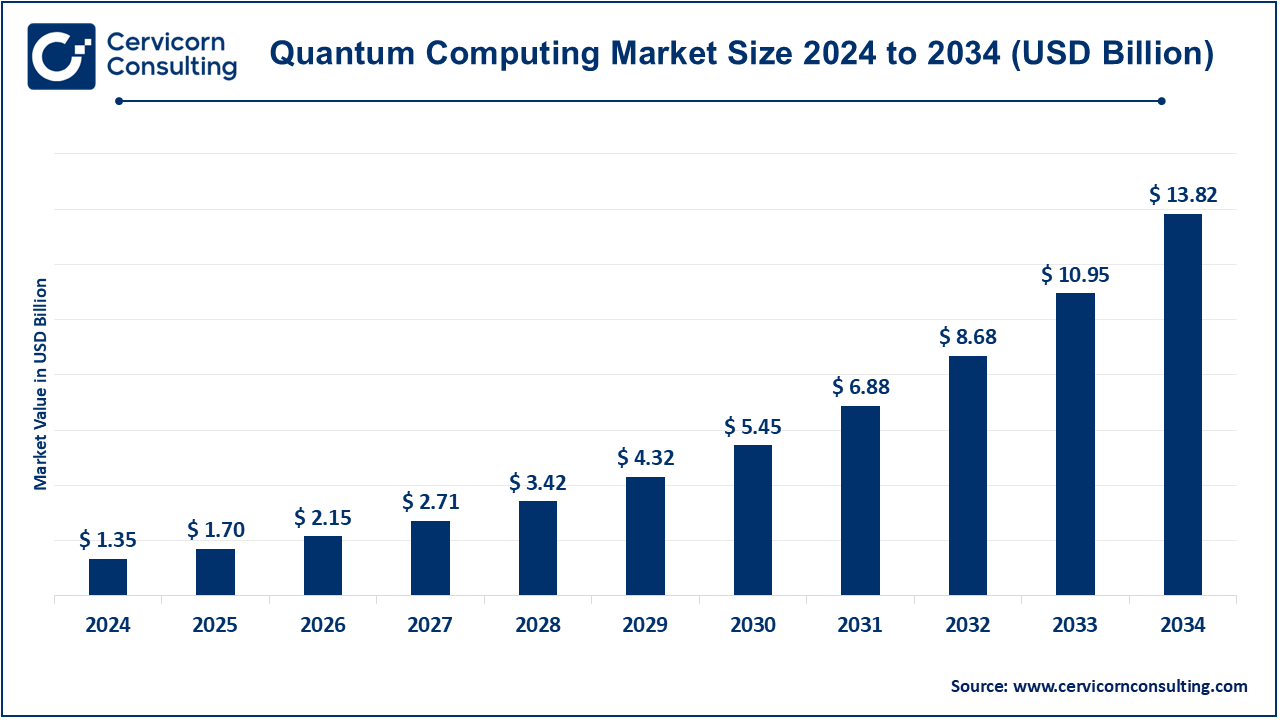
The global quantum computing market size was valued at USD 1.35 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach around USD 13.82 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 26.18% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. Quantum computing is gaining rapid and high growth in sectors like healthcare, banking, and logistics by solving complex optimization issues. More and more the main IT corporations and governments are collaborating on quantum research that is accelerating the development. The development of quantum-as-a-service models and, the increasing need for high-performance computing to enhance cryptography capabilities, among others, is causing quantum computing to gain wide adoption.
Quantum computing is an advanced type of computing that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics, including superposition, entanglement, and quantum interference, to process information. It differs from classical computers, which rely on binary bits, 0s and 1s, because quantum computers rely on quantum bits or qubits, which can perform many calculations simultaneously. This makes the computer able to do more than all those complicated issues so quickly; applications like cryptography, drug discovery, optimization, or artificial intelligence benefit greatly. In essence, industries will transform using quantum computers for issues considered insolvable under existing computers.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.7 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 13.82 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 26.18% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Component, Application, Technology, Deployment, Industry Verticals, Regions |
| Key Companies | IBM, Amazon Web Services, Hitachi, Intel, NEC, Bosch, PsiQuantum, Zapata Computing, D-Wave Quantum Inc., Rigetti Computing, Toshiba, Quantinuum, Accenture, Quantum Computing Inc, Alpine Quantum Technologies GmbH, Northrop Grumman, Microsoft, Fujitsu, Google, Huawei, Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, Iona, QC Ware, Xanadu |
The quantum computing market is segmented into component, application, technology, deployment, industry verticals and region. Based on component, the market is classified into hardware, software, and services. Based on application, the market is classified into cryptography, simulation, parallelism, machine learning, algorithms, and others. Based on technology, the market is classified into superconducting qubit, trapped ion, quantum annealing, photonic network, and others. Based on deployment, the market is classified into on-premises, and cloud. Based on industry verticals, the market is classified into banking and finance, healthcare and pharmaceuticals, defense, automotive, chemical, utilities, and others.
Hardware: Quantum computing hardware is the backbone of the market, which includes quantum processors, qubits, and specialized systems such as ion-trap and superconducting qubit platforms. Hardware innovation is critical to scaling quantum systems and improving stability, coherence, and error correction. Companies like IBM, Google, and Rigetti are developing cutting-edge quantum hardware, while innovations in cryogenics and quantum materials further enhance system performance. The high costs and complexity in quantum hardware, however, are still something of a concern, but that is being accelerated by investments in research collaborations. Hardware advances are the basis for unlocking this potential in finance, healthcare, or defense.
Software: It is the computer software that researchers use to build and test quantum algorithms and applications on the computer before running them on the actual devices. This will include quantum languages, development kits, and simulation software such as Qiskit, Cirq, or Microsoft's Quantum Development Kit. The software acts as a bridge between quantum hardware and end-user applications, helping researchers and businesses tap into quantum capabilities. While interest in the areas of quantum machine learning, cryptography, and optimization continues to surge rapidly in the market, the ecosystem that supports it grows with more convenient interfaces and more standardized frameworks making such technologies more widely accessible and easier to innovate over.
Services: Quantum computing offers consulting, training, and cloud access to quantum systems, also known as Quantum-as-a-Service (QaaS). The big technology companies offer cloud-based quantum services. Organizations can thus test quantum applications without having to invest in expensive hardware. The services support research, algorithm development, and workforce training, thereby filling the skills gap in the industry. Consulting services help businesses find use cases and integrate quantum technologies into existing workflows. The demand for quantum services is increasing because industries are looking for practical ways to explore the transformative potential of quantum computing, thereby driving growth in this segment.
Cryptography: Quantum computing is altering the face of cryptography since it supports much more advanced encryption and decryption processes. Quantum algorithms such as Shor's algorithm break traditional forms of encryption because it is easy to factor in large numbers, and therefore, a move toward quantum-resistant cryptographic standards is made. Quantum cryptography such as QKD makes the data much safer since the basis of quantum mechanics prevents unwanted access to information. The increase in data breaches and cybersecurity threats has led to increased demand for quantum cryptography solutions in areas such as banking, defense, and healthcare, which is a critical application area in the quantum computing market.
Simulation: Quantum simulation is an emerging revolution of industries in being able to accurately model chemical reactions, molecular structures, and materials, in ways impossible by classical systems, with quantum computers doing so well where complex atomic-level interactions require computational capabilities much more efficient than any possible with the best available classical systems, so quantum simulations make known phenomena inaccessible in practice by simulation with a classical system. These phenomena include superconductivity, protein folding, etc. This application is the most useful in industries requiring very accurate modeling, thus driving investment and research in quantum simulation technologies to solve real-world challenges.
Parallelism: Quantum Computation is inherently parallel. That is, several states can be computed in parallel, which exponentially accelerates computing certain tasks. In contrast, classical systems work one operation at a time, but quantum systems employ superposition for complex calculations, which are performed in parallel. The good capability of such an application is mostly in optimization problems, large-scale simulations, and applications in machine learning. Industries like logistics, finance, and healthcare can easily find a quantum parallel huge efficiency and decision-making improvement enhancer. Due to the technology difference, parallelism is the unique feature of a quantum computer, which makes its use in the economy to spread across sectors and inspire innovations.
Machine Learning: Quantum machine learning (QML) is one of the transformative applications of quantum computing, which integrates quantum algorithms with the traditional techniques of machine learning. QML provides enhanced data analysis capabilities, pattern recognition, and optimization by leveraging properties from the quantum world, such as superposition and entanglement. Its uses run from predictive analytics in healthcare and finance to optimizing logistics and detecting fraud. A quantum computer accelerates the time of training to a very complex model of machine learning. This is how a quick and accurate insight becomes possible. As both industries are pushing toward more implementation of AI solutions, QML represents an emergent focus area in the market for quantum computers that promises to be a vital innovation and a growth driver.
Algorithms: Algorithms constitute quantum computers and enable solutions that are far beyond those of classical systems. Grover's for search optimization and Shor's for factoring integers, algorithms created for quantum computing, are transforming many industries from cryptography to optimization and data analysis. Some specific applications include developing industry-specific quantum algorithms in applications like financial modeling, supply chain optimization, and drug discovery. Further improvements in the development of the algorithms increase the prospects for the future use of quantum computing. Most sectors will adapt to its implementation with increasing organizations investing in research in the quantum area.
Others: Areas of advancement such as in quantum communication, secure voting systems, and artificial intelligence. Other applications of quantum systems include weather forecasting, image processing, and risk analysis, among others. Quantum computing is, therefore, very versatile because it offers solutions to many different industries' problem-solving needs. The advancement of technology itself is a reason for the finding of new applications, which act as a driving force for innovation and market penetration as well. A good investment in research is required toward discovering new application areas for quantum computing and realizing full potential.
Banking and Finance: Quantum computing is changing the banking and finance industry by providing for superior risk analysis, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection. The mass dataset processing of quantum systems, in conjunction with simulations of sophisticated financial models, elevates the efficiency and effectiveness of operation decisions. Applications like secure quantum cryptography protect sensitive information about financial institutions from increasingly mounting cybersecurity threats. Today, financial institutions are investing in quantum technologies to stay ahead. Innovation and adoption in this sector will be on the increase with the maturity of quantum computing, thereby changing the way the banking and finance industry works and operates.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Quantum computing revolutionizes healthcare and pharmaceuticals by hastening drug development, optimizing clinical trials, and enhancing diagnostics. Quantum systems imitate molecular interactions so that the drug candidates' ability to predict these interactions can help save development time and cost. In personalized medicine, quantum algorithms analyze genomic data to customize the treatment for a patient. This also enhances imaging methods and data interpretation for the detection of diseases early. As healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies adapt to quantum solutions, the industry is experiencing transformative developments regarding new challenges and a more improved outlook for patient care.
Defense: It has greatly enhanced the defense sector through secured communication, data analysis, and the detection of threats with the advent of quantum computing. Quantum cryptography transmits secret information safely and soundly against cyber attacks. This system assists in big data analysis, discovering patterns, and, finally, anticipating future threats. This can also be utilized to improve mission planning and decision-making with the proper allocation of resources. Governments and defense organizations are shelling out massive amounts of funds for quantum research as a method of maintaining strategic advantages, placing the defense sector as the sole top vertical of quantum computing.
Automotive: The quantum is applied to automobile companies in the optimization of design, manufacturing, and logistics. In the case of design, quantum can provide a lightweight material, efficient battery technologies, and electric vehicles. In the scope of logistics, supply chain management and route optimization are improved, making it efficient in its operations. Quantum-powered machine learning helps develop autonomous vehicles faster and provide better information. As the industry is targeting innovation and sustainability, quantum computing is slowly being seen as one of the most revolutionary technologies which help drive further advancements in design and production.
Chemical: Quantum Computing is transforming the chemistry industry through very accurate simulations of molecular interactions, reaction pathways with precision, so that the advancement of new material, catalyst, or sustainable processes accelerate. Quantum Systems have been possible to provide significant chemical structure interrelations that no longer allow us to follow mere trial-and-error experiments and cut costs of research highly. Some of the applications used in optimizing industrial process applications, designing green materials and enhancing energy efficiency so on have witnessed a boom in adopting solutions through quantum which deals with the aspects of challenges that need to be overcome in sustainability and innovation. Growth coupled with increasing opportunities because of increased investment in quantum technologies.
Utilities: Utilities are also using quantum computing to optimize energy distribution and grid reliability along with renewable integration. Quantum algorithms are used for large datasets, for energy demand prediction, for power generation optimization, and minimizing transmission and distribution losses. It further advances the research in advanced materials for energy storage and conversion. This quantum computing will open new avenues of answers for many questions surrounding energy efficiency and resource management. As utilities get increasingly thrust to adopt sustainable practices, this makes the sector keen on quantum technologies and puts their potential to solve transformational advances into the limelight.
Others: Other industry verticals that accept quantum computing include logistics, retail, and agriculture. Logistics is the optimization of supply chains and route planning for doing the whole process much more efficiently and cost-effectively. Retail applications would include personalization of customer experience and even inventory management. Agriculture helps in better crop modeling, weather prediction, and resource allocation using quantum systems. All these different applications reflect the possibilities of technology as well as its ability to solve numerous problems across a large number of different sectors. It simply implies that for them, the importance of quantum computing will rise as maturity increases with market opportunity and innovation growth.
Segments The quantum computing market is diversified into four key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Each of these regions is discussed in detail below
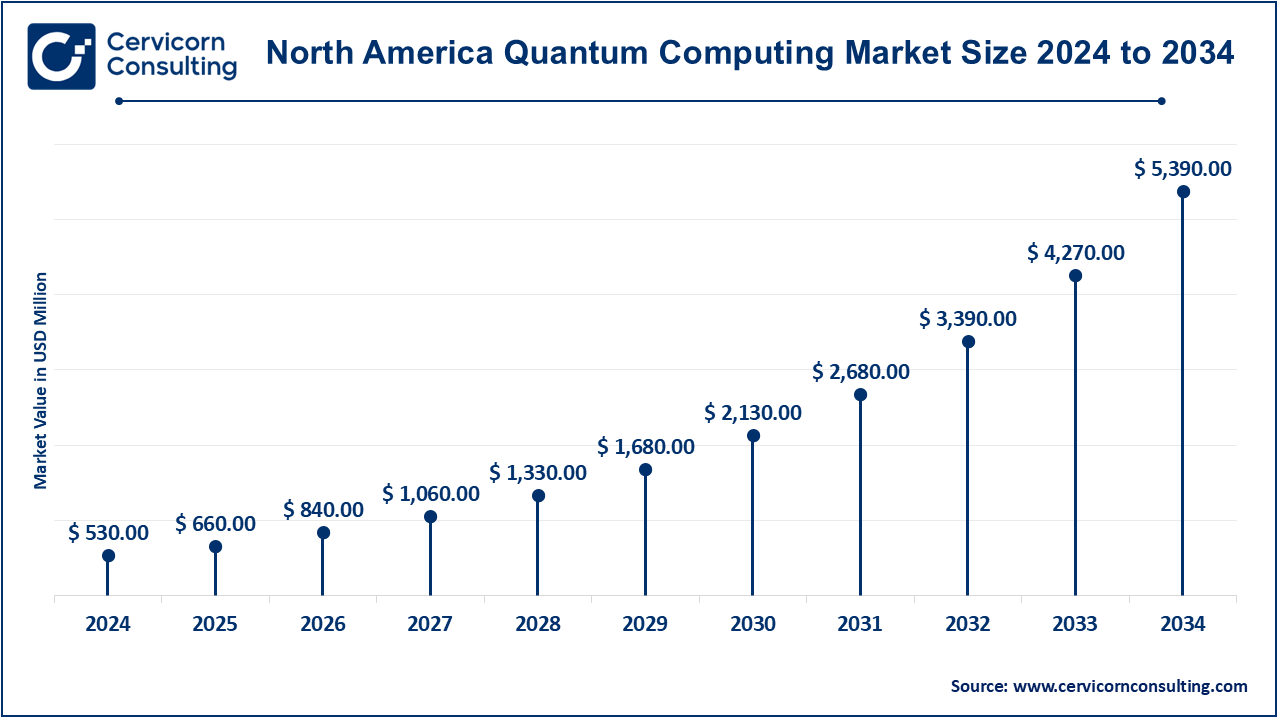
The North America quantum computing market size was estimated at USD 0.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 5.39 billion by 2034. North America is a market leader for quantum computing due to high investments, healthy government support, and main players such as IBM, Google, and Microsoft. The region consists of university institutions that are significant sources of innovation and original equipment manufacturers, while research and development are located in sectors that include finance, defense, and healthcare. It is leading the region through initiatives like the National Quantum Initiative Act, which advances growth and keeps North America on the main stage of the global quantum computing ecosystem.
The Europe quantum computing market size was valued at USD 0.46 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach around USD 4.7 billion by 2034. This is where a strong future competitor is expected in the quantum computing market. Governments, with their funding initiatives, collaboration, and new programs, especially the European Quantum Flagship Program, have triggered innovation. The United Kingdom, France, and Germany are in front in the development of research, as well as industrialization efforts, within areas such as automobiles, finance, and energy. Innovations from startups, academic institutions are the core, which has come into being around secure communication, advanced algorithms. Europe invests constantly in quantum technology and hopes to fortify its ground in the emerging quantum technology global landscape with more private and public investments.
The Asia Pacific quantum computing market size was reached at USD 0.28 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to hit around USD 2.9 billion by 2034. Asia-Pacific quantum computing market is rapidly growing led by China, Japan, and South Korea. China particularly is investing in very strong ways in quantum cryptography and research for its defense application, whereas Japan is focusing on hardware and software innovations in terms of quantum technology. New entrants are South Korea and India, focusing on quantum technology as a tool for national security and competitive economic advantage. Government support and an expanding tech ecosystem drive the adoption of this technology in manufacturing, healthcare, and finance.
Quantum Computing Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 39% |
| Europe | 34% |
| Asia-Pacific | 21% |
| LAMEA | 6% |
The LAMEA quantum computing market size was valued at USD 0.08 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 0.83 billion by 2034. The quantum computing market of LAMEA is gradually maturing as interest in developing new technologies continues to grow in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa. In Latin America, Brazil is at the forefront with a focus on both academic research and industrial applications. Countries in the Middle East, including Israel and the UAE, are investing in quantum technologies to achieve national security and innovation. Africa's adoption is in its infancy, with research initiatives as the focus. Challenges such as underdeveloped infrastructure notwithstanding, growth in LAMEA is likely to be driven by increasing global collaborations and investments.
Here are some recent CEO statements from key players in the Quantum Computing market:
Christian Klein, CEO of SAP:
“Klein anticipates significant impacts from quantum computing in the next three to four years, particularly in supply-chain management, where it could drastically reduce computation times for complex logistics”
Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of Meta Platforms.:
“Expressing skepticism, Zuckerberg stated that quantum computing is "still quite a ways off from being a very useful paradigm," suggesting a longer timeframe for its practical utility.”
Some of the major inclusions of developments in the Quantum Computing market are:
Market Segmentation
By Component
By Application
By Technology
By Deployment
By Industry Verticals
By Regions