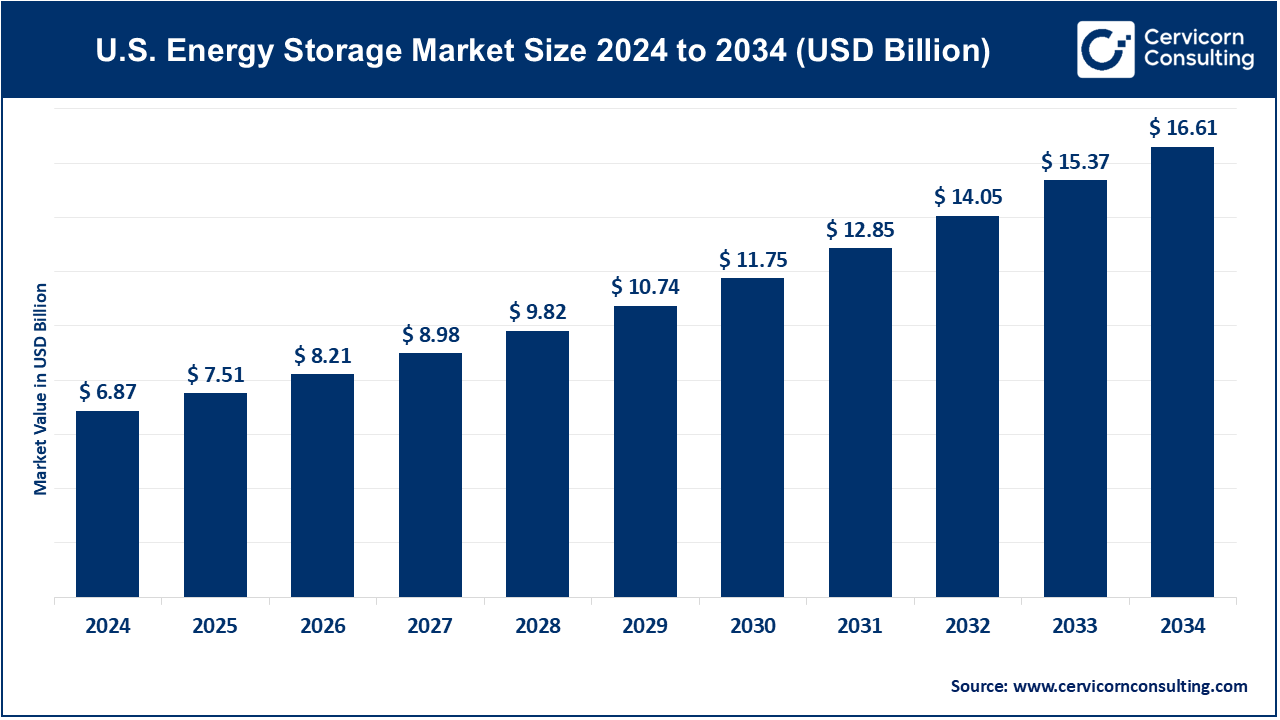
The U.S. energy storage market size was valued at USD 6.87 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 16.61 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.23% from 2025 to 2034. The energy storage market in the U.S. is experiencing rapid growth due to increasing renewable energy adoption, government incentives, the growing adoption of electric vehicles and advancements in battery technology. The rise of electric vehicles and smart grid infrastructure has further accelerated demand. States like California, Texas, and New York lead in deployments, promoting policies that encourage energy storage adoption. With the push for clean energy and carbon reduction, the market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
The U.S. energy storage market is a dynamic sector focused on delivering a range of energy solutions, including utility-scale storage, commercial and industrial storage, residential storage, microgrids, and EV charging infrastructure. Driven by technological advancements like lithium-ion and solid-state batteries and increasing demand for renewable energy integration, the market is expanding rapidly. Despite challenges like high initial costs and regulatory compliance, the market remains robust and continues to evolve.
Energy storage is defined as the process whereby energy produced at any one time may be captured and stored for later use. It is a fundamental constituent of contemporary energy systems-able to balance supply and demand-particularly in the context of increased deployment of variable renewable sources of energy, the majority of which are intermittent, like wind and solar. A variety of technologies is involved in the energy storage market, including batteries, pumped hydro, thermal storage, and flywheels. These are used in a field of applications that range from grid stabilization to providing backup power.
Key Insights Beneficial to the U.S. Energy Storage Market
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.51 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 16.61 Billion |
| Growth Rate (2025 to 2034) | 9.23% |
| Segments Covered | Service, Application, End User, Region |
| Key Players | Tesla, Inc., Fluence, NextEra Energy Resources, LG Energy Solution, AES Corporation, Siemens Energy, General Electric (GE), BYD Company Ltd., ABB Ltd., Panasonic Corporation, Sunrun Inc., Enphase Energy, Stem, Inc., Eos Energy Enterprises, Northvolt |
Increasing Renewable Energy Integration
Regulatory and Policy Support
High Initial Costs
Limited Lifespan and Degradation
Growth of Advanced Battery Technologies
Expansion of Distributed Energy Resources (DER)
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Integration of Emerging Technologies
Utility-Scale Storage: Utility-scale energy storage services are growing due to their ability to balance grid supply and demand. Advanced technologies like lithium-ion and flow batteries enable large-scale storage, supporting renewable energy integration and grid stability. These systems provide peak shaving, frequency regulation, and backup power, enhancing overall grid reliability.
Commercial & Industrial Storage: Commercial and industrial energy storage solutions are expanding as businesses seek to reduce energy costs and improve resilience. These systems allow for peak demand management, load shifting, and backup power, ensuring continuous operations and cost savings. The adoption of these systems is driven by advancements in battery technology and declining costs.
Residential Storage: Residential energy storage services are on the rise as homeowners look to increase energy independence and resilience. Home battery systems store excess solar energy for use during outages or peak demand periods, providing reliability and cost savings. The growth in residential storage is fueled by decreasing battery costs and increasing adoption of solar PV systems.
Microgrids: Microgrid energy storage services are crucial for providing reliable and resilient power to localized areas. These systems integrate renewable energy sources and storage to create independent power networks. Microgrids enhance energy security and efficiency, particularly in remote or disaster-prone areas, driving their adoption.
EV Charging Infrastructure: Energy storage solutions are essential for supporting the growing electric vehicle (EV) market. Storage systems at charging stations manage peak loads, store renewable energy, and ensure efficient power distribution. The expansion of EV infrastructure is driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and the need for sustainable charging solutions.
Renewable Energy Integration: Energy storage is crucial for integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid. These storage systems manage the intermittency of renewable power by storing excess energy during peak production and releasing it during low production periods. This capability ensures a stable and reliable energy supply, which is essential for achieving sustainable energy goals and reducing carbon emissions.
Grid Stability and Reliability: Energy storage solutions enhance grid stability and reliability by providing critical services such as frequency regulation, voltage support, and black start capabilities. These systems help maintain a resilient power grid, capable of handling fluctuations and preventing outages. By stabilizing the grid, energy storage supports consistent power delivery and enhances overall grid performance.
Peak Shaving and Load Shifting: Energy storage systems play a key role in managing energy demand through peak shaving and load shifting. By storing excess power during low-demand periods and releasing it during peak times, these systems reduce the need for expensive peak power plants. This application not only lowers energy costs for consumers but also helps utilities manage demand more efficiently.
Backup Power: Energy storage provides reliable backup power for critical infrastructure, homes, and businesses during outages. These systems ensure continuous operations and enhance energy security, especially in areas prone to natural disasters or grid failures. Backup power from energy storage systems is vital for maintaining essential services and preventing disruptions.
Energy Arbitrage: Energy storage systems enable energy arbitrage, allowing operators to buy electricity during low-cost periods and sell it during high-cost periods. This application provides financial benefits to energy storage operators by capitalizing on price differentials. Additionally, energy arbitrage helps stabilize energy prices by balancing supply and demand across different times of the day.
Utilities: Utilities are significant users of energy storage systems for grid management and stability. These storage solutions enable utilities to integrate renewable energy sources, manage peak demand efficiently, and ensure reliable power delivery to customers. By enhancing grid performance and reliability, energy storage systems drive market growth and support the transition to a more sustainable energy infrastructure.
Commercial and Industrial Users: Businesses and industrial facilities utilize energy storage to manage energy costs, ensure reliable power, and support sustainability initiatives. These systems provide critical services such as peak demand management, load shifting, and backup power, which enhance operational efficiency. By adopting energy storage, commercial and industrial users can achieve energy resilience and cost savings, driving market expansion.
Residential Users: Homeowners increasingly adopt energy storage systems to complement their solar PV installations, providing energy independence and resilience. Residential storage solutions offer reliable backup power during outages and help reduce electricity bills by storing excess solar energy for later use. This growing adoption of home energy storage systems is driven by the desire for greater energy security and financial benefits.
Government and Military: Government and military facilities rely on energy storage for energy security and operational resilience. These storage systems provide reliable power for critical operations, enhancing the sustainability and reliability of government infrastructure. By integrating energy storage, government and military entities can ensure continuous operations and reduce reliance on traditional power sources, contributing to national energy security.
Remote and Off-Grid Communities: Remote and off-grid communities depend on energy storage to provide reliable and sustainable power. These systems integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, with storage solutions to create independent power networks. By enabling energy access and resilience in remote areas, energy storage supports the development of sustainable communities and reduces reliance on fossil fuel.
Among the new players, Fluence Energy leverages advanced battery technologies and energy management software to offer innovative and scalable energy storage solutions. Stem, Inc. focuses on expanding its AI-driven energy storage platform through strategic partnerships and a strong emphasis on smart energy solutions.
Dominating players like Tesla, Inc. and NextEra Energy Resources drive market leadership through extensive project portfolios and high-quality technology standards. Tesla is known for its aggressive expansion strategy and integration of cutting-edge battery technology, while NextEra excels in operational efficiency and renewable energy projects, enhancing overall grid reliability and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
CEO Statements
David Kim, CEO of LG Energy Solution
John Ketchum, Chairman and CEO of NextEra Energy
Anders Opedal, president and CEO of Equinor
Eric Dresselhuys, CEO of ESS Tech, Inc.
Market Segmentation
By Service Type
By Application
By End-users
Chapter 1 Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of U.S. Energy Storage
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Service Type Overview
2.2.2 By Application Overview
2.2.3 By End-users Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3 Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on U.S. Energy Storage Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Markets
Chapter 4 Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Increasing Renewable Energy Integration
4.1.1.2 Regulatory and Policy Support
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High Initial Costs
4.1.2.2 Limited Lifespan and Degradation
4.1.3 Market Opportunity
4.1.3.1 Growth of Advanced Battery Technologies
4.1.3.2 Expansion of Distributed Energy Resources (DER)
4.1.4 Market Challenges
4.1.4.1 Regulatory Compliance and Standards
4.1.4.2 Integration of Emerging Technologies
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5 Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 U.S. Energy Storage Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6 U.S. Energy Storage Market, By Service Type
6.1 U.S. Energy Storage Market Snapshot, By Service Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Utility-Scale Storage
6.1.1.2 Commercial & Industrial Storage
6.1.1.3 Residential Storage
6.1.1.4 Microgrids
6.1.1.5 EV Charging Infrastructure
Chapter 7 U.S. Energy Storage Market, By Application
7.1 U.S. Energy Storage Market Snapshot, By Application
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Renewable Energy Integration
7.1.1.2 Grid Stability and Reliability
7.1.1.3 Peak Shaving and Load Shifting
7.1.1.4 Backup Power
7.1.1.5 Energy Arbitrage
Chapter 8 U.S. Energy Storage Market, By End-users
8.1 U.S. Energy Storage Market Snapshot, By End-users
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Utilities
8.1.1.2 Commercial and Industrial Users
8.1.1.3 Residential Users
8.1.1.4 Government and Military
8.1.1.5 Remote and Off-Grid Communities
Chapter 9 U.S. Energy Storage Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 U.S. Energy Storage Market Revenue Share 2024 (%)
9.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10 Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
11.1 Tesla, Inc.
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Fluence
11.3 NextEra Energy Resources
11.4 LG Energy Solution
11.5 AES Corporation
11.6 Siemens Energy
11.7 General Electric (GE)
11.8 BYD Company Ltd.
11.9 ABB Ltd.
11.10 Panasonic Corporation