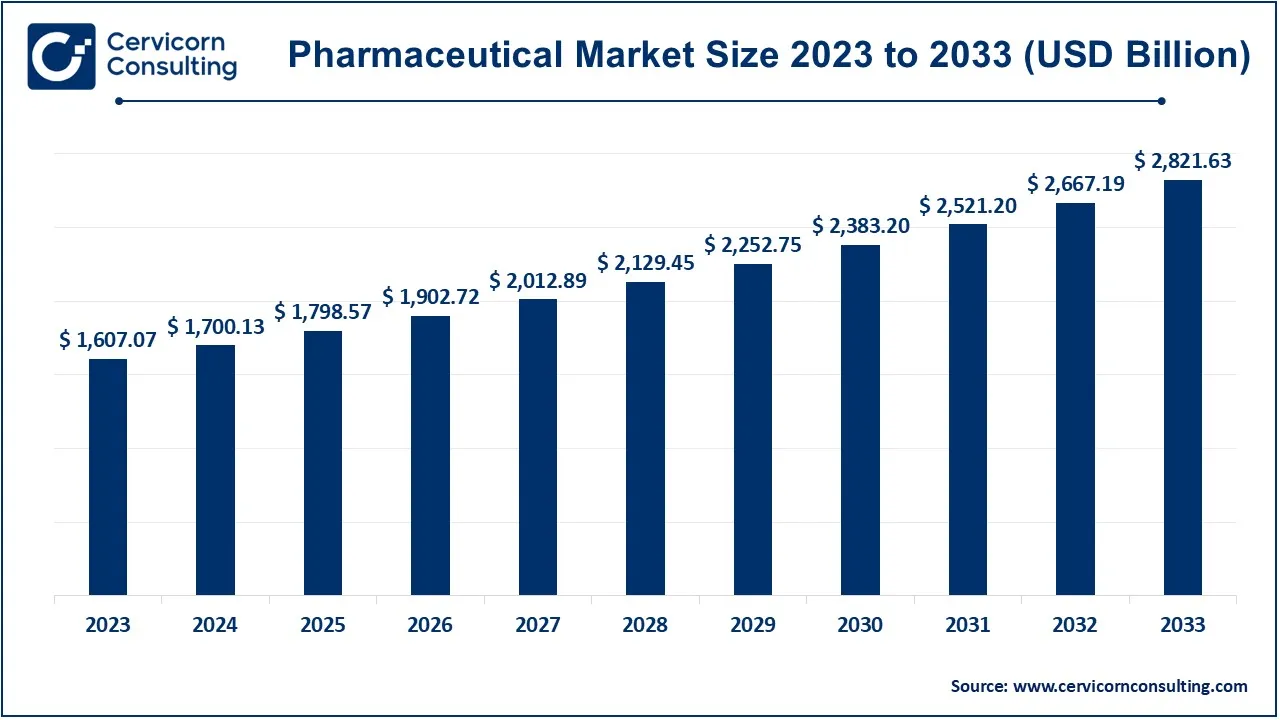
The global pharmaceutical market size was accounted for USD 1,607.07 billion in 2023 and is expected to be worth around USD 2,821.63 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.79% over the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The pharmaceutical market has experienced significant growth due to increasing healthcare needs, rising chronic diseases, and advancements in drug research. The demand for innovative treatments, including biologics and personalized medicine, has driven pharmaceutical companies to invest more in R&D. Governments worldwide are also supporting the industry by funding research and expediting drug approvals. Additionally, digital transformation, AI-driven drug discovery, and telemedicine integration are further fueling market expansion. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Latin America, are contributing to industry growth due to rising healthcare awareness and improved access to medicines. The rise of biosimilars, generic drugs, and collaborations between biotech firms and big pharma companies is also shaping the market landscape.
The pharmaceutical sector is one of the most important industries. It meets 62% of the global vaccine demand and is the world's leading supplier of generic drugs, which account for 20% of the total global supply. Billions of dollars are invested in the pharmaceutical sector every year. Research and development areas are emerging that require significant expenditure to find more effective treatments and therapies. The pharmaceutical market is considered to be one of the highly regulated sectors that continuously provide high-quality drugs for human use to achieve the desired pharmacotherapeutic effects to treat various ailments.
Industry 4.0 of the pharmaceutical industry in the future will contribute to smart automation technology and can support advanced manufacturing such as personalized medicine, additive manufacturing, localized 3D printing of treatments, etc. Industries are currently being shaped by digital transformation as digital services are being integrated into the range of offerings beyond the product. The healthcare industry is being transformed by digitalization. The pharmaceutical market in emerging markets tends to be very different from that of the developed markets. In Latin America, Asia, and certain regions of Africa, financing is predominated by private investment. Moreover, extending the reach of supply chains and improving overall efficiency are also some of the essential components of growth strategies that work well in emerging markets.
What is pharmaceutical?
Pharmaceuticals are medicines or drugs that help diagnose, treat, prevent, or cure diseases. They are created through research and carefully tested before being sold. Pharmaceutical companies follow strict rules to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these drugs. The industry includes different types of medicines, such as prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, vaccines, and biotech treatments. This industry plays a crucial role in global healthcare by improving life expectancy and quality of life. Pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in research and development (R&D) to create innovative medicines for chronic diseases like cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders. Regulatory authorities such as the FDA (U.S.), EMA (Europe), and CDSCO (India) oversee drug approval and ensure patient safety. With advancements in biotechnology, personalized medicine, and artificial intelligence in drug discovery, the pharmaceutical sector continues to evolve rapidly.
Key Insights Beneficial to the Pharmaceutical Market:
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1,700.13 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2033 | USD 2,821. 63 Billion |
| Growth Rate 2024 to 2033 | 5.79% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Drug, Molecule Type, Route of Administration, Formulation, End User, Age Group, Region |
| Key Companies | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Novartis AG, Aurobindo Pharma, AbbVie Inc., Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., Abbott Laboratories, Bayer AG, Merck & Co., Inc., AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Pfizer Inc., Amgen Inc. |
Increasing Aging Population and Healthcare Expenditure
Increased Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
Product Recalls and Reputation Damage
Regulatory Compliance
EmergingSpecialty Pharmaceuticals
Growth of Industry in Emerging Markets
Ever Changing Healthcare Landscape
Disruption in Supply Chain
Based on drug type, the global market is segmented into generic drugs and branded drugs. The branded drug segment has dominated the market in 2023.
Generic: The generic drugs segment has accounted revenue share of 32.20% in 2023. When a branded drug's patent expires, generic drugs are introduced into the market. Owing to the lower production and distribution costs of the drugs, generic drug manufacturers offer patients and healthcare systems with cheaper medication options. Also, the high availability of generic drugs has led to strong growth of the segment in the market. Furthermore, the demand for generic medications has been fueled by numerous initiatives taken by the government, insurance companies, and healthcare providers for cost control. Since generic drugs are comparatively less expensive than their brand-name counterparts, they are therefore favored by patients and healthcare systems that are seeking to cut costs.
Pharmaceutical Market Revenue Share, By Drug Type, 2023 (%)
| Drug Tye | 2023 (%) |
| Generic Drugs | 32.20% |
| Branded Drugs | 67.80% |
Branded: The branded drugs segment has accounted revenue share of 67.80% in 2023. A pharmaceutical company develops new drugs as branded drugs under patent protection. This protects its drug research investment by giving the pharmaceutical company the sole right to manufacture and sell the branded drug while the patent is in effect. Branded drug names differ from the International Nonproprietary Name (INN), also known as the generic name. Brand-name drugs can be the original drug developed by one company, or several companies can produce the same generic drug, to which each company gives its brand name.
Based on application, the market is segmented into ophthalmology, oncology, cardiovascular disease, central nervous system & neurological disorders, genetic and rare genetic diseases, others.
Oncology: There is an increase in the various forms of cancer worldwide, which has led to increased funding and research in this field, and the need for innovative and efficient treatments. Further, personalized medicine and targeted therapies have also transformed the treatment of cancer owing to the improved efficacy and reduced side effects of these therapies. In addition, the development of novel cancer drugs has accelerated through partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions.
Ophthalmology: The increasing number of eye diseases such as glaucoma and refractive errors is driving the demand for ophthalmic services and treatments. The administration of eye medications, typically in the form of eye drops, is known as ophthalmic drug administration. Topical formulations are used in the treatment of many eye diseases. These conditions include but are not limited to, bacterial infections, dry eyes, glaucoma, and eye injuries. Furthermore, advancements in tissue engineering and stem cell therapy in regenerative medicine are creating new avenues for the treatment of ocular disorders and enhancing tissue regeneration.
Cardiovascular Disease: It is anticipated that the number of patients receiving a cardiovascular disease diagnosis will rise due to the rising prevalence of these conditions in the general population and the growing global concern about them. Patients' demand for cardiovascular medications and therapies is rising concurrently with increased awareness of the available treatment options.
Central Nervous System & Neurological Disorders: Any form of disorder related to the nervous system is generally referred to as central nervous system disease. However, due to the poor understanding of the underlying causes and therapeutic approaches for these disorders, developing new drugs in this field is a challenge even for companies that have previously developed breakthrough drugs. The increasing prevalence of neurological diseases and the rising diagnosis rates in developed and emerging countries result in a large pool of patients being treated. Furthermore, advances in the diagnostics and therapy of central nervous system (CNS) diseases are expected to increase the treatment rate worldwide.
Genetic and Rare Genetic Diseases: Translational research and drug discovery for rare genetic diseases has increased rapidly. Although rare diseases have a tremendous impact overall, there is a significant gap between basic research and clinical intervention. There are now opportunities to accelerate drug development to treat rare diseases. Disease foundations and research centers worldwide are focused on better understanding rare diseases. Rare diseases are typically genetic diseases; therefore, using pharmacogenetics to develop treatments and using whole genome sequencing to identify the etiologies for such diseases are appropriate strategies.
Others: The others segment includes gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes, endocrinology, and nephrology. Gastrointestinal diseases are gastrointestinal diseases that affect the colon, small and large intestine, and rectum. The growing geriatric population, geriatric incidents, overcrowding in hospital outpatient departments (HOPD), and increasing demand for outpatient treatment are expected to increase the cases of gastrointestinal disorders. Gastrointestinal therapies include a wide range of interventions that include medications for relieving symptoms, and improving the overall function of the gastrointestinal system and the patient's quality of life. Diabetes is one of the chronic diseases that lasts for a long time and causes damage to the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, nervous system, and blood sugar regulation. The number of people with diabetes is increasing worldwide, partly due to increasing prevalence rates in emerging markets and technological advances and partly due to the increase in the world population. The prevalence of diabetes is also expected to increase due to rising obesity rates, sedentary lifestyles, and unhealthy diets. Diabetes is treated with many classes of medications that can be taken orally, intravenously, or subcutaneously. The increasing number of people with diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, and the growing need for effective drug treatments to manage the condition. Endocrine disorders are becoming increasingly common and affecting more and more teenagers, and intense research and development efforts are leading to drugs and treatments to treat these disorders.
Based on classification, the market is segmented into prescription drugs, OTC drugs. The prescription drugs segment has dominated the market in 2023.
Prescription Drugs: The prescription drugs segment has accounted revenue share of 87.10% in 2023. The increasing R&D investments by the key market players in developing new drugs that are mainly used to treat chronic diseases. With the increasing prevalence of such conditions, the demand from patients has increased due to unmet clinical needs and the desire for favorable therapy outcomes. A number of these chronic diseases are commonly observed in the patient population, necessitating the use of multiple recommended therapies. Hence, major pharmaceutical companies are involved in clinical trials for the development and ultimately approval of new products. Moreover, the rising hospitalization and prescription rates are factors that further drive the growth of the overall pharmaceutical industry.
Pharmaceutical Market Revenue Share, By Classification, 2023 (%)
| Classification | 2023 (%) |
| Prescription Drugs | 87.10% |
| OTC Drugs | 12.90% |
OTC Drugs: The OTC drugs segment has accounted revenue share of 12.90% in 2023. The increasing inclination towards self-care and healthcare trends, coupled with the empowerment of consumers to take charge of their health. OTC medicines, which are available without a prescription, allow people to treat common illnesses and health problems on their own, which is benefiting the market growth. The market has grown even more owing to increasing consumer education and awareness for over-the-counter (OTC) products, as well as convenient access through pharmacies and retail stores. Commonly used OTC categories include analgesics, allergy medications, cough and cold remedies, and digestive aids.
Based on formulation, the global market is segmented into tablets, capsules, injectable, sprays, suspension and powder. The tablets segment has generated highest revenue share in market in 2023.
Tablets: Tablets are solid dosage forms used for oral medications, they are the most widely produced and sold drug form. Because of their tamper-evident nature, affordability, ease of handling and packaging, and high production efficiency, tablets are used more frequently than capsules. Tablets are the easiest to manufacture for a variety of specializations, including antidiabetics, anti-inflammatories, antacids, vitamins, and antiallergics.
Capsules: Capsules are solid dosage forms in which the active drug is enclosed in either a hard or soft soluble container or a shell made of a suitable form of gelatin. Capsules are easier to swallow. They are also useful when the drug needs to be mixed with oil or other liquid to aid absorption in the body. There are essentially two types of capsules used for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products – hard capsules and soft capsules. Traditional capsules are generally made out of gelatin, which is a widely used animal product.
Injectable: Drugs that are injected into the body through injections are known as injectables. Injections are easy to use and have many benefits, such as self-administration, credibility, accuracy, prefilled syringes that come with fixed doses, compactness, and excellent patient comfort. Drugs can be injected into a vein (intravenously), a muscle (intramuscularly), or under the skin (subcutaneously).
Sprays: Pharmaceutical sprays are drugs administered orally or nasally through breathing. In sprays, a liquid or solid formulation is converted by atomization into a dynamic mixture that is dispersed into gas. An atomized spray, as shown below, can enter the respiratory tract and provide local or systemic medicinal effects. Once the active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) are mixed into a spray concentrate, they are pumped into the sprayer, which atomizes it during administration. These aerosols offer the advantage of rapid onset of action and avoid the first-pass effect and deterioration of the gastrointestinal tract.
Suspensions: A pharmaceutical suspension is a heterogeneous system in which finely divided solid particles are dispersed in a liquid medium. Unlike solutions in which solutes are completely dissolved, suspensions contain particles that are only partially soluble or insoluble in the liquid. Suspensions are often used to administer poorly water-soluble drugs that cannot be formulated as aqueous solutions. Drugs with an unpleasant taste should preferably be formulated as a suspension to reduce the interaction of the drug with the taste receptors in the mouth.
Powders: A drug consisting of a solid dry substance in the form of finely divided particles and used for external and internal use in the form of a dosage is called a pharmaceutical powder. In its finely divided state, it is a solid substance (between 10 nm and 1000 µm) that is usually sorted by crushing, grinding, or grinding.
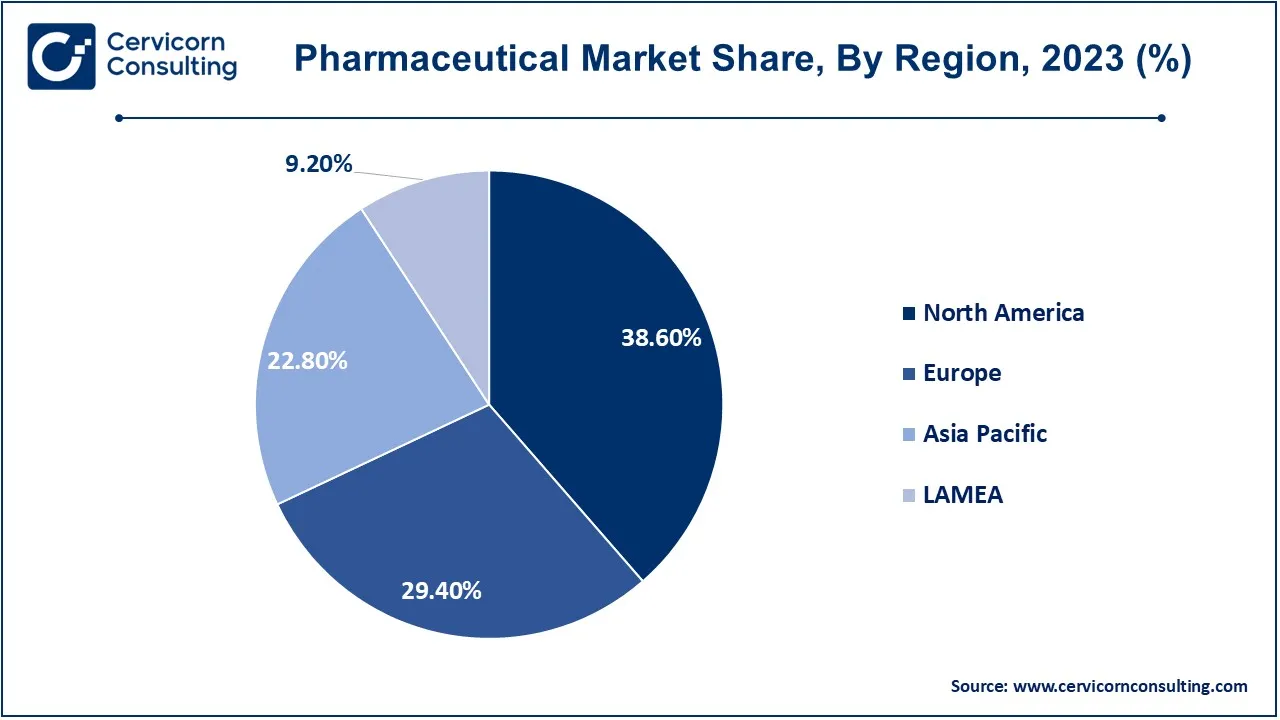
The pharmaceutical market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. North America was highest revenue holder in the market.
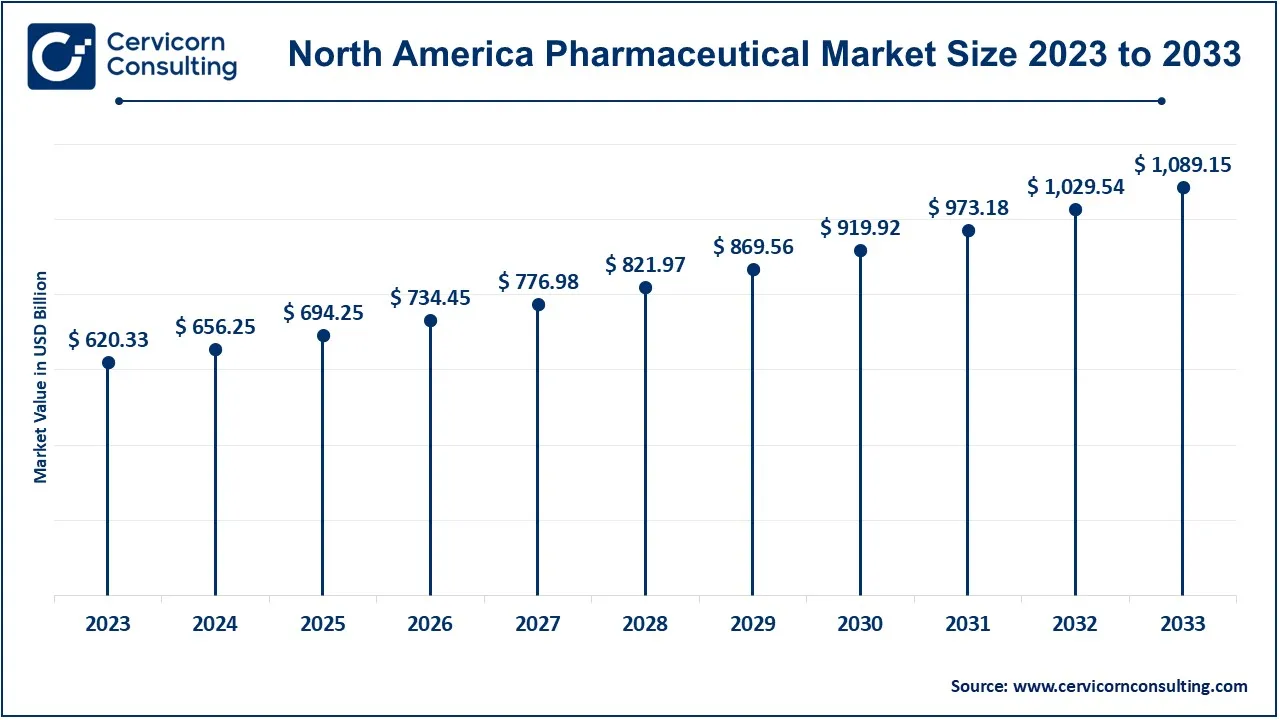
The North America pharmaceutical market size was valued at USD 620.33 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach around USD 1,089.15 billion by 2033. The growth of the market in North America is attributed to access to high-quality medicines, extensive knowledge about healthcare, high healthcare expenditure per capita, and strong GDP. Furthermore, the implementation of various strategic initiatives by both established and young pharmaceutical companies is further driving regional growth.
The Europe pharmaceutical market size was estimated at USD 472.48 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 829.56 billion by 2033. The market expansion in the European region is anticipated to be driven by factors such as rising patient awareness regarding the different diagnostic and treatment options for various medical conditions that are available in the region. The region also boasts a highly developed healthcare system with a well-established regulatory framework and a strong emphasis on research and development. In addition, growing investments in precision medicine, personalized therapies, and biotechnology are also driving the expansion of the pharmaceuticals market in Europe. Furthermore, during the projected period, higher sales of medications and vaccines for chronic illnesses are also anticipated to fuel the growth.
The Asia-Pacific pharmaceutical market size was accounted for USD 366.41 billion in 2023 and is predicted to surpass around USD 643.33 billion by 2033. Several factors including a growing aging population, increasing disposable income, improved healthcare facilities, and a faster rate of research into new therapeutics, are expected to drive market growth in the Asia-Pacific region. The demographics of the region are diverse. Apart from established countries such as Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, and Australia, there are fast-growing economies such as Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Bangladesh, and the Philippines, as well as China and India.
The LAMEA pharmaceutical market was valued at USD 147.85 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 259.59 billion by 2033. In the LAMEA region, which comprises nations like Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Africa, and others the pharmaceutical sector has expanded dramatically. The market in the LAMEA region is continuing to expand owing to population growth, a rise in chronic illnesses, better access to healthcare, and a growing healthcare infrastructure. In addition, the region's governments have passed various legislations to support domestic pharmaceutical production and also launched programs for expanding access to high-quality healthcare, which has in turn opened doors for pharmaceutical companies to grow in the region.
The global market is fragmented and includes many players such as Pfizer Inc., Johnson & Johnson Services Inc., AstraZeneca, and others. The major players are focusing on increasing their R&D investments for the development process of novel therapies to meet the unmet demand of the patient population. GSK plc acquired clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company Affinivax, Inc. in May 2022 to strengthen its vaccine R&D pipeline, gain access to new technologies, and expand its geographic reach in the Boston area.
In May 2022, the European Commission (EC) approved Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.'s T-cell therapy CARVYKTI for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Furthermore, the growing alliances and acquisitions by the players to strengthen their businesses and increase their market shares are expected to drive the future growth of the market.
CEO Statements
Steve Collis, Chairman & CEO of Cencora
Erin Satterwhite, CEO of Optum Specialty Pharmacy
Market Segmentation
By Drug Type
By Pharmaceutical Molecule Type
By Application
By Classification Type
By Formulation
By Pharmaceutical Route of Administration
By Age Group
By End User
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Pharmaceutical
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Drug Overview
2.2.2 By Pharmaceutical Molecule Type Overview
2.2.3 By Application Overview
2.2.4 By Classification Overview
2.2.5 By Formulation Overview
2.2.6 By Route of Administration Overview
2.2.7 By Age Group Overview
2.2.8 By End User
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Pharmaceutical Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Increasing Aging Population and Healthcare Expenditure
4.1.1.2 Increased Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 Product Recalls and Reputation Damage
4.1.2.2 Regulatory Compliance
4.1.3 Market Opportunity
4.1.3.1 EmergingSpecialty Pharmaceuticals
4.1.3.2 Growth of Industry in Emerging Markets
4.1.4 Market Challenges
4.1.4.1 Ever Changing Healthcare Landscape
4.1.4.2 Disruption in Supply Chain
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Pharmaceutical Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Pharmaceutical Market, By Drug
6.1 Global Pharmaceutical Market Snapshot, By Drug
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2033
6.1.1.1 Generic
6.1.1.2 Branded
Chapter 7. Pharmaceutical Market, By Pharmaceutical Molecule Type
7.1 Global Pharmaceutical Market Snapshot, By Pharmaceutical Molecule Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2033
7.1.1.1 Large Molecules
7.1.1.2 Small Molecules
Chapter 8. Pharmaceutical Market, By Classification
8.1 Global Pharmaceutical Market Snapshot, By Classification
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2033
8.1.1.1 Prescription Drugs
8.1.1.2 OTC Drugs
Chapter 9. Pharmaceutical Market, By Application
9.1 Global Pharmaceutical Market Snapshot, By Application
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2033
9.1.1.1 Cardiovascular diseases
9.1.1.2 Oncology
9.1.1.3 Diabetes
9.1.1.4 Neurological disorders
9.1.1.5 Infectious diseases
9.1.1.6 Others
Chapter 10. Pharmaceutical Market, By End User
10.1 Global Pharmaceutical Market Snapshot, By End User
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2033
10.1.1.1 Hospital
10.1.1.2 Clinics
10.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 11. Pharmaceutical Market, By Formulation
11.1 Global Pharmaceutical Market Snapshot, By Formulation
11.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2021-2033
11.1.1.1 Tablets
11.1.1.2 Capsules
11.1.1.3 Injectable
11.1.1.4 Sprays
11.1.1.5 Suspensions
11.1.1.6 Powders
11.1.1.7 Others
Chapter 12. Pharmaceutical Market, By Region
12.1 Overview
12.2 Pharmaceutical Market Revenue Share, By Region 2023 (%)
12.3 Global Pharmaceutical Market, By Region
12.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
12.4 North America
12.4.1 North America Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.3 North America Pharmaceutical Market, By Country
12.4.4 U.S.
12.4.4.1 U.S. Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
12.4.5 Canada
12.4.5.1 Canada Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
12.4.6 Mexico
12.4.6.1 Mexico Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
12.5 Europe
12.5.1 Europe Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.3 Europe Pharmaceutical Market, By Country
12.5.4 UK
12.5.4.1 UK Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.5 France
12.5.5.1 France Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.6 Germany
12.5.6.1 Germany Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
12.5.7 Rest of Europe
12.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6 Asia Pacific
12.6.1 Asia Pacific Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.3 Asia Pacific Pharmaceutical Market, By Country
12.6.4 China
12.6.4.1 China Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.5 Japan
12.6.5.1 Japan Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.6 India
12.6.6.1 India Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.7 Australia
12.6.7.1 Australia Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
12.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7 LAMEA
12.7.1 LAMEA Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.3 LAMEA Pharmaceutical Market, By Country
12.7.4 GCC
12.7.4.1 GCC Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.5 Africa
12.7.5.1 Africa Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.6 Brazil
12.7.6.1 Brazil Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
12.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
12.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Pharmaceutical Market Revenue, 2021-2033 ($Billion)
12.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
12.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 13. Competitive Landscape
13.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
13.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
13.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2021-2023
13.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2021-2023
13.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2023)
Chapter 14. Company Profiles
14.1 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
14.1.1 Company Snapshot
14.1.2 Company and Business Overview
14.1.3 Financial KPIs
14.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
14.1.5 Strategic Growth
14.1.6 Global Footprints
14.1.7 Recent Development
14.1.8 SWOT Analysis
14.2 Novartis AG
14.3 Aurobindo Pharma
14.4 AbbVie Inc.
14.5 Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
14.6 Abbott Laboratories
14.7 Bayer AG
14.8 Merck & Co., Inc.
14.9 AstraZeneca
14.10 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
14.11 Pfizer Inc.
14.12 Amgen Inc.
14.13 Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
14.14 Sanofi
14.15 Eli Lilly and Company