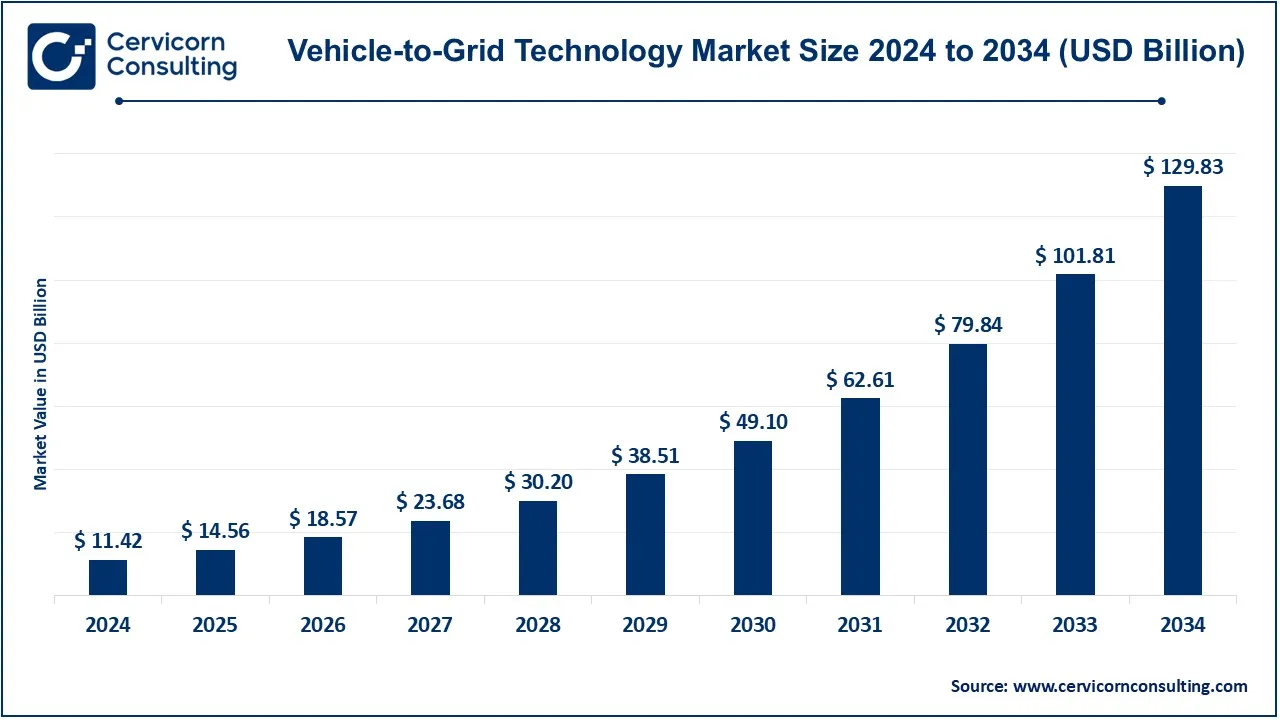
The global vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology market size was valued at USD 11.42 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 129.83 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.51% from 2025 to 2034. The U.S. V2G technology market size was valued at USD 2.46 billion in 2024.
Vehicle-to-Grid is a technology that allows electric vehicles to dynamically inter-operate with the power grid by allowing a bi-directional energy flow from the vehicle battery to the grid. This technology enables EVs to shift surplus energy during off-peak times to the grid during peak periods that can provide grid support on a distributed energy storage front. V2G systems are critical for the balance of supply and demand of energy and in the reduction of fossil fuel reliance. They support renewable energy integration and provide potential savings for EV owners in being able to sell back stored energy to the grid or use it at home during peak times. They present an advancement in managing sustainable energy, enhancing energy resiliency.
Report Highlights
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 11.42 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 129.83 Billion |
| Estimated CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 27.51% |
| Dominant Region | Europe |
| High-growth Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Vehicle Type, Components, Battery, Charging Type, Application, Region |
| Key Companies | Nuvve Holding Corp., E.ON U.K. plc., ABB Ltd., Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Enel Spa, The Mobility House GmbH, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Virta Global, Ovo Energy, Flexitricity |
The V2G technology market is segmented into vehicle type, components, battery, charging type, application and region. Based on vehicle type, the market is classified into battery electric vehicles, plug in hybrid electric vehicles and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). Based on components, the market is classified into electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), smart meters, home energy management (HEM) and others. Based on battery, the market is classified into by battery type and by charging type. Based on charging type, the market is classified into unidirectional charging and bidirectional charging. Based on application, the market is classified into domestic and commercial.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): The BEVs segment has dominated the market in 2024. BEVs are the major propulsion sources for the V2G market, having fully electric powertrains and enabling charging and discharging via V2G systems. With zero emissions, long ranges, and suitability for grid services, BEVs continue to be popular. Their relatively much larger battery capacities make them appealing for providing services to the grid, and with growing adoption, they will become central to the V2G market within the context of load management and demand response, in addition to being enablers for the V2G market.
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): PHEVs offer full flexibility with electric as well as combustion engines, making them versatile for V2G applications. They might have a comparatively lower battery capacity than BEVs; however, in times of peak demand, they can still contribute easily to provide load support via V2G commuter functions. PHEVs hold a very important position in regions where some infrastructure can support V2G. They allow the gradual switch of consumers, fully honoring the grid while transitioning to full electric vehicles. However, this greater transition relevance is tempered somewhat by the disadvantages conferred by a lower battery size with limited energy contributions compared to BEVs.
Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue Share, By Vehicle Type, 2024 (%)
| Vehicle Type | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Battery Electric Vehicles | 62.79% |
| Plug In Hybrid Electric Vehicles | 29.21% |
| Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs) | 7% |
Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs): FCVs use hydrogen as fuel, producing only water as an emission, making them a clean option for energy supply. While less common than BEVs or PHEVs, FCVs are gaining traction, especially for heavy-duty or long-range needs. Although not widely adopted in V2G systems, FCVs can theoretically supply stored energy back to the grid, adding diversity to energy sources. Future advancements in hydrogen infrastructure may boost FCVs’ participation in V2G as a clean, alternative energy resource.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE): The Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment segment has dominated the market in 2024. The EVSE, commonly called charging stations, is a very important component of V2G operation as it allows bidirectional power flow from the vehicle to the grid or from the grid to the vehicle. This includes chargers that are used for competitive energy intake as well as drawing energy back to the grid. With advancements in bi-directional charging within the EVSE, its feasibility and scalability of V2G systems have increased greatly. The establishment of higher efficiency within EVSE contributes a lot to the viability of V2G and contributes to workability in residence, commercial, and fleet applications.
Smart Meters: Smart Meters are the tools to provide real-time monitoring and communication between EVs and the grid, necessary for V2G. The meter allows the monitoring of energy used and ensures effective billing and data management, enabling utilities to learn about energy use patterns. For V2G, smart meters help facilitate a seamless integration and allow exact control of energy flow so that energy discharge from EVs matches real-time demand on the grid. In addition to that, they help in managing peak load, which is what makes them an essential aspect of V2G in both residential and commercial development.
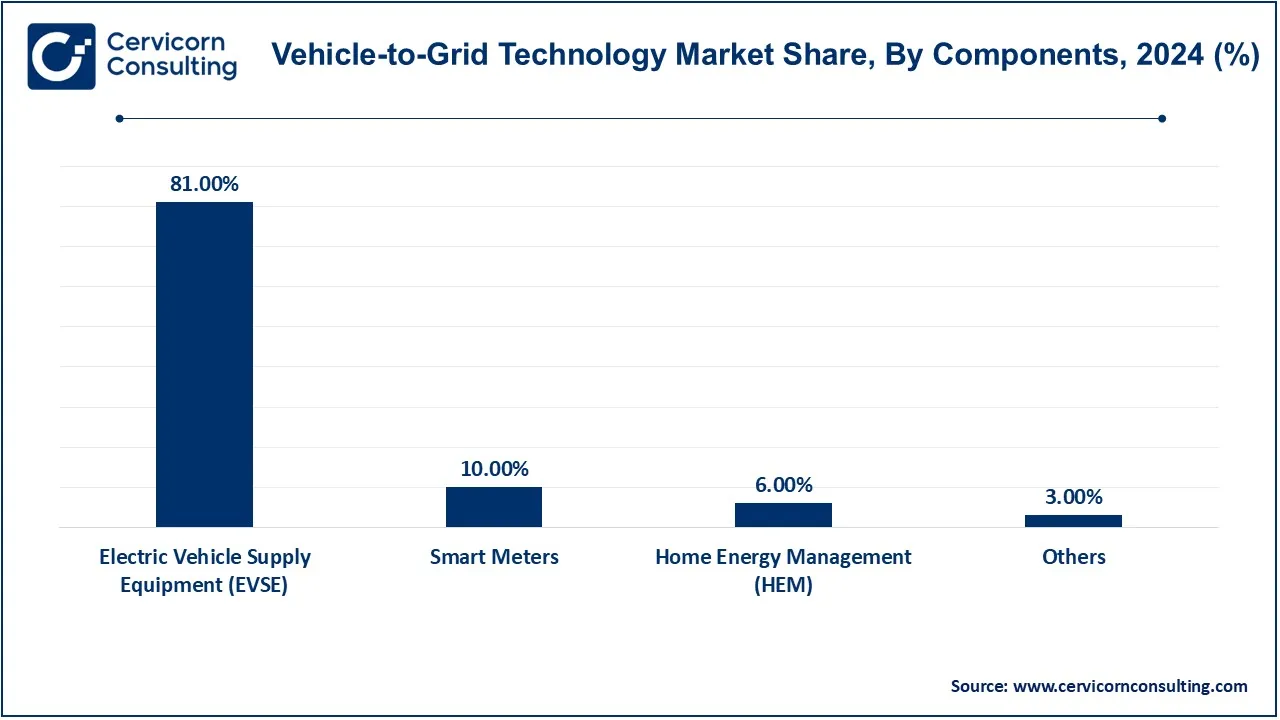
Home Energy Management (HEM): An HEM system controls and optimizes the flow of energy within homes in such a way that V2G-supporting energy utilization takes place. They first identify when and how much energy can be backed by an EV toward either a home or a grid: thus, they enable households to avoid feeding on peak energy consumption costs. With HEM, households can program automatic energizing for based on periods, price signals, or renewable generation availability at peak intervals. This kind of system allows consumers to cut costs while supporting grid stability; hence its integral role in residential V2G deployment.
Other: This category includes additional elements such as communication modules, data management systems, and energy storage systems that may be regarded as V2G functionality enhancers. Communication modules will facilitate secured transactions of information between the electric vehicles, grid operators, and consumers. Data management systems make it possible to use predictive analytics in optimizing V2G interactions in balancing the grid. Secondary storage batteries in this regard will make the V2G ecosystem more flexible and resilient as they will provide extended support to the grid in conjunction with EVs.
The V2G technology market is segmented into several key regions: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa). The Europe region has dominated market in 2024.
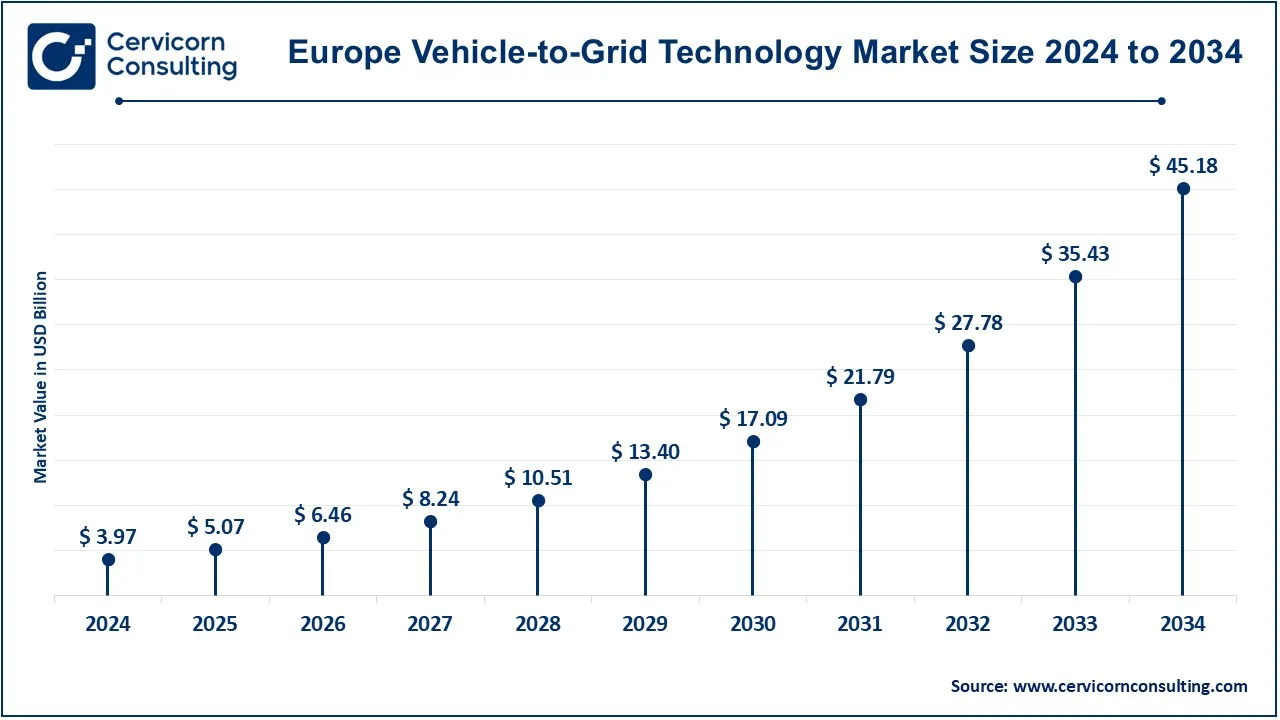
The Europe vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology market size was estimated at USD 3.97 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 45.18 billion by 2034. Europe is leading the V2G market with a major share in countries such as the UK, Germany, the Netherlands, and Norway. Given the strict emissions regulations put forth by the EU and aggressive renewable energy targets, the push for V2G development has placed it as one of the world's active markets. In Germany and the Netherlands pilot projects are being carried out on implementation of V2G in intelligent networks, while the high activity of EV in Norway opens vast opportunities for V2G. A few key initiatives in UK related to V2G are also emerging through public private partnership mode.
The North America vehicle-to-grid technology market size was valued at USD 3.28 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 37.34 billion by 2034. North America is an important shareholder of the V2G technology, taking lead in development with the U.S. and Canada. V2G adoption - prominent especially in cities where there is a high EV penetration - gained momentum due to the strong impetus for renewable energy integration and supportive government policies. US is the frontrunner of V2G technology as it has many developed projects with utility companies thanks to the existing EV infrastructure and sophisticated grid technology. Canada is also more focused on the research, development and implementation of V2G technology as a component of its clean energy strategy.
The Asia-Pacific vehicle-to-grid technology market size was accounted for USD 3.45 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 39.26 billion by 2034. The V2G technologies are developing rapidly in Asia-Pacific under the lead of Japan, South Korea, and China. In Japan, V2G came into existence, integrated into its strategy for boosting energy resilience following the earthquake of 2011, and the government continued supporting grid-friendly EV solutions. V2G is considered by China, the world’s largest rental market for EVs, as a suitable solution for managing peak loads and providing energy reserving. V2G is progressing in South Korea in terms of investments due to its importance in grid reliability. V2G has continuous energy consumption and government assistance will be very helpful in V2G development.
Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue Share, By Region, 2024 (%)
| Region | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| North America | 28.76% |
| Europe | 34.80% |
| Asia-Pacific | 30.24% |
| LAMEA | 6.20% |
The LAMEA vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology market was valued at USD 0.71 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 8.05 billion by 2034. LAMEA holds emerging potential for V2G technology, with Brazil and South Africa leading in renewable energy initiatives within Latin America and Africa, respectively. The Middle East is showing interest in V2G through its commitment to sustainable energy projects, with the UAE exploring V2G within smart city developments. The region’s adoption is slower due to infrastructure limitations, but rising renewable energy investment in Brazil and South Africa indicates potential growth in the future. LAMEA’s diverse energy needs could benefit from V2G as a cost-effective energy solution.
The V2G technology market is led by prominent players like Nuvve, The Mobility House, and Virta, who leverage their deep expertise in energy management and EV infrastructure to drive market advancements. These companies focus on integrating EVs with power grids, enabling bidirectional charging, and offering scalable solutions for both private and commercial applications. By forming strategic partnerships with automakers and utility providers, they contribute to energy resilience and grid stability. Their initiatives support global carbon reduction goals, creating a competitive edge in the rapidly growing V2G sector.
CEO Statements
Christopher Yang, Group Vice President, Toyota EV Charging Solutions
Tyler Anthony, President and CEO, Pepco Holdings
Recent partnerships in the V2G technology market signify a transformative move towards innovation and strategic collaboration. Leading companies like Nuvve Holding Corp., E.ON U.K. plc, ABB Ltd., and Honda Motor Co., Ltd. are at the forefront of developing advanced V2G systems. These systems enable electric vehicles to not only draw power from the grid but also return energy during peak demand times, thus enhancing grid stability. Such initiatives aim to optimize energy management, support renewable energy integration, and promote sustainability in transportation, ultimately driving the transition to a greener energy ecosystem. Some notable examples of key developments in the V2G technology industry include:
Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type
By Components
By Battery
By Charging Type
By Application
By Region
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Vehicle-to-Grid Technology
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Vehicle Type Overview
2.2.2 By Components Overview
2.2.3 By Battery Overview
2.2.4 By Charging Type Overview
2.2.5 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Global Impact Analysis
3.1 COVID 19 Impact on Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market
3.1.1 COVID-19 Landscape: Pre and Post COVID Analysis
3.1.2 COVID 19 Impact: Global Major Government Policy
3.1.3 Market Trends and Opportunities in the COVID-19 Landscape
3.2 Russia-Ukraine Conflict: Global Market Implications
3.3 Regulatory and Policy Changes Impacting Global Markets
Chapter 4. Market Dynamics and Trends
4.1 Market Dynamics
4.1.1 Market Drivers
4.1.1.1 Increased EV Penetration
4.1.1.2 Decentralization of the energy system
4.1.1.3 Utility Grid Stability
4.1.1.4 Consumer Demand for Sustainability
4.1.2 Market Restraints
4.1.2.1 High sensors setup costs
4.1.2.2 Concern with battery wear
4.1.2.3 Limited availability of bi-directional EVs
4.1.3 Market Challenges
4.1.3.1 Risks of Battery Degradation
4.1.3.2 Investment in High Infrastructure
4.1.3.3 Limited Bi-directional Chargeable Models of EVs
4.2 Market Trends
Chapter 5. Premium Insights and Analysis
5.1 Global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
5.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
5.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
5.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
5.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
5.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
5.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
5.3 PESTEL Analysis
5.4 Value Chain Analysis
5.5 Product Pricing Analysis
5.6 Vendor Landscape
5.6.1 List of Buyers
5.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 6. Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Vehicle Type
6.1 Global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Snapshot, By Vehicle Type
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Battery Electric Vehicles
6.1.1.2 Plug In Hybrid Electric Vehicles
6.1.1.3 Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs)
Chapter 7. Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Components
7.1 Global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Snapshot, By Components
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE)
7.1.1.2 Smart Meters
7.1.1.3 Home Energy Management (HEM)
7.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 8. Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Battery
8.1 Global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Snapshot, By Battery
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 By Battery Type
8.1.1.2 By Charging Type
Chapter 9. Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Charging Type
9.1 Global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Snapshot, By Charging Type
9.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
9.1.1.1 Unidirectional Charging
9.1.1.2 Bidirectional Charging
Chapter 10. Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Application
10.1 Global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Snapshot, By Application
10.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
10.1.1.1 Domestic
10.1.1.2 Commercial
Chapter 11. Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Region
11.1 Overview
11.2 Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue Share, By Region 2024 (%)
11.3 Global Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Region
11.3.1 Market Size and Forecast
11.4 North America
11.4.1 North America Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.3 North America Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Country
11.4.4 U.S.
11.4.4.1 U.S. Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.4.3 U.S. Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.5 Canada
11.4.5.1 Canada Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.5.3 Canada Market Segmental Analysis
11.4.6 Mexico
11.4.6.1 Mexico Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.4.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.4.6.3 Mexico Market Segmental Analysis
11.5 Europe
11.5.1 Europe Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.3 Europe Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Country
11.5.4 UK
11.5.4.1 UK Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.5 France
11.5.5.1 France Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.6 Germany
11.5.6.1 Germany Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
11.5.7 Rest of Europe
11.5.7.1 Rest of Europe Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.5.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.5.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6 Asia Pacific
11.6.1 Asia Pacific Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.3 Asia Pacific Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Country
11.6.4 China
11.6.4.1 China Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.4.3 ChinaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.5 Japan
11.6.5.1 Japan Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.5.3 JapanMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.6 India
11.6.6.1 India Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.6.3 IndiaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.7 Australia
11.6.7.1 Australia Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.7.3 AustraliaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.6.8 Rest of Asia Pacific
11.6.8.1 Rest of Asia Pacific Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.6.8.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.6.8.3 Rest of Asia PacificMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7 LAMEA
11.7.1 LAMEA Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.3 LAMEA Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market, By Country
11.7.4 GCC
11.7.4.1 GCC Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.4.3 GCCMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.5 Africa
11.7.5.1 Africa Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.5.3 AfricaMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.6 Brazil
11.7.6.1 Brazil Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.6.3 BrazilMarket Segmental Analysis
11.7.7 Rest of LAMEA
11.7.7.1 Rest of LAMEA Vehicle-to-Grid Technology Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
11.7.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
11.7.7.3 Rest of LAMEAMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 12. Competitive Landscape
12.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
12.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
12.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
12.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
12.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 13. Company Profiles
13.1 Nuvve Holding Corp.
13.1.1 Company Snapshot
13.1.2 Company and Business Overview
13.1.3 Financial KPIs
13.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
13.1.5 Strategic Growth
13.1.6 Global Footprints
13.1.7 Recent Development
13.1.8 SWOT Analysis
13.2 E.ON U.K. plc.
13.3 ABB Ltd.
13.4 Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
13.5 Enel Spa
13.6 The Mobility House GmbH
13.7 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
13.8 Virta Global
13.9 Ovo Energy
13.10 Flexitricity