Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
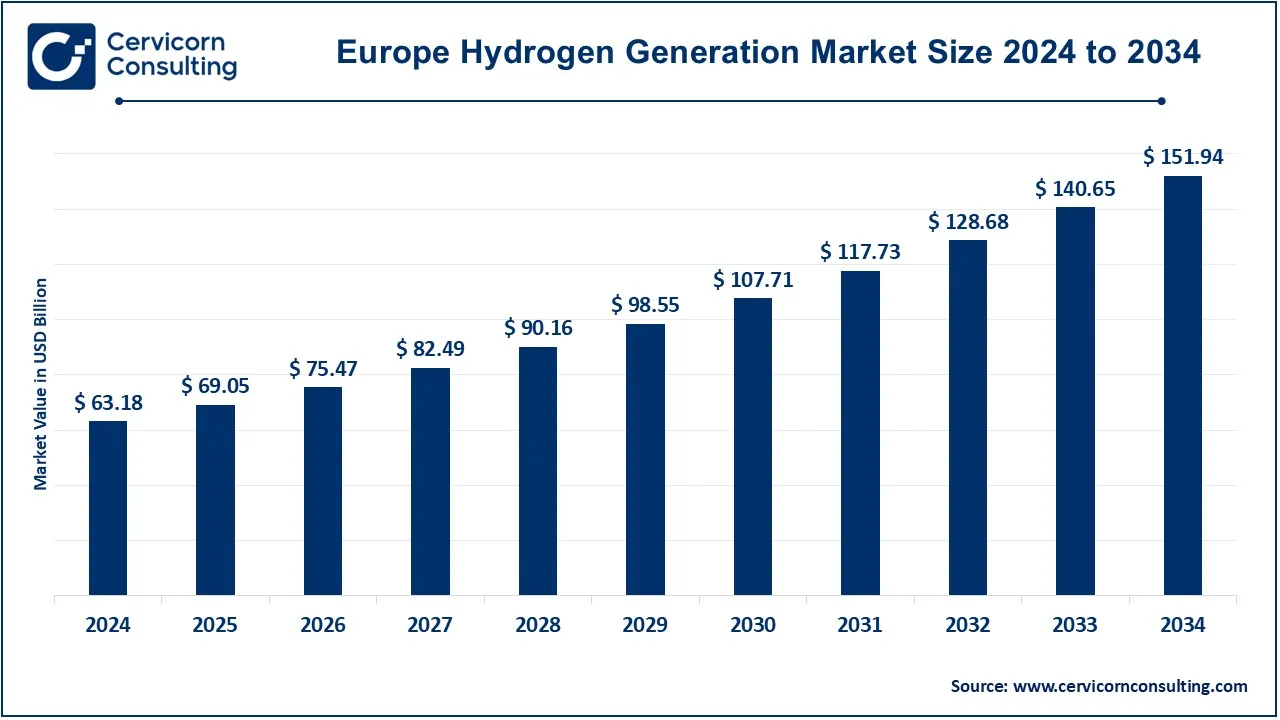
The Europe hydrogen generation market size was valued at USD 63.18 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach around USD 151.94 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.30% from 2025 to 2034.
Hydrogen generation is a process of producing hydrogen, an element most often utilized as a clean energy source in just about all industries. Different hydrogen generation techniques include steam methane reforming (SMR), which extracts hydrogen from natural gas, and electrolysis, which uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen-ideally from renewable sources to minimize pollution. Hydrogen is crucial to fuel cells of electric vehicles, industrial use, and as a green alternative to fossil fuels in power generation. With new technologies, hydrogen generation will be made increasingly user-friendly and environmentally friendly, demonstrating its grand potential to a true frontrunner in the global shift to cleaner energy systems.
Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Growth Factors
- Green Energy Transition: The green energy shift in Europe is a crucial factor for producing hydrogen, given that the EU has set aggressive decarbonization targets. The enforcement of renewable energy in transportation, industry, and generation has ignited substantial hydrogen demand. Hydrogen is seen by policymakers as a clean alternative for fossil fuels, specifically for those sectors like heavy industries and transportation that remain difficult to electrify. A more prosperous investment in renewable energy lowers the price of green hydrogen and accelerates its development.
- Government Support: The European states provide, thusly, subsidized, gifted, and enabled regulatory advantages for hydrogen. Such state support drives the production costs lower and stimulates further private investments, covering a broader array of firms entering the hydrogen market. In this light is the European Green Deal with assigned billions for hydrogen infrastructures, thereby igniting across-the-board growth. This public backing builds positive investor perceptions which will likely help the hydrogen market expand with a strong foundation of policy and regulations for upscaling production.
- Demand for Green Hydrogen: The quest for hitherto unheard of green hydrogen really provides apt strength in several industrial sectors as it holds immense environmental benefits. The industry sectors such as manufacture, steel, and chemicals seek hydrogen with an increasing disregard for their emission reduction targets. Most importantly, the chemical sector needs green hydrogen to manufacture its ammonia and methanol. Additionally, green hydrogen gains momentum as a potential fuel substitute for heavy-duty vehicles request should be considered as an impetus for further interest in addressing a number of provided in the context of the general growing hydrogen production across Europe.
- Industrial Decarbonization: Steel, cement, and chemicals amongst others are essentially looking for alternatives for fossil fuels; hydrogen offers such low carbon characterization. Hydrogen is positioned to be well suited for the hard-to-abate sector as new regulations on emissions are coming from the EU. This a big push for switching towards hydrogen in the manufacturing industries, whereby hydrogen can be mixed into the production process to reduce emissions while output remains stable. Transitioning into hydrogen helps companies comply with regulations that would induce market-wide growth across Europe.
- The Transportation Transition: With its core intention being the transition of its transportation sector to alternative energy sources, the European Union general demand for hydrogen for buses, trucks, and trains has increased. Hydrogen fuel cells have emerged as powerful alternatives mainly for long-haul and commercial vehicles-those segments where electric solutions are not practical. Such an investment toward hydrogen refueling infrastructure shall add support to this transition, thus allowing for the growth of hydrogen adoption for passenger and freight transport, which is set to take a large portion of total hydrogen demand in the region.
Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Trends
- Green Hydrogen Development: Green hydrogen, produced from renewable energy sources, is rising to capture significant attention freshly, given the industry need for sustainable solutions. Regulatory and environmental concerns have driven green hydrogen to begin to displace gray hydrogen in a number of applications. As a result of Europe’s climate aspirations encouraging the adoption of solar energy and hydrogen, generating green hydrogen becomes the focal point concerning hydrogen production in Europe. Such process is further encouraged through investment and enhanced by a focus on reducing the production of carbon efficient hydrogens.
- Infrastructure Development: Among the significant investments in hydrogen infrastructure in Europe are refueling stations and pipelines to ensure distribution and accessibility. Such investments are the foundation of hydrogen application in industry and public transport. Such infrastructures will ensure the establishment of reliable hydrogen supply chains creating a stable hydrogen economy in line with the green transition goals of Europe. It bolts towards large-scale adoption of hydrogen across European regions.
- The Hydrogen Hubs Upgrade: Hydrogen hubs or clusters permit the concentrated production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen. Such clusters would optimally be sited in locations where renewable energy resources-especially wind or solar-are easily accessible and therefore allow for green hydrogen production at low cost. These hubs support the decarbonisation objectives of Europe by realizing economies of scale, reducing costs, and boosting local industry. Individual regional hubs create local markets and feed into the overall hydrogen strategy of the EU.
- Development of Electrolyzer Technology: Enhanced R&D initiatives have recently developed more efficient electrolyzer technologies, therefore reducing the cost of producing green hydrogen. Electrolyzers are a vital part of hydrogen production by the utilization of renewable electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. Improved technology reduces production costs, becoming a more lustrous competitor with fossil fuels. The development of technology will see electrolyzers receiving more support in bringing large-scale hydrogen use into line with Europe’s sustainability ambitions.
- Blending hydrogen with gas in the natural gas grids: To enhance emission reduction and further expand hydrogen supply, Europe is implementing hydrogen blending in existing natural gas pipelines; this is one effective method for transmission. Mixed with natural gas, customers can decrease carbon intensity while utilizing the established infrastructure. Hydrogen blending enhances energy diversification helping countries to meet EU climate targets. It's a great way to integrate hydrogen into the energy system, helping to promote the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 63.18 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 151.94 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2034) |
9.30% |
| Key Segments |
Type, Delivery Mode, Process, Application |
| Key Companies |
Air Products and Chemicals, Inc., Ally Hi-Tech Co., Ltd., CALORIC, Cummins Inc., Hexagon Composites ASA, ITM Power plc, Iwatani Corporation, Linde plc, McPhy Energy, Messer, Nel ASA, NUVERA FUEL CELLS, LLC, Plug Power Inc., RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION, Siemens Energy AG |
Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Dynamics
Drivers
- Heavy Industry Applications: Heavy industries in Europe are under increasing pressure to cut down their emissions; hydrogen is to be the viable option for their decarbonization. Hydrogen, therefore, can be used in energy-intensive processes such as steel production, thus avoiding the burning of fossil fuels, especially natural gas, thus decreasing carbon emissions. As soon as it takes on a major role owing to regulatory measures targeting these industries, demand in the market becomes very strong. The use of hydrogen in industrial applications ensures emissions targets are met while promoting the hydrogen economy.
- Demand for Clean Fuel: With cleaner fuels now in focus in Europe, hydrogen has found its way into energy, heat generation, and transport. Clean hydrogen has an unspoiled environmental footprint, which is attractive to sectors that aspire to sustainability along eco-friendly lines. Such demand falls in line with the EU's strong regulatory have along climate target lines; hence hydrogen is touted as an alternative to conventional fossil fuels. Its foray into heavy-duty transport and power former cites hydrogen as a flexible energy carrier, thus underlining its application.
- Infrastructure Development: Investment in hydrogen infrastructure in Europe is crucial for supporting hydrogen generation, storage, and distribution. Building infrastructure such as pipelines, refueling stations, and storage points is thus crucial for market growth, and with increasing demand across all sectors. These EU-backed projects offer an assurance for the accessibility and distribution of hydrogen, thus necessitating its adoption by various companies. That development is in line with the climate targets of the European Union and builds the necessary basis for the hydrogen economy to prosper.
- Increased Funding for R&D: Massive injection of money into hydrogen R&D is enabling innovations in production and distribution technology. EU-backed funding initiatives allow companies to search for electrolyzer efficiency improvements and hydrogen storage solutions. Improved technology reduces costs and increases the availability of hydrogen, helping ensure the industry's sustainability in the long term. Increased funding for R&D is accelerating the commercialization of new hydrogen applications and facilitating faster and more efficient production methods vital for market growth.
Opportunity
- Expansion of Renewable Energy Integration: Hydrogen generation using renewable energy sources is a critical opportunity in Europe, driven by the EU’s renewable energy targets. Electrolysis powered by wind and solar is gaining momentum, as projects like HyDeploy and North Sea Wind Power Hub aim to integrate hydrogen into grids and industries. This shift creates opportunities for electrolyzer manufacturers and renewable energy firms.
- Energy Storage Solutions That Run on Hydrogen: With hydrogen energy storage, Europe has a game changer in this sector because it allows for long-term storage to balance the intermittent renewable sources such as wind and solar. Hydrogen can be produced when energy surplus exists, stored and converted back to electricity during peak demand. This mechanism helps stabilize the grid. For example, the Hybrit project in Sweden raises confidence in hydrogen as the answer to energy storage while dealing with the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources and offering energy security in industrial processes.
- Scaling Hydrogen Clusters: Hydrogen clusters, or hydrogen valleys, are the new centres of gravity for boosting the hydrogen economy in Europe. These clusters connect hydrogen production, distribution and use throughout industry, transport and power generation. An example is the Northern Netherlands Hydrogen Valley, which connects offshore wind with green hydrogen production and industrial applications and illustrates the potential for the efficacy of a cooperative ecosystem. Clusters foster investment, innovation, and larger-scale delivery within space; they create a resilient hydrogen supply chain for the future.
Restraints
- High Production Costs: Hydrogen production, especially green hydrogen, remains prohibitively expensive, mainly due to the energy needed for electrolysis. These elevated energy inputs render hydrogen very much illegitimate as a conceivably applicable fuel next to fossil fuels. Although renewable energy continues to decline in price, they have not yet fallen to a region empowering hydrogen to emerge as an elite economical fuel. The concern of production cost reduction remains an important point in unlocking the chances for the uptake of hydrogen as a good alternative besides other sources of energy for sectors in Europe.
- Production is Energetically Demanding: A significant amount of energy input is needed for hydrogen production, especially from electrolysis, to an extent often making it less efficient than many traditional means of energy. Hydrogen production is energy-intensive, hampering green hydrogen cost-effectiveness and slowing down market uptake. Elimination of this barrier entails improvements in electrolyzer technologies and more affordable renewable energy availability. The energy demand associated with hydrogen production presents a barrier that the industry must overcome to ensure wider use.
- Competition with Other Clean Fuels: Hydrogen runs in competition with other clean fuels—biofuels and electrification—viable alternatives in the eyes of government and consumer adoption alike. It is because producers implemented electric solutions at this time in certain respects that, in contrast, this may slow tank-dependent hydrogen assimilation. The plurality of clean fuel offerings fosters competitive pressure on hydrogen to certify itself as operationally and cost-competitive, especially in countries where biofuels and electrification are embedded more robustly.
Challenges
- Scaling Production Efficiently: The scale of hydrogen production to meet demand while remaining efficient is, therefore, extremely challenging. Cost-effective production requires technological breakthroughs and investment in fixed capital. Efficient scaling is of vital importance for achieving decarbonization targets in Europe, hindered by high costs and infrastructure needs. Affordable production methods remain barred from slashing the hydrogen market shareholder limits on proposed large-scale uptake.
- Building Infrastructure: The development of hydrogen infrastructure-dispensing stations and pipelines-through huge capital investments and detailed planning. Transportation and storage of hydrogen are quite complicated, and they require specific types of facilities and equipment to ensure safety. The absence of necessary facilities may render hydrogen out of reach and hence render its applicability in commercial industries and transport very minimal. Such hurdles however need to be addressed when it comes to the prospects of incorporating hydrogen into the European energy outlook.
- Technology Standardization: The lack of homogenous standards for hydrogen technology has so far impeded its adoption across regions and industries. There are inconsistent technology and safety standards; hence companies will face increased challenges in hydrogen production, storage, and distribution. Standardization must occur to promote cross-border hydrogen trading in building an integrated hydrogen market in Europe. Technology standards will allow efficient and secure hydrogen deployment across sectors.
Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Segmental Analysis
The Europe hydrogen generation market is segmented into delivery mode, process, type, and application. Based on delivery mode, the market is segmented into captive and merchant. Based on process, the market is segmented into steam reformer, electrolysis and others. Based on type, the market is segmented into blue, green, and grey. Based on application, the market is segmented into petroleum refinery, metal, chemical and others.
Delivery Mode Analysis
Captive: Captive hydrogen generation means the on-site production of hydrogen for the convenience of regular availability and for generally lower transport costs. Such mode is rather common among large producers of the chemical industry and refineries, where a continuous supply of relatively large quantities of hydrogen is demanded. More so, captive production affords advanced technologies such as electrolysis, which further promotes the production of green hydrogen. Captive hydrogen systems have been slowly becoming popular in Europe as a growing focus on carbon emissions reduction and energy security takes precedence now.
Merchant: Merchant hydrogen production refers to the production of hydrogen at a centralized facility and delivered to various industries as required. This model shall help industries with varied hydrogen demand, for example metal and automobile sector, wherein hydrogen is required and used only in certain phases of the production process. However, the merchant delivery model is becoming even more reinforced because of growth in hydrogen adoption in smaller enterprises and decentralized networks in Europe. This is crucial for maintaining flexibility and security of supply, particularly in areas where there is no dedicated hydrogen production.
Process Analysis
Steam Reformer: Steam methane reforming (SMR) is a widely used hydrogen production process, especially in traditional applications like petroleum refining and ammonia production. Although effective, SMR is carbon-intensive; thus, efforts to decarbonize this process are underway, such as capturing carbon emissions generated during production. With Europe’s push for greener hydrogen solutions, investment in low-emission SMR technologies is anticipated to maintain SMR’s relevance, especially as a bridge technology until green hydrogen processes become more viable and cost-effective.
Electrolysis: Electrolysis is a process that produces hydrogen by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, ideally sourced from renewable energy. This method produces “green” hydrogen with minimal environmental impact, aligning with Europe’s sustainability goals. As Europe increases renewable energy production, electrolytic hydrogen production is poised to become a dominant method, particularly with advancements in offshore wind and solar projects. The Europe's commitment to green hydrogen and significant subsidies are expected to accelerate electrolysis adoption across various industries.
Others: The other processes of hydrogen production such as biomass gasification and thermochemical water splitting, which offer additional pathways for low-carbon hydrogen. These technologies are still at various stages of development but may well be of interest to those resources-rich regions where the support of the renewable energy facility can't provide consistent support for electrolysis. Investments across the EU in innovation have thus catalyzed such research into the other H2 production techniques which may play a key role in meeting particular sectoral needs and fulfilling the overall hydrogen targets for Europe.
Application Analysis
Petroleum refinery: Hydrogen is a necessary constituent used in the hydrocracking process where heavier hydrocarbons get broken down into lighter and more valuable products. With an increasing focus on less-emission fuels, demand has risen for clean hydrogen from refineries pursuing low-carbon production technologies to observe such aspects. The overall European push toward the radical decarbonization of the oil and gas industry causes considerable shifts in this sector itself with different methods of hydrogen production aiming at environmental conservation practices to achieve a lower carbon rate in the refining industry.
Chemical: Hydrogen finds use within the chemical industry, especially for the production of ammonia, methanol, and other essential products. Due to increasingly stringent environmental regulations, chemical producers are now turning to the production of green hydrogen to reduce emissions and improve production efficiency. Commitment in Europe to transition into a more sustainable model for its chemical sector is driving investments into clean hydrogen to facilitate eco-efficient chemical processes and, thus, provide the industry an opportunity to meet its ESG targets. Supporting this development within the chemical sector is the promotion of EU financing for green hydrogen.
Metal: In metal production processes, hydrogen is known to help in the reducing and smelting processes especially in steel making, where the prime source of reduction has been coal for a long time. The drawback of using current processes is however the quest for cleaner ways to perform reduction and minimization of carbon emission. Europe’s steel sector is actively exploring hydrogen to replace fossil fuels in blast furnaces, as initiatives like the European Green Deal promote emissions reductions. As more metal producers adopt hydrogen, demand in this segment is projected to go up, thus driving investments in captive and merchant hydrogen generation.
Others: The other applications include nuclear generation, electrical machines, and maker processes, using hydrogen for heat treatment and creating controlled atmospheres. In Europe, while the decarbonization effort continues, industries that have traditionally did not utilize hydrogen are adopting it on this path towards sustainability practices. Furthermore, other research of hydrogen potentials for new applications is underway, further expanding its applicability over multiple industries and boosting demand for efficient low-emission hydrogen production modalities.
Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Top Companies
- Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
- Ally Hi-Tech Co., Ltd.
- CALORIC
- Cummins Inc.
- Hexagon Composites ASA
- ITM Power plc
- Iwatani Corporation
- Linde plc
- McPhy Energy
- Messer
- Nel ASA
- NUVERA FUEL CELLS, LLC
- Plug Power Inc.
- RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
- Siemens Energy AG
CEO Statements
Seifi Ghasemi, CEO of Air Products
- "Our partnership with Associated British Ports on the UK’s first large-scale green hydrogen facility at the Port of Immingham exemplifies our commitment to decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors. This green hydrogen facility is poised to significantly reduce greenhouse emissions and foster a sustainable energy transition in the UK."
Tom Linebarger, CEO of Cummins Inc
- Cummins is dedicated to advancing zero-emission technologies and green hydrogen solutions as part of a broader energy transition. Our strategic investments and collaborations across Europe aim to bring hydrogen infrastructure to scale, supporting decarbonization and green job creation in various European industries."
Recent Developments
Recent partnerships and funding activities in the European Hydrogen Generation market underscore the drive for innovation and collaboration among top industry players. Companies like Air Products and Chemicals, Ally Hi-Tech, CALORIC, Cummins Inc., and Hexagon Composites are advancing green hydrogen projects, such as large-scale electrolysis facilities, in response to Europe’s increasing push for renewable energy solutions. These initiatives aim to address hard-to-decarbonize sectors and leverage resources like offshore wind and nuclear energy, aligning with Europe’s ambitious hydrogen production and sustainability targets by 2030. Some notable examples of key developments in the Europe Hydrogen Generation Market include:
- In December 2023, H2 Energy Europe secured government funding to establish a 20MW electrolytic hydrogen production facility at Milford Haven port, marking South Wales' first project in this sector. By 2030, the UK aims to produce 10 gigawatts of low-carbon hydrogen, primarily through electrolysis, which will leverage offshore wind, renewable energy, and nuclear power growth.
- In September 2021, Masdar and VERBUND Green Hydrogen GmbH partnered to build a green hydrogen plant in central Spain to support the decarbonization of Europe’s hard-to-abate sectors. Announced at COP28 in Dubai, this initiative builds on a prior agreement to address rising European hydrogen demand.
Market Segmentation
By Delivery Mode
By Process
- Steam Reformer
- Electrolysis
- Others
By Type
By Application
- Petroleum Refinery
- Metal
- Chemical
- Others
By Geography
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Nordic Countries
- Russia
- Turkey
- Rest of Europe
Chapter 1. Market Introduction and Overview
1.1 Market Definition and Scope
1.1.1 Overview of Europe Hydrogen Generation
1.1.2 Scope of the Study
1.1.3 Research Timeframe
1.2 Research Methodology and Approach
1.2.1 Methodology Overview
1.2.2 Data Sources and Validation
1.2.3 Key Assumptions and Limitations
Chapter 2. Executive Summary
2.1 Market Highlights and Snapshot
2.2 Key Insights by Segments
2.2.1 By Delivery Mode Overview
2.2.2 By Process Overview
2.2.3 By Type Overview
2.2.4 By Application Overview
2.3 Competitive Overview
Chapter 3. Market Dynamics and Trends
3.1 Market Dynamics
3.1.1 Market Drivers
3.1.1.1 Heavy Industry Applications
3.1.1.2 Demand for Clean Fuel
3.1.1.3 Infrastructure Development
3.1.1.4 Increased Funding for R&D
3.1.2 Market Restraints
3.1.2.1 High Production Costs
3.1.2.2 Production is Energetically Demanding
3.1.2.3 Competition with Other Clean Fuels
3.1.3 Market Challenges
3.1.3.1 Scaling Production Efficiently
3.1.3.2 Building Infrastructure
3.1.3.3 Technology Standardization
3.2 Market Trends
Chapter 4. Premium Insights and Analysis
4.1 Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Dynamics, Impact Analysis
4.2 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
4.2.3 Threat of Substitute Products
4.2.4 Rivalry among Existing Firms
4.2.5 Threat of New Entrants
4.3 PESTEL Analysis
4.4 Value Chain Analysis
4.5 Product Pricing Analysis
4.6 Vendor Landscape
4.6.1 List of Buyers
4.6.2 List of Suppliers
Chapter 5. Hydrogen Generation Market, By Delivery Mode
5.1 Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Snapshot, By Delivery Mode
5.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
5.1.1.1 Captive
5.1.1.2 Merchant
Chapter 6. Hydrogen Generation Market, By Process
6.1 Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Snapshot, By Energy
6.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
6.1.1.1 Steam Reformer
6.1.1.2 Electrolysis
6.1.1.3 Others
Chapter 7. Hydrogen Generation Market, By Type
7.1 Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Snapshot, By Type
7.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
7.1.1.1 Blue
7.1.1.2 Green
7.1.1.3 Grey
Chapter 8. Hydrogen Generation Market, By Application
8.1 Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Snapshot, By Application
8.1.1 Market Revenue (($Billion) and Growth Rate (%), 2022-2034
8.1.1.1 Petroleum Refinery
8.1.1.2 Metal
8.1.1.3 Chemical
8.1.1.4 Others
Chapter 9. Hydrogen Generation Market, By Region
9.1 Overview
9.2 Europe
9.2.1 Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.3 Europe Hydrogen Generation Market, By Country
9.2.4 UK
9.2.4.1 UK Hydrogen Generation Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.4.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.4.3 UKMarket Segmental Analysis
9.2.5 France
9.2.5.1 France Hydrogen Generation Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.5.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.5.3 FranceMarket Segmental Analysis
9.2.6 Germany
9.2.6.1 Germany Hydrogen Generation Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.6.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.6.3 GermanyMarket Segmental Analysis
9.2.7 Rest of Europe
9.2.7.1 Rest of Europe Hydrogen Generation Market Revenue, 2022-2034 ($Billion)
9.2.7.2 Market Size and Forecast
9.2.7.3 Rest of EuropeMarket Segmental Analysis
Chapter 10. Competitive Landscape
10.1 Competitor Strategic Analysis
10.1.1 Top Player Positioning/Market Share Analysis
10.1.2 Top Winning Strategies, By Company, 2022-2024
10.1.3 Competitive Analysis By Revenue, 2022-2024
10.2 Recent Developments by the Market Contributors (2024)
Chapter 11. Company Profiles
11.1 Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
11.1.1 Company Snapshot
11.1.2 Company and Business Overview
11.1.3 Financial KPIs
11.1.4 Product/Service Portfolio
11.1.5 Strategic Growth
11.1.6 Global Footprints
11.1.7 Recent Development
11.1.8 SWOT Analysis
11.2 Ally Hi-Tech Co. Ltd.
11.3 CALORIC
11.4 Cummins Inc.
11.5 Hexagon Composites ASA
11.6 ITM Power plc
11.7 Iwatani Corporation
11.8 Linde plc
11.9 McPhy Energy
11.10 Messer
11.11 Nel ASA
11.12 NUVERA FUEL CELLS LLC
11.13 Plug Power Inc.
11.14 RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
11.15 Siemens Energy AG
...
