The global healthcare IT market size was reached at USD 768.07 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 3,367.90 billion by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.93% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The market is expected to grow owing to the rising usage of smartphones along with increasing demand for remote patient monitoring. The rising initiatives being taken by various governments for the promotion of the technologically advanced systems is further expected to propel the demand for the market.
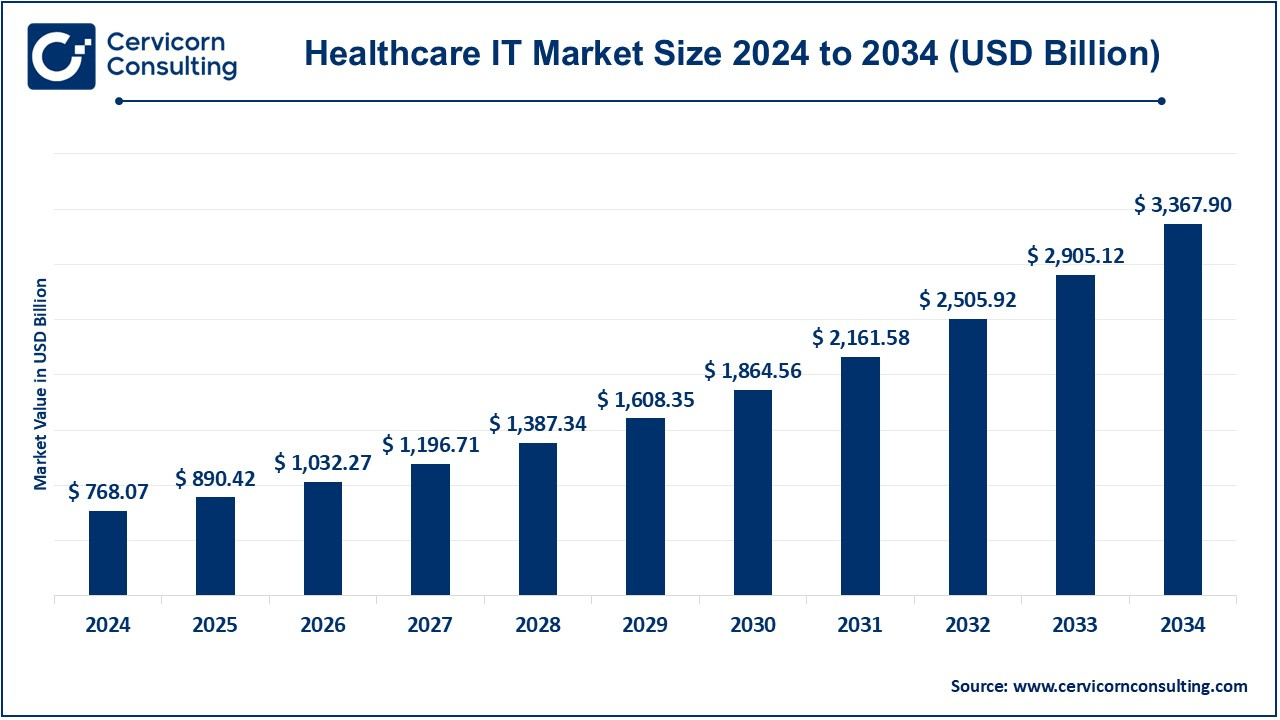
The healthcare IT market is expected to grow at a significant pace owing to technological advancements, urgent requirements for formal and efficient healthcare delivery, and the ever-growing need for safe management of data. Such a sector is very vast and includes activities like Electronic Health Records (EHRs), telemedicine platforms, healthcare analytics, and mobile health apps. Spending increases in digital infrastructure, governmental drives on healthcare modernization, and ramp-up in the use of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) are turning things around for the healthcare market, resulting in better patient outcomes and operational efficiencies. Devices have become more connected through the integration of wearable tools and IoT, and they have started to monitor health and provide personalized health care. Barriers like privacy concerns from users about their information, high costs related to implementation, and behaviors caused by regulations continue to persist. Integration and collaboration of healthcare providers, IT vendors, and reputable policymakers to a smarter space is essential for bringing in sustainability and accessibility to the healthcare IT market.
Report Scope
| Area of Focus | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 890.42 Billion |
| Expected Market Size in 2034 | USD 3,367.90 Billion |
| Projected CAGR 2025 to 2034 | 15.93% |
| Dominant Region | North America |
| High-growth Region | Asia-Pacific |
| Key Segments | Delivery Mode, Application, End-Use, Region |
| Key Companies | Accenture, Agfa- Gevaert Group, Athenahealth, Inc. (Acquired by Hellman & Friedman and Bain Capital), Carestream Health, eMDs, Inc., GE Healthcare, Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP, IBM, IQVIA, McKesson Corporation, Novarad, Optum, Inc., Oracle, Philips Healthcare, SAP, SAS Institute, Inc., Verisk Analytics, Inc. |
Healthcare Consumerism
Interoperability Solutions
High Implementation Costs
Data Security Concerns
Expansion in Emerging Markets
AI and Blockchain Innovations
Resistance to Change
Regulatory Challenges
Hardware: Hardware involves all physical devices, equipment, and stuff that supports digital health technologies. Such technological entrance into healthcare through hardware involves discovery tools, biomedical imaging devices, devices that can be worn, and haptic hardware photography such as cameras and sensors used for remote meetings as well as laboratory services. Furthermore, servers and storage hardware are core in terms of EHR hosting and support for healthcare analytics. An eloquent illustration is the internet of things, which is making everything possible as far as monitoring patients' vital signs and chronic conditions in real time. Supplying good-quality, reliable hardware solutions will ensure that healthcare IT systems work properly and a great patient outcome is achieved by continually monitoring and data collection.
Healthcare IT Market Share, By Delivery Mode, 2024 (%)
| Delivery Mode | Revenue Share, 2024 (%) |
| Solutions | 61% |
| Hardware | 39% |
Solution: The solutions include various software operations and services to heighten care, facilitate operations, and obtain better patient results. This is comprehensively inclusive of EHRs and telemedicine; healthcare analytics and patient management systems are also of relevance to solutions in this arena. One good model to follow is the kind of cloud software solution that has scope for availability, security, and scalability of information so that remote discussion between providers is possible. Solutions integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning can provide predictive insights for the organizations to make decisions based on data. It also introduces a process of moving to digital, which is critical as it works best in enabling health systems to be more efficient in both costs and better provision of patient care.
Computerized Provider Order Entry Systems (CPOE): CPOE systems enable medical professionals to electronically place orders for medications, laboratory tests, and therapies, thereby reducing human error and increasing efficiency. When orders are digitized, CPOE systems eliminate the risks associated with the handwritten prescription documents and guarantee the correct delivery of the medications. In practitioners' hands, they're caregivers communicating with pharmacy, laboratory, and the other departments. They cause the care to reach the patient. It helps to make simple flow of communication among health professionals. It will provide an impact on the life of the patient. This technology works well with all other health information technology (health IT) systems, enhancing workflows and reducing errors, which, in turn, might affect the safety and efficiency of patients.
Electronic Prescribing Systems (E-Prescribing Solutions): E-prescribing systems allow clinicians to electronically transmit prescriptions to pharmacies, thereby decreasing prescription errors that are hallmarks of handwritten prescriptions. These systems optimize the medication order process, improve drug safety through electronic medication history review, and increase the patient’s adherence to medication by facilitating drug interactions from real-time information. E-prescribing, as well, reduces fraud and prescription drug misuse, which can improve patient safety. As these systems are now integrated into wider aspects of healthcare IT infrastructure, they enable to unobtrusive communication between healthcare professionals and pharmacists streamlining the process of prescription, improving efficiency, accuracy and reliability.
Laboratory Information Systems (LIS): LIS processes the laboratory data management and automation of test ordering, spec tracking, and results reporting. These systems provide clean, safe data input, thus minimizing human error, simplifying the work flow in the laboratory. Data integration with EHRs allows LIS to provide fast, accurate laboratory results to all healthcare professionals, allowing for quick and immediate clinical data decision making. These systems, in turn, also contribute to making billing, management of patient records, and laboratory performance better. Laboratory information obtained in the digital domain improves the accuracy of diagnosis, improves resource allocation and leads to improved patient results through the real time availability of trending test results.
Clinical Information Systems (CIS): Clinical information systems provide information on patients, processes, and ultimately substantiate the clinical decision-making processes with scientific evidence. It serves as a general term for a variety of tools that might encompass electronic health records (EHR), electronic medical records (EMR) and other types of software which aid a clinician in delivering the best possible care. CIS enhances patient outcomes by making available to clinicians a rich, real-time stream of patient data, to support informed and better-informed decision making and communication. They also support clinical guidelines, reducing variability in care, minimizing errors, and enhancing coordination among multidisciplinary teams, which ultimately leads to better patient care.
Regulatory Information Management (RIM) Systems: RIM systems are designed to ensure compliance with healthcare regulations and manage the lifecycle of regulatory documents. These systems allow the submission, monitoring and organization of regulatory documents, covering drug approvals, clinical trial data, and compliance records. RIM systems facilitate the retention of healthcare organisations in step with the changing regulatory landscape, the improvement of workflow, and the reduction of the risk of noncompliance. Representing an extension of clear documentation and audit trail functions, RIM systems facilitate increased transparency, accountability, and governance in the regulatory, reducing time and cost related regulatory affairs management.
Medical Imaging Information Systems (MIIS): Medical Imaging Information Systems (data management, storage, retrieval) process medical imaging data (X-rays, MRIs, CT scans), etc. These systems allow, on the one hand, the consolidation and sharing of an imaging data set within the healthcare networks, as on the other between radiologists and clinical and specialist colleagues. MIIS facilitate workflow optimization, minimize the quantity of physical films, power image analysis with digital tools, and thus allow for faster and more correct diagnoses. Integrating electronic health records (EHRs) these systems guarantee that imaging data are available to health care professionals at all times, and assist with timely, integrated care.
Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR systems are digitised substitutes for patients' paper medical records, which combine full medical record information such as medical history, medication history, allergies and test results. These systems have the positive effects of improving care coordination through real-time access to the medical history of a patient and minimizing errors, whereas improved decision-making and consequently better practice is observed as a result. It helps in improving communication between providers, streamlines administrative tasks which helps in compliance with prevailing healthcare regulations. Used in conjunction with other health IT systems including CPOE and LIS. This helps with more efficient clinical workflows for a more patient-centric approach.
Tele-healthcare: Tele-healthcare, or telemedicine, allows the distance consultation between clinicians and patients over digital networks. This technology expands access to healthcare, especially in underserved areas, by eliminating geographical barriers. Tele-healthcare applications consist of video consultations, remote monitoring and digital health platforms that deliver real-time patient information to health practitioners. These systems decrease the necessity of face-to-face contact, increasing convenience and lowering the cost of healthcare. With growing demand for accessible, point-of-care healthcare, tele-healthcare is also expanding, which provides a cost-effective means for providing quality care while improving patient engagement and satisfaction.
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM): Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) consists of all processes that are executed by health care providers for managing claims, collections and revenue generation. RCM solutions automate billing, claims processing, payment posting, coding, and support all of the steps below, ensuring the compliance of all of the above with insurance regulations as well as helping to minimize billing errors. Through greater administrative and financial accuracy, RCM systems optimize processes and speed up the process of acquiring reimbursements. These solutions also support financial forecasting, track patient payments, and reduce claim denials, optimizing the financial health of healthcare organizations and allowing them to focus on delivering quality care to patients.
eClinical Solutions: eClinical solutions are digital platforms that provide comprehensive tools for managing clinical trials, electronic data capture (EDC), and clinical research. These solutions automate the whole clinical trial workflow, from patient recruitment to data collection and regulation compliance. Through automation of data entry, improvement of collaboration and with the ability to run real-time analysis, eClinical solutions streamline time and cost of clinical trials. They guarantee adata's and decisions' quality consistency while speeding up the process of invention and enhancing the clinical research results. With the pressure on clinical trial efficiency, eClinical solutions still develop.
Population Health Management (PHM): Population Health Management (PHM) solutions use a health data analysis of a population to detect trends, control chronic diseases and improve the delivery of care. Various PHM tools help different healthcare organizations identify at-risk prolonged populations, helping initiate interventions, by using data from sources such as EHRs, claim data, and patient surveys. Promoting care coordination, reducing healthcare costs, and increasing benefits to patients as a whole, these tools are really meant for the best. With increasing need for patient-centered value-based care approaches, PHM systems are becoming highly important for facilitating preventive care, minimizing readmissions, and promoting community health.
Digital Healthcare Supply Chain Management: Healthcare supply chain management solutions for digital healthcare leverage technology to enhance the procurement, storage, and distribution of medical supplies, medical equipment and drugs. This system helps in real-time inventory management, waste reduction, and ensuring that health workers have a stock of necessary items for their jobs. Among the tasks that are automated include supply chain management through digital means, which increases efficiency, reduces the number of human errors, and keeps tabs on the cost-control strategies in an organization for healthcare operations. Integration with other medical informatics systems, such as RCM and EHR guarantees persistent and adequate distribution of resources to help in operation for safe and effective processes and a resilient long-lasting healthcare unit.
Clinical Alarm Management: Solutions for clinical alarm management systems enable healthcare institutions to monitor, triage, and control clinical alarms in real time. These systems reduce alarm fatigue, allowing health care professionals to react proactively in critical situations and keep them from unnecessary interruption. Clinical alarm management systems can enhance patient safety and staff efficiency by applying algorithms to screen out less urgent alarms and consolidate alerts. These solutions increase response time, decrease alarm saturation, and increase patient success, which makes them indispensable in high-risk environments such as ICUs and emergency departments.
Healthcare Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Healthcare CRM systems coordinate patient contact, process communications more efficiently, and facilitate patient advocacy. These technologies enable healthcare professionals to get insights into patient preferences, communication records and treatment plans. By enabling personalized, timely outreach, healthcare CRMs enhance patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment, and overall care quality. These systems also enable marketing, scheduling and patient retainment processes. With increasing emphasis in the healthcare industry's attempt to provide patient-centered care, CRM solutions are of central importance for ensuring the long-term relationship with the patient, as well as enhancing the overall patient experience.
Technology Solutions in Healthcare Payers: Technology solutions for healthcare payers, including insurers and managed care organizations, streamline administrative tasks, improve claims processing, and enhance member services. These solutions help automate claims adjudication, fraud detection, and billing, improving efficiency and reducing operational costs. They also allow insurance companies to provide tailored flexible plans in line with data analytics and member demand. Emphasizing the transformation of the payer experience, these solutions can be used to streamline administrative tasks, engage members more actively, and assist with value-based care efforts, thereby leading to greater alignment in between payers, providers, and patients.
Healthcare Analytics: Healthcare analytics solutions are based on big data and state-of-the-art algorithms and work with patient data to detect trends and provide assistance in decision making. These are the tools that allow the providers of health care to increase patient outcomes, decrease costs, and increase operational efficiency. Predictive analytics allows pre-diagnosis of diseases, whereas population health analytics helps plan interventions for the risk populations. Healthcare analytics tools are able to offer insights of actionable value using data aggregations from multiple sources. With a growing data-driven approach to health care decisions at the forefront, there is a growing need for analytics inhealth care systems that can further improve the delivery of care and decrease inefficiencies.
Healthcare Providers: The Healthcare Providers segment has dominated the market in 2024. Healthcare organizations (e.g., hospitals, clinics, doctor's offices) are end-users of health products (ie, health informatics products). These agencies are using electronic health record (EHR) tech, telemedicine, and CDS to improve care delivery and operational efficiency, but also to improve the patient experience. Health care IT underlying automation of administrative tasks, workflow management from unit to unit and from unit to care team, and regulatory compliance in provider organizations. Implementation of these solutions led to an increase in workflow productivity, improvements in patient care, a decrease in errors, and increased satisfaction in patients which makes healthcare IT increasingly important in modern healthcare facilities.
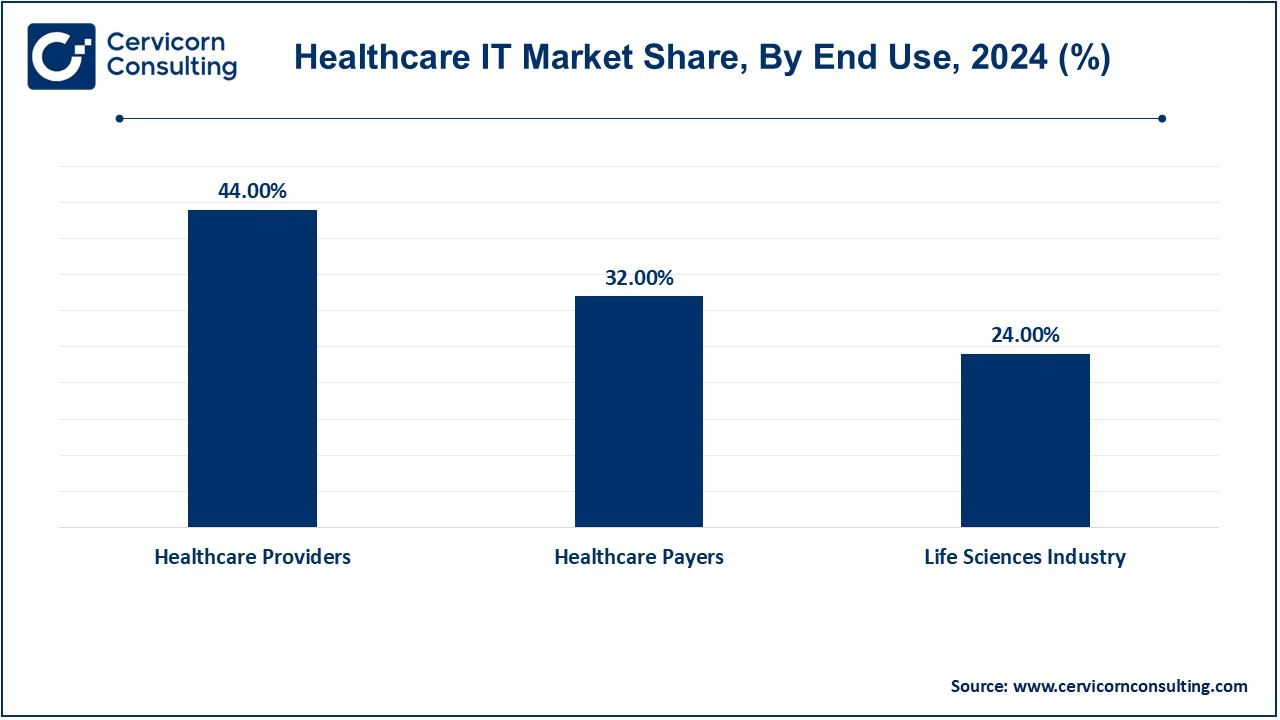
Healthcare Payers: Health ICT apps are employed by healthcare payers (insurance companies, accountable care organizations) for claims, invoicing and regulatory compliance. Revenue cycle systems, analytics, and fraud detection systems facilitate automation, optimization, and claim quality enhancement. The payer can further increase its capability to control risk, to price more effectively, to design tailored insurance products, by using predictive analytics. IT solutions also will be beneficial to payers for the mobilization and provision of services of members, in reality, and for a supportive and robust healthcare ecosystem.
Life Sciences Industry: The life sciences industry, as a broad industry of pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device companies, is rare to be involved in health information technology as part of the research, development and regulatory compliance processes. Clinical trial management systems (CTMS), electronic lab notes and analytical data warehousing hold the potential to accelerate drug development and clinical research (e.g., by promoting optimization and boosting patient safety. Health IT has the potential to be just one tool to augment the bridging of time-varying patient data streams and thereby support evidence-based inquiry and precision medicine. The life sciences industry can harness the technologies used for workflow processing, accelerate innovation and guarantee the safety and validity of the novel therapeutics.
The healthcare IT market is segmented into various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA. Here is a brief overview of each region:
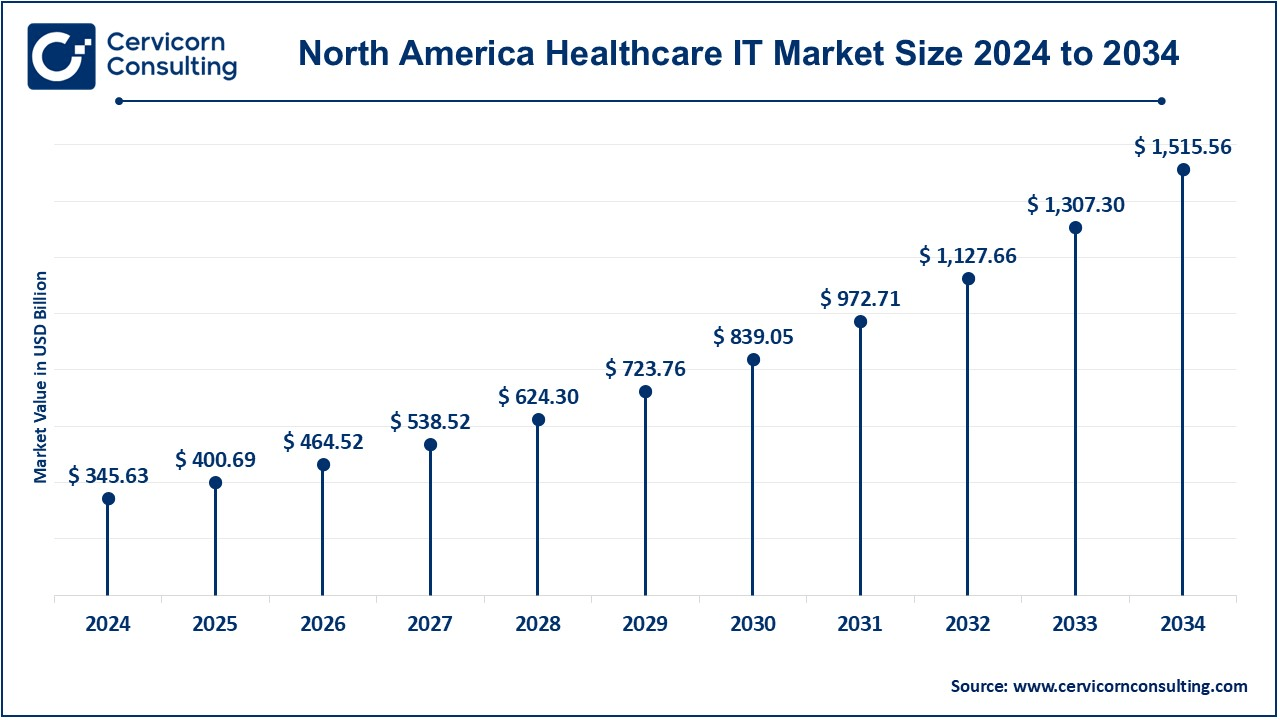
The North America healthcare IT market size was valued at USD 345.63 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 1,515.56 billion by 2034. A major reason for this is the advanced healthcare infrastructure present in the North American market, with evidence-based phenomenal advancement adoption of its facilities in the field of health services through digital health technologies, as well as high healthcare expenditure. In the U.S., almost all health facilities are using Electronic Health Records (EHR) as well as telemedicine and with health IT across public and private sectors. Health-related innovations are seen to increase business advances, especially government initiatives like HITECH Act and meaningful use incentives for stimulating the growth of healthcare IT. With a significantly-higher-than-average spending in healthcare and the mega-graphics-prone population, North America seems likely to dominate the global market.
The Europe healthcare IT market size was estimated at USD 184.34 billion in 2024 and is predicted to surpass around USD 808.30 billion by 2034. The growth of Europe region is driven by sound healthcare infrastructure. Additional support was the governments of the European region also initiative for digitization. The countries like the UK, Germany, and France are using telemedicine, health analytics and electronic health records to possible better care for patients, reduce costs, efficiency in the systems. The harmonization of the Interoperability EU focus, GDPR style data privacy regulations, and government healthcare actions have pressed the distribution of healthcare IT solutions in public and private sectors alike. Europe still remains a very key player in global healthcare IT growth even as it combats related regulatory complexities.
The Asia-Pacific healthcare IT market size was accounted for USD 153.61 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to reach around USD 173.58 billion by 2034. The Asia-Pacific is expanding at a rapid pace driven by the increased need for healthcare facilities such technical advancements and government initiatives. Countries like China, India, and Japan have moved towards digital health adoption. All this entails the adoption of telemedicine, electronic health records (EHR), and mobile health application solutions for their large populations and rapidly growing healthcare demand. The increase in health insurance plans, healthcare infrastructure investments, and focus on ensuring access to quality healthcare put in efforts to drive market growth. In shifting its health service transformation into digital form, the region has opportunities emerging in largely more-remote and underserved areas.
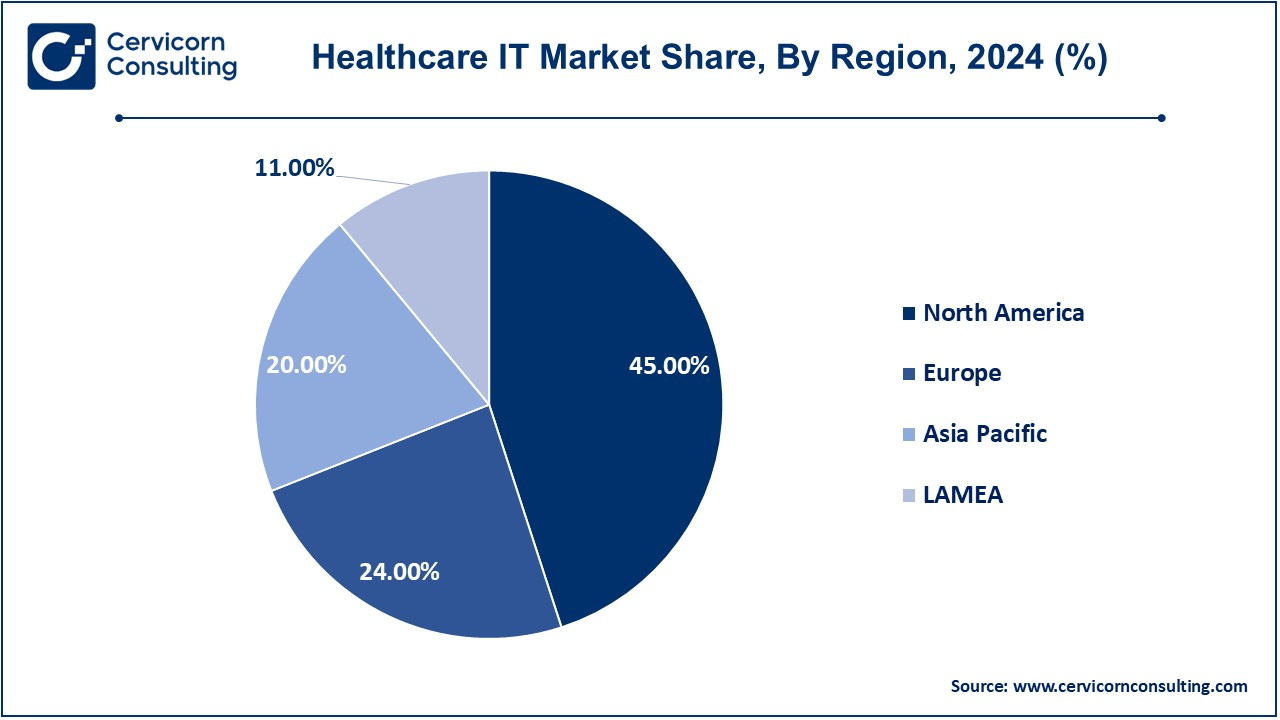
The LAMEA healthcare IT market was reached at USD 84.49 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 370.47 billion by 2034. The LAMEA is growing marginally due to a rise in healthcare demands, an increase in government spend, and the further adoption of e-health solutions. Countries across the Latin America have deployed telemedicine and electronic health records (EHR), thus, utilizing mobile health options to spread healthcare education and help telepathy and other health consulting channels in different regions. The Middle East is working hard to modernize its healthcare infrastructure and shift towards smart health solutions. At the same time, the less developed digital infrastructure, regulatory barriers, and economy in some areas may also slow down the adoption velocity. However, because the LAMEA market is still growing in its potential to expand in the years to come.
Market Segmentation
By Delivery Mode
By Application
By End-Use
By Region